GNSS receiver pulse per second-based clock synchronization method
A clock synchronization, second pulse technology, applied in the direction of automatic power control, satellite radio beacon positioning systems, measurement devices, etc. problem to avoid calculation errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
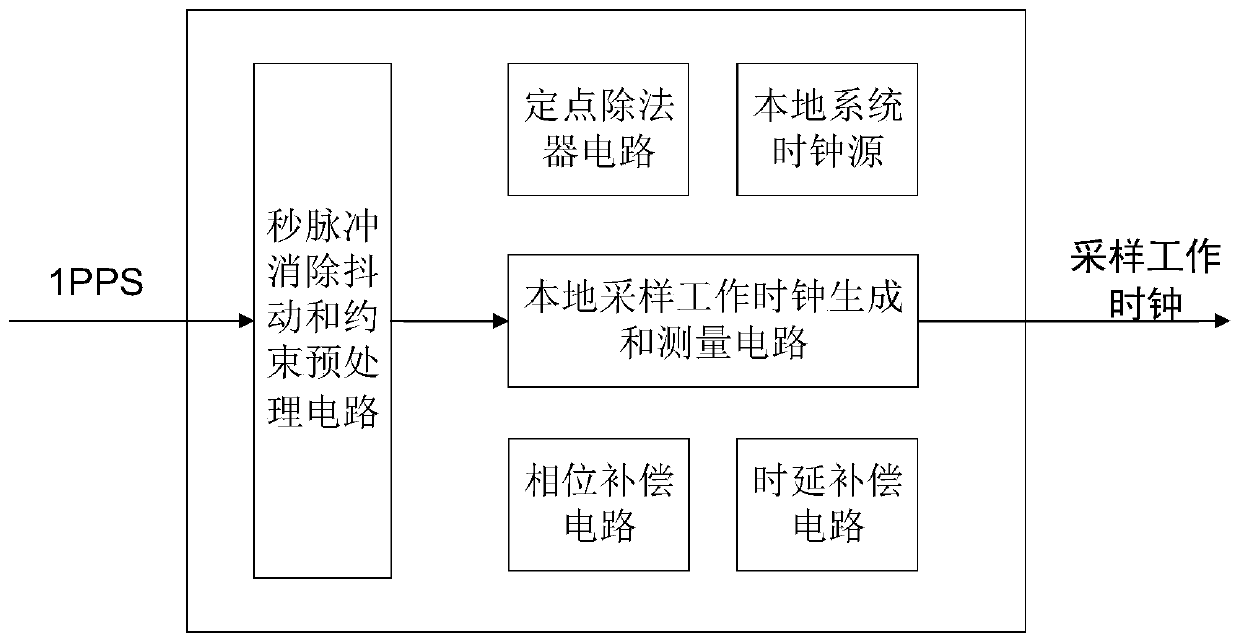
[0019] Attached below figure 1 The present invention is further described.
[0020] The principle of the 1PPS second pulse elimination jitter and constraint preprocessing circuit is to use the clock signal to continuously sample the input 1PPS second pulse signal for n times, and send each sampling result to the shift register. If the n sampling results are all 1, then It is considered that the real signal is 1, otherwise it is 0. Under normal circumstances, the GNSS receiver outputs a 1PPS second pulse signal every 1 second, and the accuracy of the 1PPS signal is ±20ns. In order to prevent the receiver from malfunctioning, the 1PPS signal appears multiple times within 1 second, using a constraint preprocessing circuit The module is used to monitor 1PPS signal. The detection method is: start counting at the falling edge of a certain second pulse, and count the current system clock. If a new second pulse appears before the count value reaches (99%*system clock frequency), it ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com