Method for inactivating microorganisms in drinking water based on photoelectrochemical reactor
A technology of photoelectrochemistry and chemical reaction, applied in chemical instruments and methods, light water/sewage treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as transportation and storage process safety, reduce disinfection energy consumption, and increase sterilization rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
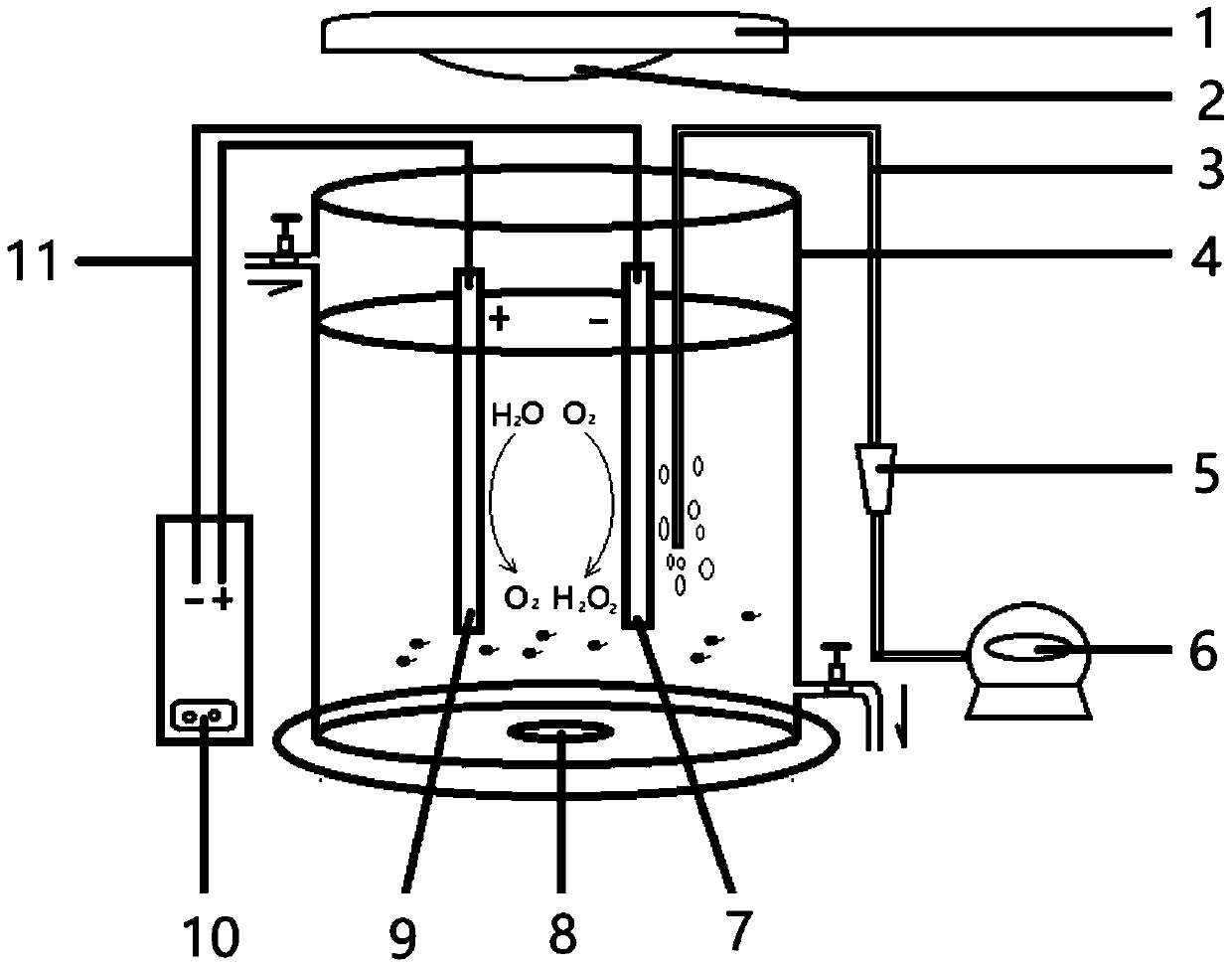
[0037] The structure of the photoelectrochemical reactor used in this embodiment is as follows figure 1 shown.
[0038] 1. Pretreatment of drinking water:
[0039] Inject drinking water to be treated into the photoelectrochemical reactor with an injection volume of 1000mL, accounting for 85% of the capacity of the photoelectrochemical reactor. Add 0.20g of sodium sulfate, turn on the magnetic stirring and aeration switch, and aerate the air for 20 minutes to improve the dissolution rate in the water. oxygen concentration.
[0040] 2. Disinfection treatment of drinking water
[0041] Connect the DC steady current power supply of the photoelectrochemical reactor, turn on the lamp tube of the solar simulator, and treat for 3 hours; water molecules are decomposed into hydroxyl radicals at the anode, and oxygen is reduced to hydrogen peroxide at the cathode. With the continuous increase of the concentration of hydrogen peroxide, the ultraviolet disinfection effect in synergy wit...
example 2
[0047] The photoelectrochemical reactor used in this embodiment is as shown in Example 1.
[0048] 1. Pretreatment of drinking water:
[0049] Inject drinking water to be treated into the photoelectrochemical reactor with an injection volume of 1000mL, accounting for 85% of the capacity of the photoelectrochemical reactor. Add 0.20g of sodium sulfate, turn on the magnetic stirring and aeration switch, and aerate the air for 20 minutes to improve the dissolution rate in the water. oxygen concentration.
[0050] 2. Disinfection treatment of drinking water
[0051] Switch on the DC steady-current power supply of the photoelectrochemical reactor, turn on the lamp tube of the solar simulator, and treat for 2.5 hours; water molecules are decomposed into hydroxyl radicals at the anode, and oxygen is reduced to hydrogen peroxide at the cathode. With the continuous increase of the concentration of hydrogen peroxide, the ultraviolet disinfection effect in synergy with sunlight is very...
example 3
[0057] The photoelectrochemical reactor used in this embodiment is as shown in Example 1.
[0058] 1. Pretreatment of drinking water:
[0059] Inject drinking water to be treated into the photoelectrochemical reactor with an injection volume of 1000mL, accounting for 85% of the capacity of the photoelectrochemical reactor. Add 0.20g of sodium sulfate, turn on the magnetic stirring and aeration switch, and aerate the air for 20 minutes to improve the dissolution rate in the water. oxygen concentration.
[0060] 2. Disinfection treatment of drinking water
[0061] Switch on the DC steady-current power supply of the photoelectrochemical reactor, turn on the lamp tube of the solar simulator, and treat for 2.5 hours; water molecules are decomposed into hydroxyl radicals at the anode, and oxygen is reduced to hydrogen peroxide at the cathode. With the continuous increase of the concentration of hydrogen peroxide, the ultraviolet disinfection effect in synergy with sunlight is very...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com