A Method of Underwater Acoustic Media Access Control Based on Reservation Scheduling Mechanism
A technology of media access control and underwater sound, applied in advanced technology, broadcast service distribution, climate sustainability, etc., can solve problems such as low applicability of communication networks, communication efficiency prone to conflicts, and short effective information transmission time. Achieve the effect of reducing the average transmission delay, reducing the time for handshaking, and improving channel utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] In order to better understand the technical content of the present invention, specific embodiments are provided below, and the present invention is further described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
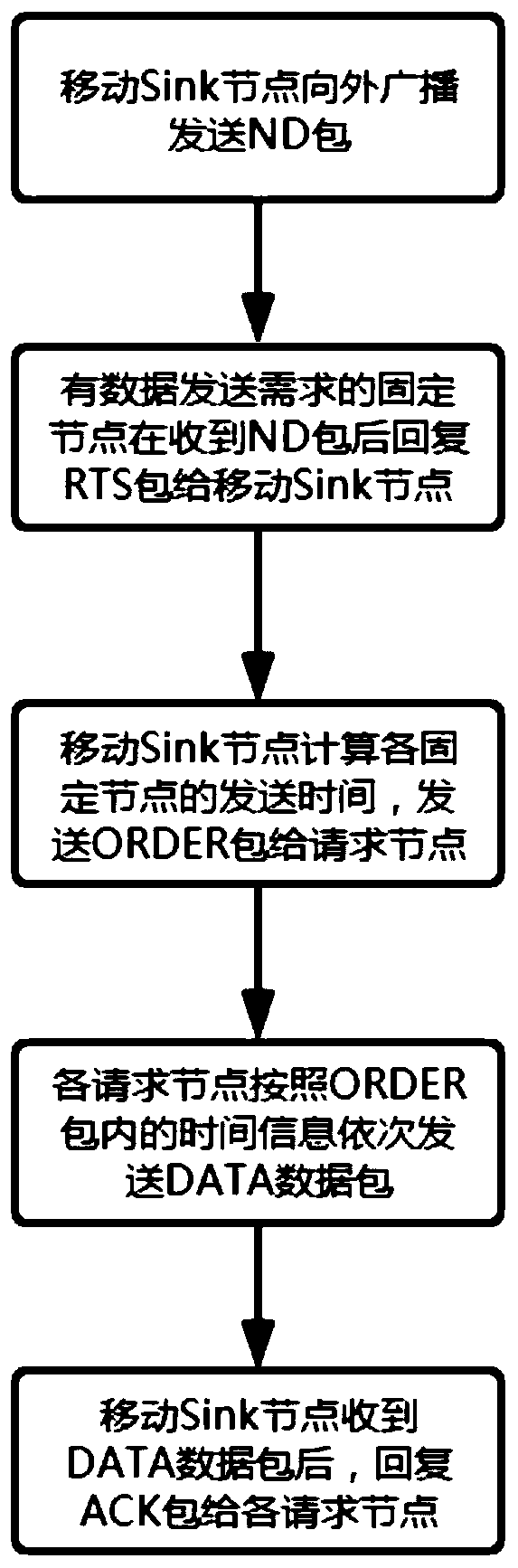
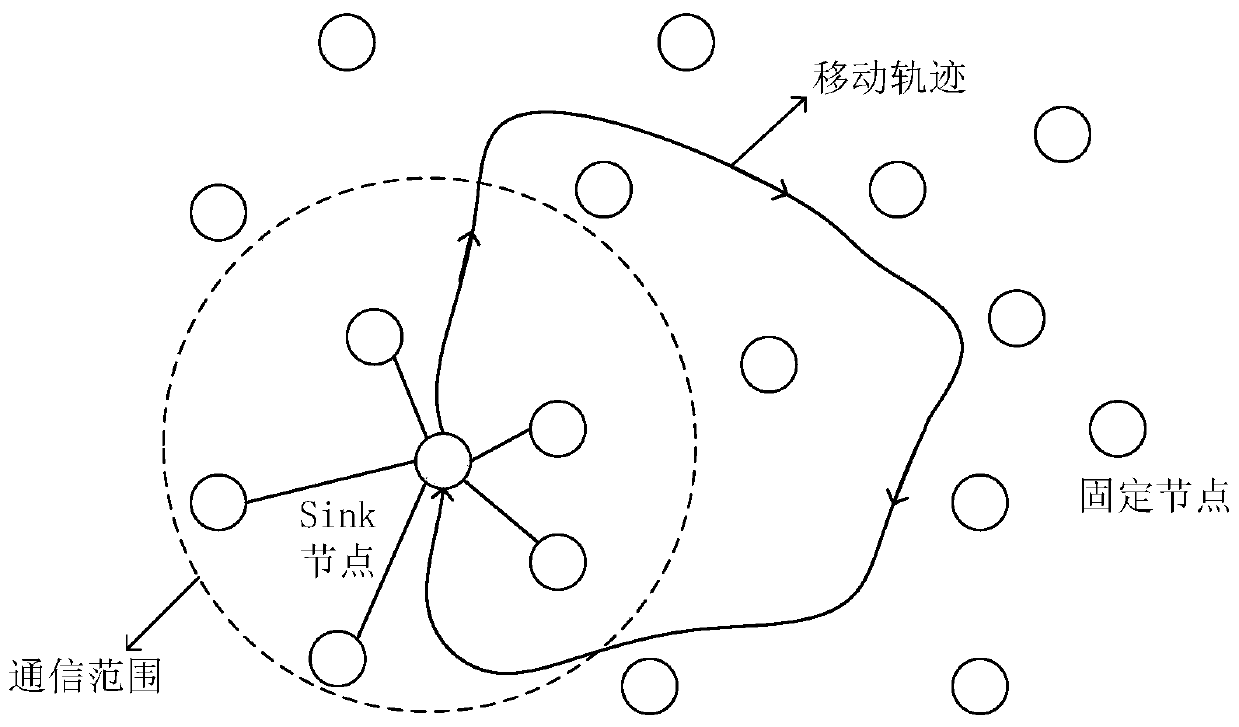
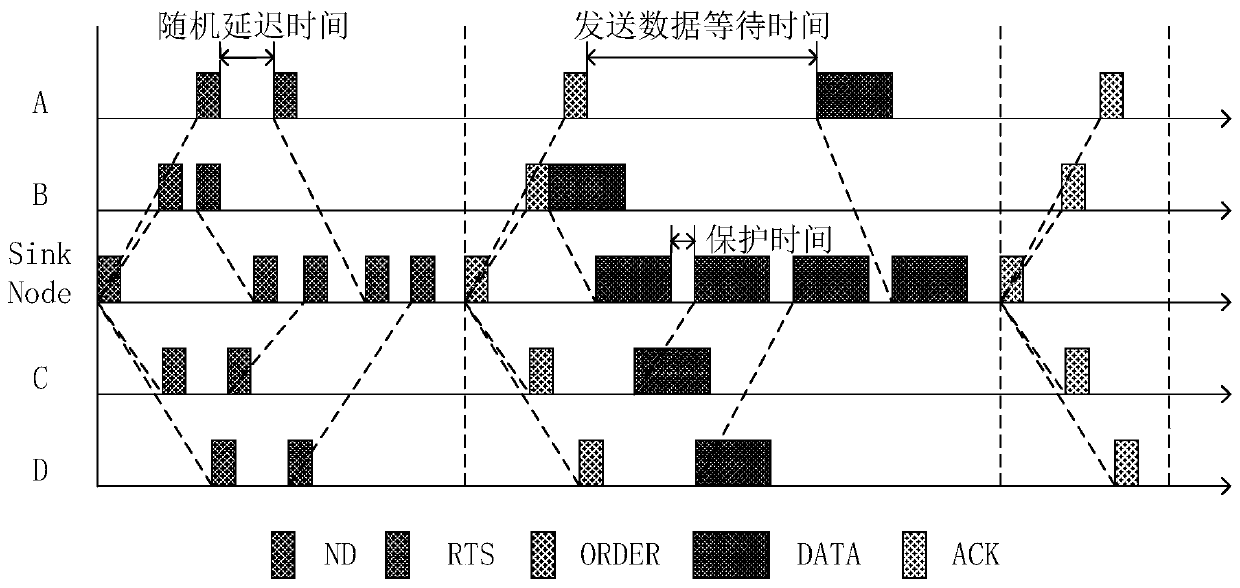
[0029] see Figure 1 to Figure 3 , an underwater acoustic media access control method based on a reservation scheduling mechanism, which includes several fixed nodes A, B, C, D and a unique mobile sink node, and communicates in the following ways:
[0030] S1, the mobile sink node broadcasts and sends the ND packet to the outside, and the ND packet includes the destination address, the source address and the sending time;
[0031] S2. The fixed node that receives the ND packet, if there is a need for data transmission, select a random delay time, and after the delay time is exhausted, send an RTS packet to the mobile sink node for data transmission reservation. The RTS packet contains the destination address and source. Address and delay time and other informa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com