Method of diagnosing dysbiosis
A technology of flora imbalance and bacteria, applied in disease diagnosis, biochemical equipment and methods, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve problems that are difficult to determine or predict the exact relationship between microbiota
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0126] Example 1: Bioinformatics process
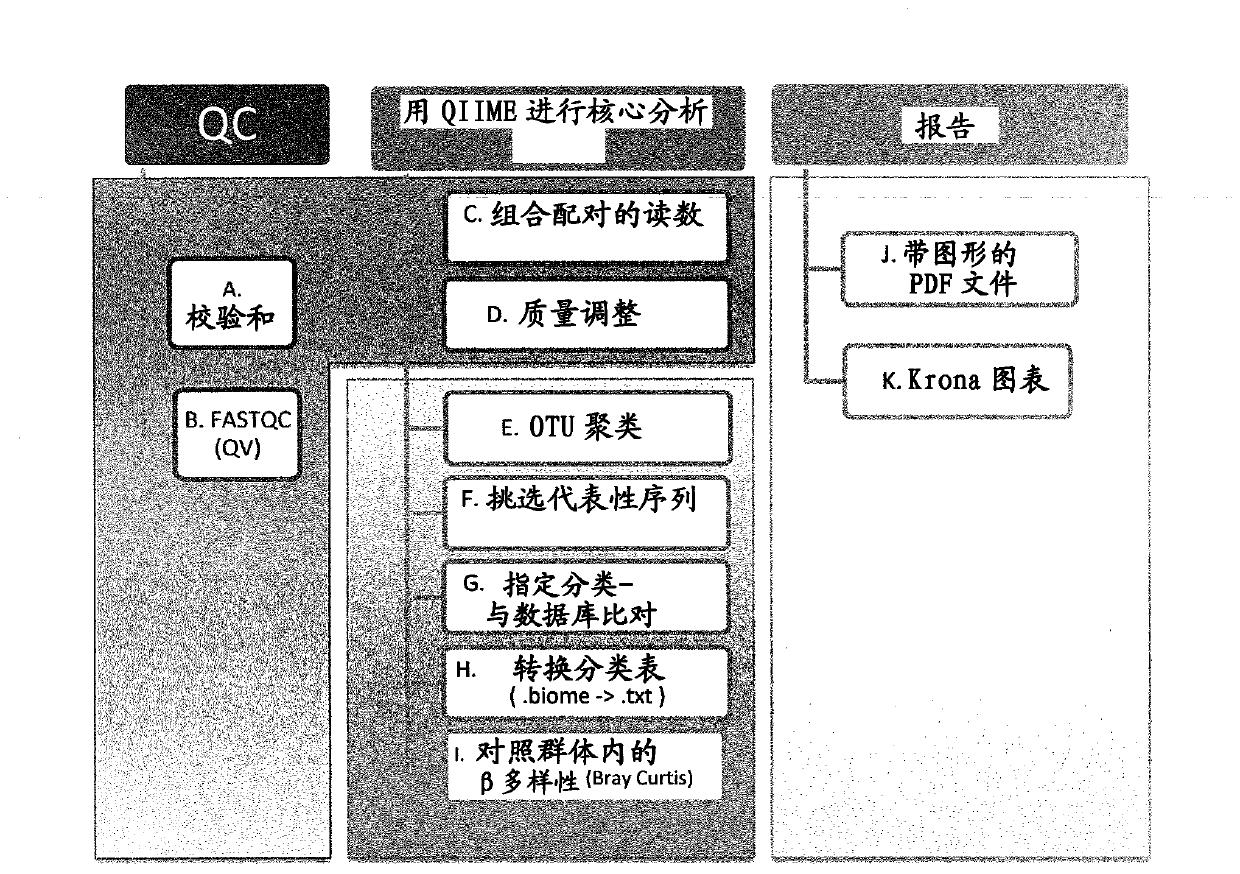
[0127] A "bioinformatics pipeline" is a set of computational tasks applied sequentially to raw nucleic acid sequencing data in the form of FASTQ files (produced by a MiSeq (Illumina) high-throughput sequencing instrument). To ensure consistency, a set of informatics procedures were implemented in the process, which increased the reproducibility and validity of the results. Open source programs and databases are used in the process. figure 1 An overview of the bioinformatics pipeline is given.
[0128] Primary quality control analysis of raw FASTQ files
[0129] Raw sequences of individual samples analyzed in the MiSeq instrument are in FASTQ format (fastq.gz). Sequences for each sample are provided as two compressed FASTQ files; one for forward strand reads and one for reverse strand reads.
[0130] The integrity of the downloaded FASTQ file is checked using the ExactFile program based on the MD5 sums algorithm ( figure 1 , Box A...
Embodiment 2
[0170] Embodiment 2 Relative to healthy individual, to the diagnosis of subject's flora imbalance
[0171] sample
[0172] Fecal samples were collected using a DNA genotek OMNIgene GUT (OMR-200) collection device, which is used to stabilize DNA for quantitative gut microbiome profiling. After each stool sample was received by the laboratory, it was frozen at -20°C for no longer than 3 months. Prepare each sample for the extraction process by taking a pea-sized sample and aliquoting the fecal material into Pathogen Lysis Tubes (Catalog #: 19091 Qiagen). Each sample was centrifuged at 13000 rpm for 5 minutes and the supernatant was discarded. For consistency, more solid feces can be used to fill approximately half the volume of the pathogen lysis tube if desired. Pathogen lysis tubes containing fecal samples were then stored in a -20 °C freezer until further processing. The samples were processed in batches for a total of 48 samples. DNA was extracted from fecal samples usi...
Embodiment 3IB
[0191] Example 3 IBS subtype prediction
[0192] Predictive models using machine learning algorithms and supervised classification (such as random forest and naive Bayesian algorithms) to predict IBS subtypes: IBS-D (diarrhea), IBS-C (constipation), and IBS-M (mixed) . A training dataset was generated using microbiome profiles from individuals, classified by clinicians into three subtypes using Rome IV criteria:
[0193] · IBS-D (diarrhea type), n=78
[0194] · IBS-M (mixed type), n=22
[0195] · IBS-C (constipation type), n=78
[0196]The purpose of the prediction algorithm is to detect reproducible differences in microbiome profiles between groups of individuals with known IBS subtypes, which can be used to predict subtypes in individuals with unknown IBS subtypes. In this case, the Naive Bayes classifier was used as it showed improved performance compared to other algorithms. Bayesian classifiers are known to be used in a variety of domains, such as spam filtering prog...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com