Method for changing fabric structure
A fabric structure and fabric technology, applied in the direction of fabric, fabric surface trimming, heating/cooling fabric, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption, complicated process, and low production efficiency, and achieve low energy consumption, simple process, and high production efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
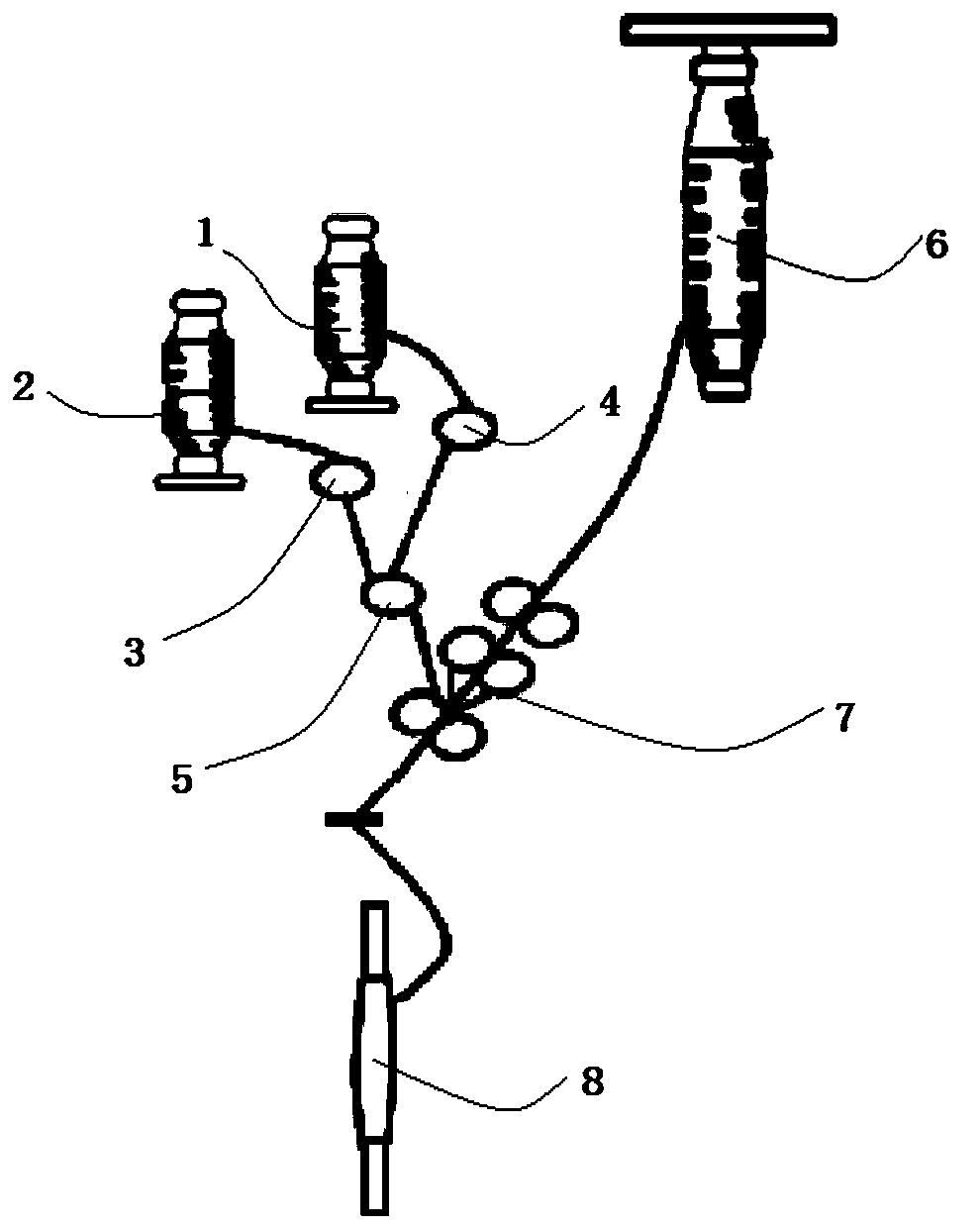
[0057] see Figure 1 to Figure 4 Shown, the present invention provides a kind of method that can change fabric structure, comprises the steps:
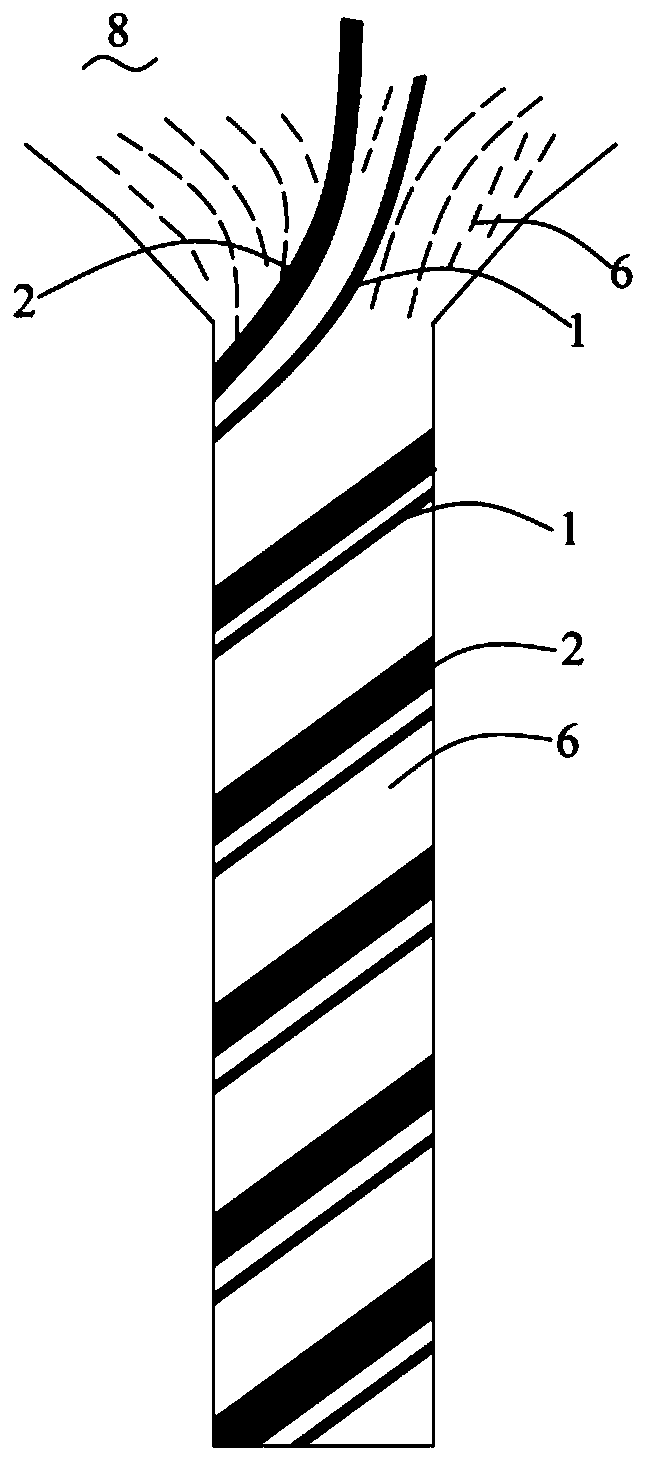
[0058] S1, using ring spinning to prepare dewy composite core-spun yarn 8;
[0059] The fiber roving 6 is a cotton roving, which is composed of fibers with a dry weight of 7.8g / 10M and a cut length of 35-60mm; the polymer filament 2 is a single-component low-melting polyester filament with a fineness of 150D; the elastic fiber is long Silk 1 is spandex filament with a fineness of 40D.
[0060] On the ring spinning frame, the cotton roving is fed from the bell mouth, and the cotton roving sliver is obtained after being drafted by the drafting device 7, wherein the total drafting ratio of the drafting device is 24.6, and the drafting ratio of the rear drafting area is 1.5; Spandex filament 1 and low-melting point polyester filament 2 pass through the first tension disc 4 and the second tension disc 3 respectively, pass through the god...
Embodiment 2-4
[0076] The method for changing the fabric structure provided in Examples 2-4 is different from that in Example 1 in that the heat treatment temperatures are 90°C, 100°C, and 120°C, respectively. Except for the above differences, other operations are basically the same and will not be repeated here.
[0077] The properties of the fabrics prepared in Examples 1-4 were compared, as shown in Table 2 below.
[0078] Table 2 embodiment 1-4 and comparative example 1 prepare the fabric performance comparison
[0079]
[0080] According to Table 2, as the heat treatment temperature increases, the yarn diameter of the obtained fabric is smaller, the surface density is larger, the coil length is shorter, the anti-pilling ability is stronger, and the mechanical properties are better. However, when the heat treatment temperature reaches 120°C, the appearance of the fabric becomes denser, the handle becomes harder, and the comfort of the fabric begins to deteriorate.
[0081] It should...
Embodiment 5-6
[0083] The method for changing the fabric structure provided by Examples 5-6 is different from that of Example 1 in that the heat treatment time is 30s and 10s respectively. Except for the above differences, other operations are basically the same and will not be repeated here.
[0084] project Example 1 Example 5 Example 6 Heat treatment time / s 60 30 10
[0085]The properties of the fabrics prepared in Comparative Example 1 and Examples 5-6 are shown in Table 3 below.
[0086] Table 3 embodiment 1, embodiment 5-6 and comparative example 1 prepare the fabric performance comparison
[0087]
[0088] According to Table 3, with the prolongation of heat treatment time, the higher the degree of shrinkage of the yarn, the tighter the fabric, and the stronger its surface density, maximum bonding strength, anti-pilling ability, and tensile breaking strength. When the heat treatment time is 60s, the obtained fabric 12 has the best mechanical properties ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fineness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fineness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fineness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com