Treatments for heart failure and cardiac ischaemic reperfusion injury
A heart failure, heart technology, applied in the inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase-4, treatment or prevention of heart disease such as heart failure and cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury, in the field of heart failure and cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury, It can solve the problems of insufficient promotion of left ventricular function, time-consuming, and small improvement of cardiac function, and achieve the effect of reducing or minimizing cardiomyocyte apoptosis in vitro
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
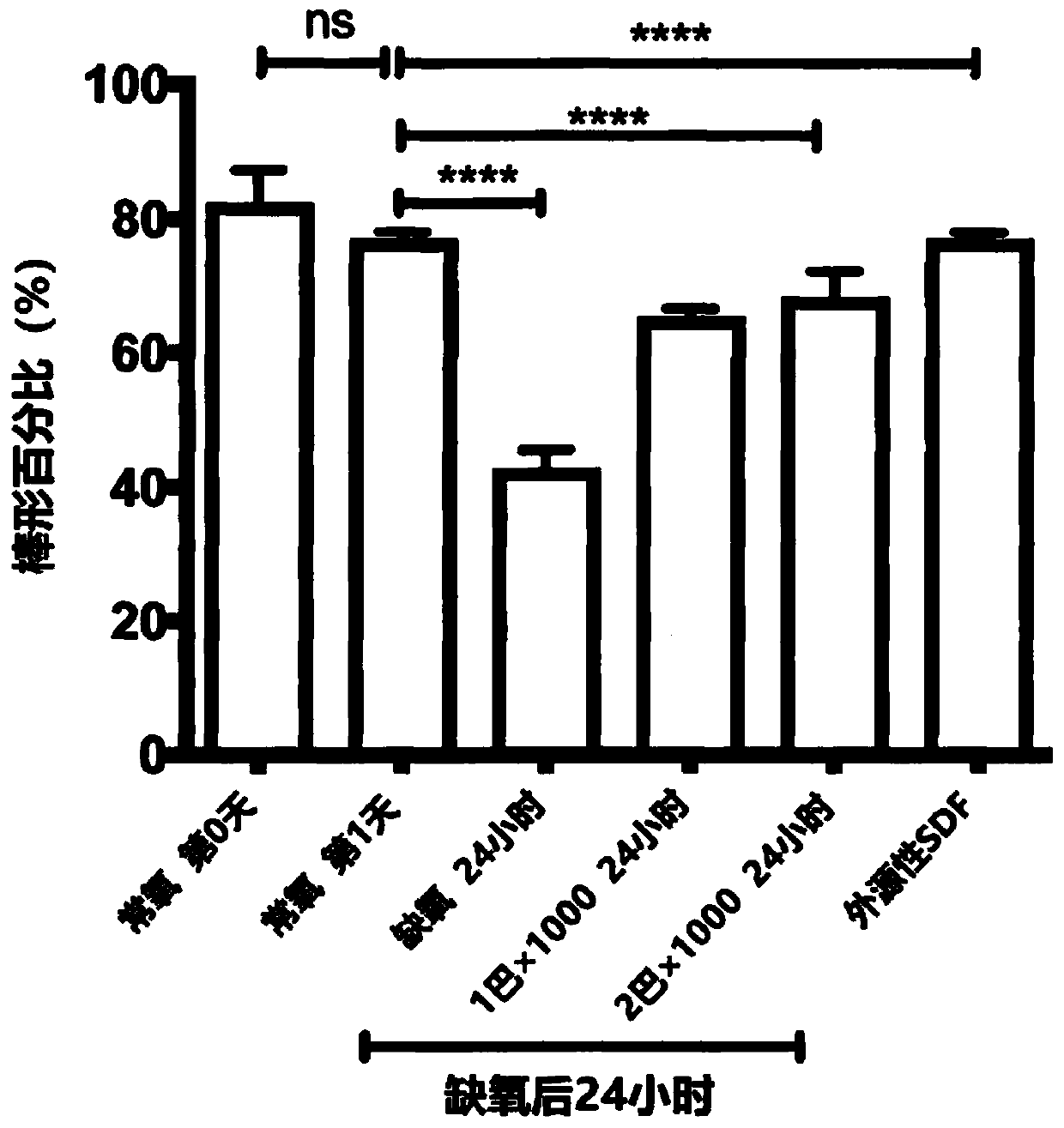
[0160] Example 1: Effect of Shock Wave Treatment on Hypoxia-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis in Rats
[0161] Primary rat cardiomyocytes were isolated using the Langendorff method, in which the explanted heart was perfused retrogradely through the aorta with oxygenated hypocalcium solution and collagenase solution. The hearts were then cut into small pieces and stirred in a collagenase solution to release the cells. Cells were washed and cardiomyocytes were positively selected using low speed centrifugation and adhesion to laminin-coated culture plates (dishes).
[0162] Rat cardiomyocytes were exposed to severe hypoxia for 30 minutes (0% O 2 ,100%N 2 ). The group that received shock wave therapy (1 bar or 2 bar, 1000 pulses) was treated immediately after returning to normoxia. Shock waves were delivered from below the culture dish by direct contact between the shock wave applicator on the handpiece of the Swiss Dolarclast (EMS) shock wave system and the ultrasound gel. ...
Embodiment 2
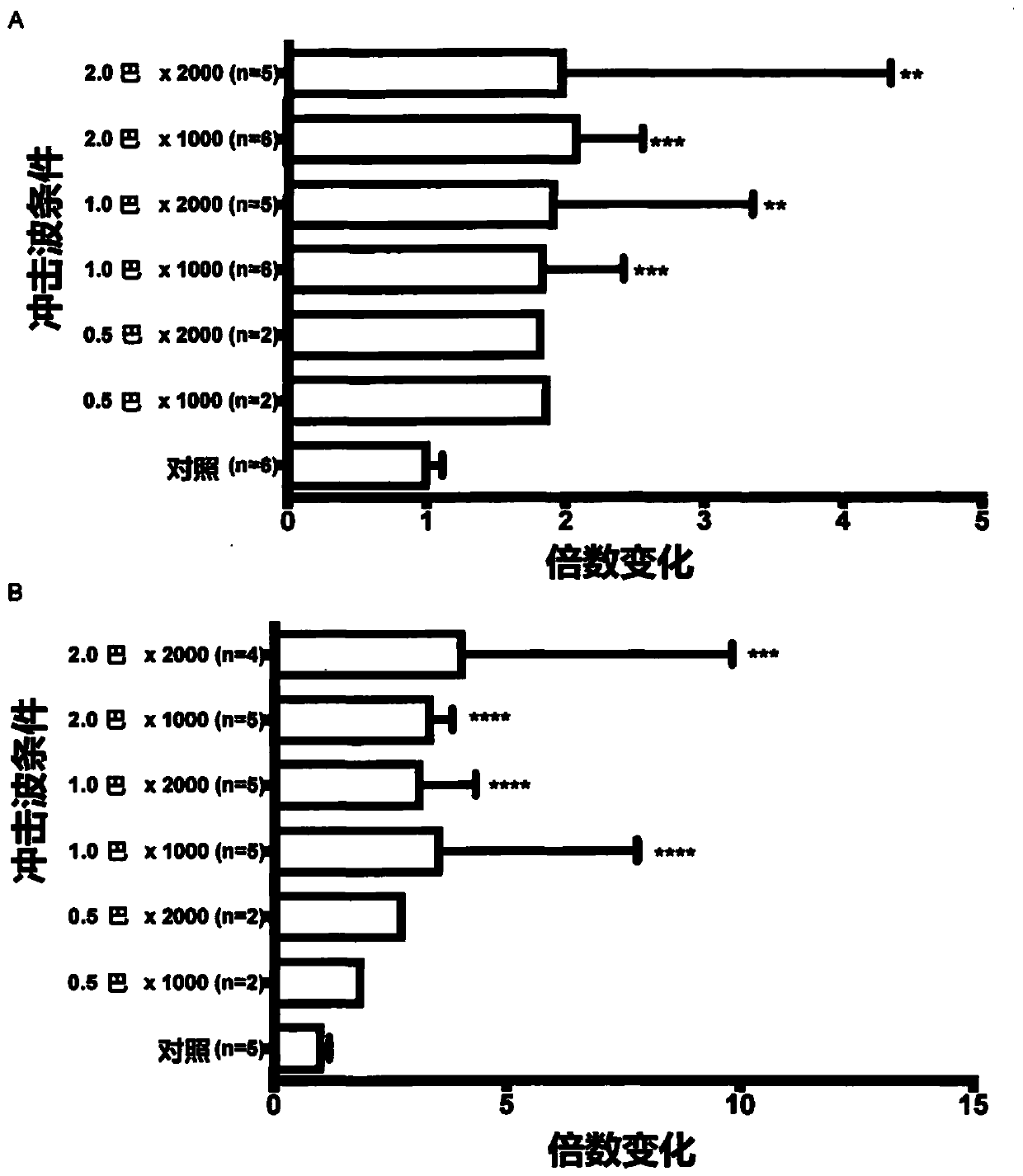
[0163] Example 2: Effect of Shockwave Treatment on Gene Expression in Human Ventricular Tissue
[0164] Explanted human ventricular tissue was cut into small pieces and cultured individually in 24-well plates in M 199 medium. Exposure to various shock wave conditions was performed by temporarily placing tissue pieces in 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes in M 199 medium. A shock wave applicator is described in Example 1 which uses an ultrasonic gel coupled directly to the tube. Then place the tissue block in the incubator (37°C and 5% CO 2) in their respective media for a 4-hour time point and then stored in RNA-Later at -80°C. Sample batches were thoroughly homogenized in Trizol using a power homogenizer. Purify RNA using chloroform and commercial spin columns. Use a Nanodrop spectrophotometer to check the quality of RNA and perform reverse transcription reactions. At Applied Biosystems TM Evaluation of SDF1 (stromal-derived factor 1), VEGFA (vascular endothelial growth facto...
Embodiment 3
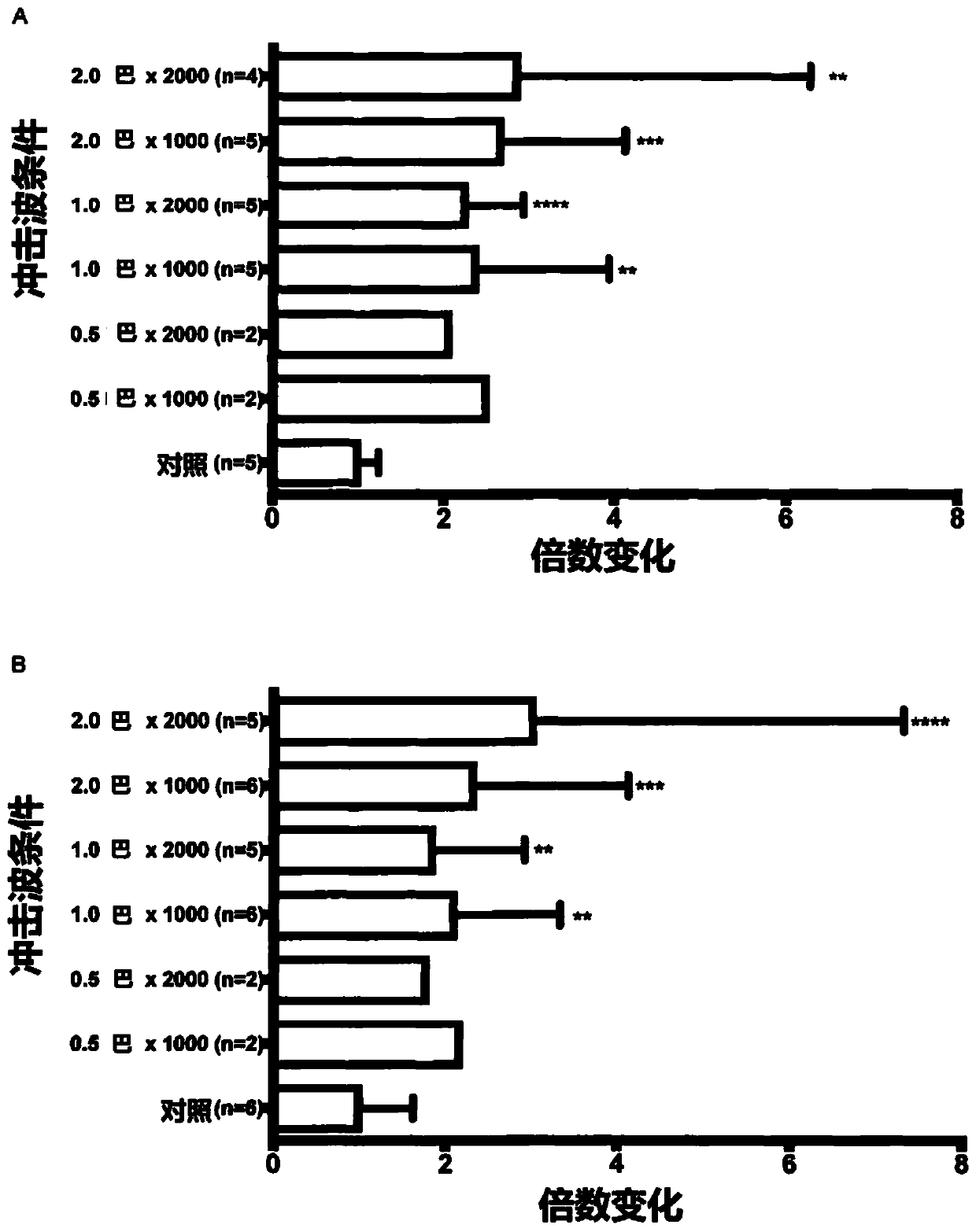
[0165] Example 3: Effect of Shock Wave Treatment on SDF-1 Gene Expression in Endothelial Cells and Human Cardiac Fibroblasts
[0166] Human ventricular tissue was dissociated using collagenase, and single cell suspensions were washed, plated and cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FCS. HUVECs were harvested from human umbilical cords and cultured in EGM2. Cells were subcultured for 3-5 generations for experiments.
[0167] Human cardiac fibroblasts and HUVEC were subjected to shock wave treatment as described in Example 1, and when the time point was reached, the medium was removed and the cells were lysed with Trizol. According to the method described in Example 2, SDF1 gene expression was measured at various time points after shock wave treatment. The result is as Figure 5 shown.
[0168] In human cardiac fibroblasts, SDF1 gene expression continued to increase at the 24-hour time point, whereas SDF1 gene expression reached maximum expression in HUVEC between 2-6 ho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com