A segmented semiconductor refrigeration chip
A technology for semiconductors and refrigerating chips, applied in the field of semiconductor refrigerating chips with segmented structure, can solve the problem of lack of integral research on the number of segments, and achieve the maximum cooling temperature difference and the improvement of cooling capacity, cooling coefficient and cooling temperature difference. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
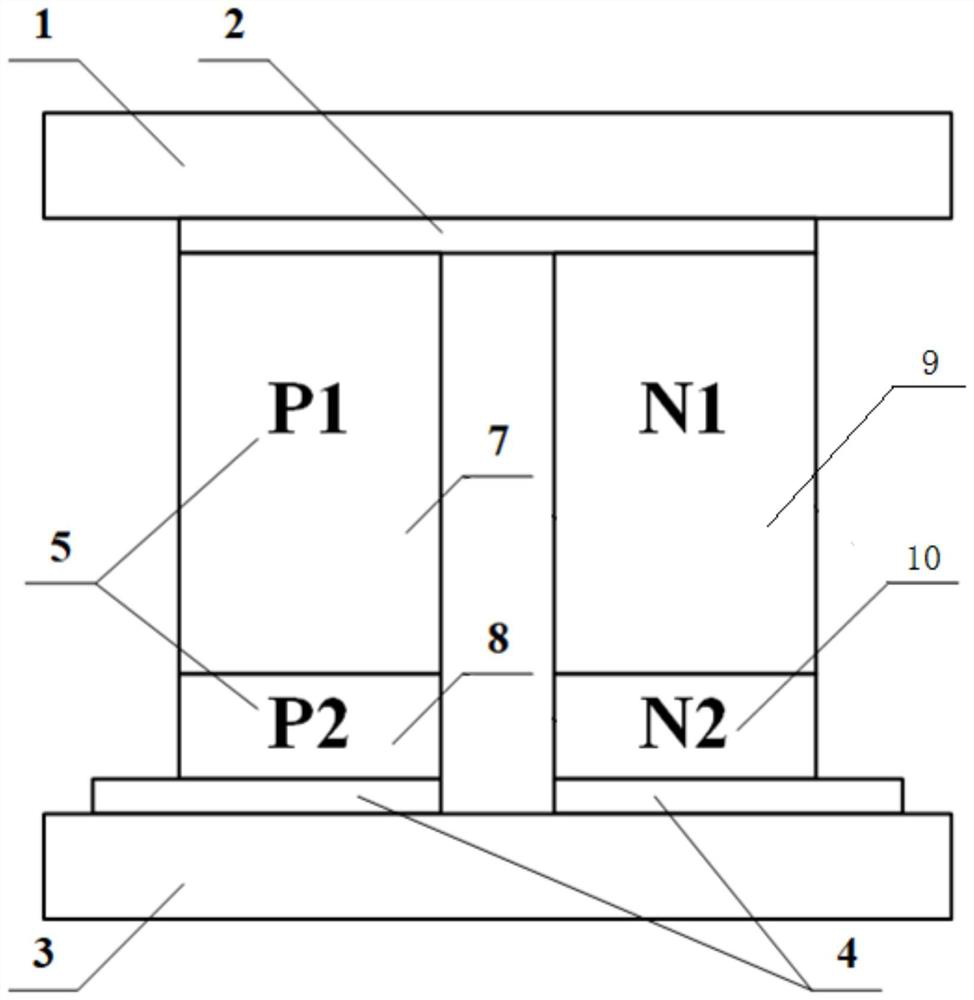
[0041] In this embodiment, on the basis of the semiconductor refrigeration sheet TEC12706, the thermoelectric arm in the refrigeration unit is divided into two sections. The length ratio of the P-type cold-end thermoelectric arm section 7 to the P-type hot-end thermoelectric arm section 8 is 1:1, and the length ratio of the N-type cold-end thermoelectric arm section 9 to the N-type hot-end thermoelectric arm section 10 is 1:1 . That is, the length of each section is 0.75mm, and its semiconductor materials are bismuth telluride and its alloys.
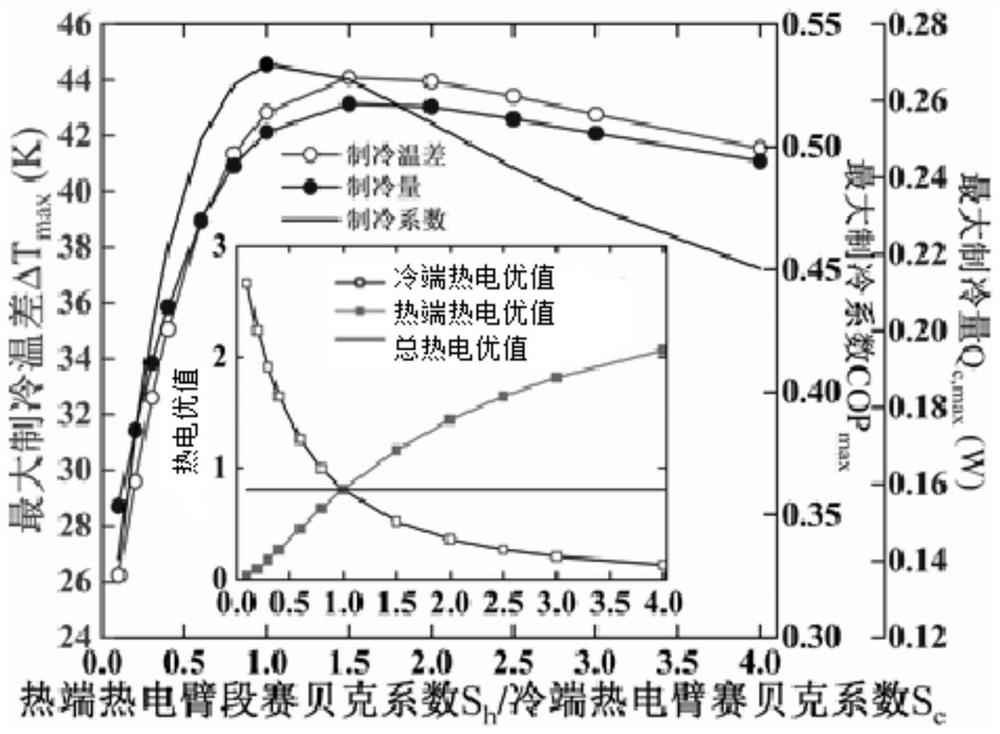
[0042] Such as figure 2 As shown, under the condition that the overall thermoelectric figure of merit (ZT) remains unchanged, the ratio of Seebeck coefficient (S h / S c ) On the overall performance. Experiments have shown that the ratio of Seebeck coefficient of the hot and cold end thermoelectric arms (S h / S c When) is 1, the maximum coefficient of refrigeration (COP) can be reached.
Embodiment 2
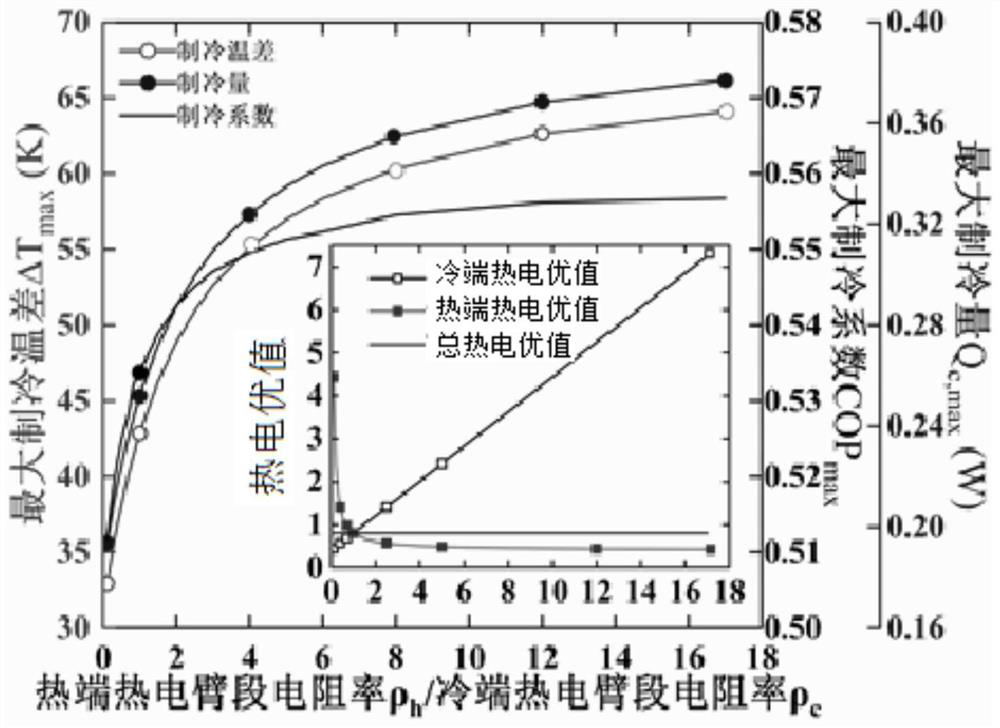
[0044] In this embodiment, the overall thermoelectric figure of merit (ZT) value remains unchanged, and the ratio of Seebeck coefficient (S h / S c ) Is 1, the thermal conductivity and resistivity of the two sections have an effect on the overall cooling performance, such as image 3 with Figure 4 Shown. Experiments show that the resistivity ratio of the thermoelectric arm section at the hot and cold ends (ρ h / ρ c ) And the ratio of thermal conductivity (λ h / λ c When) is 6 or more, higher refrigeration performance can be achieved, and the required physical property gap is smaller.
Embodiment 3
[0046] In this embodiment, under the condition that the total thermoelectric arm length is unchanged, the Seebeck coefficient ratio (S h / S c ) Is 1, the resistivity of the thermoelectric arm section at the hot and cold ends (ρ h / ρ c ) And the thermal conductivity ratio (λh / λc) of the hot and cold end thermoelectric arm sections (λh / λc) is 6, the effect of the change in the ratio of the best cold end thermoelectric arm length to the total length on the cooling performance, such as Figure 5 Shown. Experiments show that in L c When / L is 0.8, that is, the ratio of the length of the P-type cold-end thermoelectric arm section (7) to the P-type hot-end thermoelectric arm section (8) is 4:1, and the N-type cold-end thermoelectric arm The ratio of the length of the section (9) to the length of the N-type hot-end thermoelectric arm section (10) is 4:1, and the overall refrigeration performance is the best. It can increase the refrigeration capacity by 151.8%, increase the refrigerati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com