Water-saving irrigation method and system based on fuzzy logic control theory
A technology of control theory and fuzzy logic, applied in control/regulation systems, non-electric variable control, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as inability to accurately establish models, complexity, and low utilization of irrigation water.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
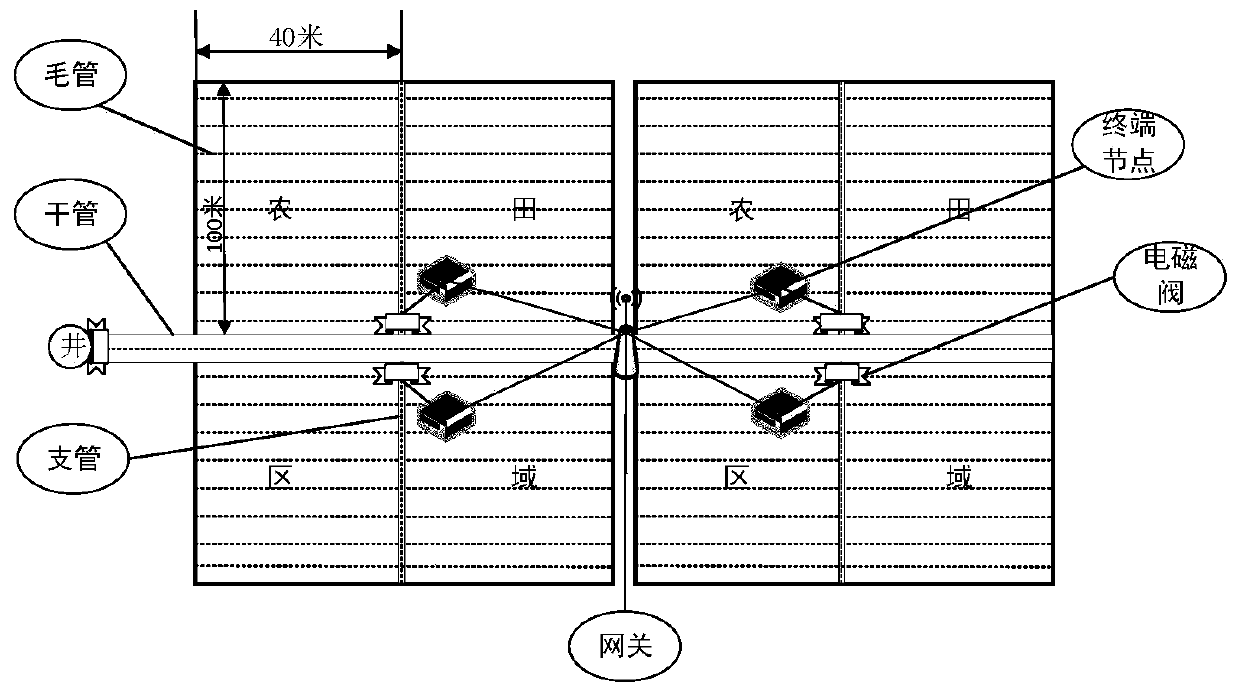
[0079] In order to avoid the waste of water resources when irrigating crops in the prior art, this embodiment provides a water-saving irrigation method based on fuzzy logic control theory. The water-saving irrigation method of this embodiment is designed for large-scale, large-scale operation of farmland. In the choice of irrigation method, the method of drip irrigation can be selected in practice. Using the drop tank method, although the short-term investment is large, the long-term benefits are high, and it is easy to combine with the modern automation mode. According to the environmental requirements of the farmland, the large-scale and large-scale farmland is divided into several areas, and pipelines are laid on the farmland.
[0080] see figure 1 , The pipelines laid in farmland include dry pipes, branch pipes and capillary pipes. The main pipe is the main pipe, which is generally buried underground and laid for a long distance, directly connected to irrigation water s...
Embodiment 2
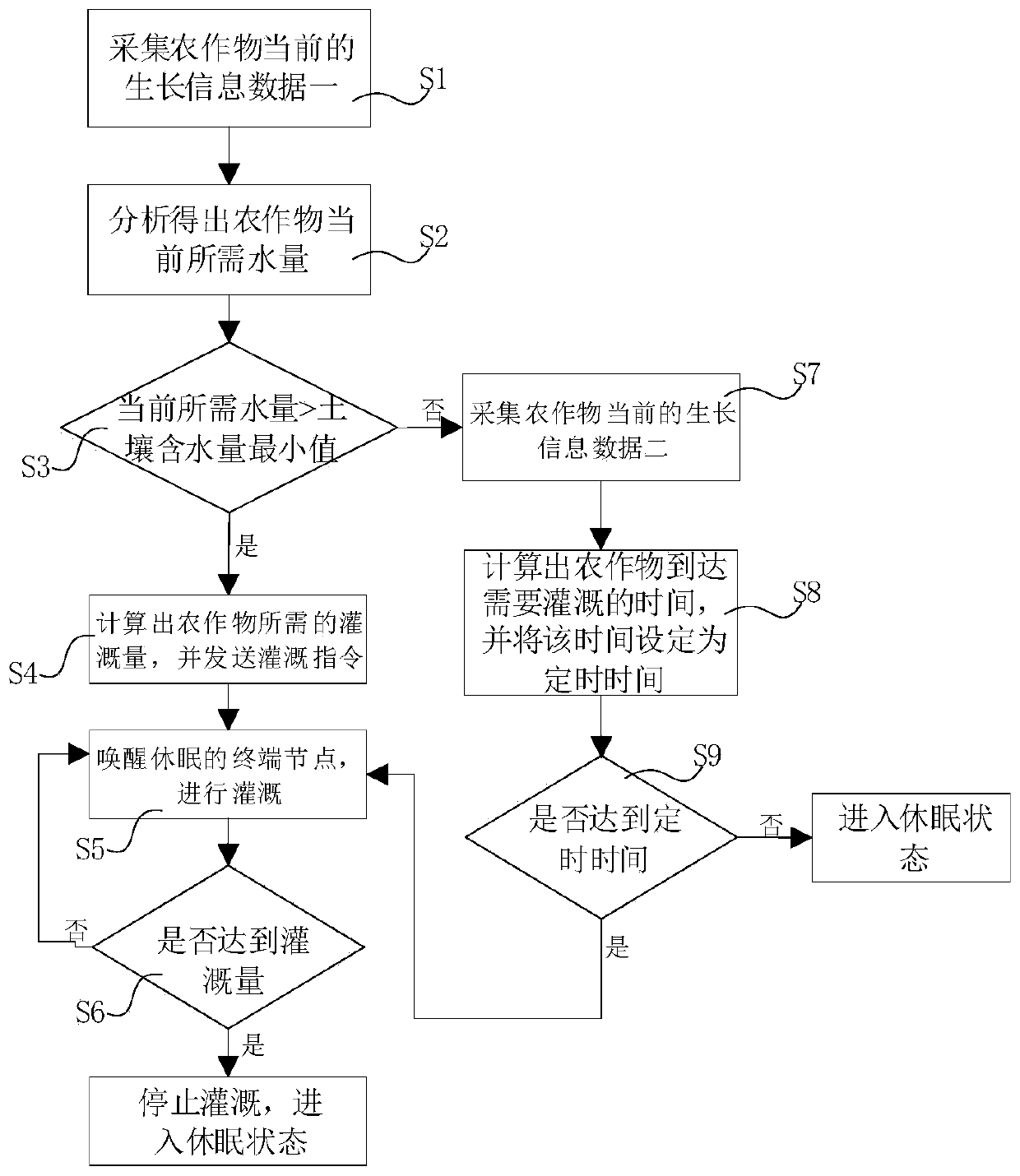
[0122] This embodiment provides a water-saving irrigation method based on fuzzy logic control theory, which specifically describes the calculation method of water irrigation amount on the basis of Embodiment 1. Among them, the calculation method of water irrigation is realized through fuzzy control algorithm. The fuzzy control algorithm in this embodiment is used in conjunction with the fuzzy control system.
[0123] like Figure 4 As shown, the soil moisture suitable for the normal growth and development of crops is taken as the given value r, that is, the minimum value of soil water content required by crops is taken as the given value r. Among them, the system design takes cucumber planting as an example to start the description.
[0124] Mark the soil moisture collected in real time as y, then the input variables of the fuzzy control system are soil moisture error e=r-y, the rate of change of soil moisture error ec=d / dt, and the output variable u is the length of irrigatio...
Embodiment 3
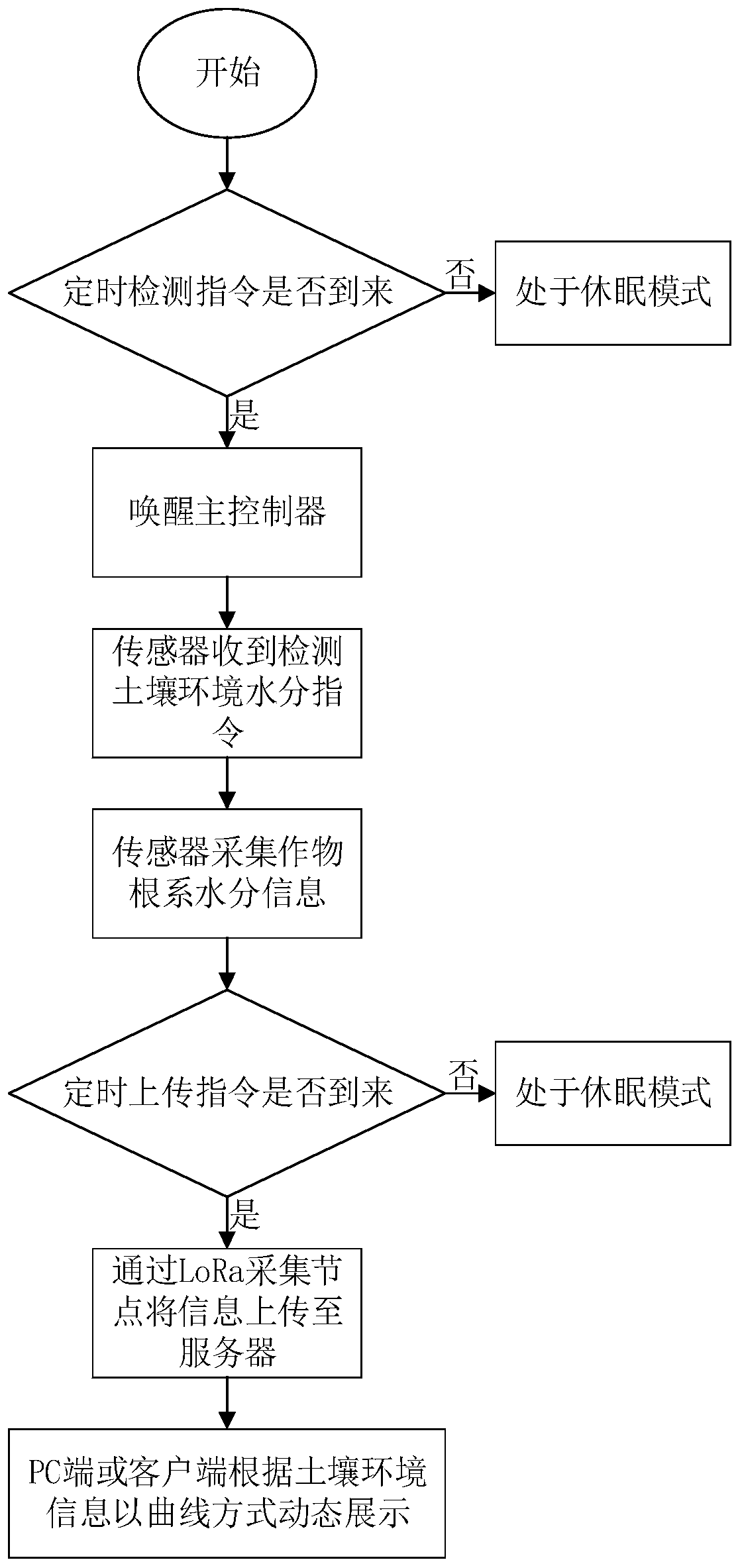
[0175] This embodiment proposes a water-saving irrigation system based on fuzzy logic control theory, which is used in conjunction with the water-saving irrigation method based on fuzzy logic control theory in Embodiment 1.
[0176] The water-saving irrigation system based on fuzzy logic control theory of the present embodiment adopts a closed-loop decision model based on adaptive fuzzy logic, and the design of the closed-loop decision model includes the following six parts:
[0177] ① Determine the input variable of the fuzzy logic controller, that is, the current soil moisture error and the rate of change of the error; the output variable is the control amount irrigation time length.
[0178] ②Use the fuzzy PID control principle and the membership function of each language variable obtained in combination with the characteristics of the irrigation system to make a fuzzy control rule table for eliminating errors.
[0179] ③Use triangular fuzzy sets to fuzzify precise input qu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Inner ring diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Outer ring diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com