Method for high-throughput targeted identification of M1-generation mutation of physicochemical mutated plant and obtaining of mutant
A high-throughput, physical and chemical technology, applied in the field of identification and mutant acquisition, can solve the problem of low mutation efficiency of target genes, and achieve the effect of saving time and cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
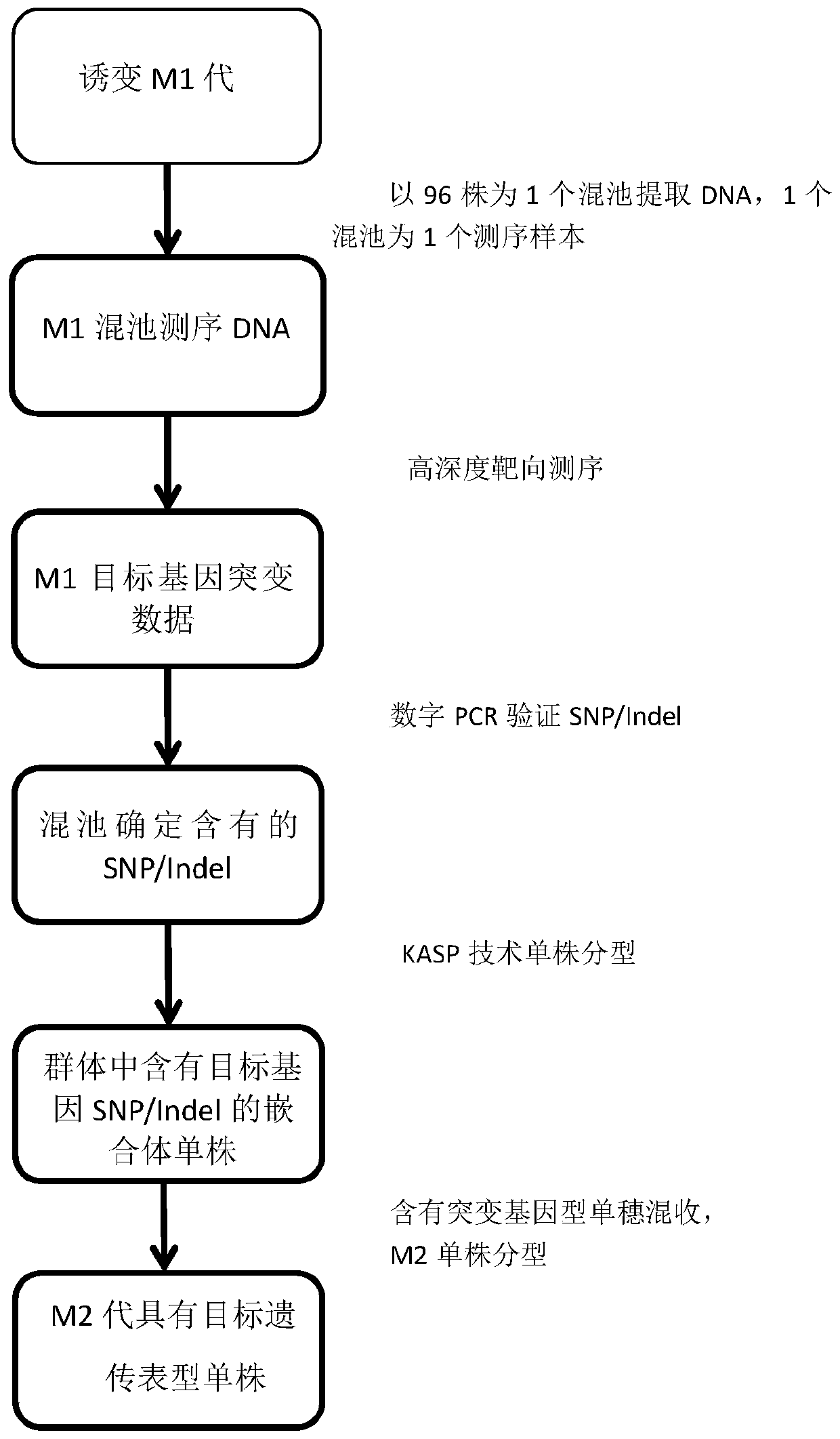
[0048] a kind of like figure 1 The high-throughput targeted identification of physical and chemical mutagenesis plant M1 generation mutations of the present invention and the method for obtaining mutants specifically include the following steps:
[0049] 1. Use 80MeV / u carbon ion ( 12 C 6+ ) with a dose of 180Gy to irradiate 20,000 seeds of rice variety 638S to obtain the M1 generation of rice variety 638S (hereinafter referred to as 638S).
[0050] 2. Plant 20,000 seedlings of the 638S M1 generation in individual plants. Take 96 plants as a group, each group has 8 rows, and each row has 12 plants, 100 groups are planted, a total of 9600 plants, and each group is numbered 1-100.
[0051] 3. Taking each group as a unit, take an equal amount of leaves from each individual plant, mix a total of 96 equal parts in a centrifuge tube to extract DNA, and extract a total of 100 copies of DNA, and the DNA number corresponds to the number 1-100 of each group .
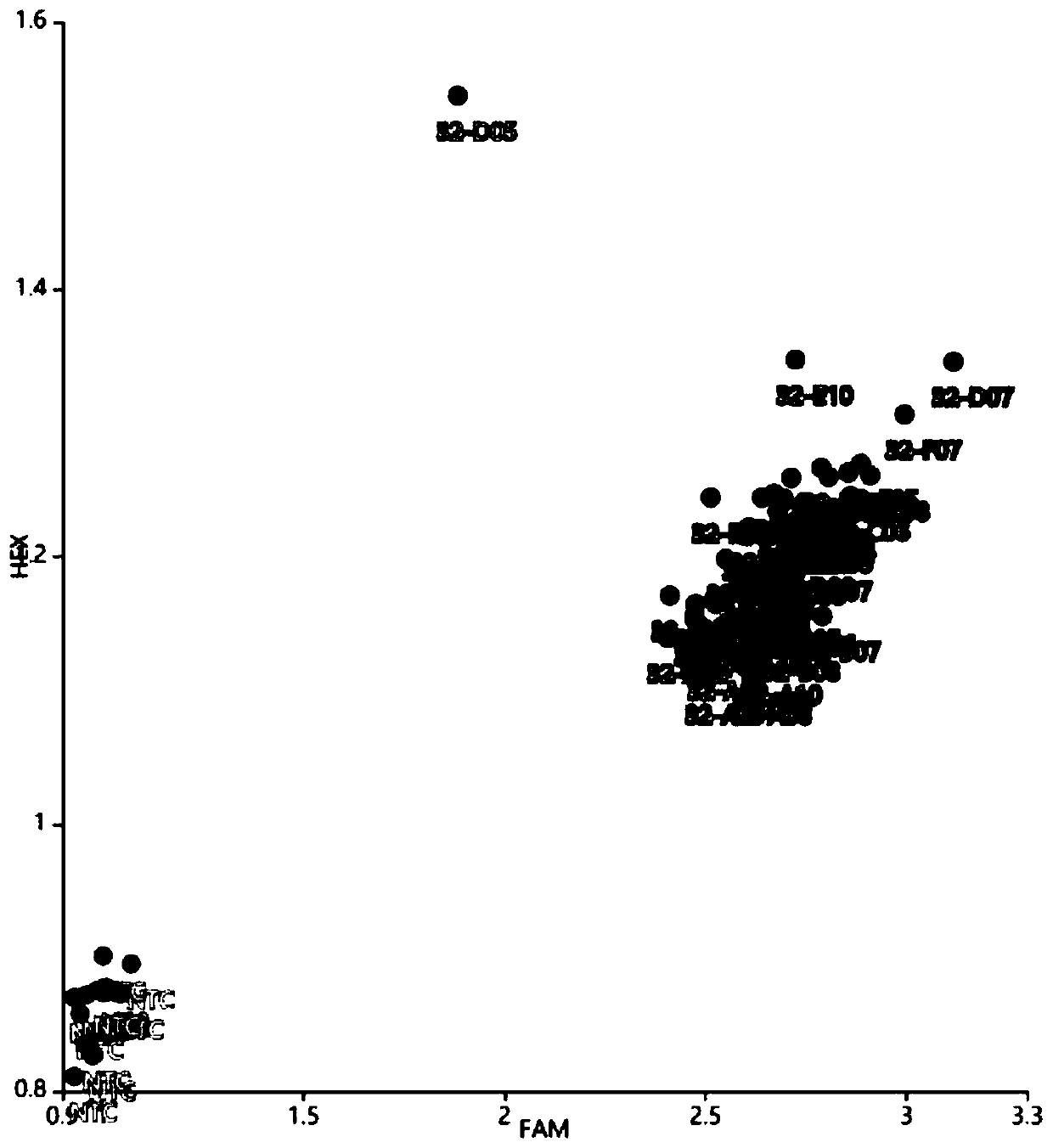
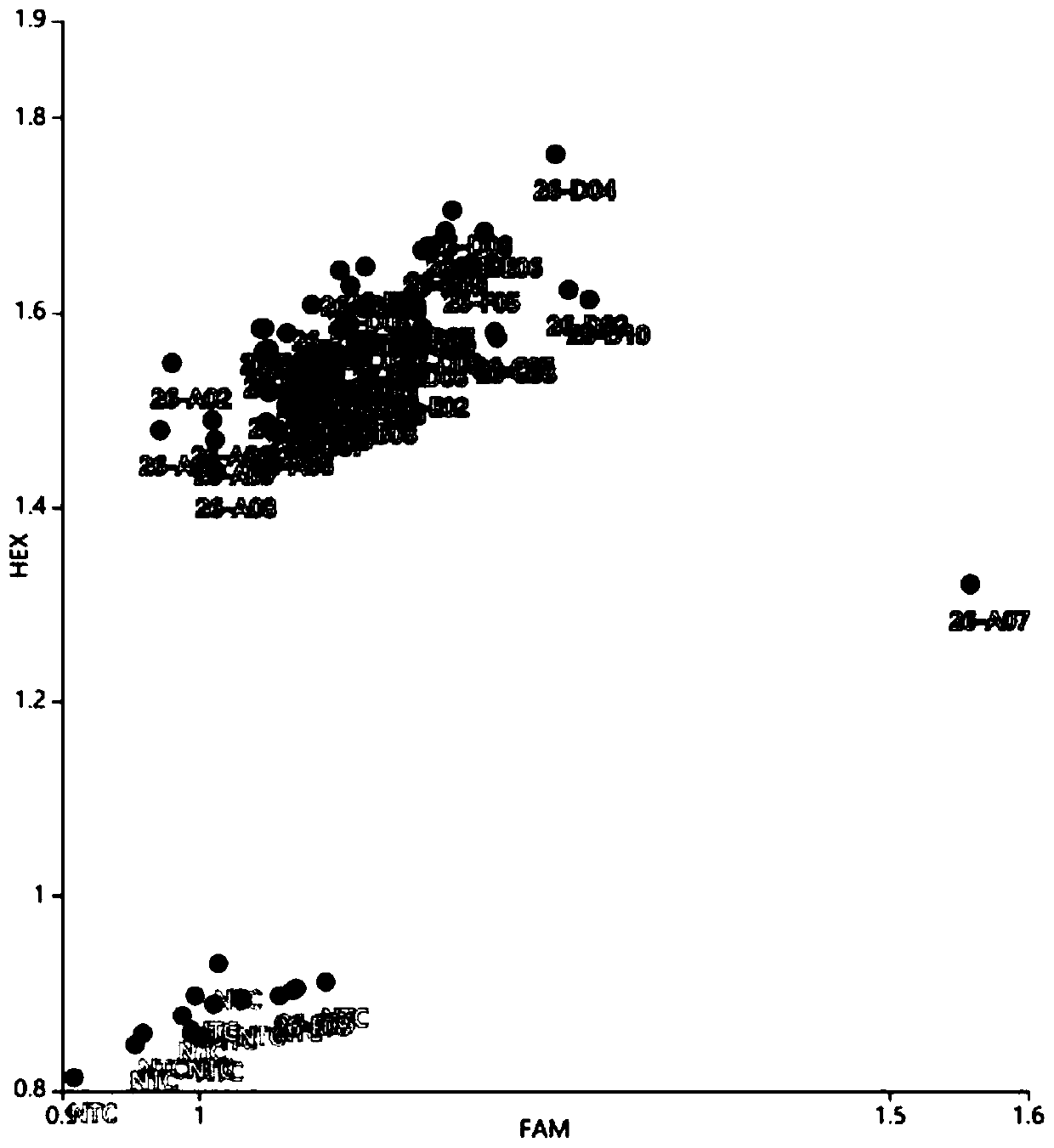
[0052] 4. Using the ...
Embodiment 2
[0069] a kind of like figure 1 The high-throughput targeted identification of physical and chemical mutagenesis plant M1 generation mutations of the present invention and the method for obtaining mutants specifically include the following steps:
[0070] 1. Take 20,000 seeds of rice variety Huahang 31, soak the seeds in clear water for 16 hours in a constant temperature incubator at 28°C, remove the seeds and control the moisture. The seeds were again soaked in 1% (w / w) ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) solution for 8 hours in a constant temperature incubator at 28° C., and the seeds were fished out and dried. Rinse the seeds with clear water, change the water 8 times, and plant after germination at 37°C for sowing and seedling raising. Take 96 plants as a group, each group has 8 rows, and each row has 12 plants. Populations were numbered 1-100.
[0071]2. Taking each group as a unit, take an equal amount of leaves from each individual plant, mix 96 equal parts in a centrifuge tu...
Embodiment 3
[0083] a kind of like figure 1 The high-throughput targeted identification of physical and chemical mutagenesis plant M1 generation mutations of the present invention and the method for obtaining mutants specifically include the following steps:
[0084] 1. use 60 Co-γ rays irradiated 100,000 seeds of rice variety Huazhan with a dose of 350Gy to obtain the M1 generation of rice variety Huazhan.
[0085] 2. After cultivating 100,000 seeds of Huazhan M1 generation, 96 plants are used as a group, each group has 8 rows, each row has 12 plants, and 500 groups are planted, with a total of 48,000 plants, and each group is numbered 1 -500.
[0086] 3. Taking each group as a unit, take an equal amount of leaves from each individual plant, mix a total of 96 equal parts in a centrifuge tube to extract DNA, and extract a total of 500 copies of DNA, and the DNA number corresponds to the number 1-500 of each group .
[0087] 4. Using the DNA of each population as a sequencing sample, co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com