Application of TBK1 as E3 ubiquitin ligase
A ubiquitin ligase and virus technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of strong virus virulence and incomplete virus inactivation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
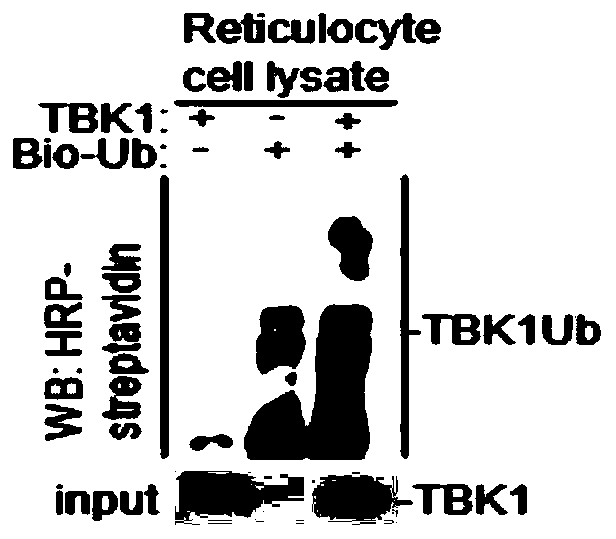
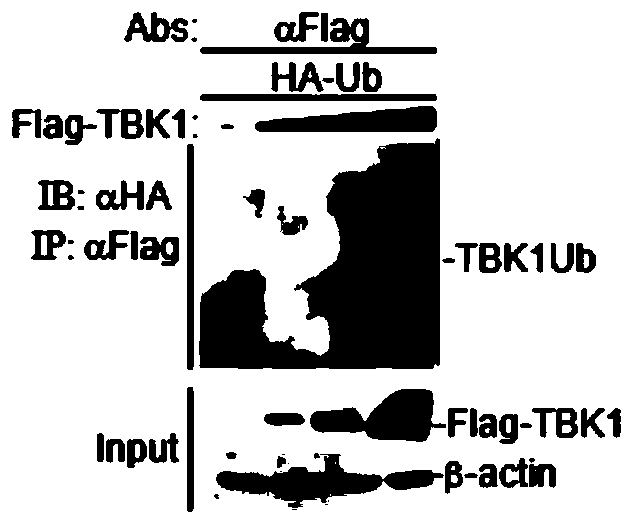
[0034] Example 1 Study on the activity of TBK1 as an E3 ubiquitin ligase
[0035] 1.1 In vitro ubiquitination experiment of TBK1
[0036] 1.1.1 In vitro transcription of plasmids
[0037] (1) According to the instructions of the in vitro transcription kit (TNT Quick Coupled Transcription / TranslationSystems kit), use the pCDNA3.1-Flag-TBK1 plasmid (1 μg) to be detected and the control plasmid pCDNA3.1 (1 μg) with TNT Quick Master Mix ( 24μL), Methionine (1.2μL), 0.5μg / μL plasmamid (2μL), H 2 O (2.8 μL) was mixed to prepare a reactant;
[0038] (2) Put the above reactant at 30° C. for 60-90 min to obtain the in vitro transcription product pCDNA3.1-Flag-TBK1 protein.
[0039] 1.1.2 Ubiquitination analysis experiments:
[0040] (1) According to the instructions of the in vitro ubiquitin kit (Enzo Life Sciences), the above in vitro transcription product pCDNA3.1-Flag-TBK1 protein (7.5 μL) was mixed with dH 2 O (14μL), 10×Ubiquitionylation Buffer (5μL), 100U / ml IPP (10μL), 50mM...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 Degradation of FMDV structural protein VP3 signaling pathway molecular analysis
[0056] 2.1 Experimental steps
[0057] (1) HEK-293T cells were paved in 12-well plates, and when the cells grew to 60%-80%, the plasmids of signaling pathway molecules (pCDNA3.1-HA-VISA, pCDNA3.1-HA-RIG-I, pCDNA3. 1-HA-IRF3-5D, pCDNA3.1-HA-IRF7, pCDNA3.1-HA-TBK1, pCDNA3.1-HA-MITA, pCDNA3.1-HA-RIG-I, pCDNA3.1-HA-MDA5) 1 μg of each, respectively co-transfected with 1 μg of FMDV VP3 plasmid into 293T cells;
[0058] (2) Collect the sample 24 hours after transfection, wash it 1-2 times with cooled PBS, add 100 μL of SDS loading buffer for lysis, and detect the expression of VP3 protein by WB method.
[0059] 2.2 Experimental results
[0060] The result is as image 3 As shown, only in the presence of TBK1 plasmid, VP3 protein is not expressed, therefore, only TBK1 in the above signaling pathway molecules can inhibit the expression of VP3 protein, indicating that TBK1 can degrade ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Example 3 Analysis of TBK1 degrading FMDV structural protein VP3
[0062] 3.1 Experimental steps
[0063] (1) HEK-293T cells were plated in 12-well plates, and when the cells grew to 60%-80%, transfected with pCDNA3.1-Flag-VP3 plasmid and pCDNA3.1-HA-TBK1 plasmid, in which pCDNA3.1-Flag - VP3 plasmid 1 μg (constant amount), pCDNA3.1-HA-TBK1 plasmid 0.5 μg, 1 μg, 1.5 μg, 2 μg (increasing variable), or pCDNA3.1-HA-TBK1 plasmid 2 μg (constant amount), pCDNA3.1-Flag - VP3 plasmid 0.5 μg, 1 μg, 1.5 μg, 2 μg (increasing variable) for co-transfection;
[0064] (2) Collect the sample 24 hours after transfection, wash it 1-2 times with cold PBS, add 100 μL of SDS loading buffer to lyse, and detect the expression of pCDNA3.1-Flag-VP3 plasmid and pCDNA3.1-HA-TBK1 plasmid by WB .
[0065] 3.2 Experimental results
[0066] The result is as Figure 4 Shown: Whether the content of the pCDNA3.1-Flag-VP3 plasmid remains unchanged and the variable of the pCDNA3.1-HA-TBK1 plasmid inc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com