Co2-enabled regeneration and reuse of responsive adsorbents
A technology for adsorbing materials and pollutants, which is applied in the field of CO2-triggered switchable adsorption and desorption, and can solve the problem that PEI is not suitable for large-scale industrial use.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
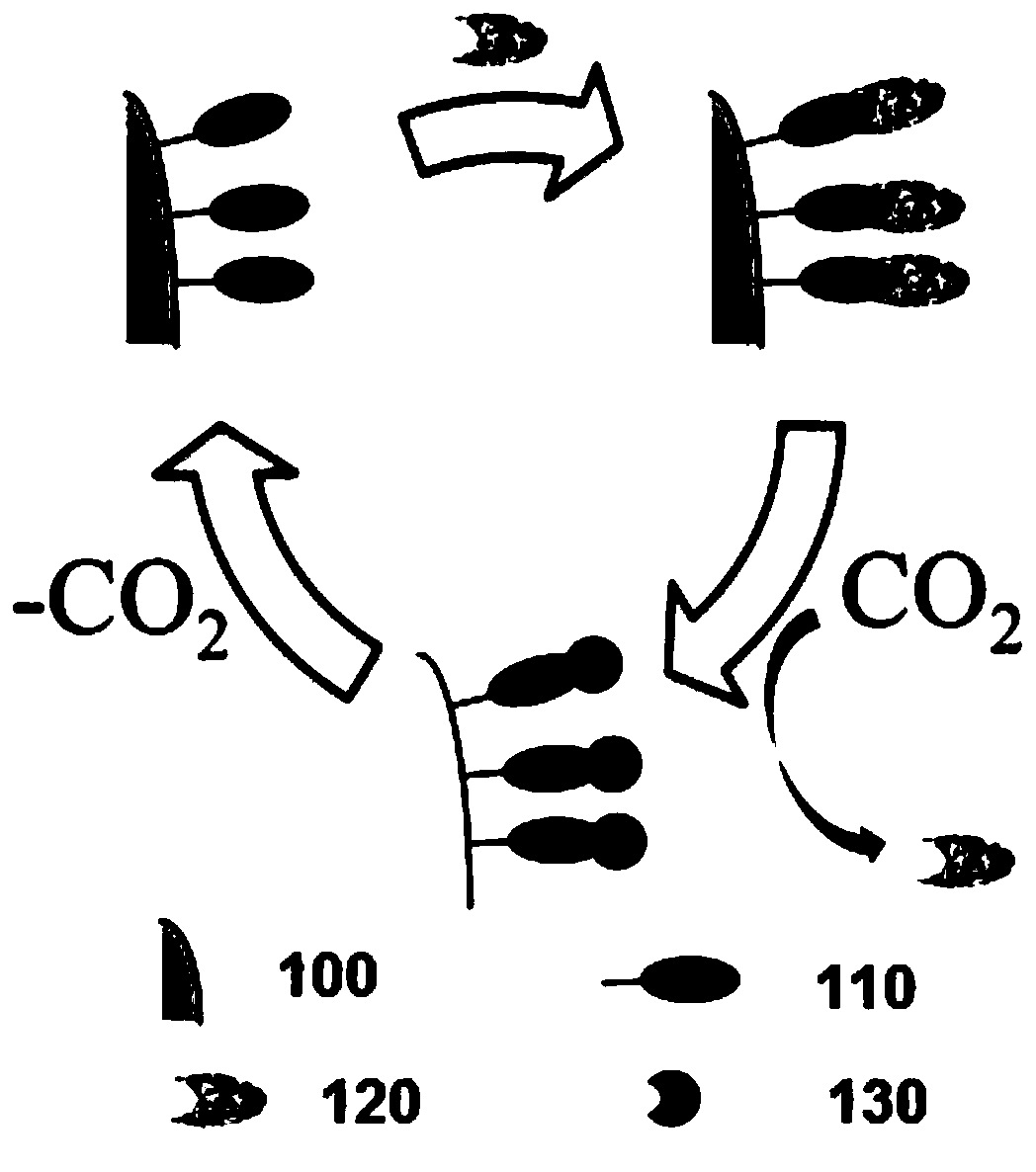
[0076] As one of the most common types of heavy metal pollution widely present in wastewater sources in the electronics, paint, wiring, and printing industries, copper is selected in this example to illustrate the CO 2 Auxiliary adsorption and desorption processes. In addition, according to the complexation mechanism of polymers and metals, Cu 2+ 、Cd 2+ , Pb 2 , Pb 4+ 、Cr 3+ 、Co 2+ 、Ni 2+ , Zn 2+ A variety of other multivalent chelatable heavy metals can also be used in the present embodiment method (as shown in Example 3 below).
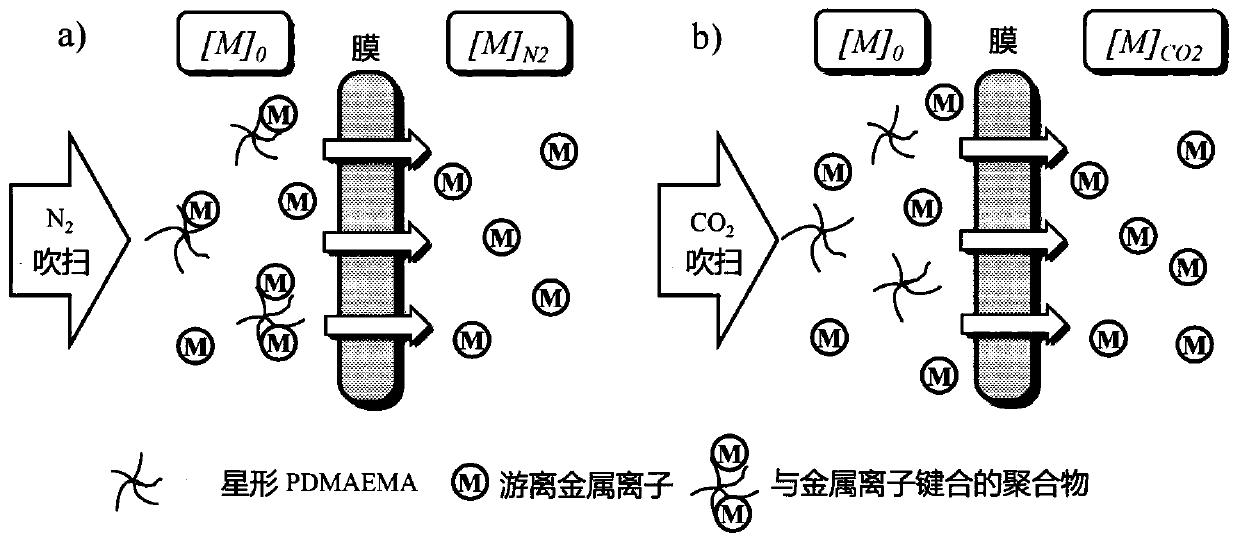
[0077] to CO 2 Auxiliary Cu 2+ The removal process and the adsorbent regeneration process are described. Among them, the linear and star-shaped PDMAEMA were dissolved in 0.1M NaNO 3 solution and adjust the pH to approximately 5.5. By adding Cu(NO 3 ) 2 "6H 2 O dissolved in 0.1M NaNO 3 , made of Cu 2+ solution, used as a waste water substitute. The 0.1M NaNO 3 As used to stabilize the solution and obtain accurate Cu in the experime...
Embodiment 2
[0079] As a typical adsorption capacity determination method, 1mmol / L Cu(NO 3 ) 2 The solution was continuously injected with 10 mL of a 0.268 mg / mL PDMAEMA solution which had been adjusted to the desired pH prior to injection. At the same time, Cu-ISE and pH electrodes are also used to continuously measure Cu 2+ Concentration and pH. During this process, the N 2 Continuously bubble through the solution to stabilize the pH and avoid atmospheric CO 2 Impact. Adsorption capacity (Q e ) is calculated according to the following formula:
[0080]
[0081] Among them, C 0 is the total concentration of copper, C v is the measured free Cu 2+ Concentration, V is the solution volume, m is the mass of adsorbent polymer.
[0082] at 25°C with N 2 While purging, by adding a designed amount of Cu(NO 3 ) 2 solution to determine the adsorption isotherm. In this way, during the addition, different polymer / Cu ratios can be achieved and the corresponding Cu measured by Cu-ISE 2...
Embodiment 3
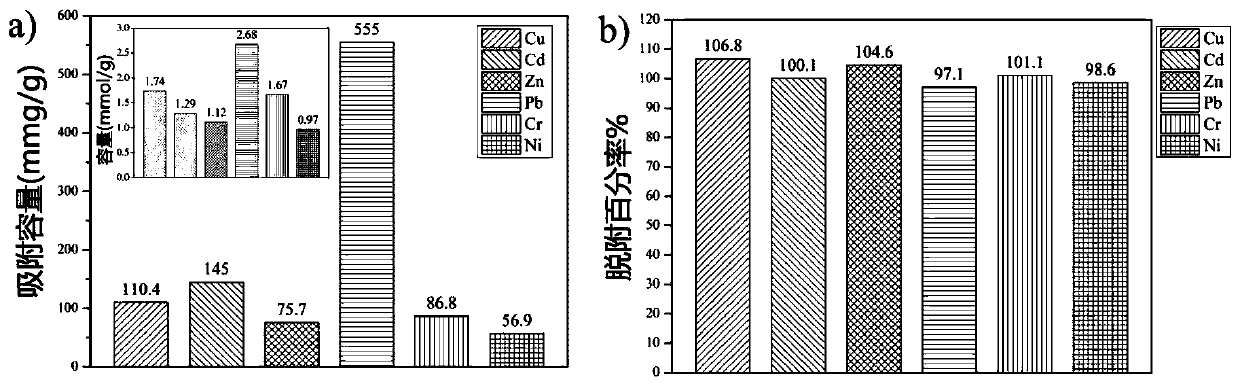
[0086] In the following examples, in addition to Cu 2+ In addition, several other metal ions were tested. These metal ions are Cd 2+ , Zn 2+ , Pb 2+ 、Cr 3+ and Ni 2+ , and in order to simulate the actual wastewater treatment conditions, the ultrafiltration step in the evaluation process does not use NaNO 3 Ionic background.
[0087] In this method, in order to avoid the formation of anionic coordination bonds, all metal salts are nitrates. As a typical method, metal nitrate and star-shaped PDMAEMA (POSS-PDMAEMA) were first dissolved in DI water at concentrations of 0.4mmol / L and 27.3mg / L to form two identical solutions, respectively. The pH of each solution was adjusted to 5.5. Among them, the molar ratio of [metal]:[DMAEMA unit] is about 2.5:1, and the excess of the metal relative to the polymer ensures that the maximum adsorption capacity is obtained in the equilibrium state. Before reaching adsorption or desorption equilibrium by filtration, one of the same solutio...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com