Maize small-grain mutant and application thereof
A technology for mutants and small grains, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and molecular biology, can solve the problems of shrinking and shrinking of mutant grains, functional differences of NRT1.5, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1 Phenotype Analysis of Maize Small Kernel Mutant mn2-m1
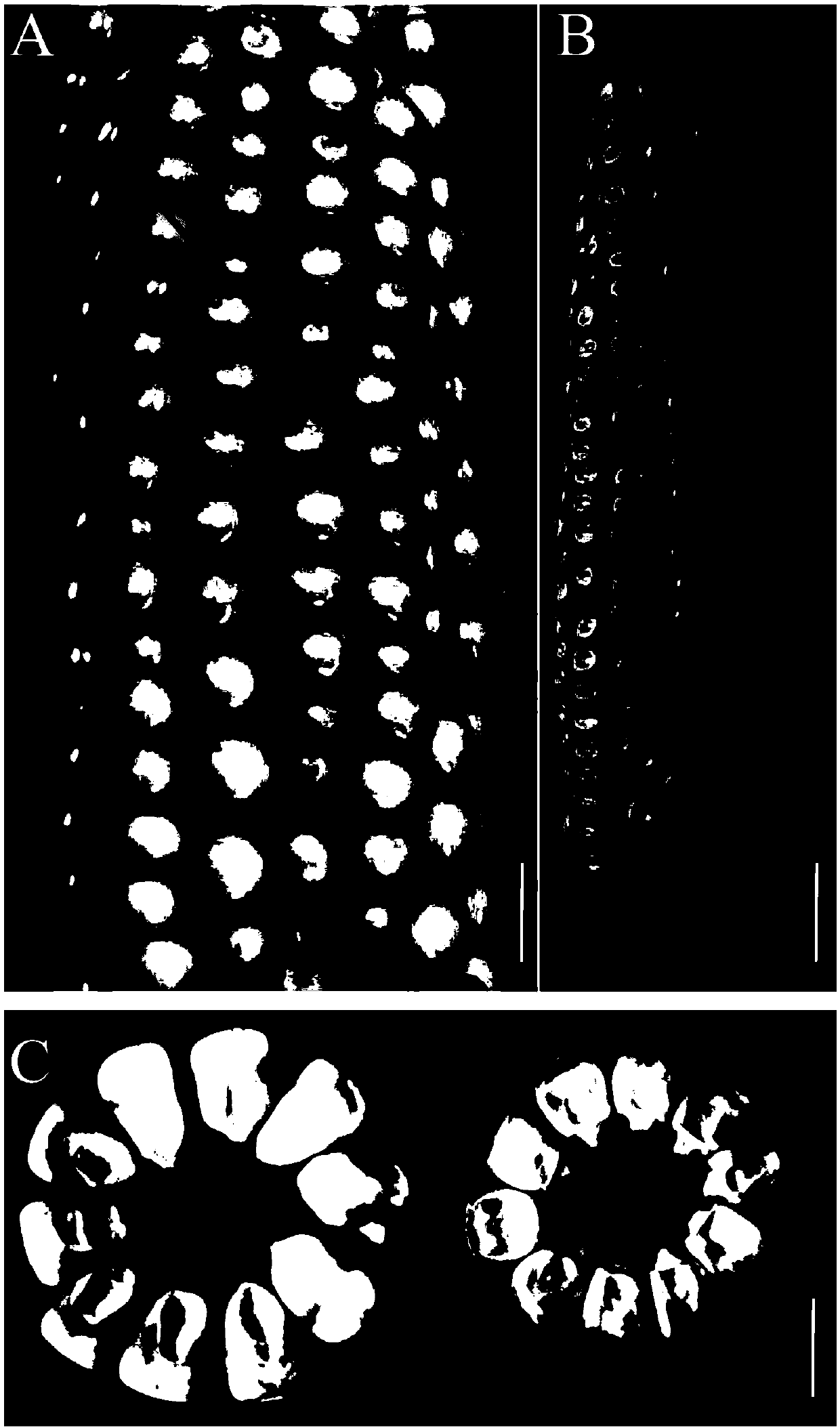
[0029] The small-grain mutant mn2-m1 of maize was discovered by the applicant in a pile of eliminated breeding materials. After testing, the mutant spontaneously showed small kernels from the early stage of pollination, and the kernels appeared small and shrunken after maturity (such as figure 1 shown), and its embryonic development is also affected (as figure 2 shown), which was significantly smaller than that of the wild type.
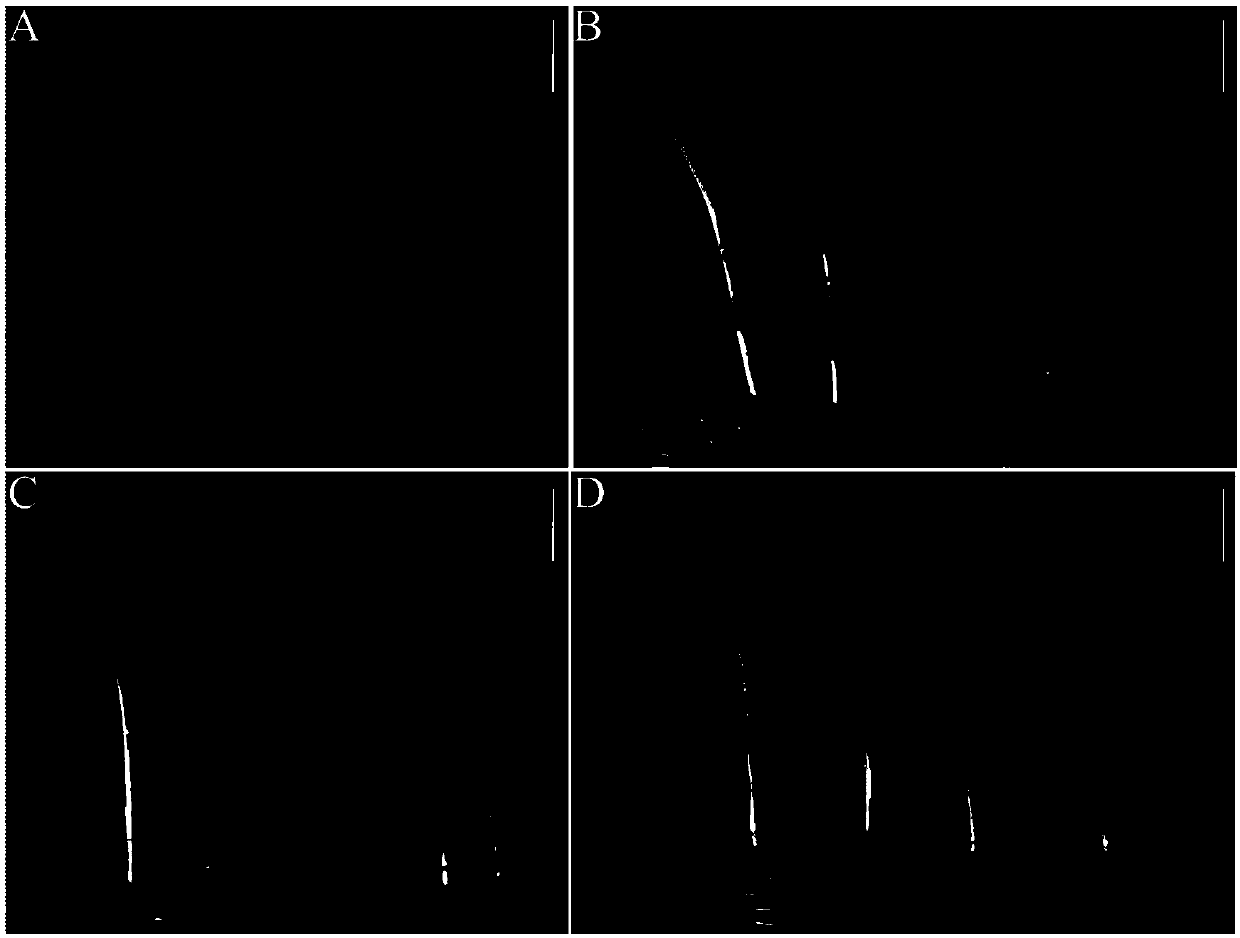
[0030] The experiments shown in Table 1 showed that the length, width, thickness and 100-grain weight of the mutant mn2-m1 grains were all reduced compared with the wild type, and its seedling development was also affected (such as image 3 shown).
[0031] Figure 1-3 and the a / A, b / B, c / C, d / D involved in Table 1 are from the F2 population of mn2-m1 and maize inbred lines B73, Chang 7-2, Zheng 58 and Qi 319, respectively.
[0032] Table 1 Analysis of grain traits
[003...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 Genetic Analysis
[0037] F1S was obtained by crossing the small corn mutant mn2-m1 with common maize inbred lines B73, Chang 7-2, Zheng 58 and Qi 319, and F2S was obtained by selfing F1S. Genetic analysis was carried out on the F2 segregation population, and the results showed that mn2-m1 The granule phenotype of is controlled by a recessive single gene (see Table 2 below).
[0038] Table 2 Phenotype segregation analysis of five parents and their F1 and F2 populations
[0039]
[0040] WT, wild type; χ2 (0.05,1) =3.84.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 Allelic Mutant
[0042] In 2016, mn2-m2 was obtained from the eliminated breeding material, and its phenotype was similar to mn2-m1. In order to verify whether they come from the same site mutation, we hybridized mn2-m1 / B73 with mn2-m2, and found that their F1 showed a 1:1 segregation, which indicated that both mn2-m1 and mn2-m2 came from the MN2-M mutation ( See Table 3).
[0043] Table 3 F hybridization between mn2-m1 / B73 and mn2-m2 1 Grain Phenotype Isolation
[0044] hybrid ear Wild type mutant Separation ratio chi-square value P-value spike-1 154 139 1.11 0.77 0.3<P<0.5
[0045] chi-square value (0.05,1) =3.84.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com