Process for supercritical or subcritical partial delignification and filling of a lignocellulosic material
A lignocellulose and delignification technology, applied in the field of modification of lignocellulosic materials, can solve the problems of expensive, slow implementation of wood composite materials, complex implementation, etc., and achieve the effect of performance improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0292] Embodiment 1: According to the processing method of the present invention, wherein step (1) uses supercritical CO in the presence of a mixture of 50% water-50% ethanol (volume %) 2 Do it in static mode.
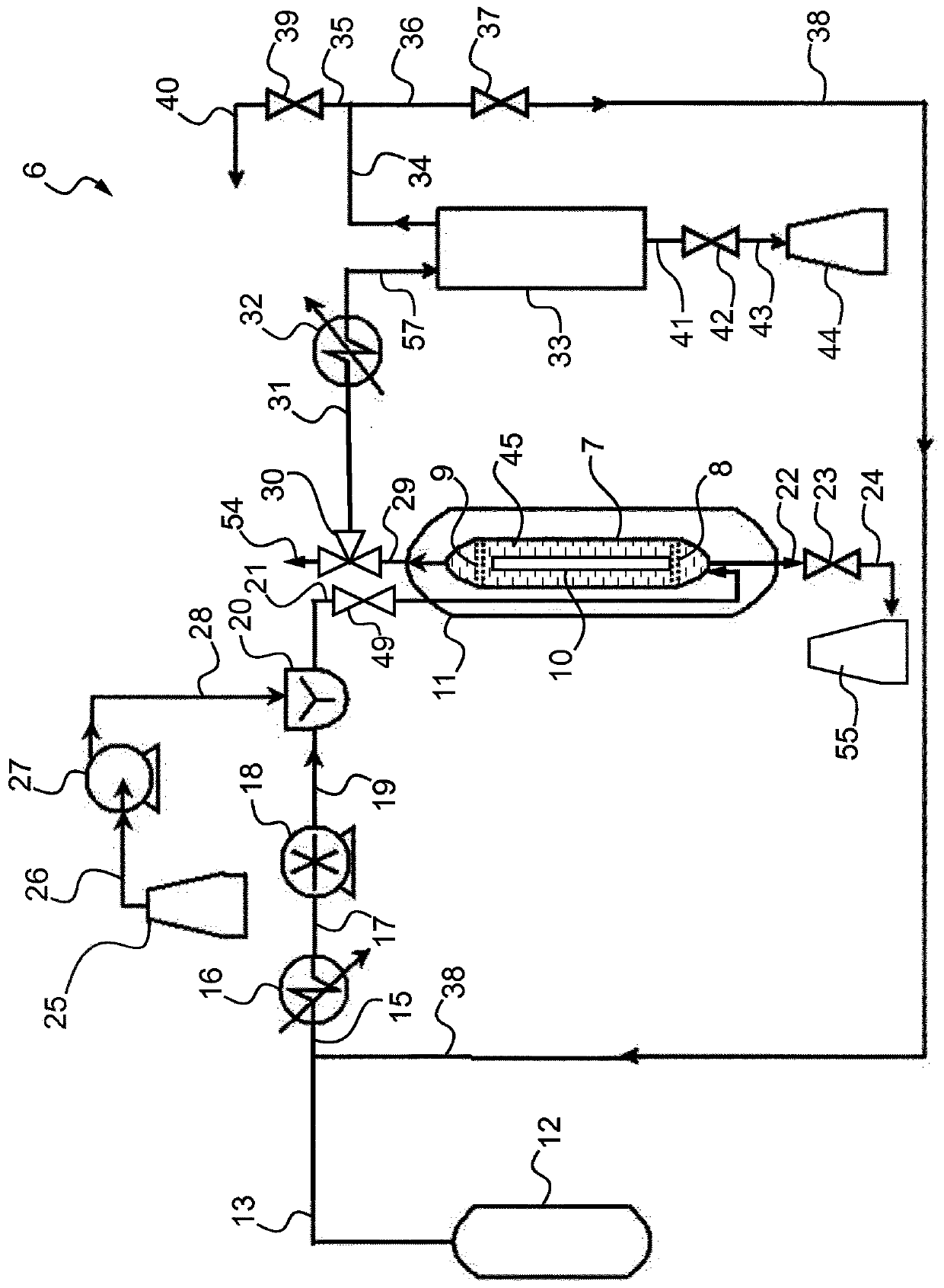
[0293] exist figure 2 In the device 6 of the present invention, in static mode, a structure of beech cross-cut dry wood with dimensions 17 mm x 17 mm x 9 mm (1 x L x h) was subjected to the treatment method according to the invention.
[0294] The extraction step (1) was carried out under the following conditions: pressure 1.76 MPa (17.6 bar), temperature 180° C., a certain amount of co-solvent 50% water-50% ethanol (vol %) and treatment duration 2 hours.
[0295] At the end of this extraction step (1), the high pressure unit (0.5 L) is depressurized and the wood pieces are recovered as well as the lignin-containing extract.
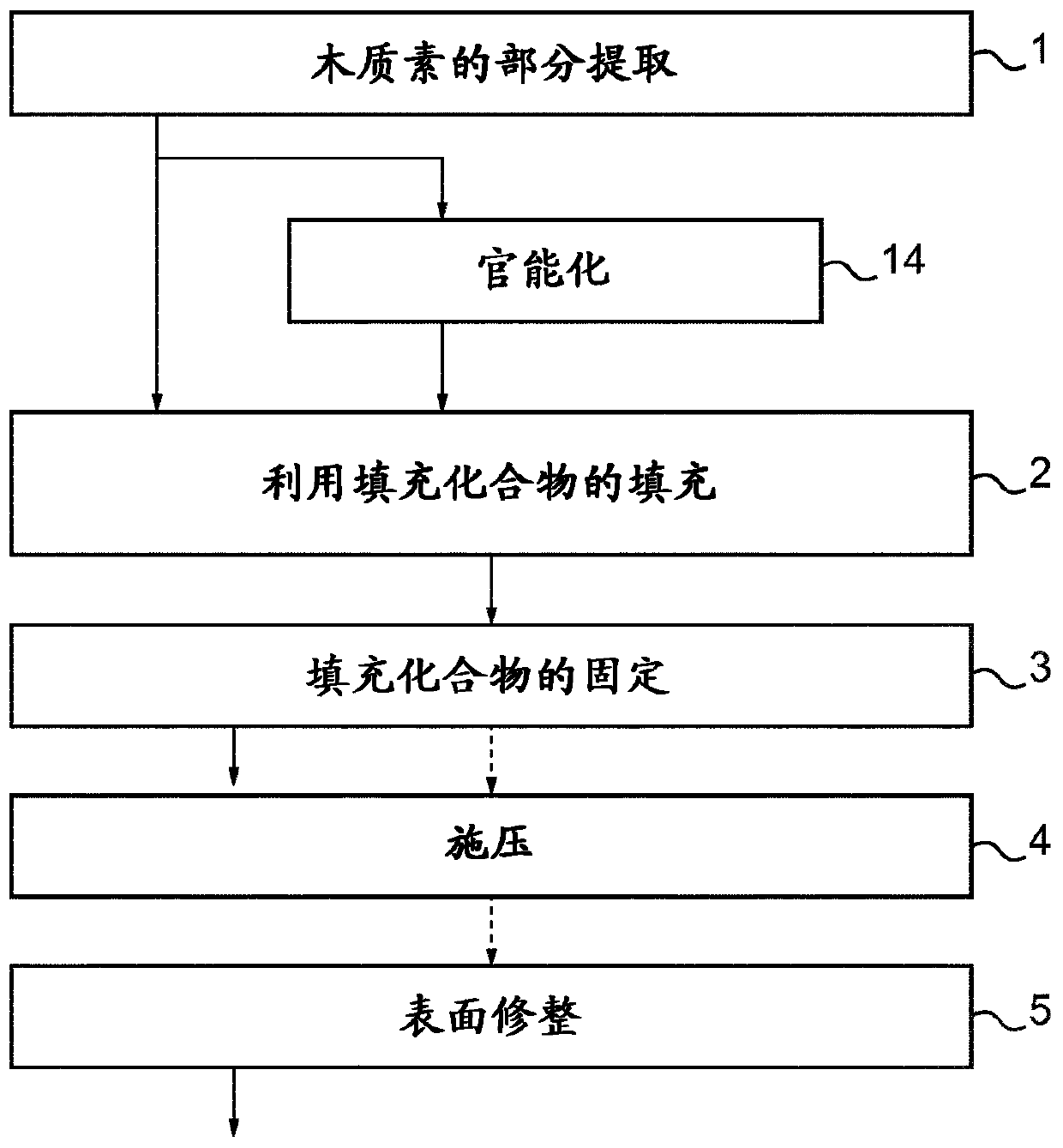
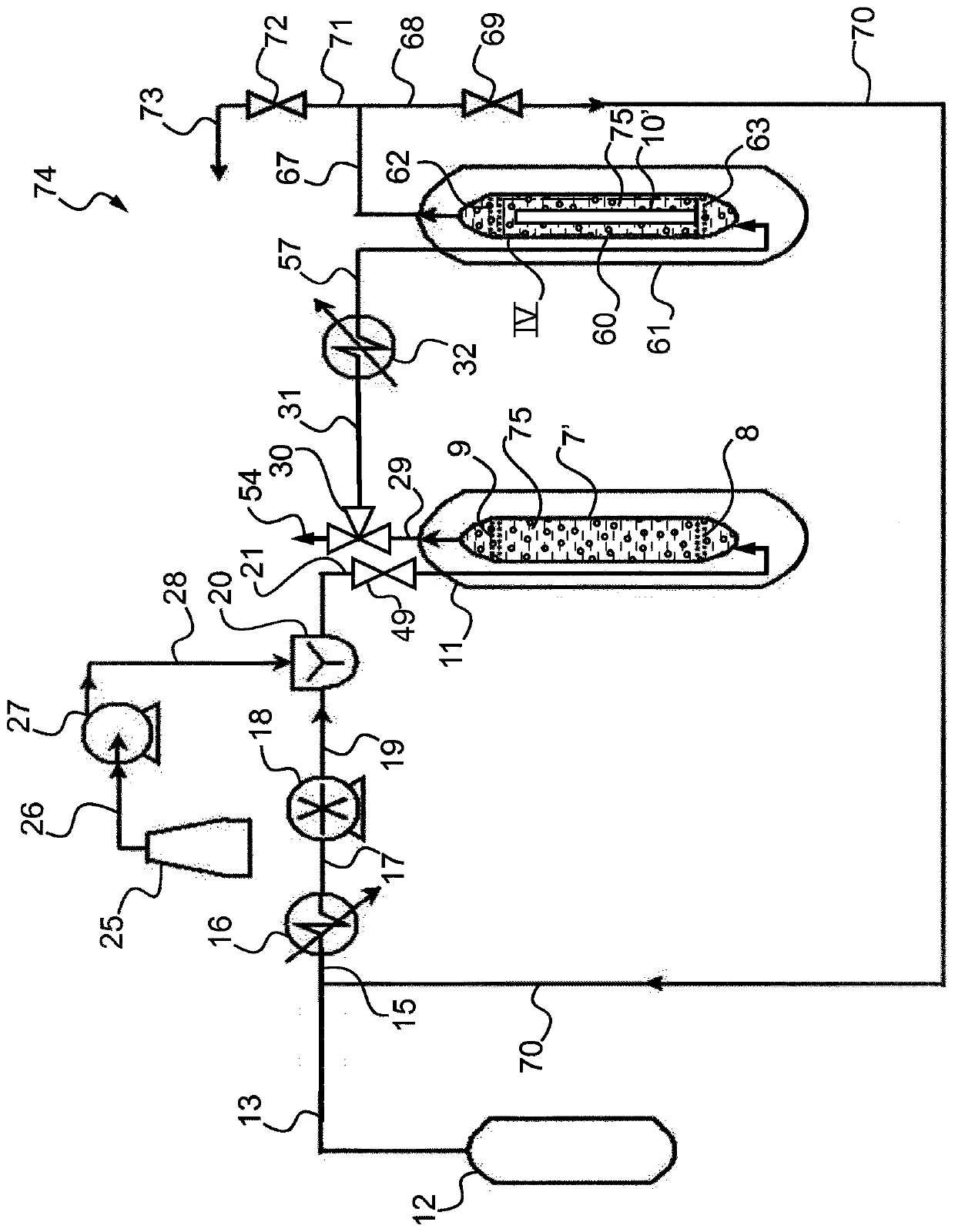
[0296] The filling step (2) and trimming step (3) of the structure of lignocellulosic material thus obtained is carried out by image 3 equi...
Embodiment 2
[0300] Embodiment 2: according to processing method of the present invention, wherein step (1) uses supercritical CO 2 It was performed in dynamic mode in the presence of a co-solvent mixture of 50% water-50% ethanol (% by volume).
[0301] In dynamic mode and in the presence of a water / ethanol co-solvent, a beech cross-cut dry wood of dimensions 200 mm x 90 mm x 18 mm (1 x L x h) was processed by a partial extraction step of the lignin according to the process of the invention. Structure (planks).
[0302] The extraction was carried out for 2 hours at a pressure of 2.02 MPa (202 bar) and a temperature of 118°C. pump the CO 2 and water / ethanol mixture were continuously introduced into the high pressure unit (2 L) at flow rates of 100 g / min and 5.34 g / min, respectively.
[0303] At the end of this extraction step (1), the high pressure unit is depressurized and the planks and lignin-containing extract are recovered.
[0304] The filling step (2) and trimming step (3) of the...
Embodiment 3
[0305] Embodiment 3: according to the processing method of the present invention, wherein step (1) is carried out by supercritical and enzymatic means
[0306] According to the present invention, under the conditions of a pressure of 20 MPa (200 bar), a temperature of 165 ° C and a duration of 3 h in static mode, with supercritical CO 2 Structure of pre-treated dry wood with dimensions 17mm x 17mm x 10mm.
[0307] The structure of the pretreated lignocellulosic material was then placed in a solution containing the enzyme (laccase) at a concentration of 5 g / L at a temperature of 50 °C, a duration of 48 h and stirring (100 trs / min). Adjust the pH of the enzyme solution using a buffer solution to maintain a value between 4.7 and 5.
[0308] Treated wood and extracts (which contain lignin) were recovered at the end of the enzyme treatment and dried in an oven to characterize them.
[0309] The filling step (2) and trimming step (3) of the structure of lignocellulosic material th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com