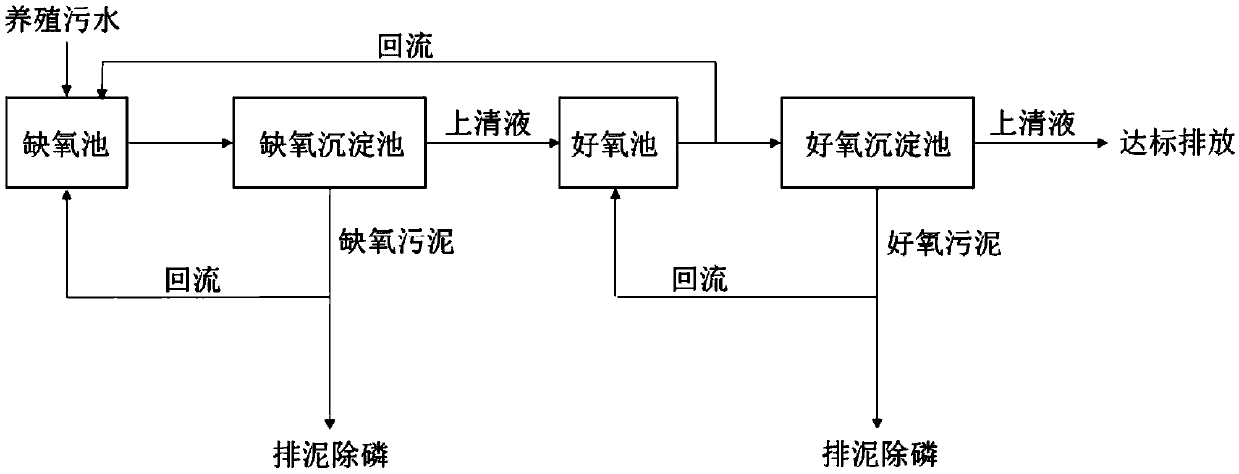
Farming wastewater phosphorous biochemical removal process
A technology for aquaculture sewage and biochemical phosphorus removal, which is applied in the field of aquaculture sewage biochemical phosphorus removal technology, can solve the problems of neglecting the phosphorus removal effect of anoxic stage sludge and the nitrification effect of nitrifying bacteria, and achieves low treatment cost, reduced treatment cost, Effective Phosphorus Removal
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A biochemical phosphorus removal process for aquaculture sewage, comprising the following steps:
[0029] 1) Feed the aquaculture sewage (COD=2000mg / L, ammonia nitrogen=600mg / L) into the anoxic tank for 25h anoxic treatment;
[0030] 2) Let the effluent from the anoxic tank enter the anoxic sedimentation tank by gravity, and carry out natural precipitation for 15 hours to obtain anoxic sludge and supernatant, and part of the anoxic sludge is returned to the anoxic tank (the return flow is 100% of the water inflow of the anoxic tank %), partly excludes phosphorus (the daily efflux is 3% of the anoxic pool capacity);
[0031] 3) The supernatant in the anoxic sedimentation tank is automatically flowed into the aerobic tank, and aerobic treatment is carried out for 20 hours;
[0032] 4) Return part of the effluent from the aerobic tank to the anoxic tank (the return flow rate is 200% of the water intake in the anoxic tank), and part of it flows into the aerobic sedimentati...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A biochemical phosphorus removal process for aquaculture sewage, comprising the following steps:
[0036] 1) Feed the aquaculture sewage (COD=2000mg / L, ammonia nitrogen=600mg / L) into the anoxic tank for 30h anoxic treatment;
[0037] 2) Let the effluent from the anoxic tank flow into the anoxic sedimentation tank, and carry out natural precipitation for 15 hours to obtain anoxic sludge and supernatant, and part of the anoxic sludge is returned to the anoxic tank (the return flow is 150% of the influent water in the anoxic tank. %), partly excludes phosphorus (the daily efflux is 8% of the anoxic pool capacity);
[0038] 3) The supernatant in the anoxic sedimentation tank is automatically flowed into the aerobic tank, and aerobic treatment is carried out for 25 hours;
[0039] 4) Return part of the effluent from the aerobic tank to the anoxic tank (the return flow rate is 300% of the water intake in the anoxic tank), and part of it flows into the aerobic sedimentation t...
Embodiment 3
[0042] A biochemical phosphorus removal process for aquaculture sewage, comprising the following steps:
[0043] 1) Feed the aquaculture sewage (COD=2000mg / L, ammonia nitrogen=600mg / L) into the anoxic tank for 40h anoxic treatment;
[0044] 2) Let the effluent from the anoxic tank flow into the anoxic sedimentation tank by gravity, and carry out natural precipitation for 20 hours to obtain anoxic sludge and supernatant, and part of the anoxic sludge is returned to the anoxic tank (the return flow is 200% of the water intake of the anoxic tank. %), partly excludes phosphorus (the daily efflux is 10% of the anoxic pool capacity);
[0045] 3) The supernatant in the anoxic sedimentation tank is automatically flowed into the aerobic tank, and aerobic treatment is carried out for 30 hours;
[0046] 4) Return part of the effluent from the aerobic tank to the anoxic tank (the return flow rate is 500% of the water intake in the anoxic tank), and part of it flows into the aerobic sedim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com