Integrated micro-molding gradient degradation woven artificial ligament and preparation method thereof
A technology of artificial ligaments and degradation machines, applied in ligaments, prostheses, medical science, etc., to achieve good wear resistance and fatigue performance, avoid secondary processing, dense pore structure, and stable structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] A preparation method of an integrated micro-molding gradient degradation woven artificial ligament:
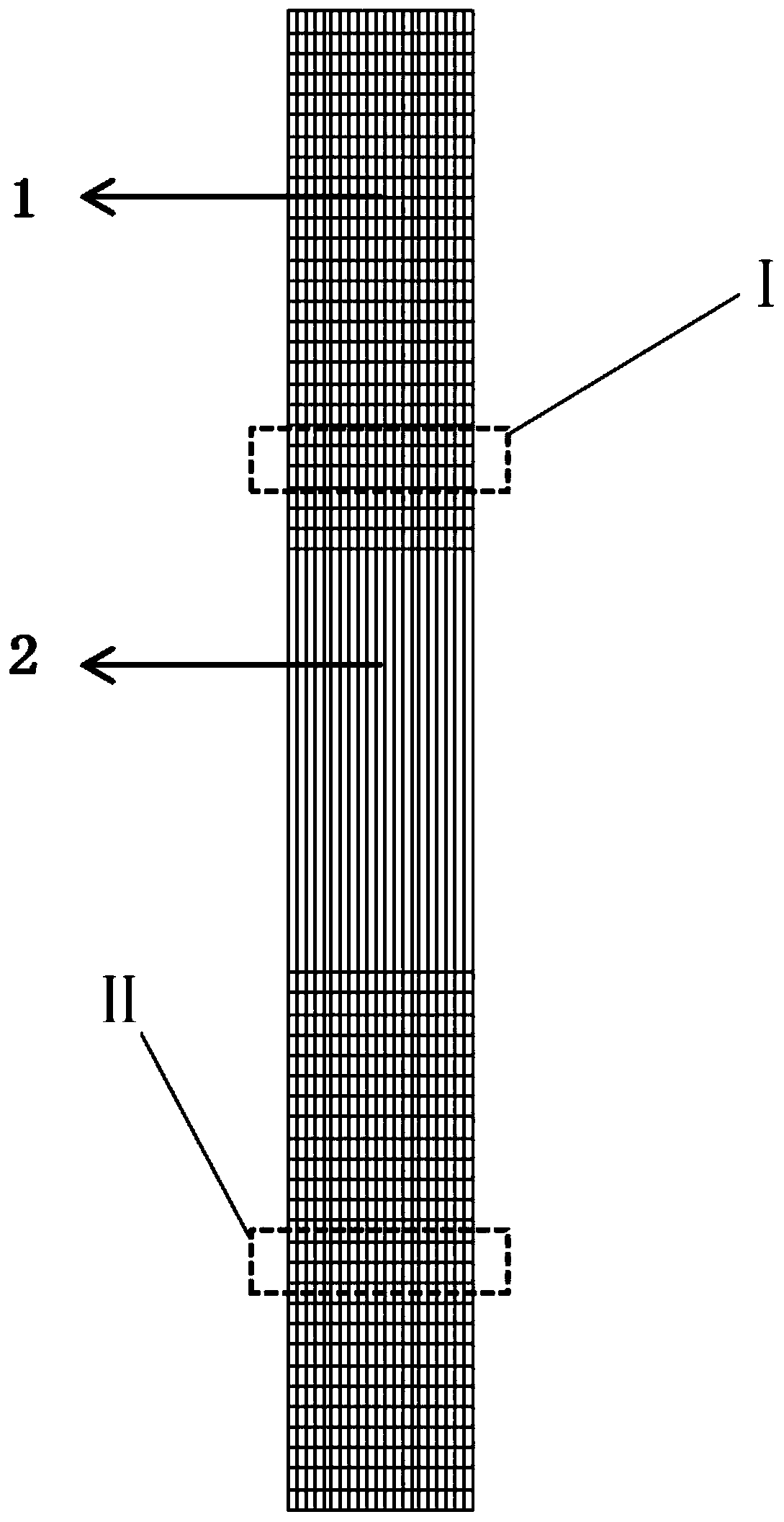
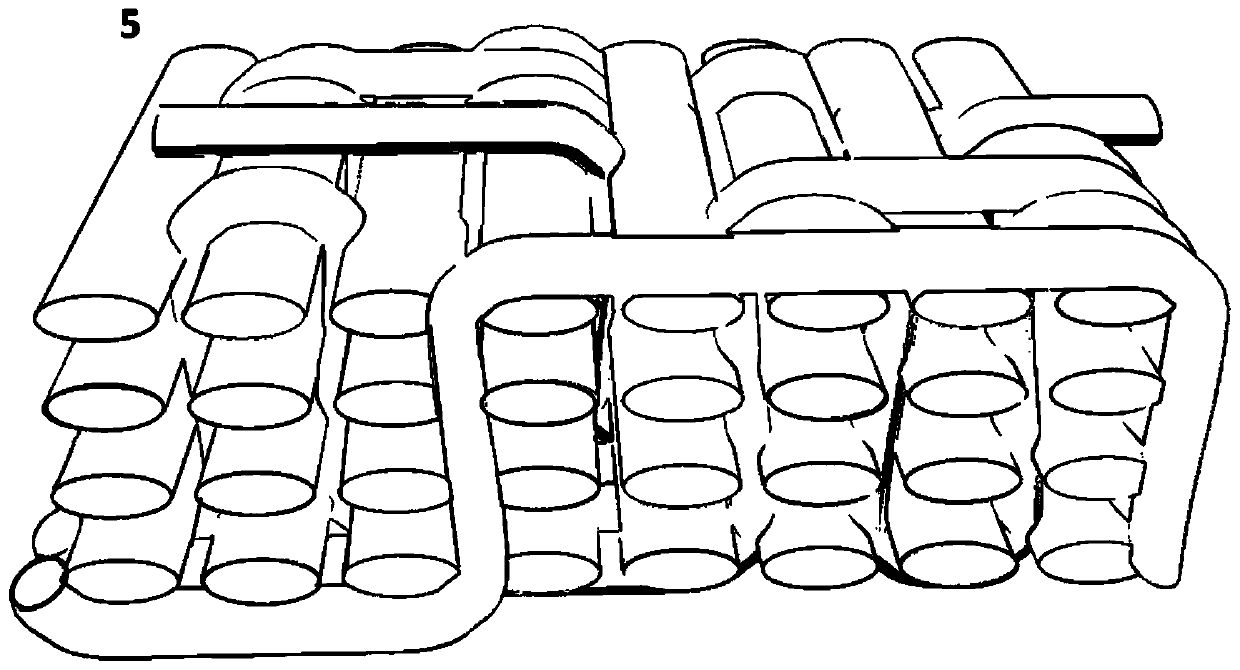
[0041] The first step is to determine the weave diagram of the multi-layer fabric. The fabric weave is twill; the twill weave is used as the double-layer surface weave, and the double-layer weave structure diagram is obtained by means of tubular jointing and compounding. The jointing method is the top joint and bottom joint method, and the number of joints is 16 per cycle;
[0042] The second step is to determine the map on the machine. Warp density: 500 pcs / 10cm, weft density: 50 pcs / 10cm, the way of drawing in healds is straight threading method, the number of threads per reed: 4 pcs / reed, reed number 200.
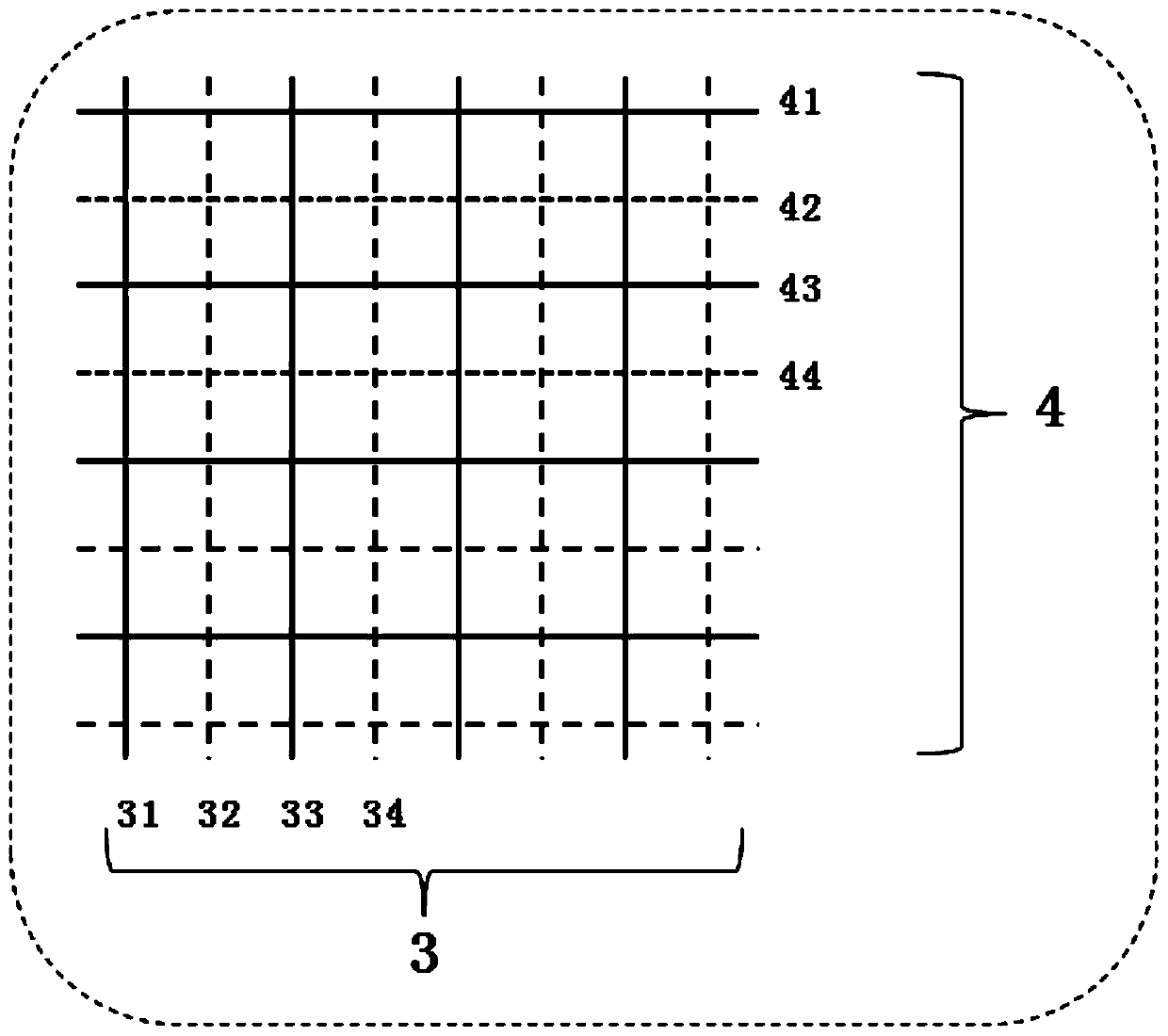
[0043] The third step is to weave on the machine. The yarns used in surface warp 31 and surface weft 41 are 0.2mm PGLA monofilament, and the yarns used in inner warp 32 and inner weft 42 are 0.2mm PPDO monofilament. Surface warp: inside warp = 1:1, surface weft...
Embodiment 2
[0048] A preparation method of an integrated micro-molding gradient degradation woven artificial ligament:
[0049] The first step is to determine the weave diagram of the multi-layer fabric. The fabric weave is plain weave; the plain weave weave is used as the double-layer surface weave, and the double-layer weave structure diagram is obtained by lamellar jointing and compounding. The jointing method is the bottom joint method, and the number of joints is 32 per cycle; Using this two-layer organizational chart as the lower-level organizational chart, a four-layer organizational chart is obtained by sheet-like jointing and compounding. The jointing method is the bottom joint method, and the number of joints is 32 per cycle.
[0050] The second step is to determine the map on the machine. Warp density: 1200 strands / 10cm, weft density: 150 strands / 10cm, the way of drawing in healds is the straight-through method, the number of penetrations per reed: 8 strands / reed, and the numb...
Embodiment 3
[0055] A preparation method of an integrated micro-molding gradient degradation woven artificial ligament:
[0056] The first step is to determine the weave diagram of the multi-layer fabric. The fabric weave is plain weave; use the plain weave weave as a double-layer surface weave, and obtain a double-layer weave structure diagram in a sheet-like jointing and compounding method. The jointing method is the bottom joint method, and the number of joints is 64 per cycle; Using the weave diagram as the basic weave, the method of tying is the up-and-down method. Repeat the above steps 3 times to obtain a 10-layer fabric weave.
[0057] The second step is to determine the map on the machine. Warp density: 2000 threads / 10cm, weft density: 300 threads / 10cm, the drawing method is partition threading method, the number of threads per reed: 16 threads / reed, and the number of reeds is 200.
[0058] The third step is to weave on the machine. 1. The yarn used for surface warp and weft of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com