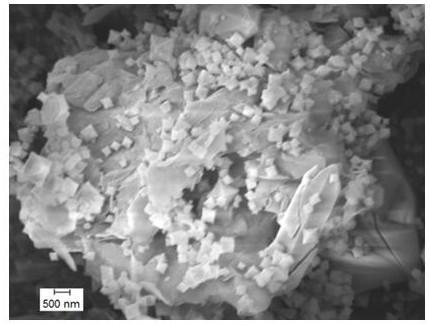
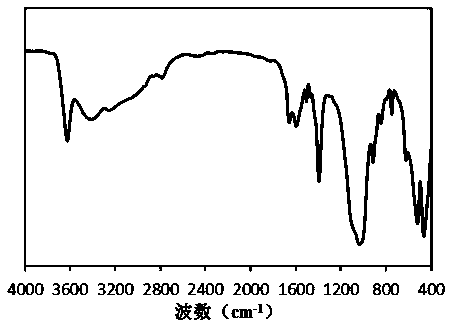
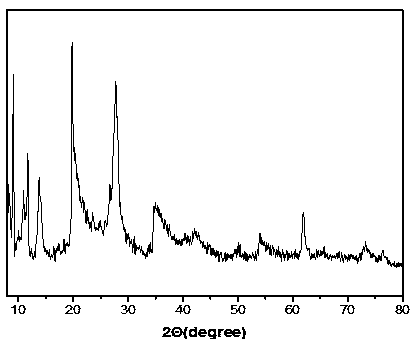
Montmorillonite-loaded iron salt MOFs adsorbent and preparation method thereof
A montmorillonite and adsorbent technology, which is used in the preparation of montmorillonite-supported iron salt MOFs adsorbents, can solve the problems of high price of organic ligands and exploration of adsorbed dyes, and achieves good adsorption performance, efficient adsorption effect, and good adsorption performance. The effect of the application foreground
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] First, weigh out 0.5 g FeCl 3 • 6H 2 Put O and 1.2 g of terephthalic acid in a beaker, add 30 mL of N,N’-dimethylformamide and stir to dissolve. Secondly, add 0.4 g of acidified montmorillonite and stir at room temperature for 1 hour to make the raw materials uniformly dispersed. Then, the mixture was transferred to a 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene lined stainless steel reactor, and the temperature was raised to 120°C for 12 h. After the reactor was cooled to room temperature, the reaction mixture was taken out, and the product was collected by centrifugation at a certain speed. The product was washed twice with N,N'-dimethylformamide and absolute ethanol to remove the unreacted iron salt and organic compound. body. Finally, vacuum drying was carried out at 80°C for 10 h to obtain a light yellow powder, that is, the montmorillonite supported iron salt MOFs adsorbent. The highest removal rate of methylene blue by this adsorbent is 99.10%.
Embodiment 2
[0031] First, weigh 0.5 g Fe(NO 3 ) 3 • 9H 2 O and 0.1 g of trimesic acid were added to a beaker, 50 mL of N,N’-dimethylformamide and water were added, and stirred to dissolve. Secondly, add 0.9 g of acidified montmorillonite and stir for 2 h at room temperature to make the raw materials uniformly dispersed. Then, the mixture was transferred to a 100 mL polytetrafluoroethylene lined stainless steel reactor, and the temperature was raised to 160°C for 17 hours. After the reactor was cooled to room temperature, the reaction mixture was taken out, and the product was collected by centrifugation at a certain speed. The product was washed with N,N'-dimethylformamide and absolute ethanol 4 times to remove unreacted iron salt and organic compound. body. Finally, vacuum drying was carried out at 100°C for 12 h to obtain a light yellow powder, that is, the montmorillonite supported iron salt MOFs adsorbent. The highest removal rate of methylene blue by this adsorbent is 99.64%.
Embodiment 3
[0033] First, weigh 5 g Fe(NO 3 ) 3 • 9H 2 O and 1.2 g of terephthalic acid were put into a beaker, 60 mL of N,N’-dimethylformamide was added, and the mixture was stirred to dissolve. Secondly, add 3.5 g of acidified montmorillonite and stir for 2 h at room temperature to make the raw materials uniformly dispersed. Then, the mixture was moved to the reactor, and the temperature was raised to 180°C for 20 h. After the reactor was cooled to room temperature, the reaction mixture was taken out, and the product was collected by centrifugation at a certain speed. The product was washed with N,N'-dimethylformamide and absolute ethanol 4 times to remove unreacted iron salt and organic compound. body. Finally, vacuum drying was carried out at 170°C for 14 h to obtain a light yellow powder, namely, montmorillonite loaded iron salt MOFs adsorbent. The highest removal rate of methylene blue by this adsorbent is 98.96%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com