A method for obtaining submandibular gland of mouse embryo
A technology of mouse embryos and acquisition methods, which is applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems that the submandibular gland glands cannot be completely attached to the tongue, the submandibular gland tissue is incomplete, and there are many steps, so as to reduce operation steps, reduce operation difficulty, and ensure integrity sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] This embodiment provides a method for obtaining the submandibular gland of mouse embryos. The method has simple steps and is easy to operate. The integrity of the extracted submandibular gland tissue is high. Specific steps are as follows:
[0027] Step 1: After the pregnant mouse is killed, the uterus containing the embryo is completely dissociated.
[0028] Step 2: Open the uterine wall and free the embryo completely.
[0029] Step 3: Obtain the jaw tissue from the embryo under a microscope.
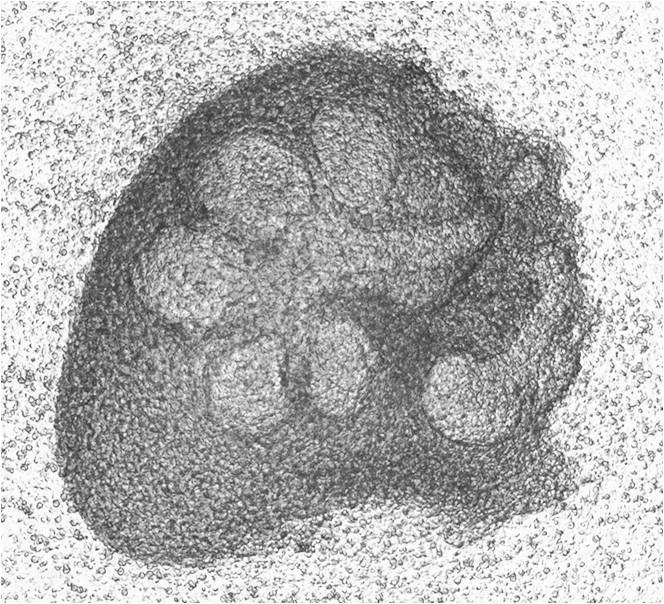
[0030] Step 4: Place the mandibular tissue under a microscope, zoom in on the field of view and fix it. After separating the superficial tissue, pinch off the connection between the submandibular gland, the tongue body and the duct, and obtain the complete embryonic submandibular gland.
Embodiment 2
[0032] This embodiment provides a method for obtaining the submandibular gland of mouse embryos. The method has simple steps and is easy to operate. The integrity of the extracted submandibular gland tissue is high. Specific steps are as follows:
[0033] Step 1: C57BL mice with a gestational age of 12 days were killed by cervical dislocation, and the chest and abdomen of the mice were disinfected by soaking in 75% alcohol. The skin, muscles and peritoneum were cut in a straight line from the pubic symphysis in the midline of the mouse abdomen to expose the abdominal cavity to the sword. Under the protrusion, the abdominal skin and muscles are retracted to expose the uterus, the uterus is lifted with small curved forceps, and the free uterus of the mesentery is cut and separated with scissors. During this process, the uterus and embryos are prevented from being squeezed, and the free uterus containing the embryo Place them in a 100mm Petri dish filled with 25mL storage medium,...
Embodiment 3
[0038] This embodiment provides a method for obtaining the submandibular gland of mouse embryos. The method has simple steps and is easy to operate. The integrity of the extracted submandibular gland tissue is high. Specific steps are as follows:
[0039] Step 1: C3H mice with a gestational age of 13 days were killed by cervical dislocation, and the chest and abdomen of the mice were disinfected by soaking in 75% alcohol. The skin, muscles and peritoneum were cut in a straight line from the pubic symphysis in the midline of the abdomen of the mice to expose the abdominal cavity to the sword. Under the protrusion, the abdominal skin and muscles are retracted to expose the uterus, the uterus is lifted with small curved forceps, and the free uterus of the mesentery is cut and separated with scissors. During this process, the uterus and embryos are prevented from being squeezed, and the free uterus containing the embryo Place them in a 100mm petri dish filled with 25mL storage med...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com