Remote DNA strand displacement method of magnesium ion induced E6-type DNA ribozyme allosterism
A DNA chain and magnesium ion technology, applied in the field of molecular computing, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of DNA coding and limiting the application flexibility of strand replacement technology, and achieve the effect of increasing flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
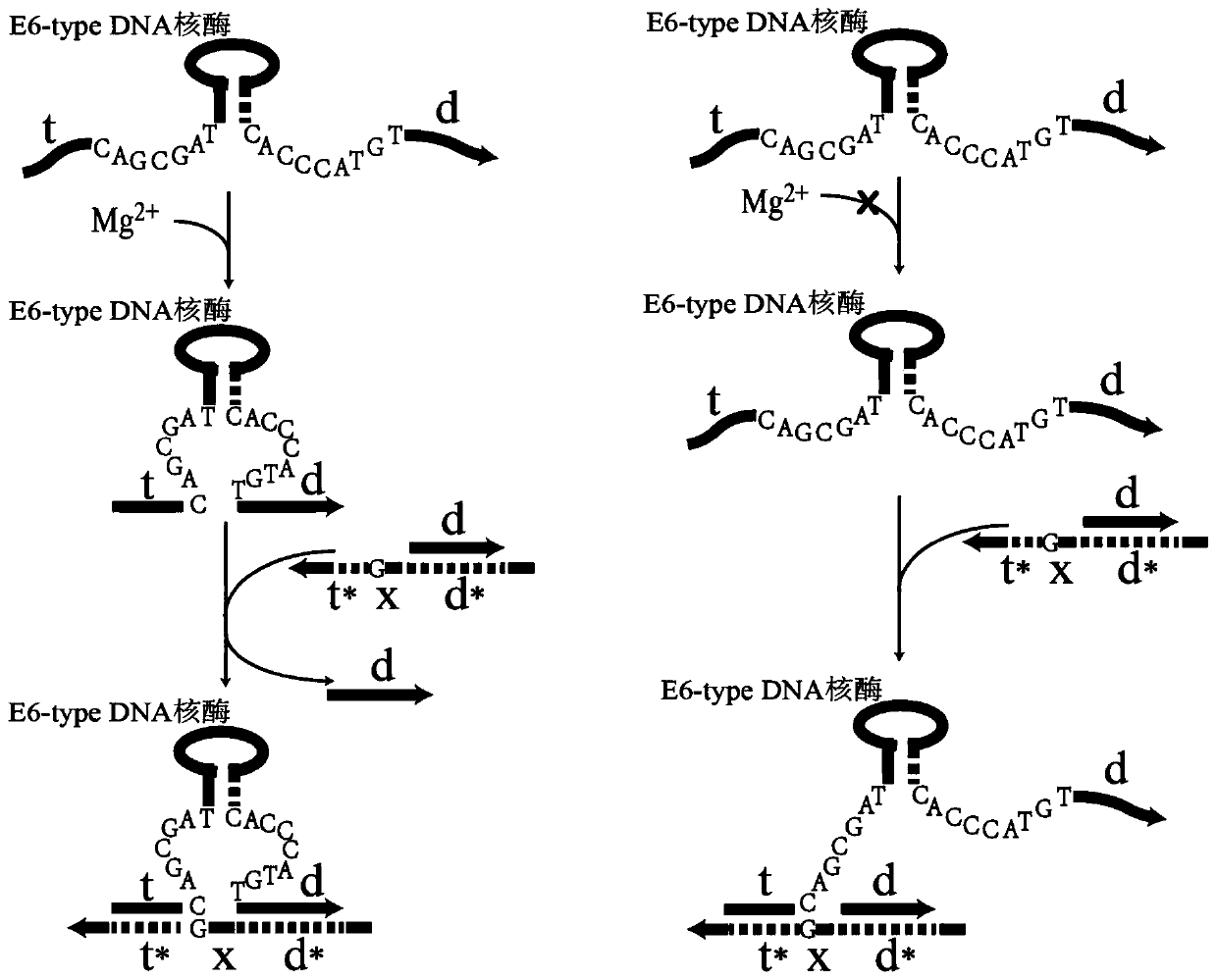
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown, the E6-type DNAzyme consists of at least 5 DNA sequence fragments: substrate binding arms t and d, 2 conserved domain DNA fragments (5'-CAGCGAT-3' and 5'-CACCCATGT-3') and 1 DNA sequence fragment with hairpin structure. Among the above five DNA sequence fragments, except for the conserved domain DNA fragments, the others are designable parts, and the specific base arrangement depends on the specific application target. DNA duplex [d,t*Xd*] is the target duplex for strand displacement, where t* and d* are DNA fragments complementary to the binding arms t and d of the E6-type DNAzyme substrate, respectively. Such as figure 1 As shown, when magnesium ion Mg2+ is added, the E6-type DNAzyme undergoes allosterism, and the substrate binding arms t and d are close to each other, constituting the toehold t for strand...
Embodiment 1D
[0032] Example 1 DNA Remote Strand Displacement Verification
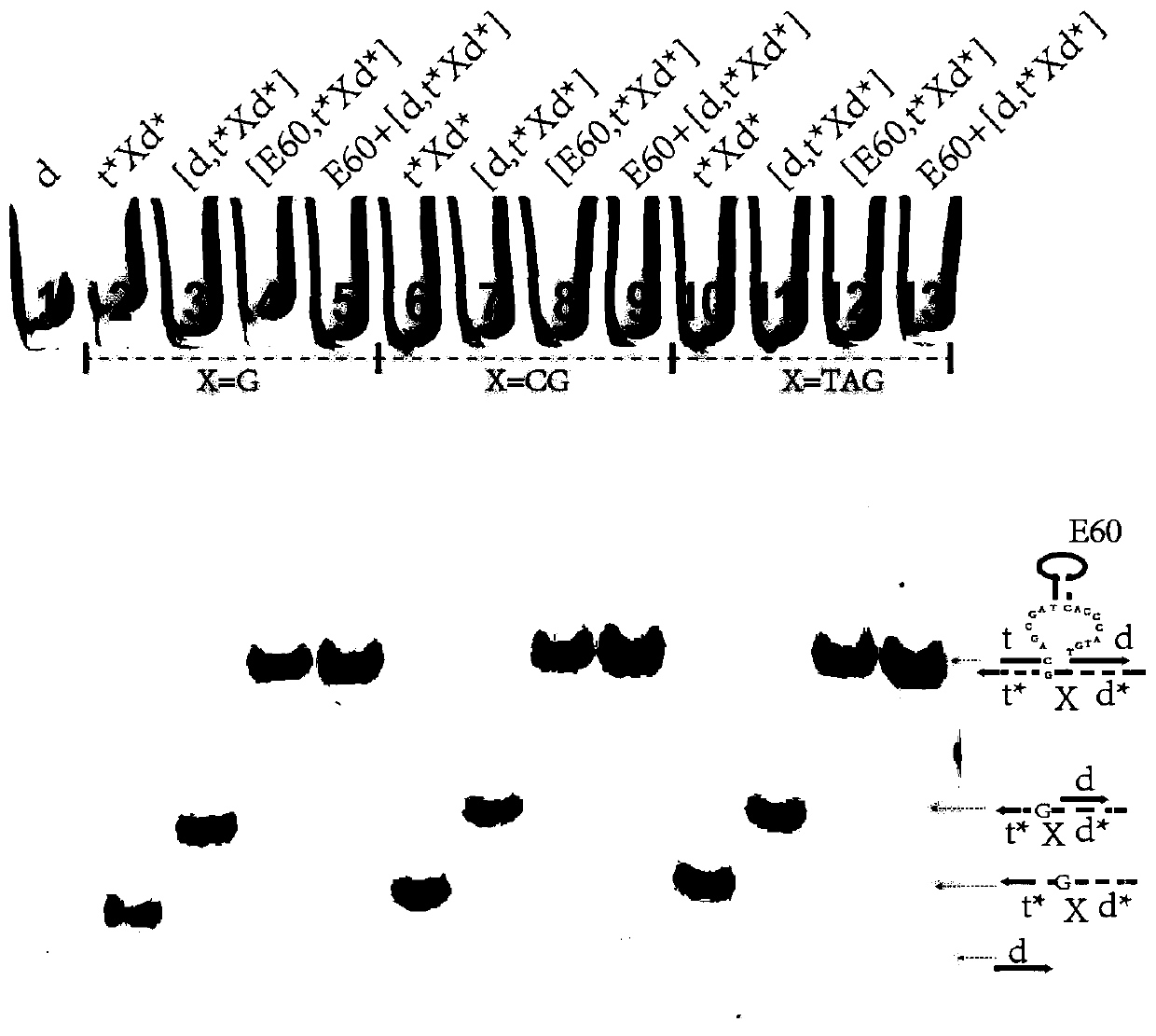
[0033] image 3 for figure 1 PAGE electrophoresis results of long-range strand displacement of E6-type DNAzyme (E60) in the presence of magnesium ions. image 3 The middle lanes 2-5 are the case where the DNA fragment X is a single base G, the lanes 6-9 are the cases where the DNA fragment X is two bases CG, and the lanes 10-13 are the cases where the DNA fragment X is three bases TAG . The electrophoresis bands in lanes 3 and 4 indicate that the complex DNA double strand [d, t*Xd*] and [E60, t*Xd*] can be stably generated. For the solution containing DNA double strand [d, t*Xd*], When E6-type DNAzyme E60 is added, E60 binds to the DNA sequence t*Xd* through the foothold t, and due to the action of magnesium ions, E60 undergoes allosterism, making the substrate binding arm t located at the 5'-end of E60 and on it The substrate-binding arm d at the 3'-end of t is spatially close to form a continuous foothold t a...
Embodiment 2
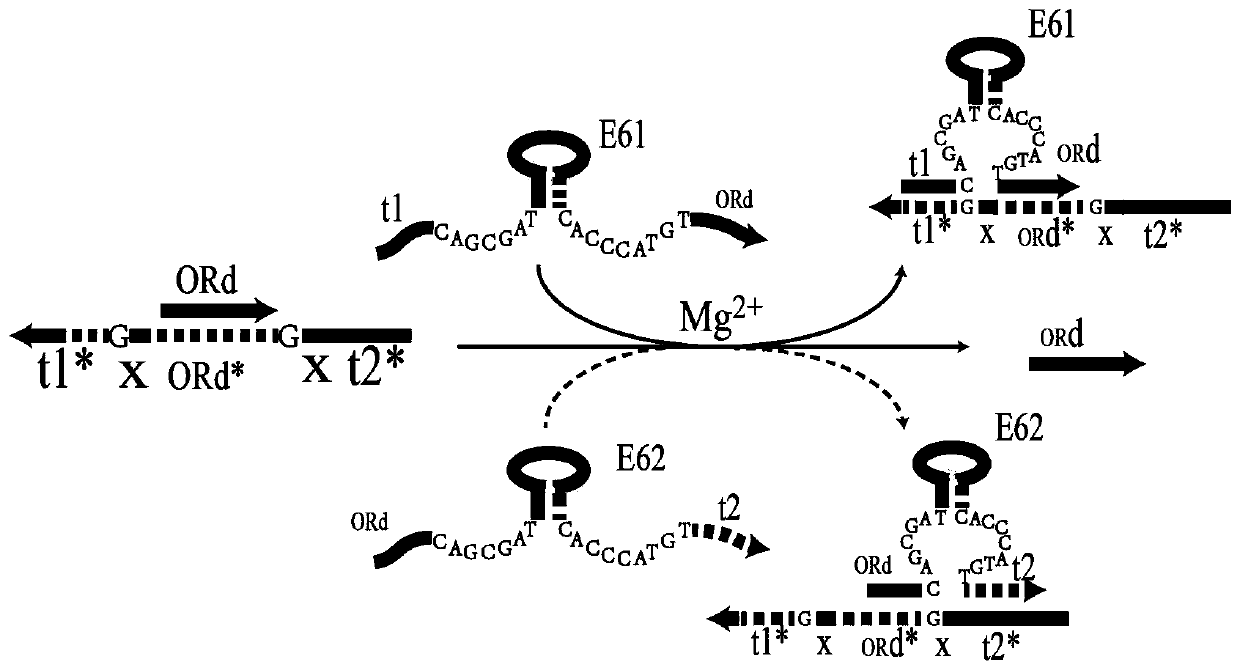
[0038] DNA OR gate
[0039] Such as Image 6 As shown, under the induction of magnesium ions, when E6-type DNAzyme E61 or E62 is mixed with DNA double strand [ORd, t1*XORd*Xt2*] alone (lane 5 and lane 6), E61 or E62 can both DNA The single-stranded ORd is displaced from the double-stranded [ORd,t1*XORd*Xt2*] to form the output of the DNA OR gate; at the same time, when E61 and E62 are simultaneously mixed with the DNA double-stranded [ORd,t1*XORd*Xt2*] (Swimming lane 7), it is also possible to replace the single-stranded DNA ORd from the double-stranded [ORd,t1*XORd*Xt2*] to form the output of the DNA OR gate. It can be seen that under the induction of magnesium ions, the DNA OR gate is realized by long-range strand displacement. Figure 7 Fluorescent detection results for DNA OR gates are given. Under the action of magnesium ions, adding E61 or E62 alone can significantly increase the fluorescence signal, and when E61 and E62 are added at the same time, the increase in flu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com