Flame-retardant processing of polyester-based synthetic fiber structure
A technology of synthetic fibers and structures, applied in the direction of fiber type, fiber treatment, flame retardant fibers, etc., can solve the problems of color flower, poor dispersion, chalky spots, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0084] Hereinafter, reference examples showing the synthesis method of the flame retardant of the present invention, production of the flame retardant processing agent of the present invention, and examples of flame retardant processing of the present invention are listed together with comparative examples to describe the present invention in detail. However, the present invention is not limited by these Examples.
[0085] It should be noted that the following non-volatile components in the flame retardant processing agent refer to the ratio of the flame retardant in the flame retardant processing agent, and the surfactant and defoamer are included together with the flame retardant in the flame retardant processing agent , refers to the ratio of the total amount of flame retardant, surfactant and defoamer.
[0086] The average particle size of the flame retardant is the volume-based median particle size obtained by measuring the particle size distribution of the flame retardan...
reference example 1
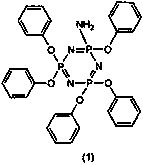
[0091] (Synthesis of Aminopentaphenoxycyclotriphosphazene)
[0092] 521 g (1.50 moles) of hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene was added to a 10 L flask equipped with a stirrer, a thermometer and a reflux condenser, and 2000 mL of toluene was added for dissolution to obtain a toluene solution of hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene.
[0093] A solution obtained by adding 3000 mL of THF (tetrahydrofuran) to 784 g (6.75 moles) of sodium phenate was added dropwise to the toluene solution of the above-mentioned hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene at an internal temperature of 20° C. to 35° C., then heated and refluxed for 1 hour. Next, THF was distilled off from the obtained reaction mixture, followed by stirring at 110° C. for 8 hours.
[0094] The reaction mixture thus obtained was washed with 2000 mL of a 2% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution, and then washed twice with 1000 mL of desalted water. Toluene and a small amount of water were distilled off from the obtained toluene layer to obtain 892 g...
reference example 2
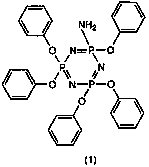
[0105] (Synthesis of 2,2-diamino-4,4,6,6-tetraphenoxycyclotriphosphazene)
[0106] Add 521 g (1.50 moles) of hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene into a 5 L flask with a stirrer, a thermometer and a reflux condenser, add 2150 mL of ether, stir while cooling in a water bath, and dissolve to obtain the ether of hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene solution.
[0107] While stirring the above solution, 766 g of 25% ammonia water (11.3 moles as ammonia) was added dropwise thereto at an internal temperature of 25° C. or lower, and reacted at an internal temperature of 30° C. for 2 hours. The resulting reaction mixture was transferred to a separatory funnel, the aqueous layer was separated, and the ether layer was washed with desalted water until neutral.
[0108] After the obtained ether layer was dehydrated, ether was distilled off to obtain 276 g of 2,2-diamino-4,4,6,6-tetrachlorocyclotriphosphazene as a pale yellow solid. Yield 59.6%.
[0109] The analysis results of the above pale yellow s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com