Method for realizing ultra-narrowband absorption and sensing by utilizing structural symmetry breaking
An ultra-narrow-band, light-absorbing technology, applied in optical components, optics, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as the enhancement of light absorption efficiency, and achieve the effect of high-sensitivity refractive index sensing and ultra-narrow-band selective perfect absorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] In the present invention, metal and dielectric film materials can be arbitrarily selected to realize ultra-narrow-band perfect light absorption with symmetry breaking. feel. Firstly, nano-grooves are introduced into the grating structure with a metal substrate. By making the distance between the center of the nano-groove and the center of the original cell of the grating ≠ 0, the symmetry of the grating structure is broken, and the symmetry of the grating structure is used. The highly localized and significantly enhanced light field in the nanogroove is realized, thereby obtaining ultra-narrow-band light absorption and high-sensitivity sensing.
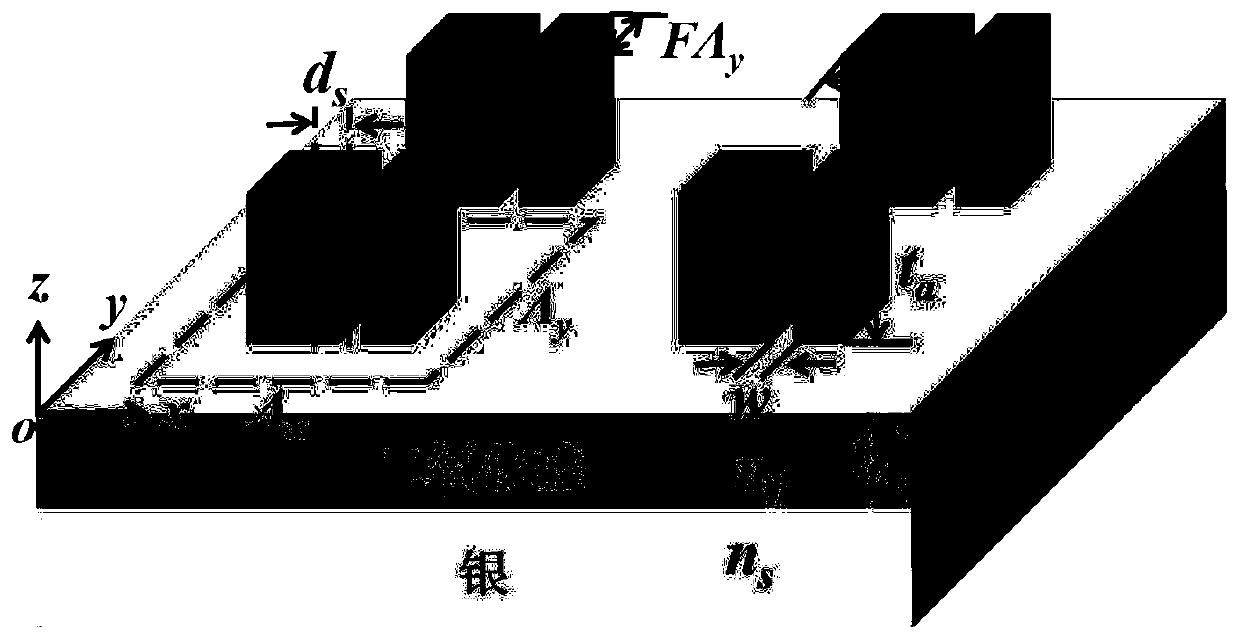
[0027] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of a two-dimensional grating structure with a metal substrate and nanogrooves. The substrate is a metal with a refractive index n s . Above the substrate is a layer of thickness t b The low refractive index dielectric buffer layer, the refractive index n b . Above the buffer laye...
Embodiment 2
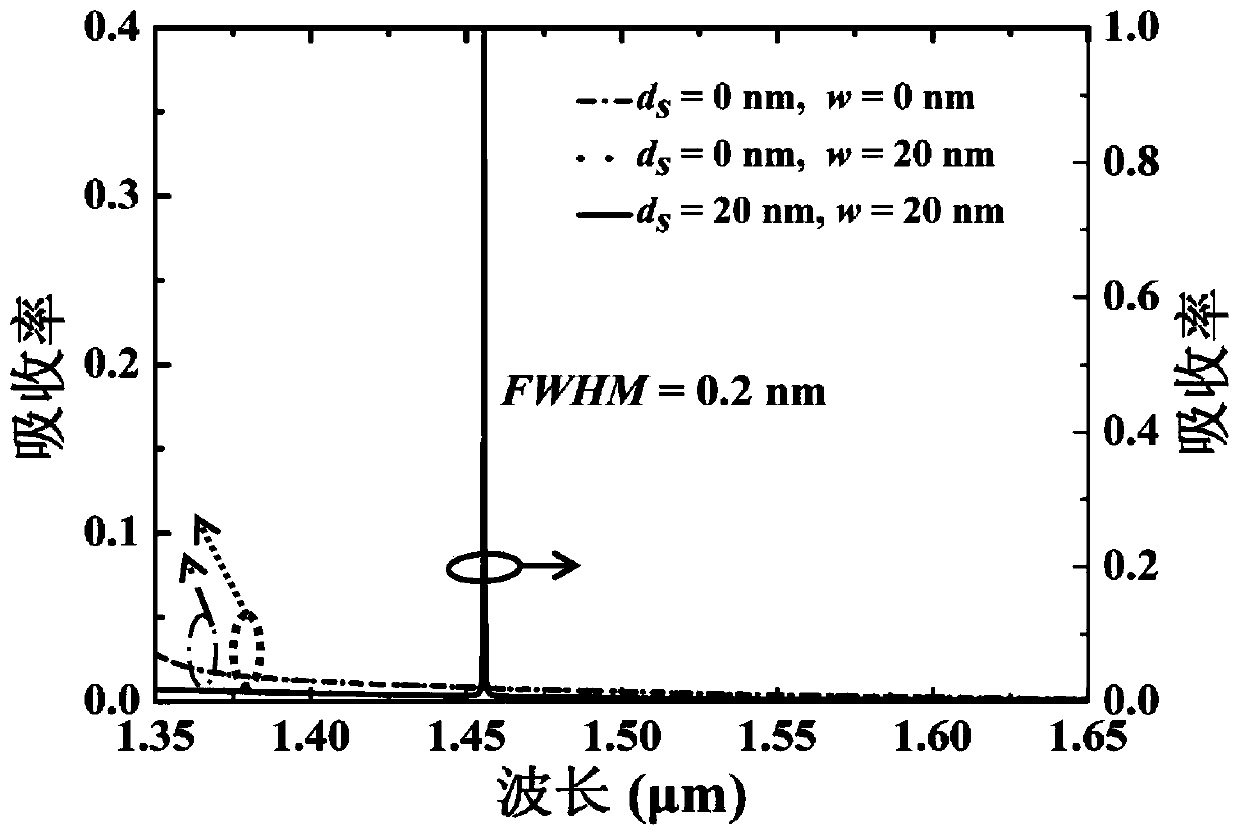
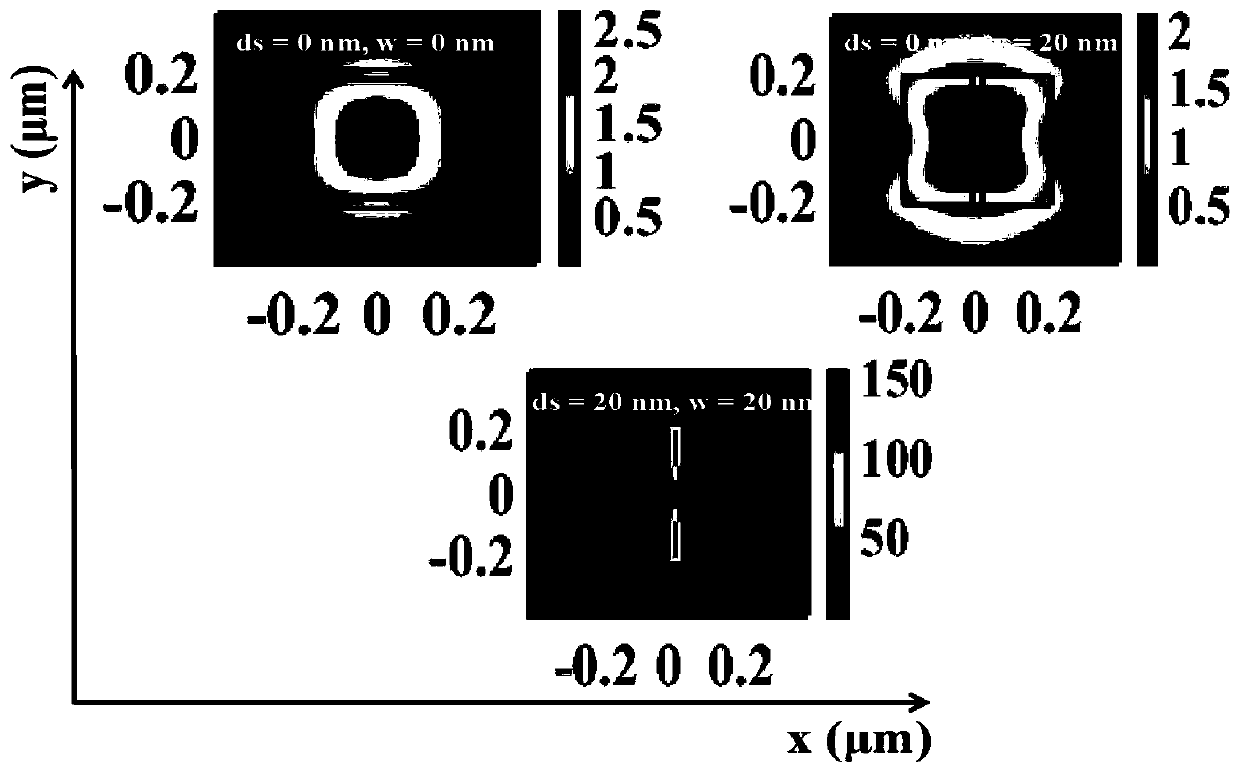
[0031] In order to reveal the physical mechanism corresponding to the ultra-narrow-band light absorption of the symmetry-breaking structure, the rigorous coupled-wave theory is used to calculate the symmetry cases (d s = 0) and the symmetry breaking case (d s ≠0), the electric field distribution of the grating structure at the resonant absorption wavelength of 1455.8nm, we get image 3 .
[0032] image 3 For the structure of the present invention in the symmetrical case (d s = 0) and the symmetry breaking case (d s ≠0), the normalized electric field amplitude distribution of the 1455.8nm absorption peak light wave on the xoy plane. From image 3 It can be seen that for a symmetric structured grating, that is, d s = 0, w = 0 (symmetrical and no nanogrooves), and d s =0, w=20nm (symmetrical and with nano-grooves), regardless of whether there are nano-grooves in the grating, due to the local effect of the high-refractive index grating on the light field, although the elec...
Embodiment 3
[0034] For the symmetry-breaking grating structure (d s ≠0), under the condition of groove width w=20nm, select different groove positions d s , such as d s take d respectively s =20nm,d s =30nm, d s = 40nm, d s = 50nm, d s =60nm, d can be calculated using vector diffraction theory s The absorption spectrum curve of the structure when it changes;
[0035] Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that when d s When increasing from 20nm to 60nm, the ultra-narrow band absorption peak has a significant red shift, and the absorption peak wavelength moves from 1455.8nm to 1498.1nm, that is, as the asymmetry of the grating structure increases (that is, the d s ), the narrow-band absorption peak moves to the long-wave direction, but the corresponding low-absorption sideband remains unchanged, and the structure still maintains excellent ultra-narrow-band selective absorption characteristics.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com