Constant-current constant-voltage wireless charging system based on topology switching
A technology of constant current, constant voltage and wireless charging, which is applied in current collectors, electric vehicles, electrical components, etc., and can solve problems such as large reactive power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
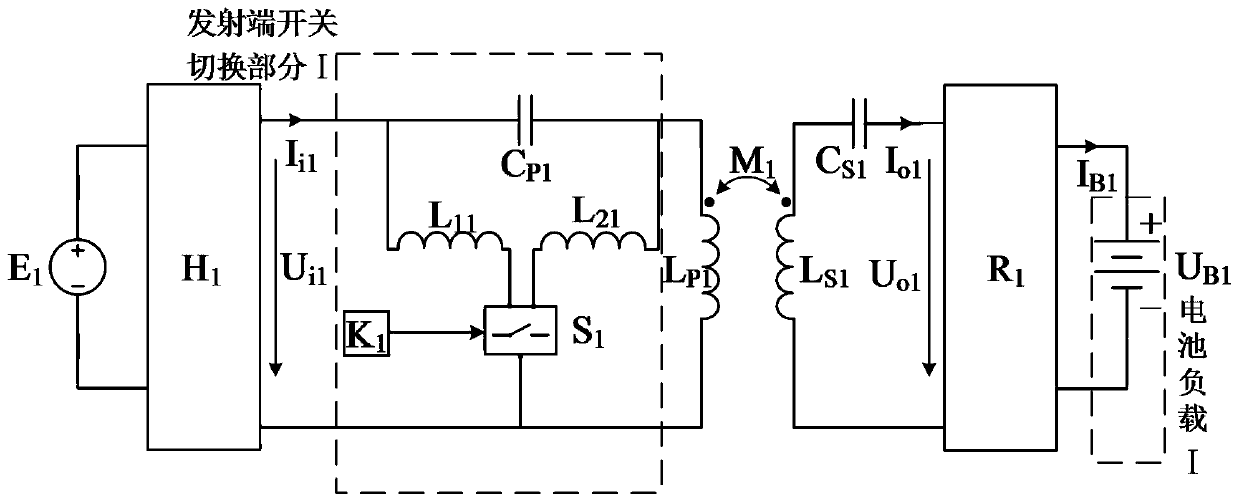
[0091] Theoretical analysis is carried out aiming at the first scheme adopted in the present invention.
[0092] Such as figure 1 The circuit shown, let C P1 Satisfy C S1 Satisfy which is:
[0093]
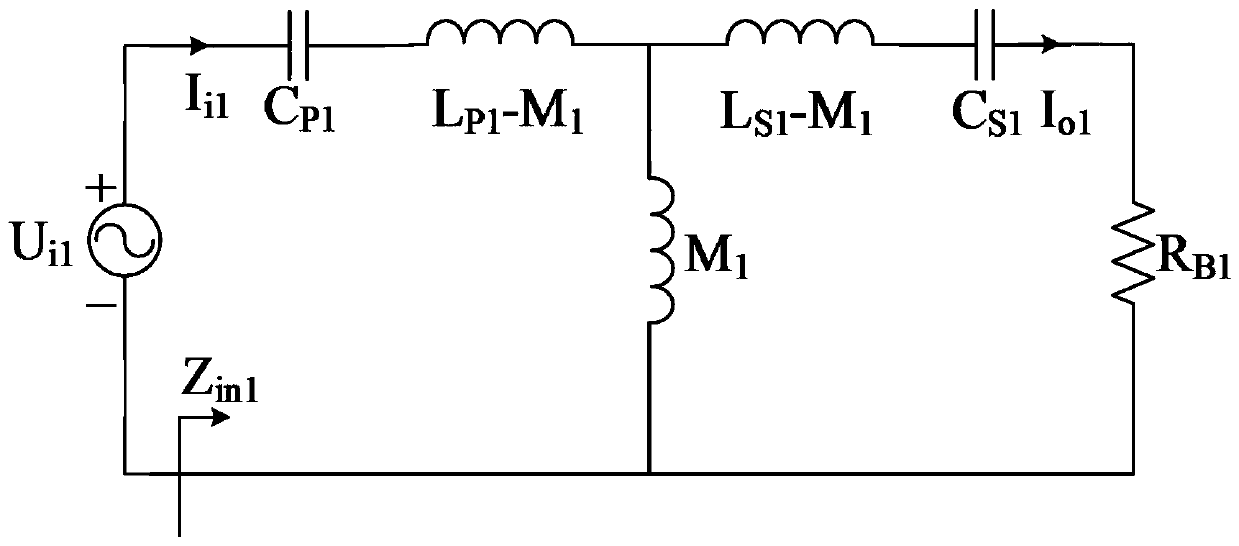
[0094] When switching the switch (S 1 ) is disconnected, the equivalent circuit of the system is as follows image 3 shown. The equivalent impedance of the input end of the system (the output side of the high-frequency inverter) is derived through the principle of series and parallel connection of component impedance, and combined with formula (26) to simplify, the equivalent impedance of the system is obtained as:
[0095]
[0096] Among them, R B1 is the equivalent resistance value of the battery load (I). Equation (26) shows that the high-frequency inverter (H 1 ) The switching element works in a zero-phase switching state, in which there is no reactive power loss.
[0097] According to the principle of impedance shunting in parallel, the AC output current I ...
Embodiment 2
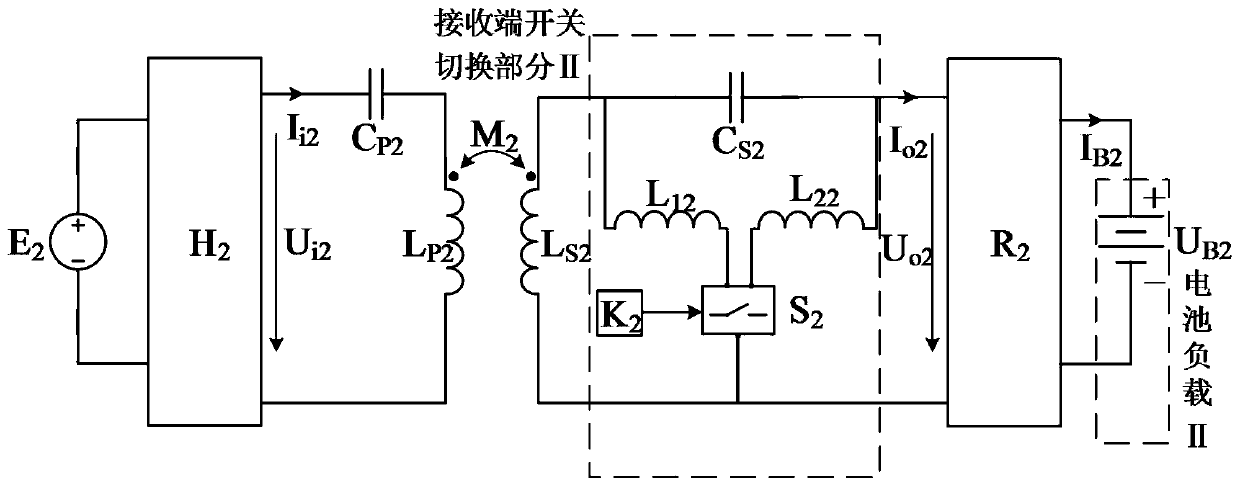
[0113] A theoretical analysis is carried out aiming at the second scheme adopted in the present invention.
[0114] Such as figure 2 The circuit shown, let C P2 Satisfy C S1 Satisfy which is:
[0115]
[0116] When switching the switch (S 1 ) is disconnected, the equivalent circuit of the system is as follows Figure 4 shown. The equivalent impedance of the input end of the system (the output side of the high-frequency inverter) is derived through the principle of series-parallel connection of element impedance, and combined with formula (33) to simplify, the equivalent impedance of the system is obtained as:
[0117]
[0118] Among them, R B2 is the equivalent resistance value of the battery load (II). Equation (34) shows that the high-frequency inverter (H 2 ) The switching element works in a zero-phase switching state, in which there is no reactive power loss.
[0119] According to the principle of impedance shunting in parallel, the AC output current I ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com