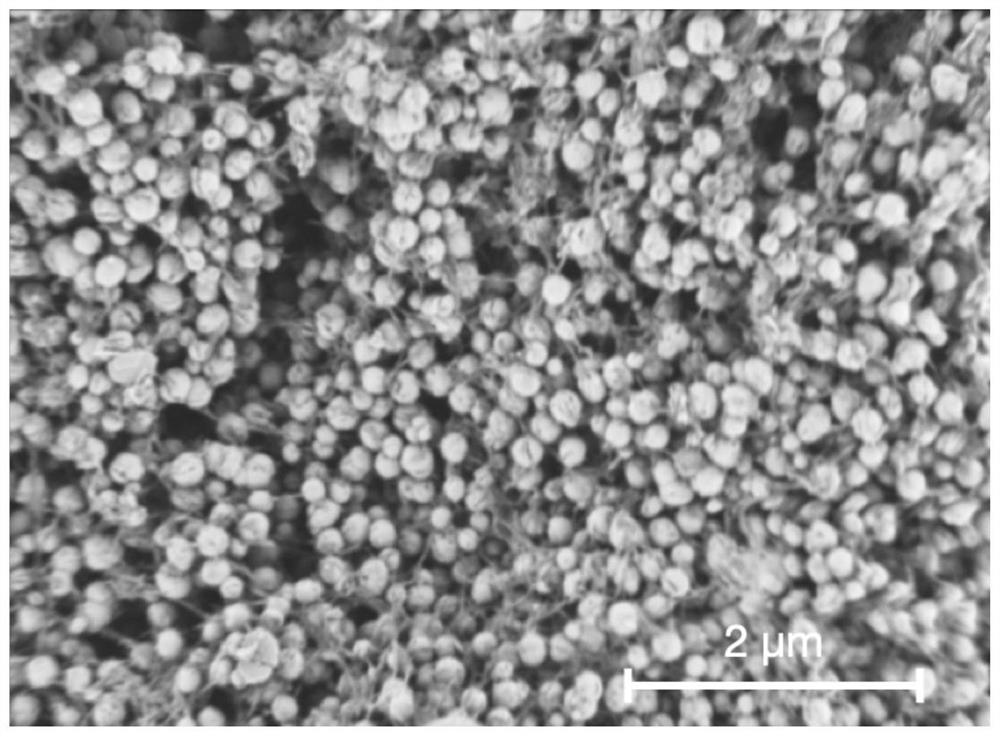
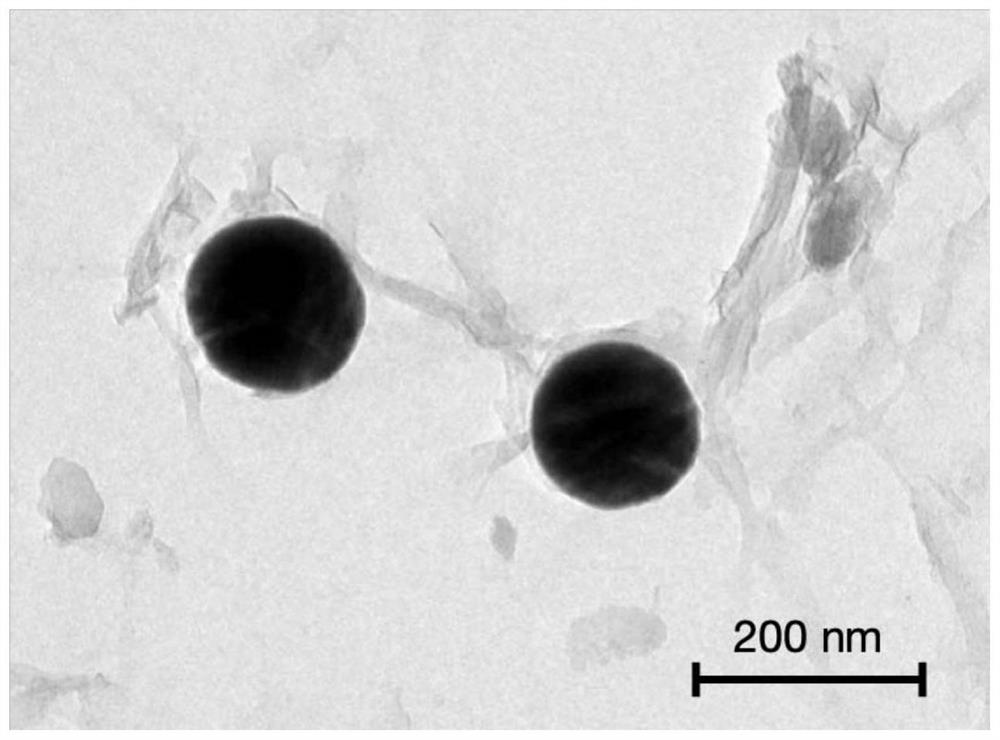
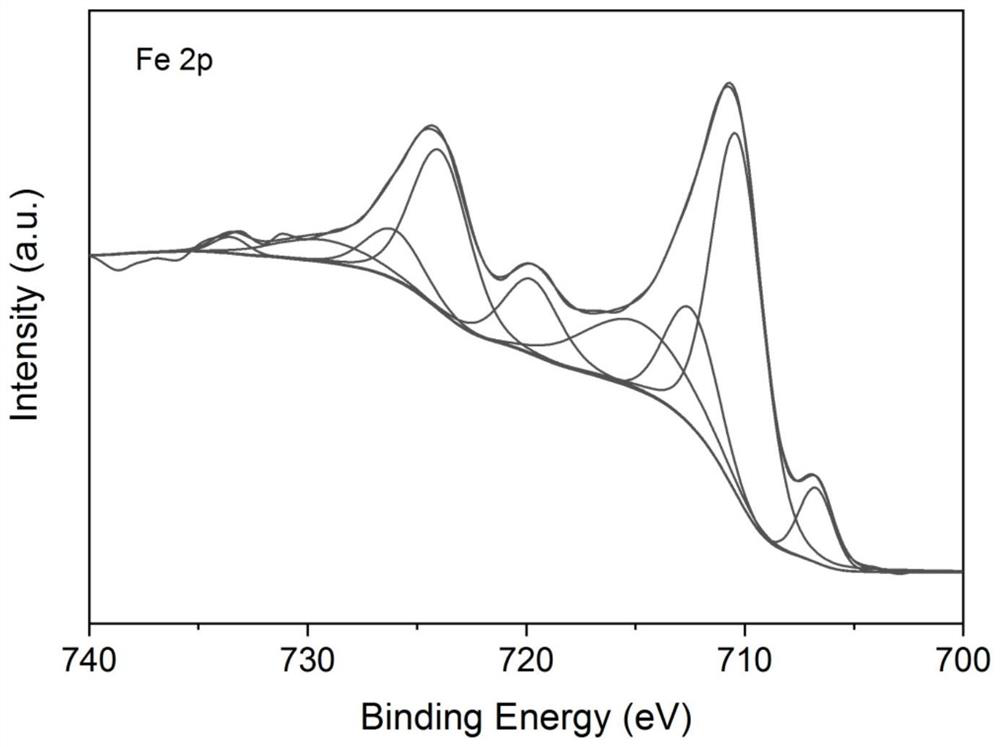
Application of iron-based cellulose nano composite material in water environment
A nano-composite material and cellulose technology, applied in water pollutants, alkali metal compounds, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of reduced reactivity, less active sites, and low loading capacity, so as to improve dispersibility and Stability, improving the phenomenon of easy agglomeration, and improving the effect of adsorption efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] The iron-based cellulose nanocomposites can first be mixed with Fe-containing 3+ In-situ synthesis of nano-cellulose iron ion mixed solution in aqueous solution, and then by mixing with sodium borohydride aqueous solution, the iron-based cellulose nanocomposite material with the three-dimensional network structure was prepared by the liquid phase reduction method. The preparation method includes but is not limited to The following steps:
[0026] S1: Disperse the nanocellulose solution into deionized water, stir and inject inert gas to obtain a nanocellulose dispersion;
[0027] S2: mixing an aqueous solution containing iron ions with the nanocellulose to obtain a mixed solution of nanocellulose iron ions;
[0028] S3: adding an aqueous solution of sodium borohydride to the mixed liquid to carry out a reduction reaction, and the obtained solid is the iron-based cellulose nanocomposite material with a three-dimensional network structure.
[0029] In the above step S1, ...
Embodiment 1
[0035] Disperse 14 mL of 0.01% w / w cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) into 6 mL of deionized water, mix evenly with a rotary stirrer, and pass through nitrogen for 10 minutes to prepare a dispersion liquid containing CNC.
[0036] 6.76g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O solid was dissolved in 480mL deionized water, and then 3+ Slowly mix the aqueous solution with the CNC dispersion liquid, and form a uniform dispersion system after stirring for 5 minutes to obtain the cellulose nanocrystal iron ion mixed solution (CNC-Fe 3+ ).
[0037] Transfer 0.2M 500mL sodium borohydride aqueous solution to the mixed solution of nanocellulose whiskers and iron ions (CNC-Fe 3+ ), after mixing evenly, let it stand for 10-20min to remove the supernatant, and carry out magnetic separation. First, wash 3-5 times with water, then wash 3-5 times with absolute ethanol, and store it in absolute ethanol solution to obtain a three-dimensional Reticulated cellulose nanowhiskers / nano zero-valent iron composite (CNC-nZVI). ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Disperse 14 mL of 0.01% w / w cellulose nanofibers (CNF) into 6 mL of deionized water, mix evenly with a rotary stirrer, and pass through nitrogen for 10 min to prepare a dispersion containing CNF.
[0045] 6.76g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O solid was dissolved in 480mL deionized water, and then 3+ Slowly mix the aqueous solution of the CNF dispersion with the CNF dispersion, and form a uniform dispersion system after stirring for 5 minutes to obtain the cellulose nanofiber iron ion mixed solution (CNF-Fe 3+ ).
[0046] Transfer the 0.2M 500mL sodium borohydride aqueous solution to the nanocellulose fiber iron ion mixed solution, mix well and let it stand for 10-20 minutes to remove the supernatant, and perform magnetic separation. First, wash with water for 3-5 times, and then pass through absolute ethanol Wash for 3-5 times and store in absolute ethanol solution to prepare a three-dimensional net-like cellulose nanofiber / nano zero-valent iron composite (CNF-nZVI).
[0047] Perf...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com