Patents
Literature
118 results about "Georeference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Georeferencing means that the internal coordinate system of a map or aerial photo image can be related to a ground system of geographic coordinates. The relevant coordinate transforms are typically stored within the image file (GeoPDF and GeoTIFF are examples), though there are many possible mechanisms for implementing georeferencing. The most visible effect of georeferencing is that display software can show ground coordinates (such as latitude/longitude or UTM coordinates) and also measure ground distances and areas. In other words, Georeferencing means to associate something with locations in physical space. The term is commonly used in the geographic information systems field to describe the process of associating a physical map or raster image of a map with spatial locations. Georeferencing may be applied to any kind of object or structure that can be related to a geographical location, such as points of interest, roads, places, bridges, or buildings.
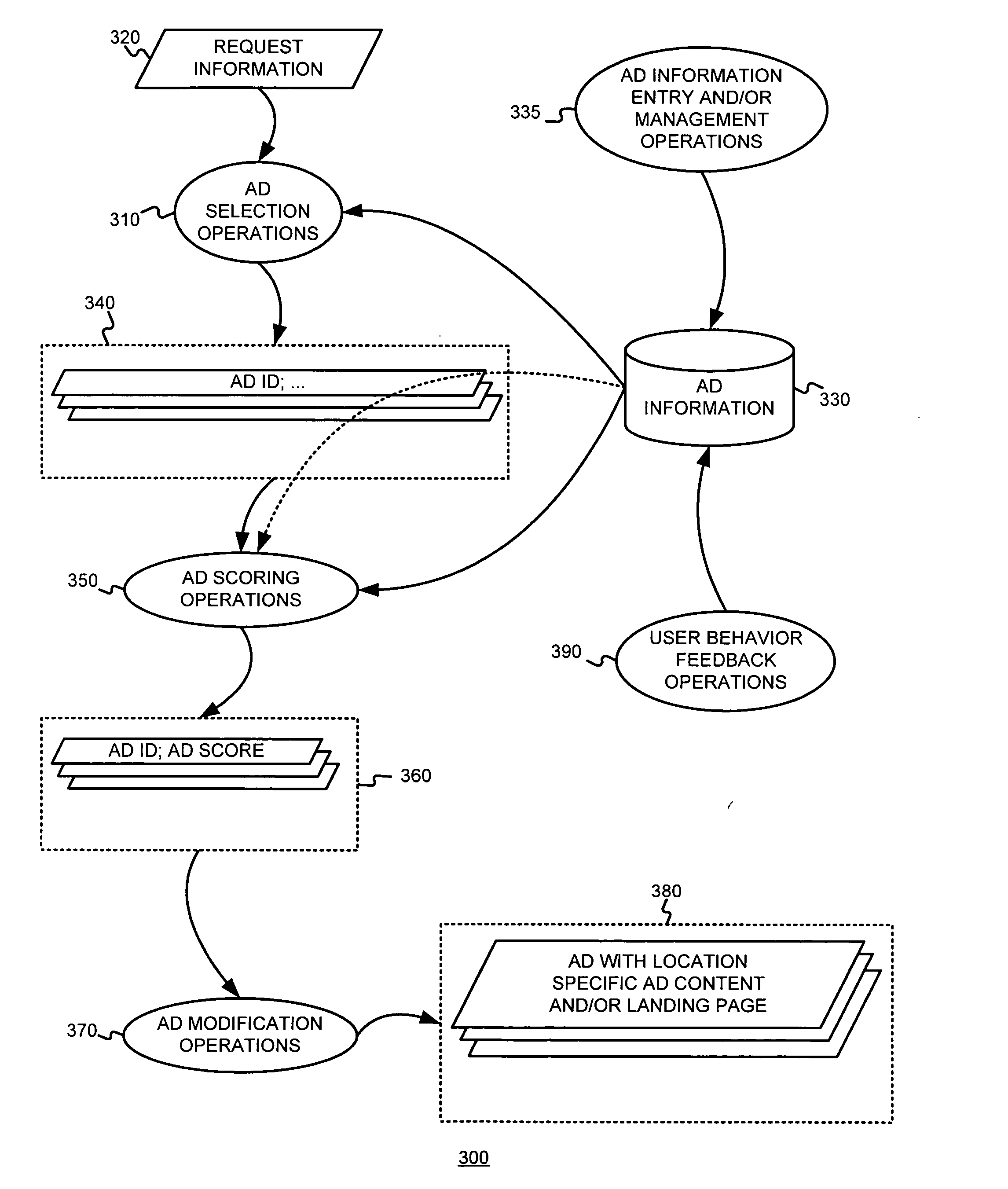
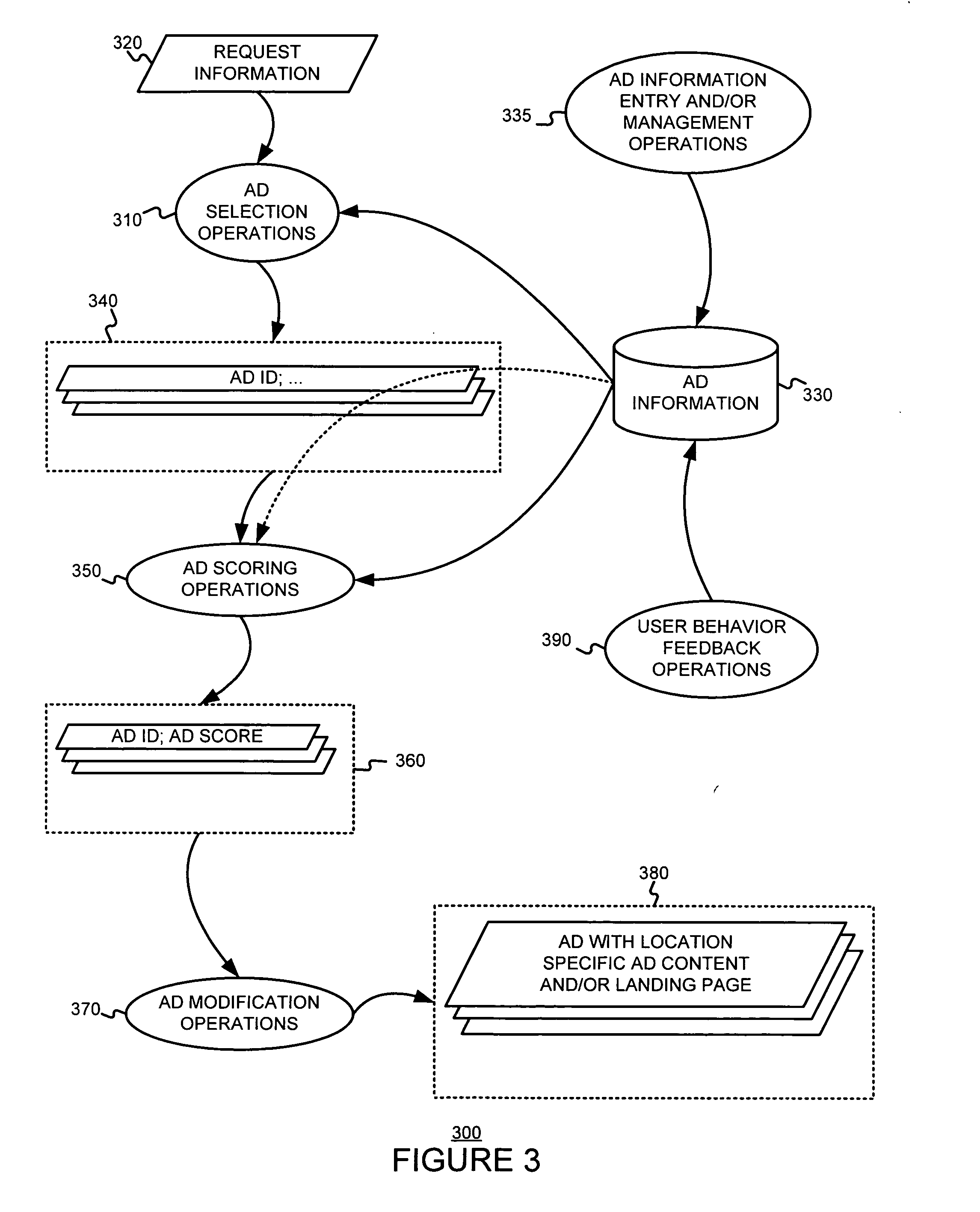
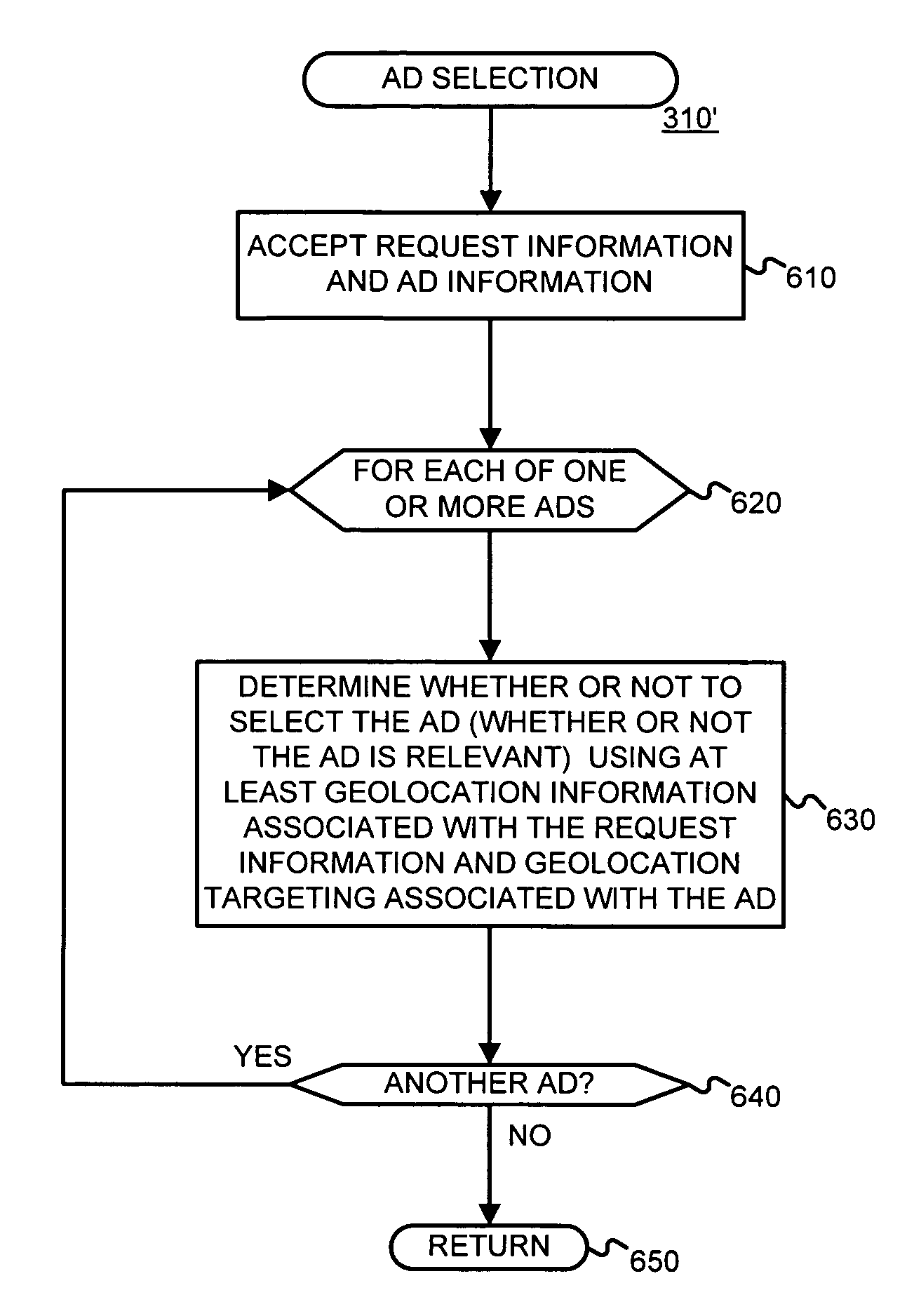
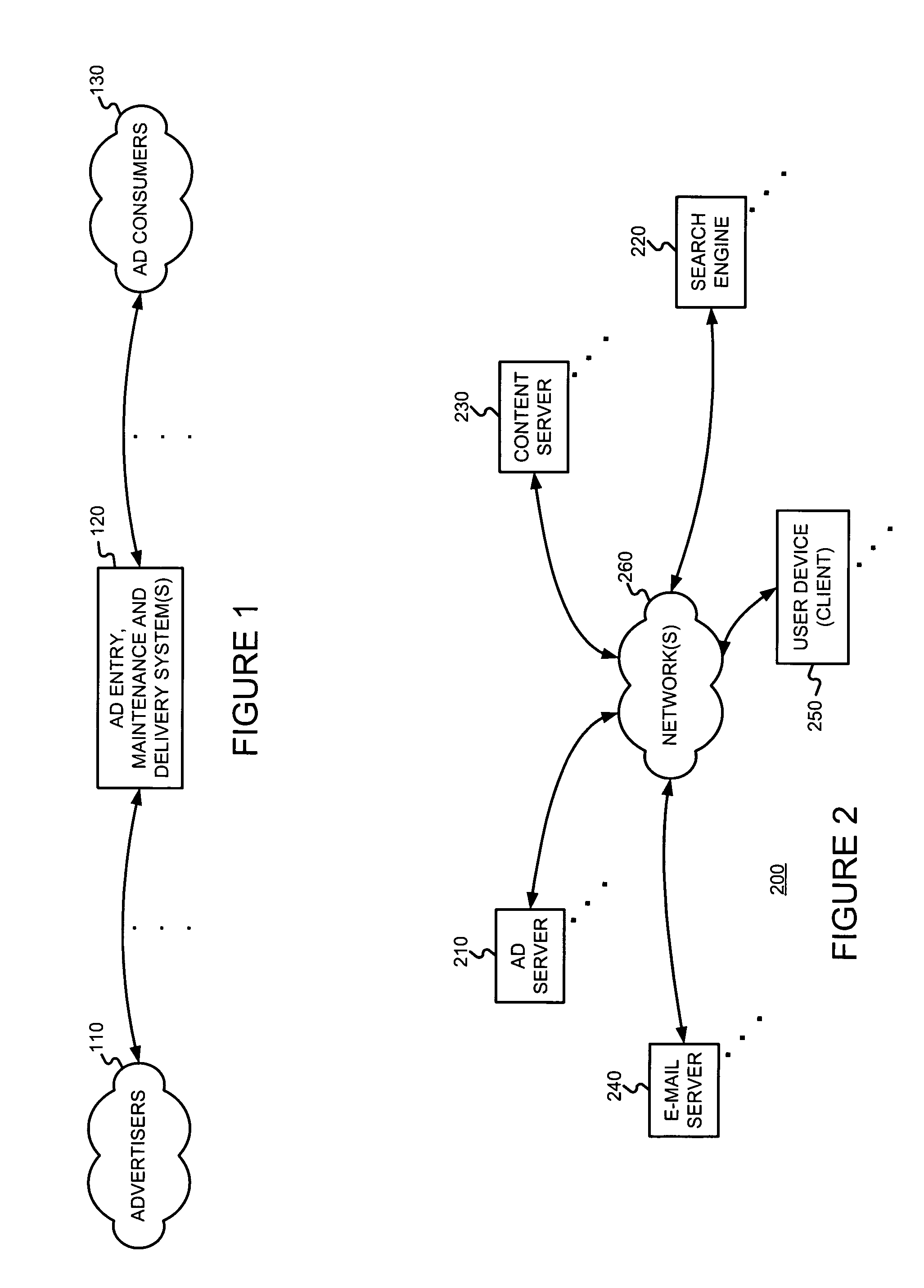
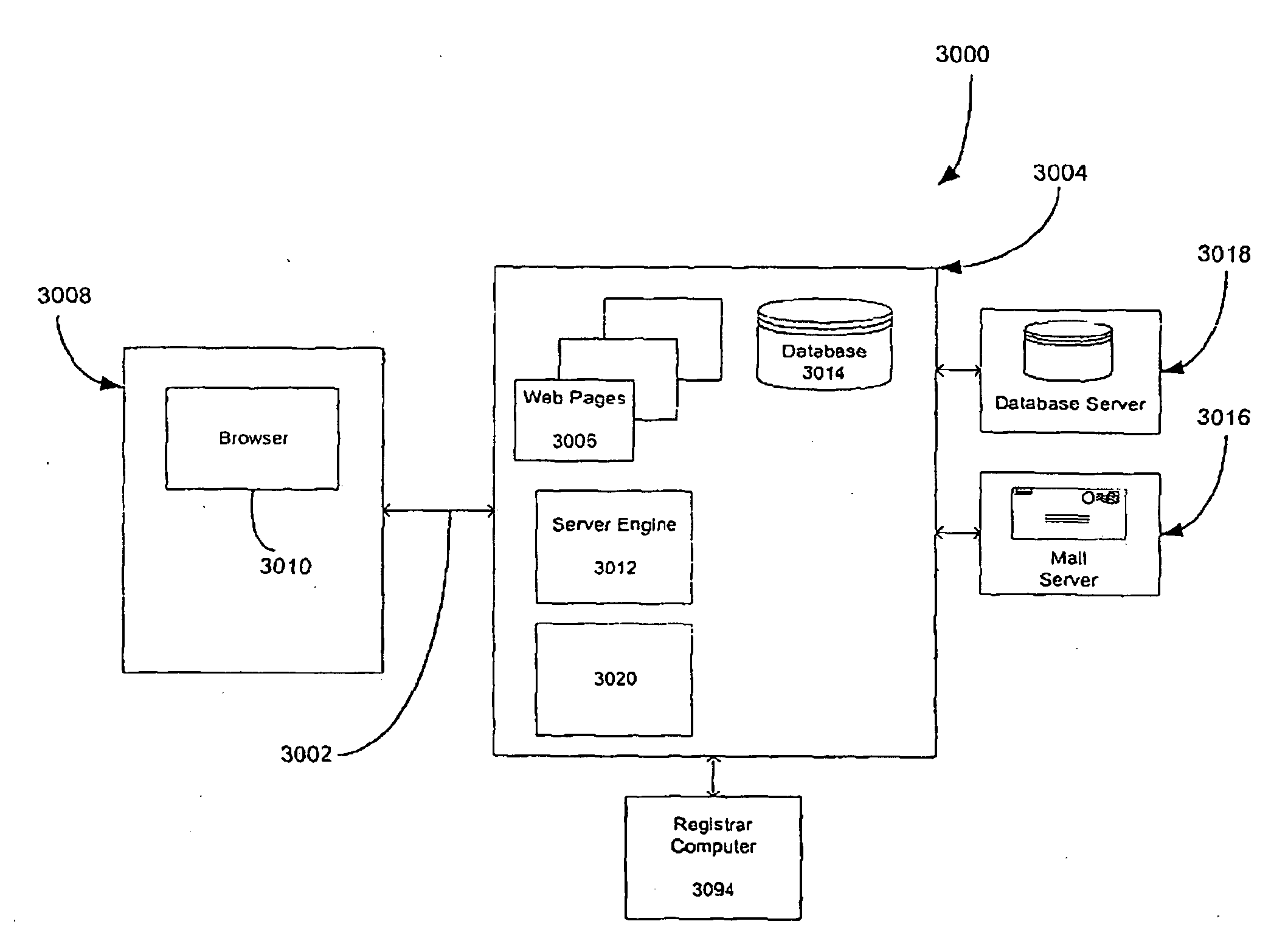
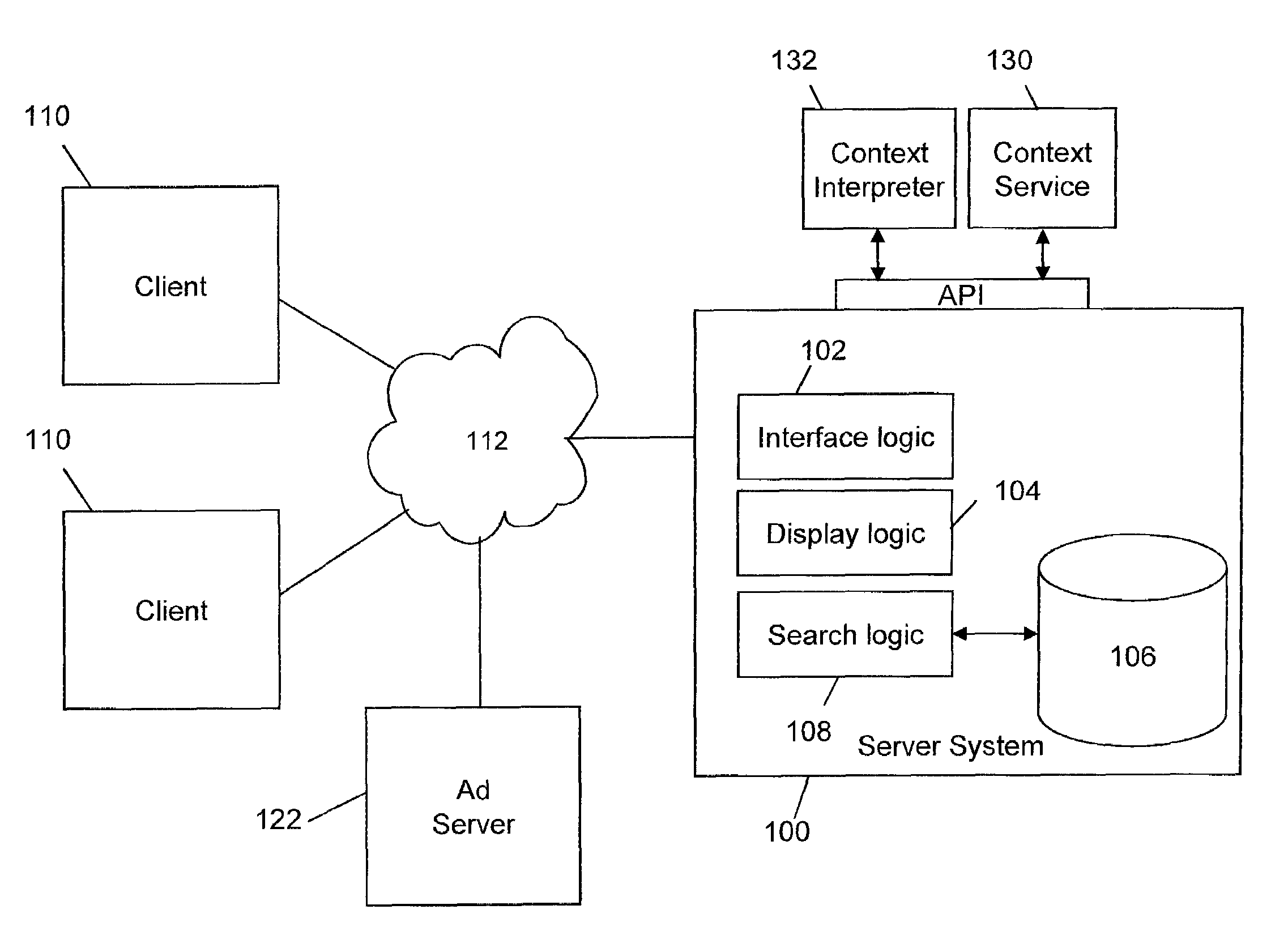
Determining and/or using location information in an ad system
ActiveUS20050050027A1Improve performanceImprove the usefulnessDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsEllipseLongitude
The usefulness, and consequently the performance, of advertisements are improved by allowing businesses to better target their ads to a responsive audience. Location information is determined (or simply accepted) and used. For example, location information may be used in a relevancy determination of an ad. As another example, location information may be used in an attribute (e.g., position) arbitration. Such location information may be associated with price information, such as a maximum price bid. Such location information may be associated with ad performance information. Ad performance information may be tracked on the basis of location information. The content of an ad creative, and / or of a landing page may be selected and / or modified using location information. Finally, tools, such as user interfaces, may be provided to allow a business to enter and / or modify location information, such as location information used for targeting and location-dependent price information. The location information used to target and / or score ads may be, include, or define an area. The area may be defined by at least one geographic reference point (e.g., defined by latitude and longitude coordinates) and perhaps additional information. Thus, the area may be a circle defined by a geographic reference point and a radius, an ellipse defined by two geographic reference points and a distance sum, or a polygon defined by three or more geographic reference points, for example.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Determining and/or using location information in an ad system
ActiveUS7668832B2Improve performanceImprove the usefulnessDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsEllipseLongitude
The usefulness, and consequently the performance, of advertisements are improved by allowing businesses to better target their ads to a responsive audience. Location information is determined (or simply accepted) and used. For example, location information may be used in a relevancy determination of an ad. As another example, location information may be used in an attribute (e.g., position) arbitration. Such location information may be associated with price information, such as a maximum price bid. Such location information may be associated with ad performance information. Ad performance information may be tracked on the basis of location information. The content of an ad creative, and / or of a landing page may be selected and / or modified using location information. Finally, tools, such as user interfaces, may be provided to allow a business to enter and / or modify location information, such as location information used for targeting and location-dependent price information. The location information used to target and / or score ads may be, include, or define an area. The area may be defined by at least one geographic reference point (e.g., defined by latitude and longitude coordinates) and perhaps additional information. Thus, the area may be a circle defined by a geographic reference point and a radius, an ellipse defined by two geographic reference points and a distance sum, or a polygon defined by three or more geographic reference points, for example.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
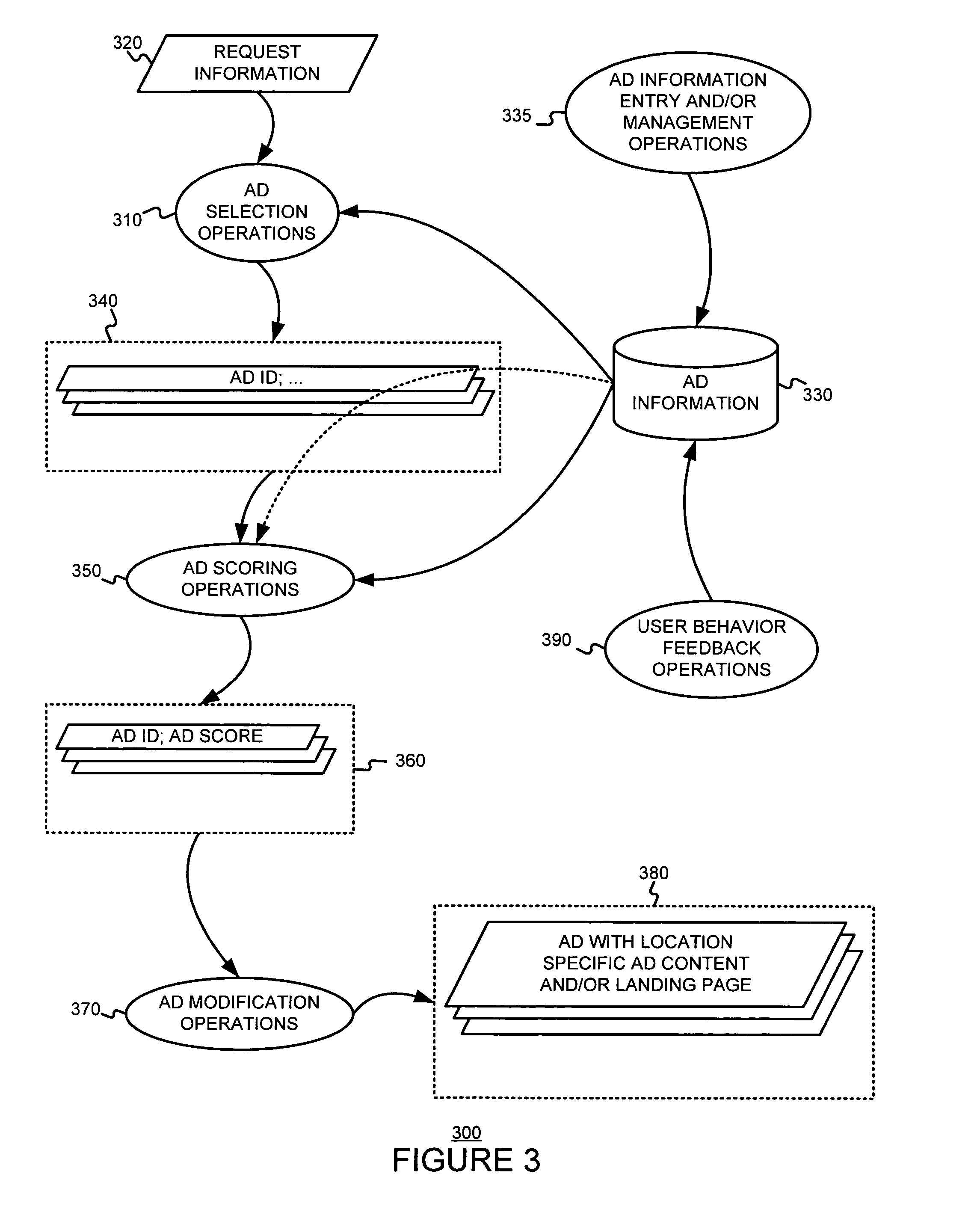
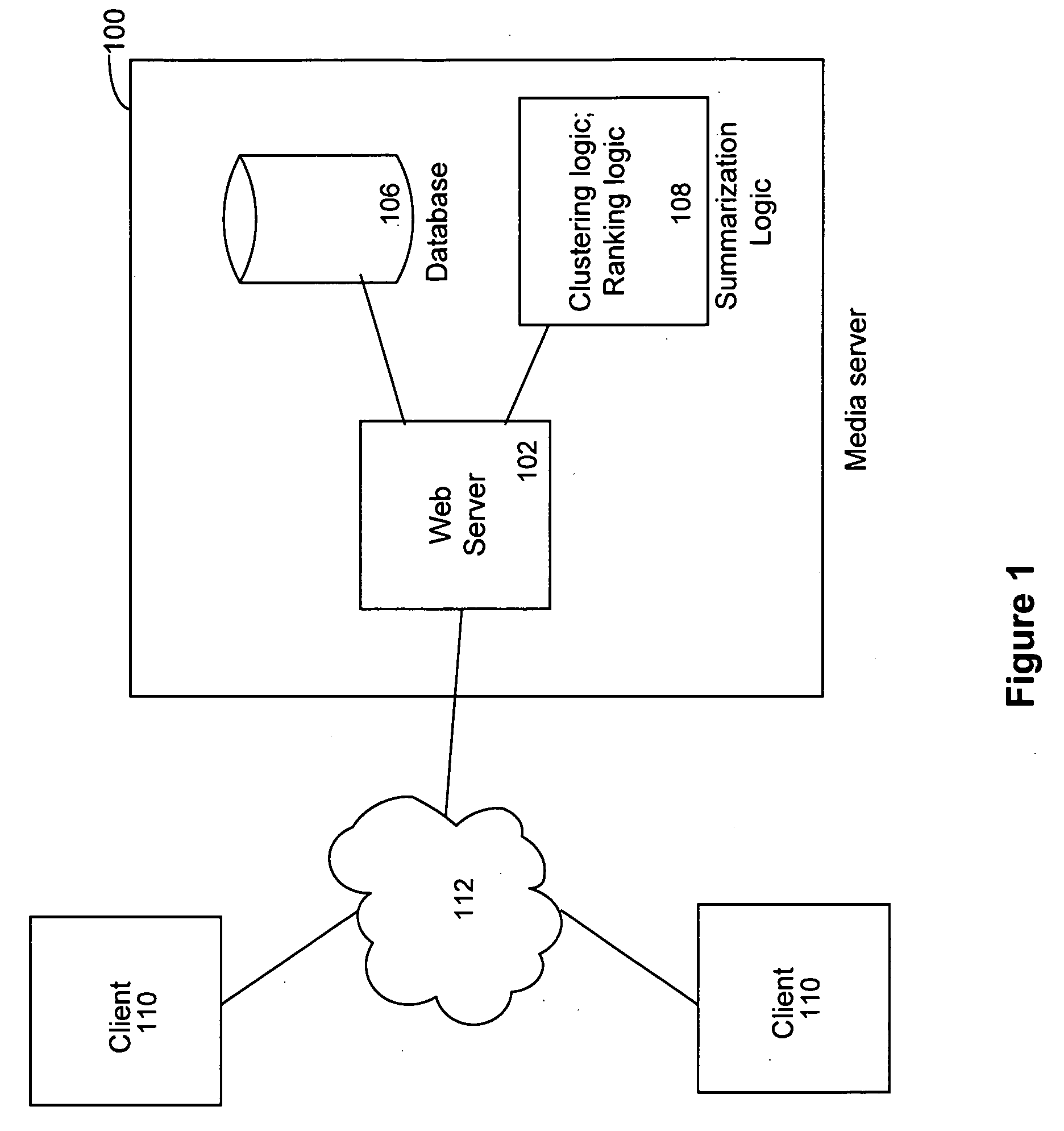
Summarization of media object collections
In one example, an apparatus and method are provided for summarizing (or selecting a representative subset from) a collection of media objects. A method includes selecting a subset of media objects from a collection of geographically-referenced (e.g., via GPS coordinates) media objects based on a pattern of the media objects within a spatial region. The media objects may further be selected based on (or be biased by) various social aspects, temporal aspects, spatial aspects, or combinations thereof relating to the media objects and / or a user. Another method includes clustering a collection of media objects in a cluster structure having a plurality of subclusters, ranking the media objects of the plurality of subclusters, and selection logic for selecting a subset of the media objects based on the ranking of the media objects.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
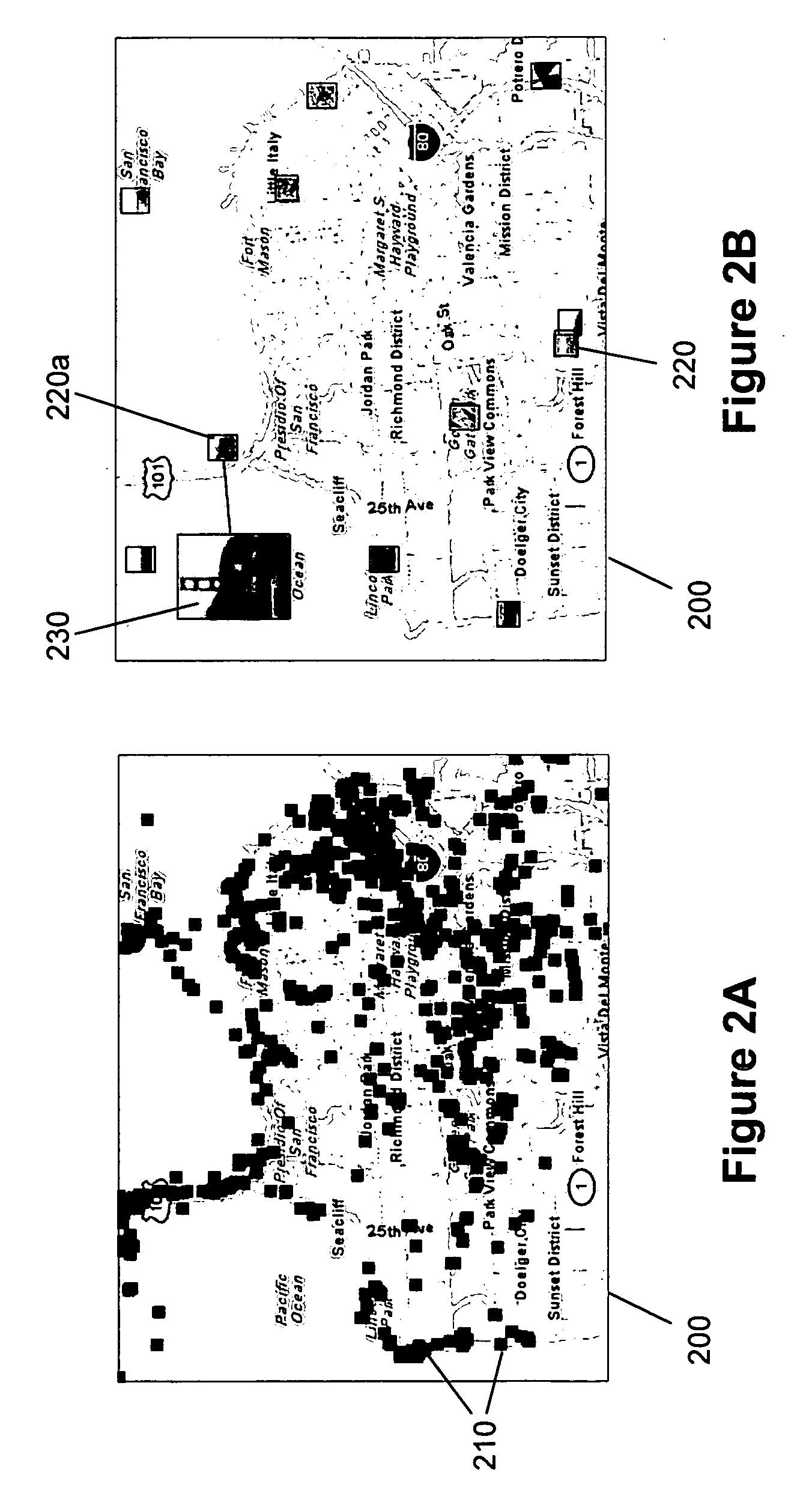
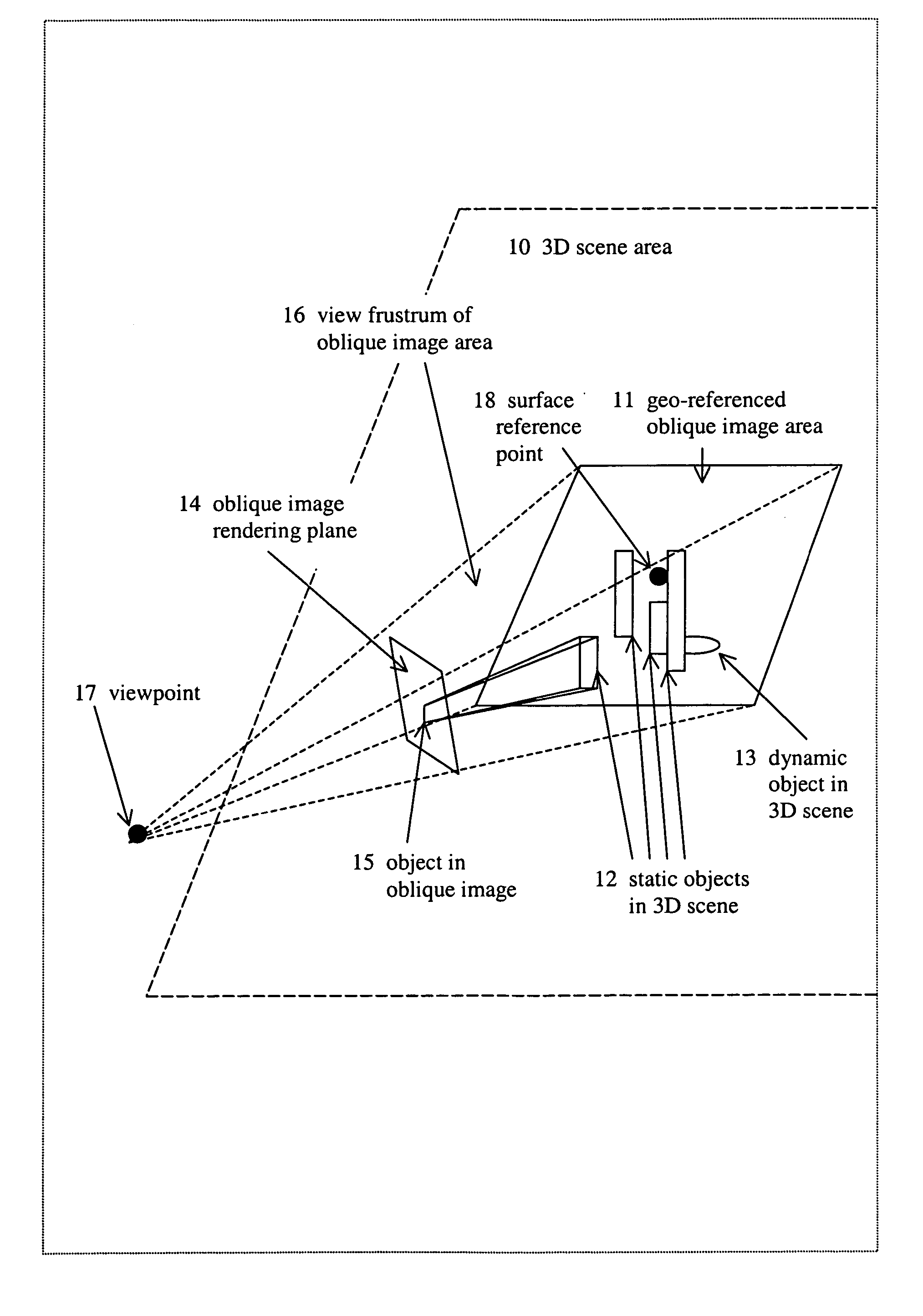
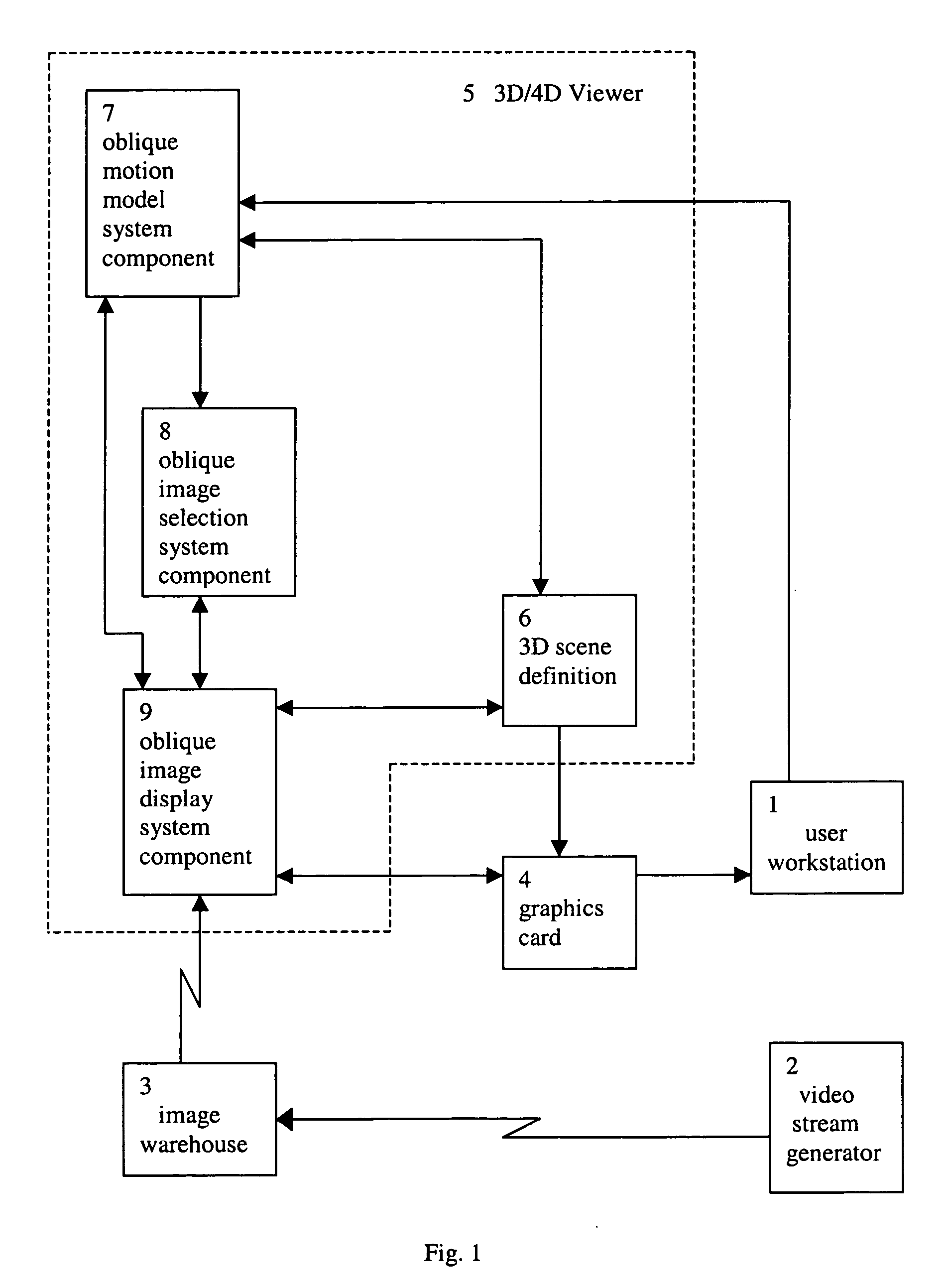
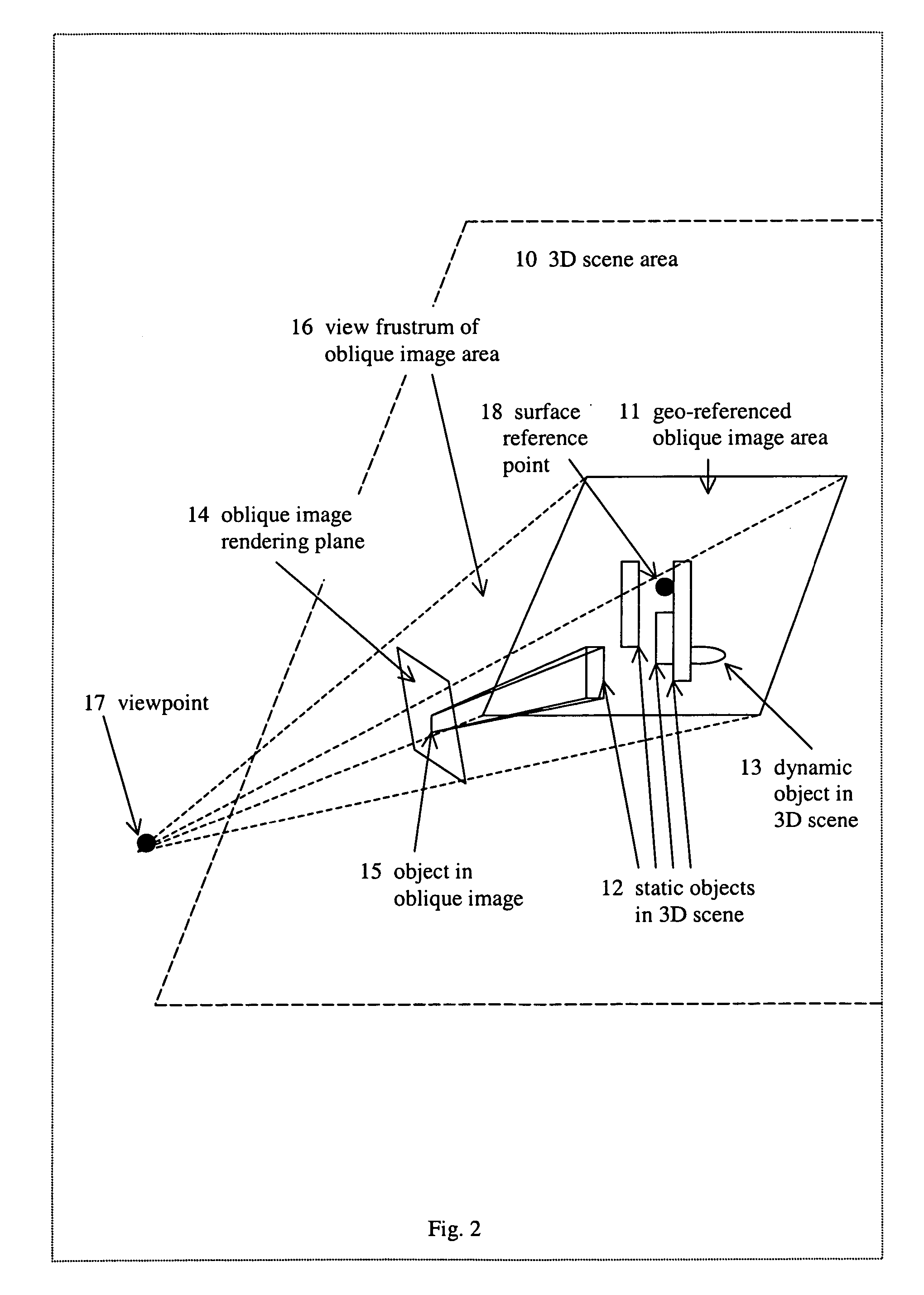
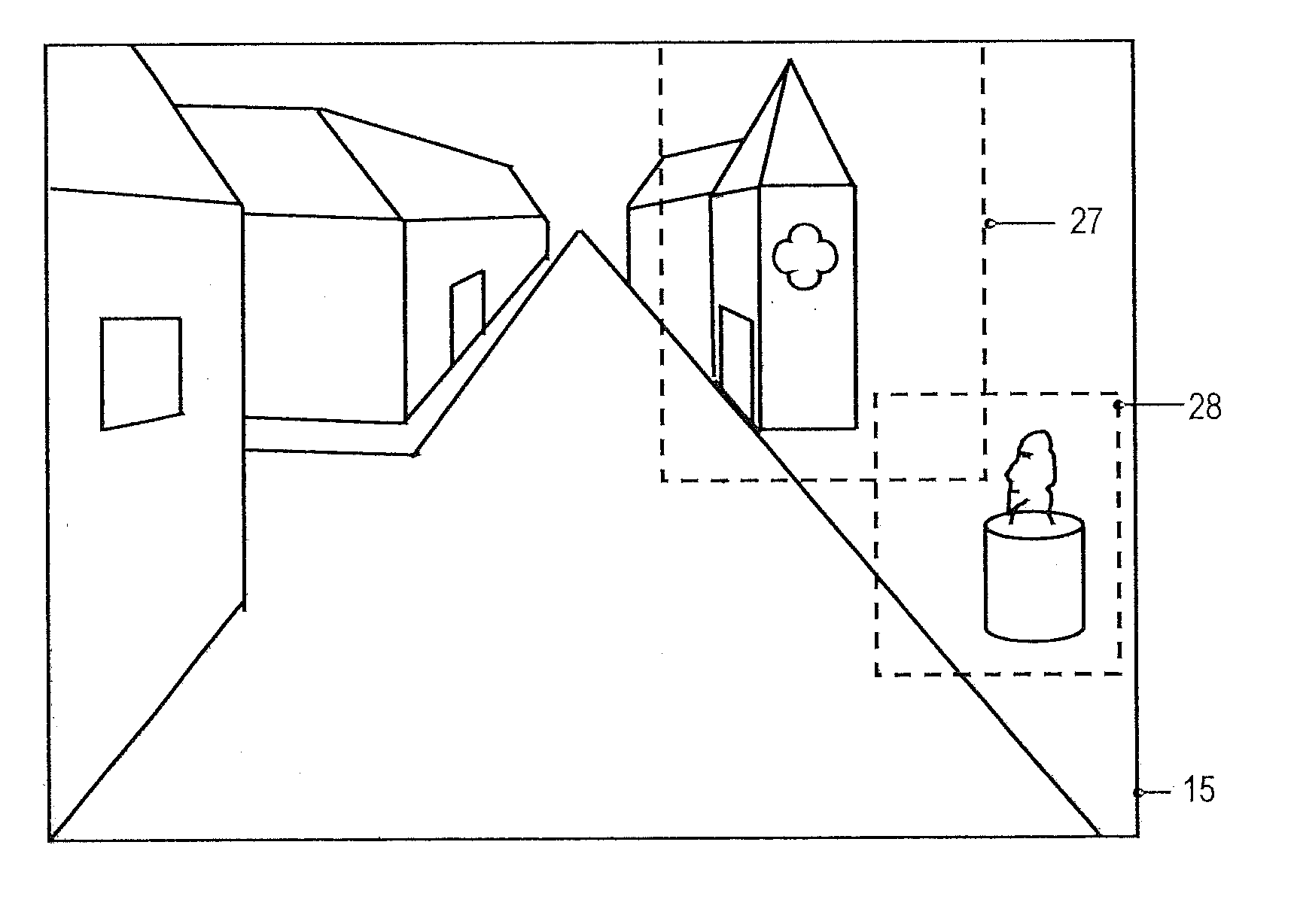
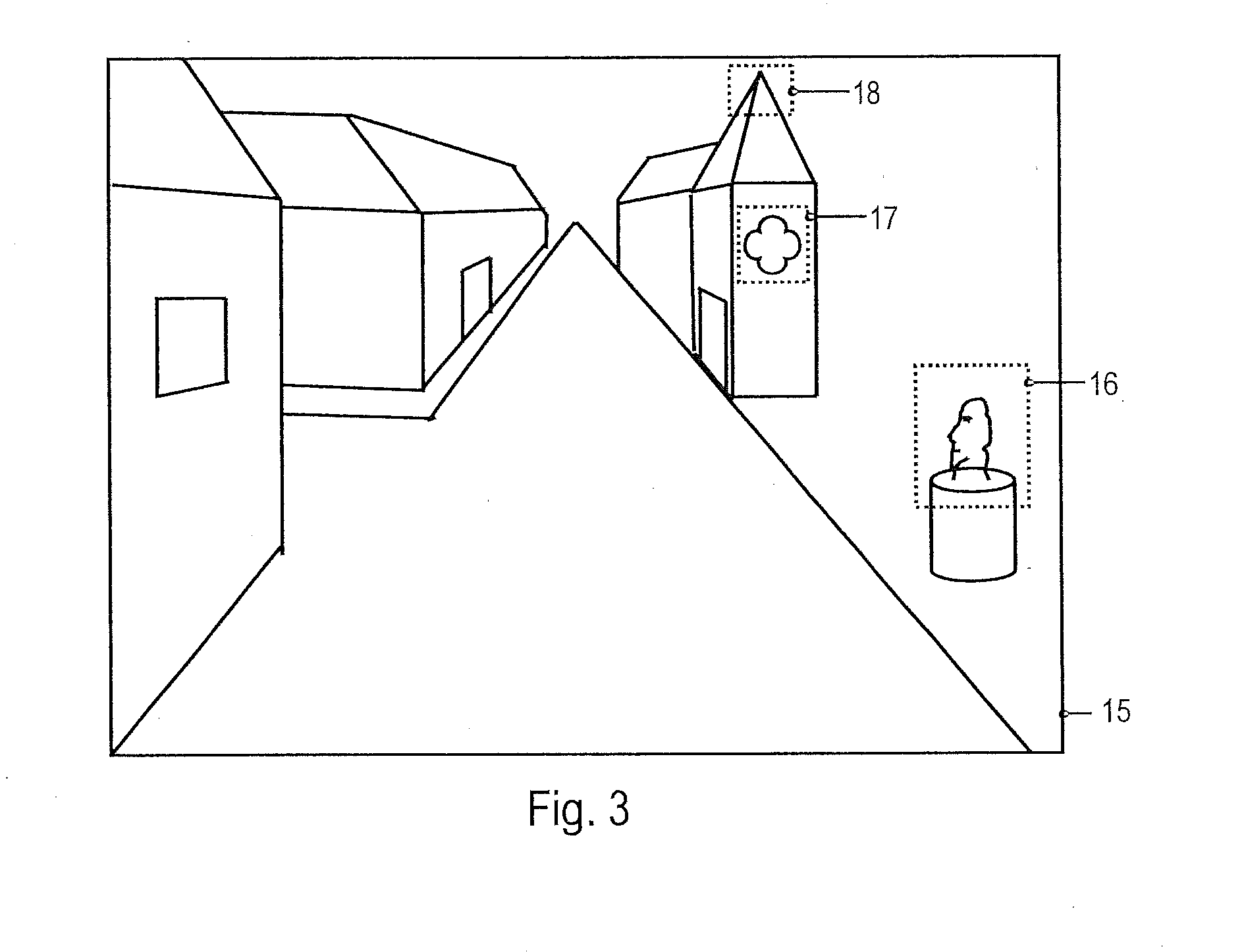
System for viewing a collection of oblique imagery in a three or four dimensional virtual scene
A system for selecting oblique images from a collection of geo-referenced oblique images and viewing them within the context of a virtual, three- or four-dimensional (3D space and time) geographic scene, providing the ability to analyze and interact with the oblique image being viewed. The system automatically selects and displays the best fit oblique image from an image warehouse based on the user's current 3D / 4D viewpoint, and continuously maintains the geo-registration of the oblique image as the user adjusts the viewpoint.
Owner:BALFOUR TECH
Parking regulation enforcement system
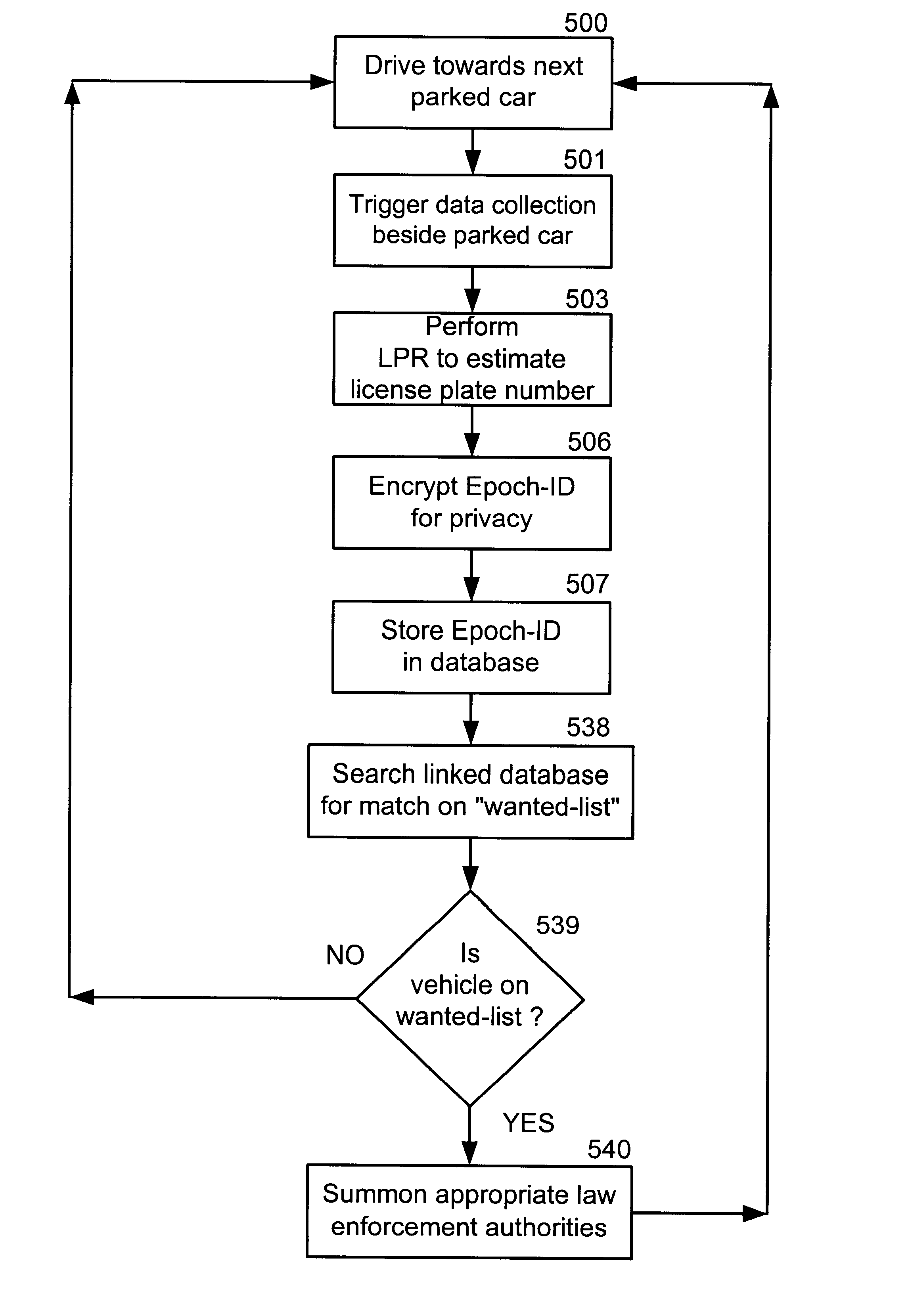
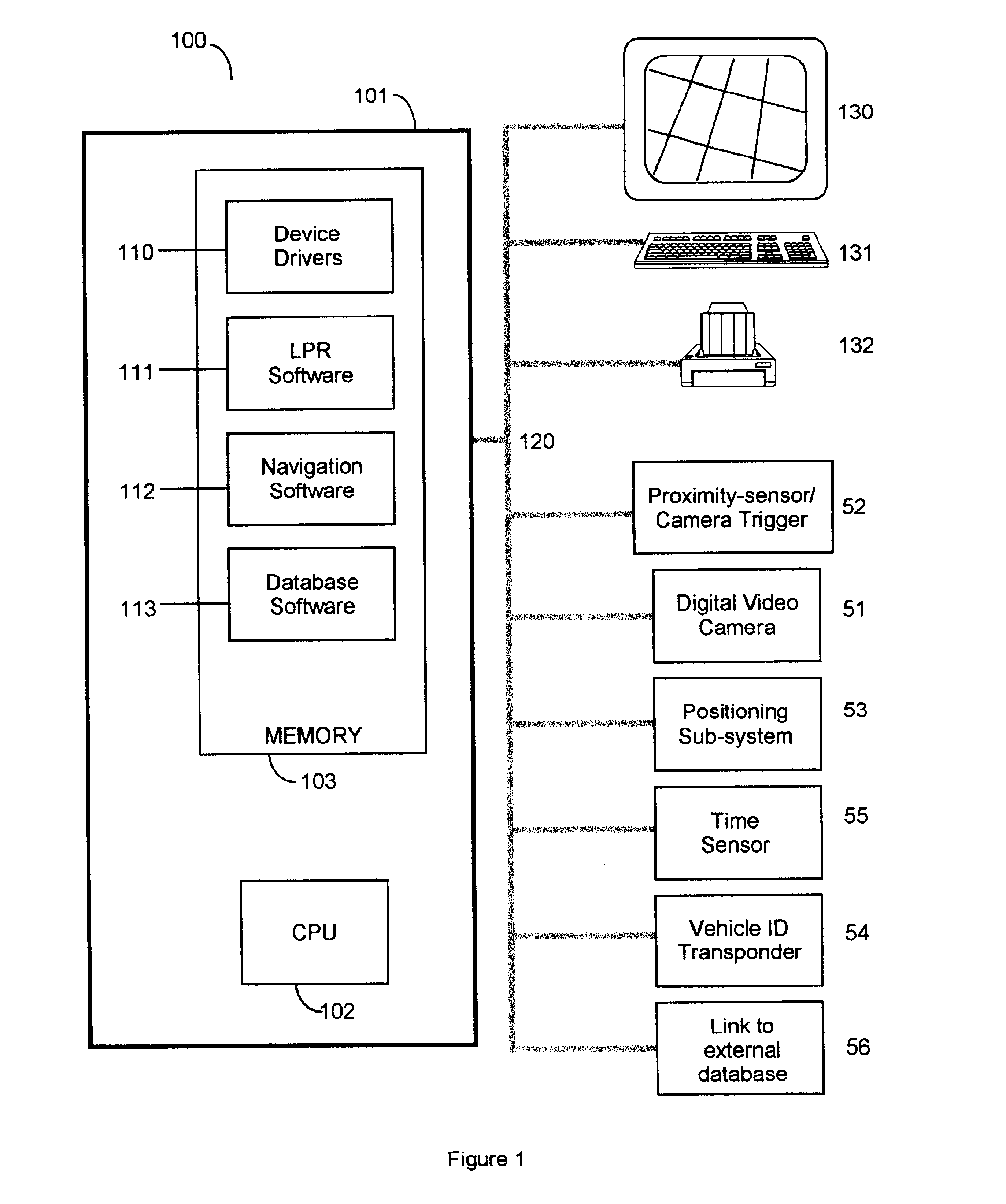
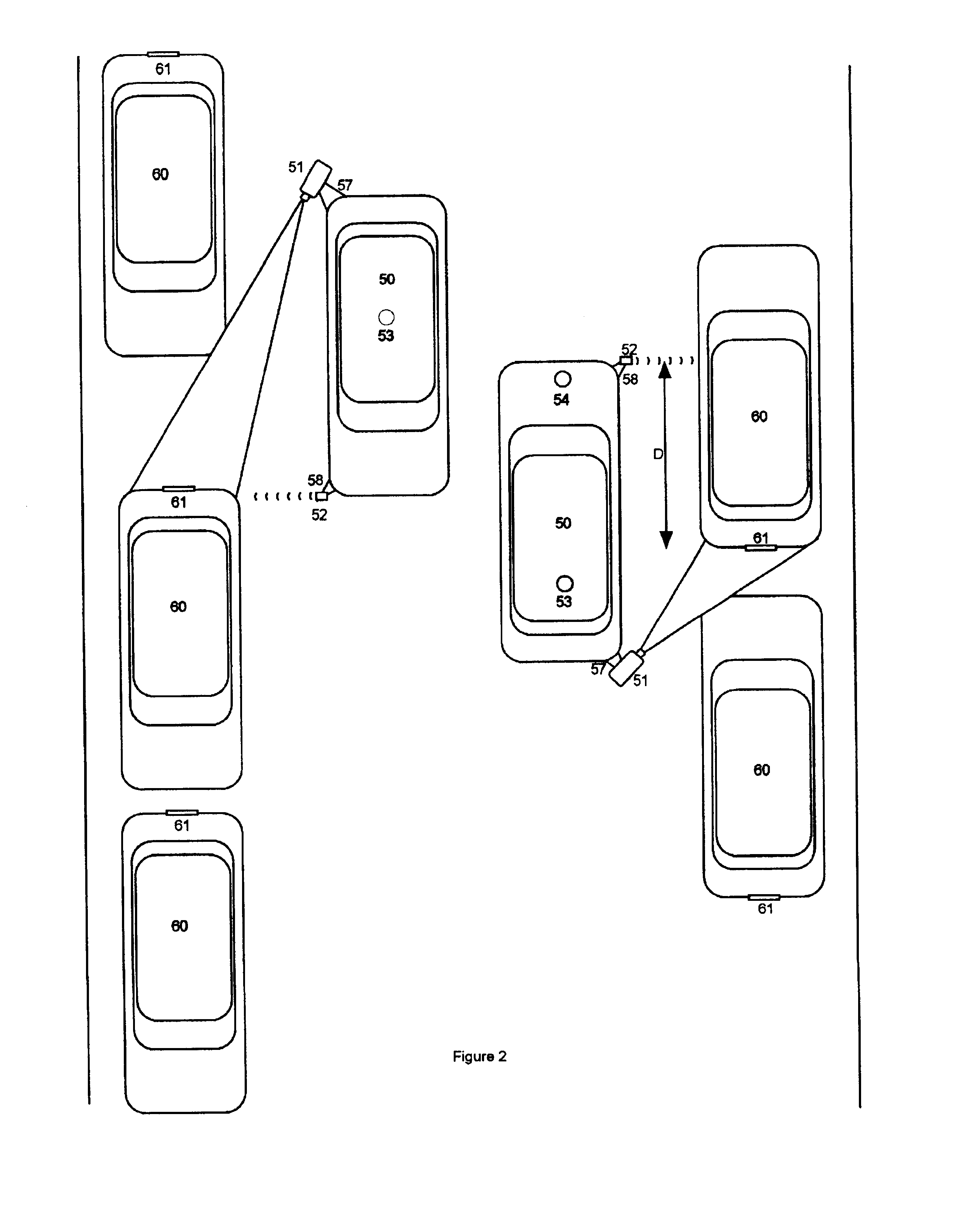
A video camera mounted on a parking enforcement patrol vehicle and connected to a computer near the operator. The system is driven along a patrol route where parked vehicles are governed by a posted time limit. The system enforces the local parking regulation by automatically determining whether or not each parked car has been parked longer than the posted time limit. Violations are detected by applying a License Plate Recognition algorithm to the images. Each license plate number is time-tagged, geo-referenced and entered into a local database. When the patrol vehicle re-traces the patrol route after the posted parking time limit has expired, the database is searched to flag vehicles that were observed at the same location during the previous circuit and therefore in violation of the parking regulations. When the system detects a parking violation, it prints a parking citation that the operator affixes to the offending parked vehicle.
Owner:AUTO VU TECH INC
Unified geographic database and method of creating, maintaining and using the same
InactiveUS20050283503A1Increase addressing resolutionInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsDomain nameCredit card
The present invention involves a Universal Geographic Database (“UGD”). The UGD is an automated, central or distributed, registry of real-world locations and location-related information for businesses and other entities, analogous to the registry of domain names for Internet and web sites. By this central registry, businesses and other entities are facilitated to post their location and location-related information in a single place, for all users who need or want it; and users can refer to this single place, via the Internet, Web, and other telecommunications devices, to obtain accurate, complete and timely location and location-based information about the registered businesses and other entities. Each record of the UGD is keyed by a proprietary location address (PLA) based on the World Geographic Referencing System (WGRS), and optionally may have one or more proprietary location addresses (PLAs), which also may serve as keys. Associated with the PLA keys, each UGD record generally includes the full name for the business or other entity, its street address, and miscellaneous contact information (e.g., telephone number, facsimile number, e-mail address, internet website address, wireless website address). Other more dynamic, customized information (e.g., store hours, credit cards accepted, inventory, prices, specials, hours, parking) also may be available in the UGD record or linked to the UGD record. Users of any device or service can access the UGD through one or more location name servers (LNS), which can provide access to the UGD or other location-based information linked to the UGD or LNS. Based on the WGRS, PLAs provide, in addition to unique keys for UGD records, a user-friendly notation for location naming in the real-world and on all types of location-sensitive electronic devices, from web phones to in-car navigation systems. Given the UGD, these ULA / PLAs are as important to real-world businesses as their domain names because these WGRS addresses drive real-world commerce to physical business locations just as domain names drive e-commerce Internet or web sites.
Owner:WGRS LICENSING
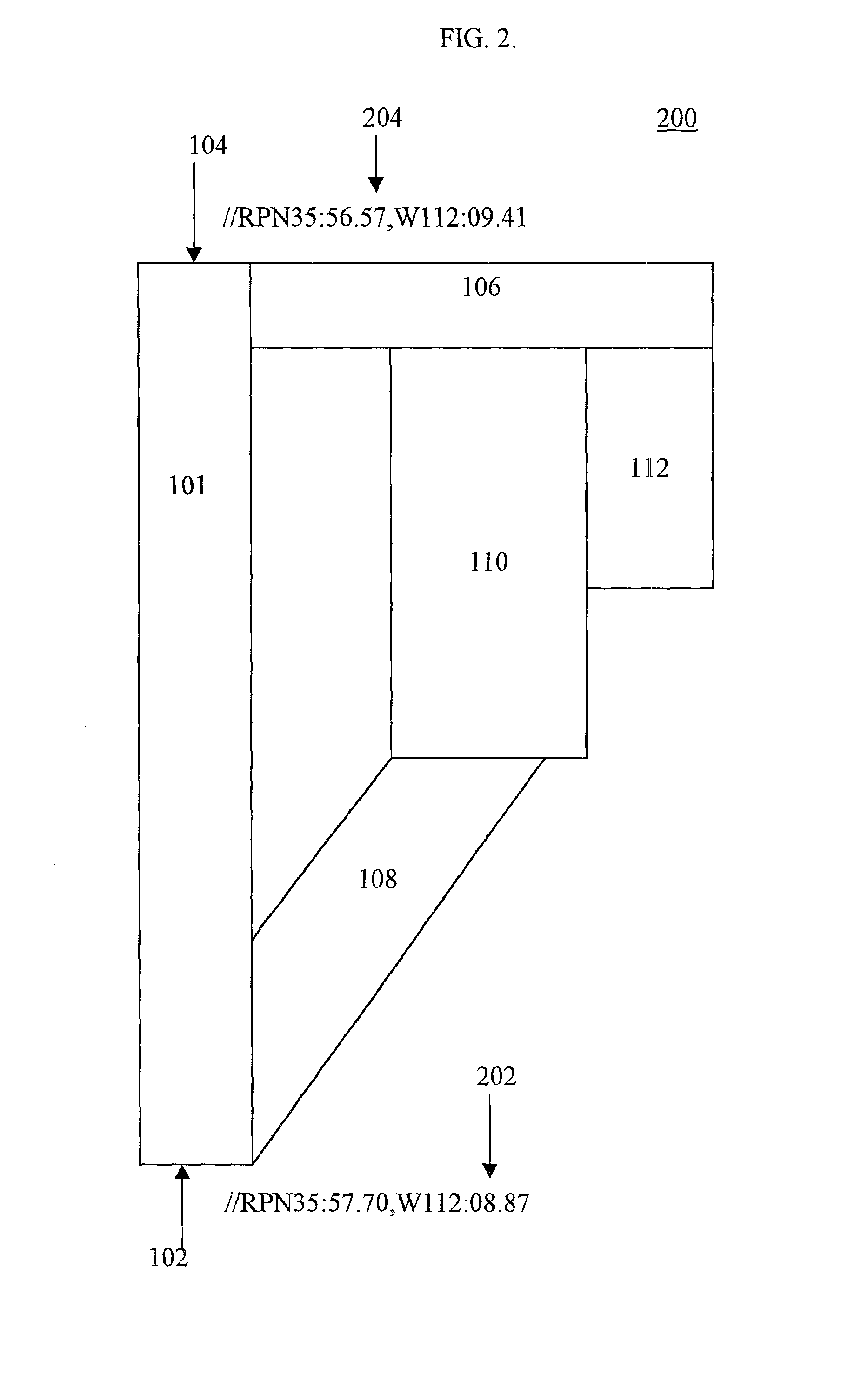
System and method for geographically referencing an improvement image
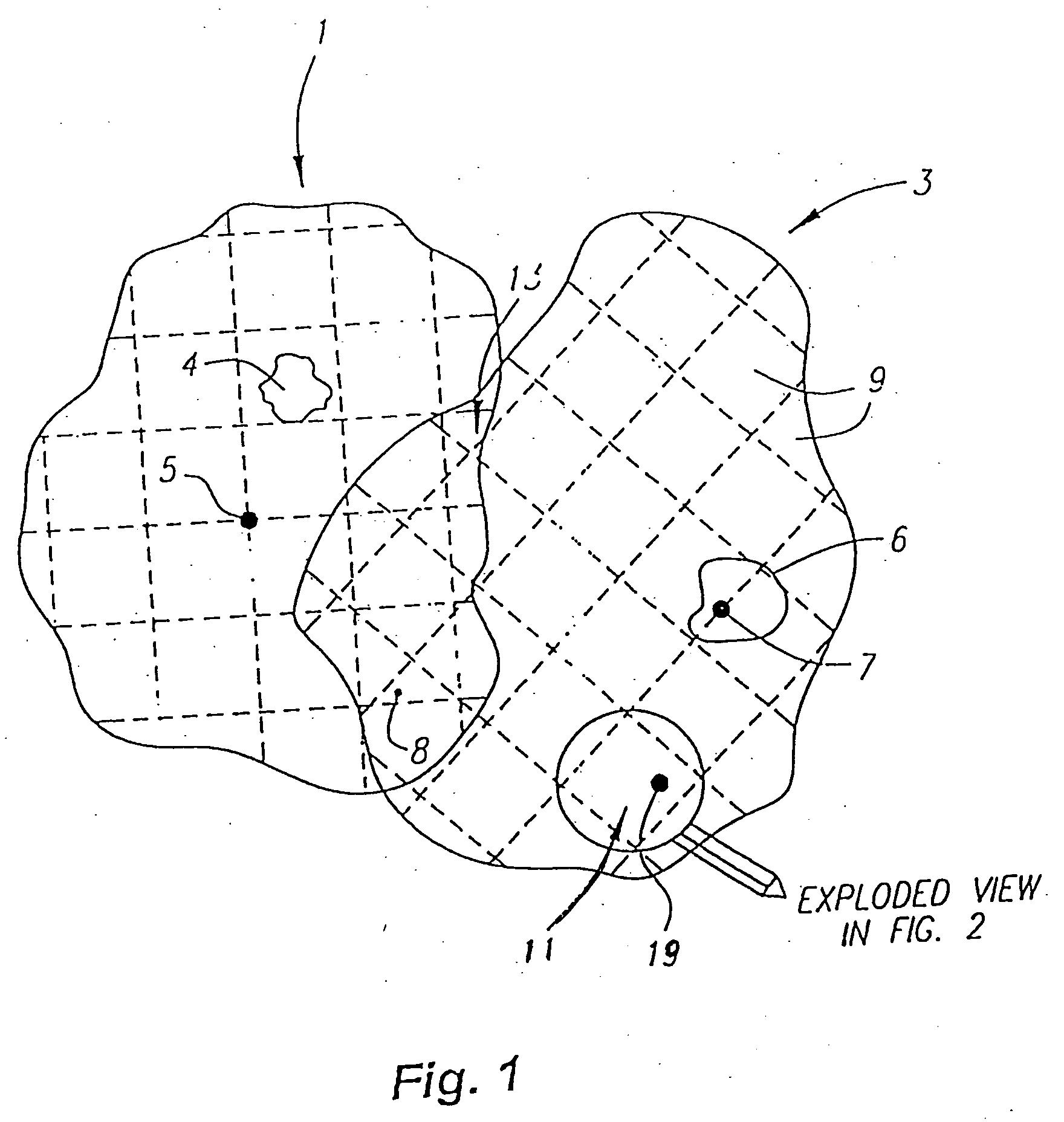
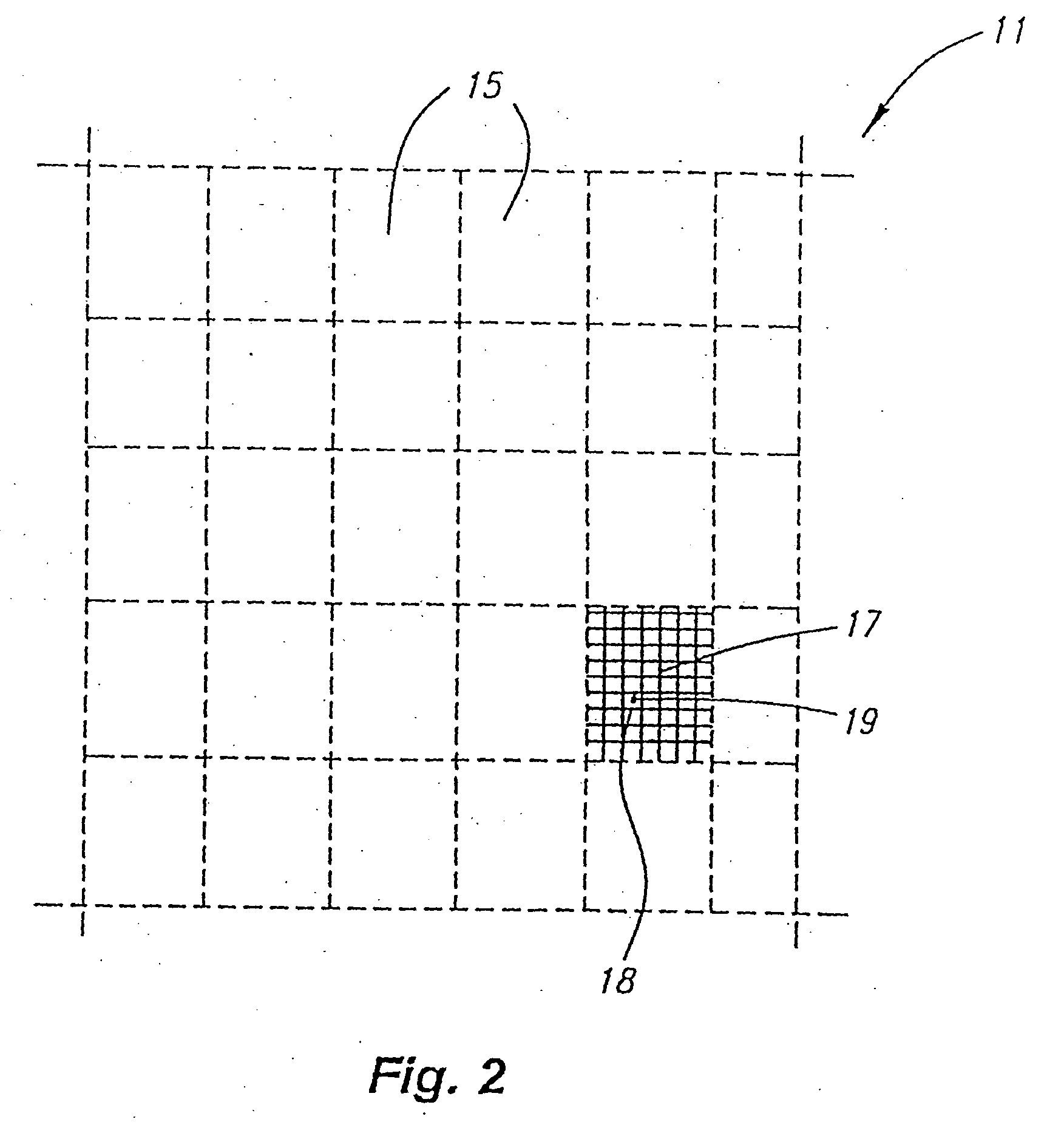
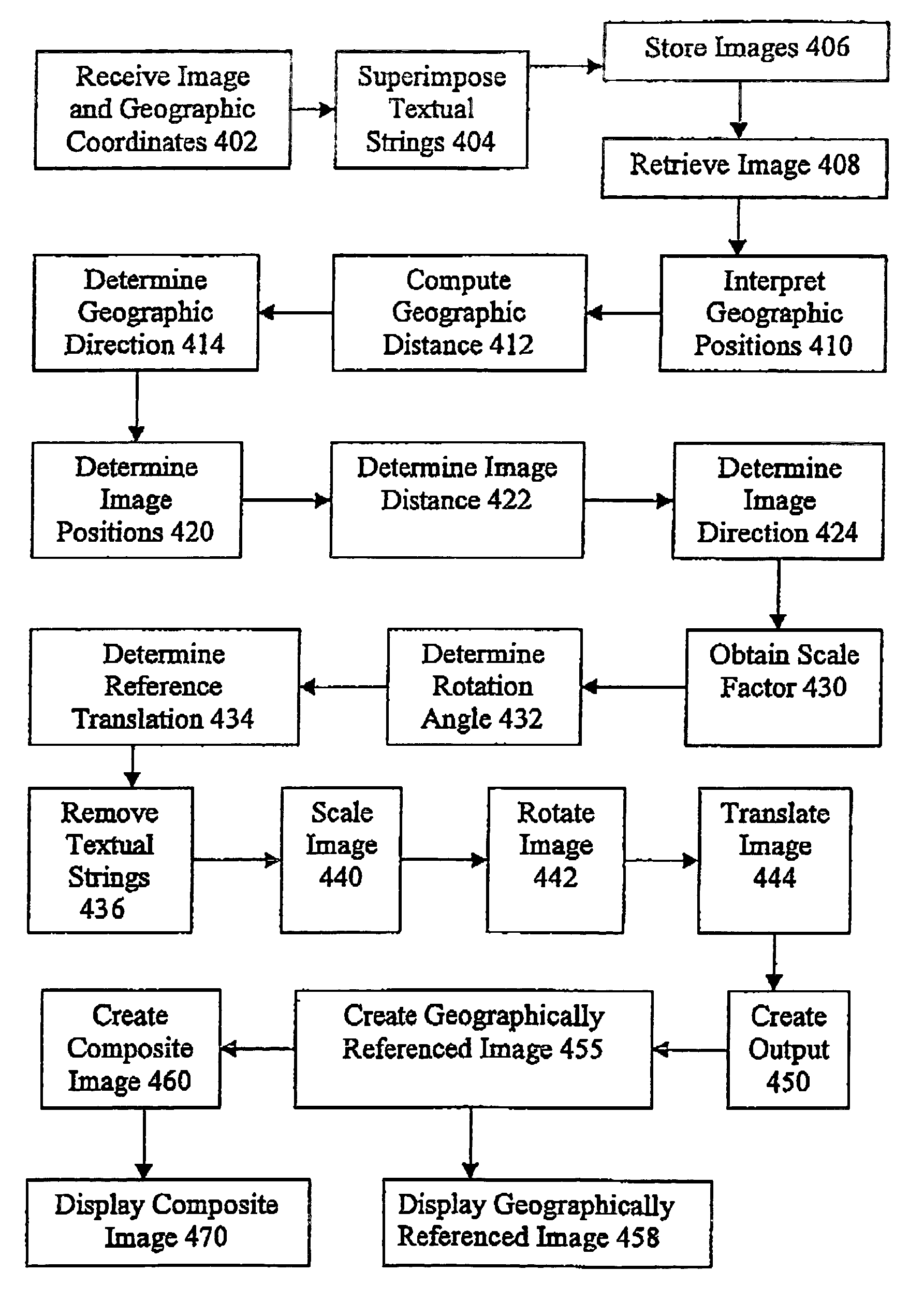
InactiveUS7003138B2Facilitate reliable, accurate and automatic adaptation of the improvement imageCharacter and pattern recognitionMaps/plans/chartsReference imageImage conversion
The instant invention is a system and method for converting improvement images to geographically referenced chart symbols and for combining improvement images with other geographically referenced information to create composite images. The instant invention provides for marking specific reference points on the improvement image with textual strings and using a system configured to recognize textual strings, to understand the information, and to determine the appropriate translation, rotation angle, and scale factor of the improvement image to render a geographically referenced image.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Unified geograhic database and methods of creating, maintaining and using the same
ActiveUS20090077100A1Instruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition dependentLocation based information
Owner:WGRS LICENSING
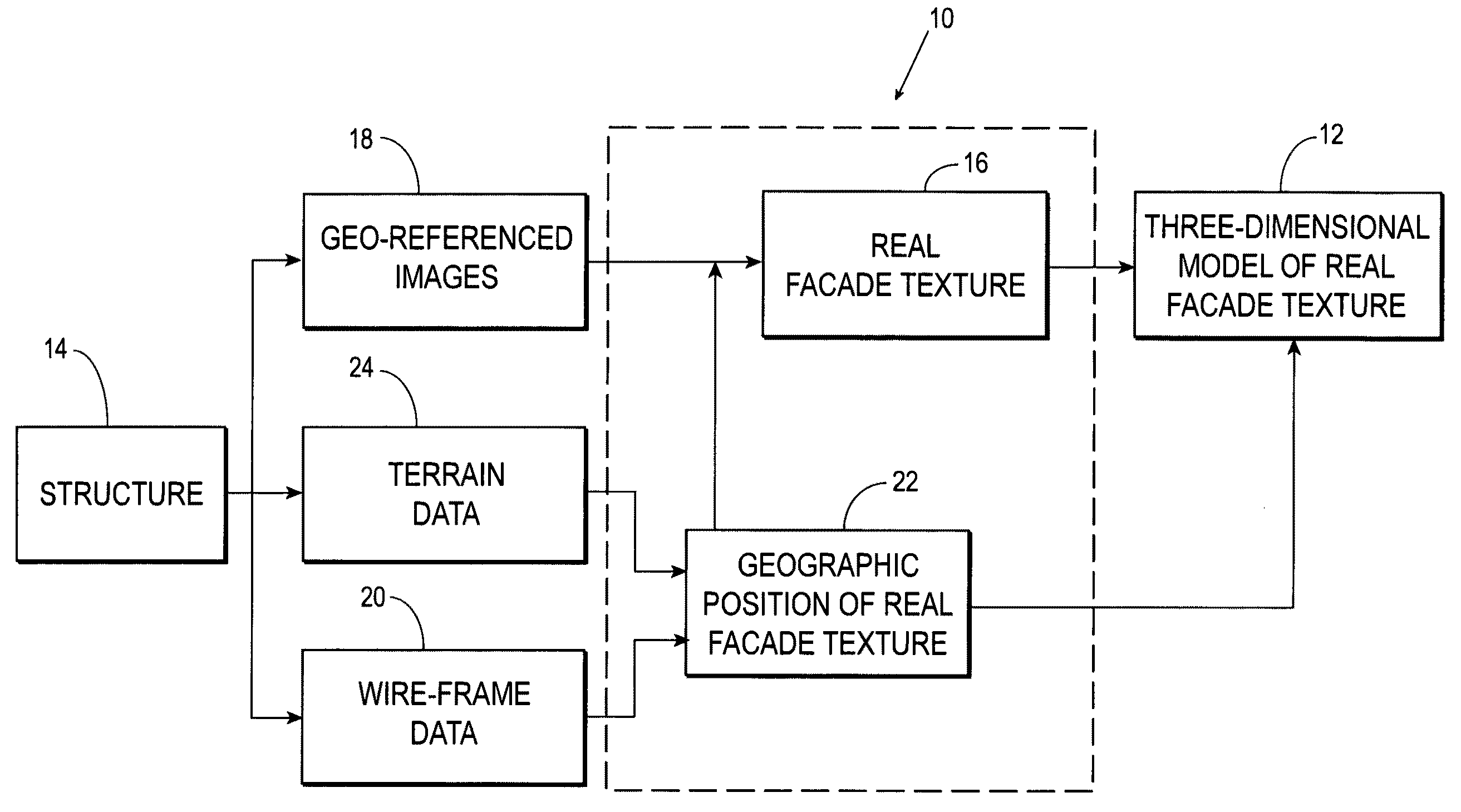
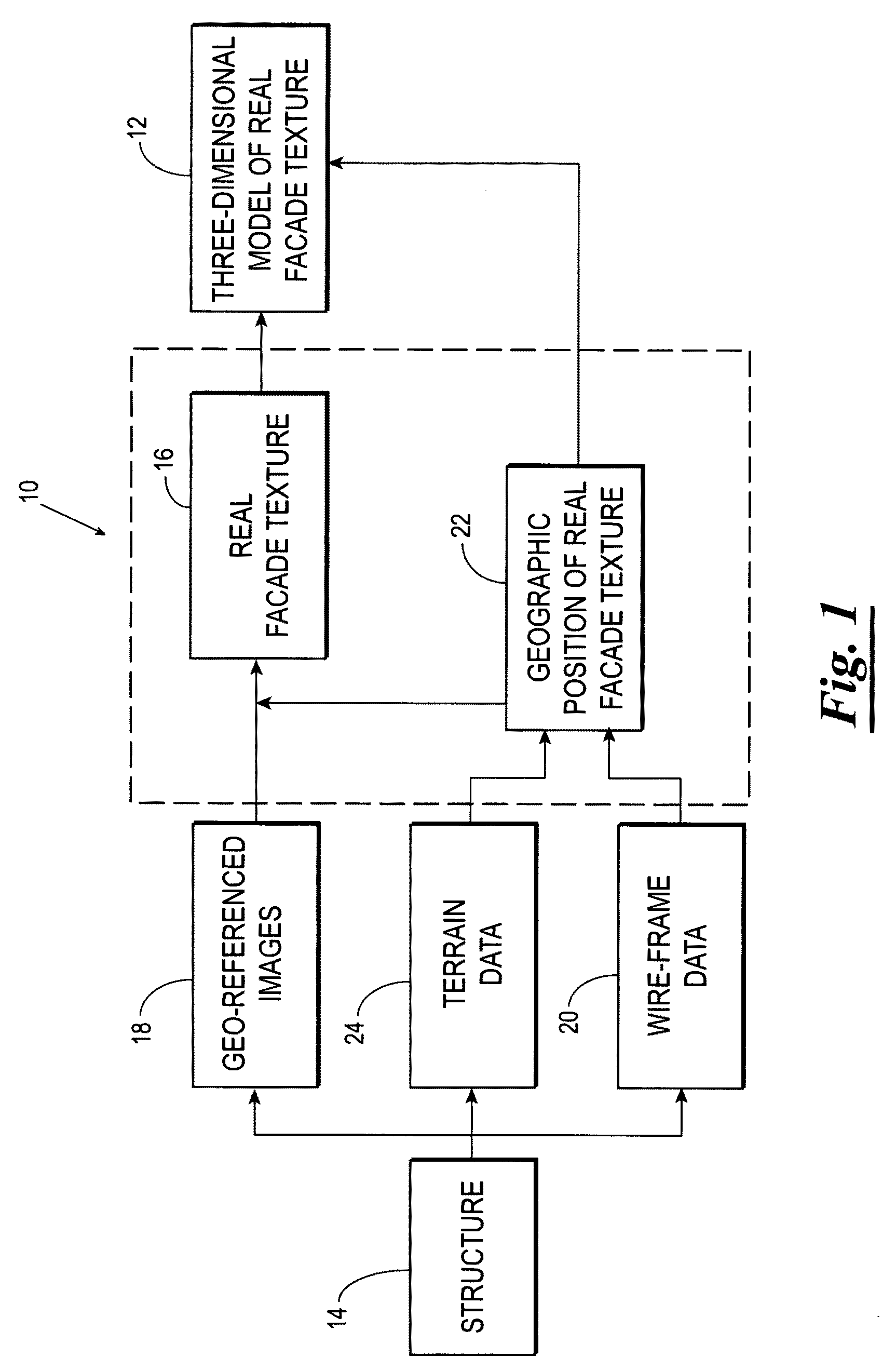
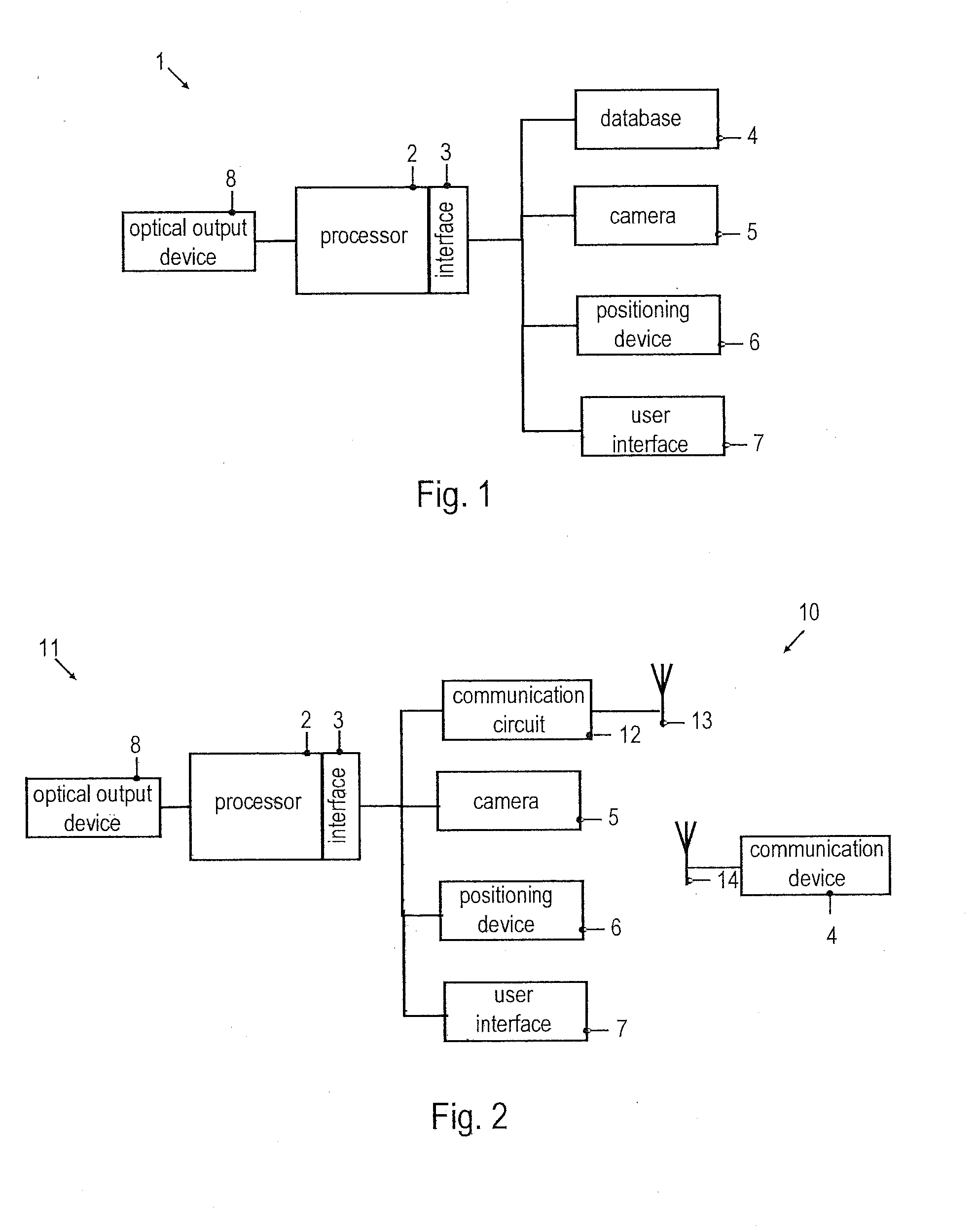
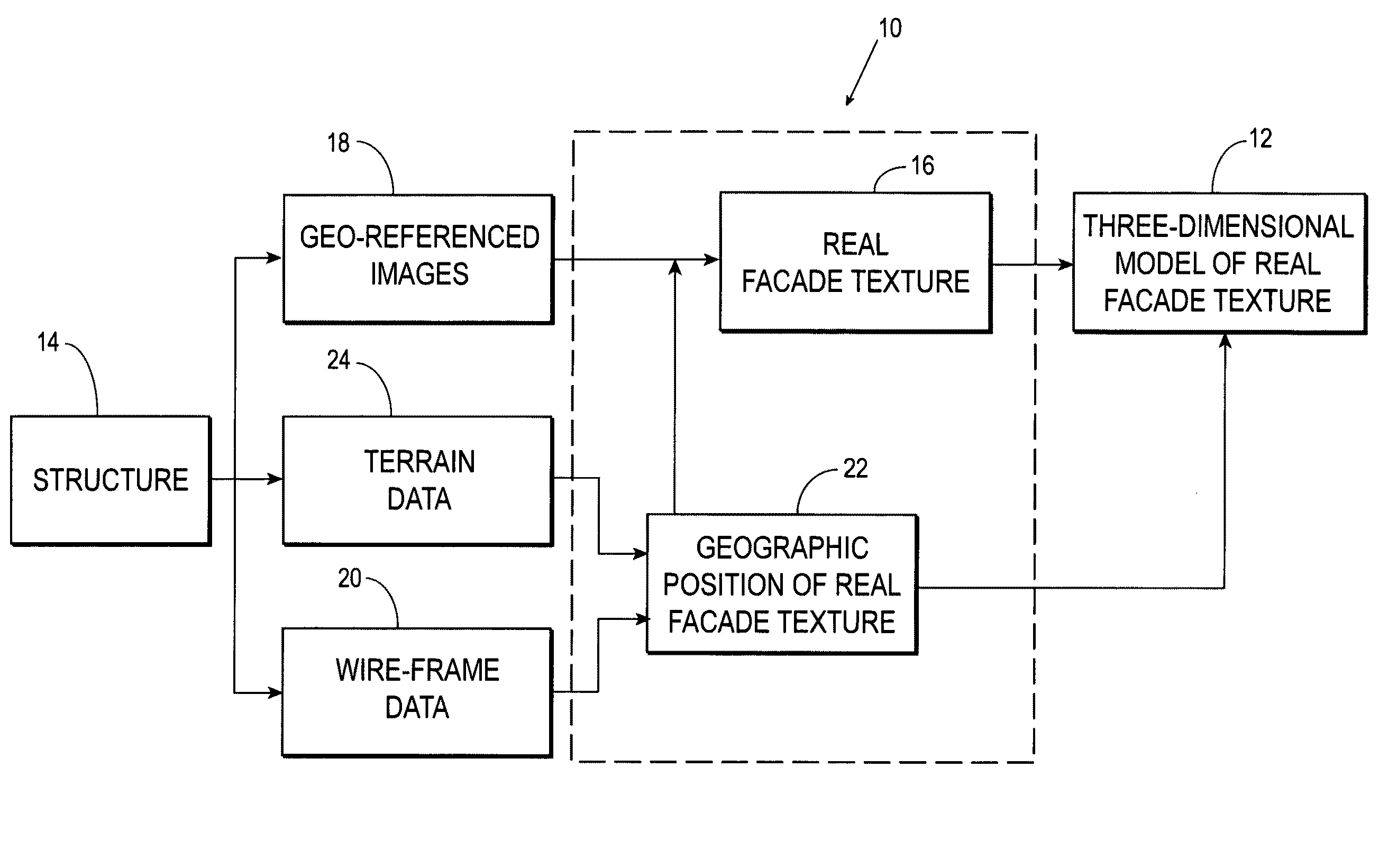
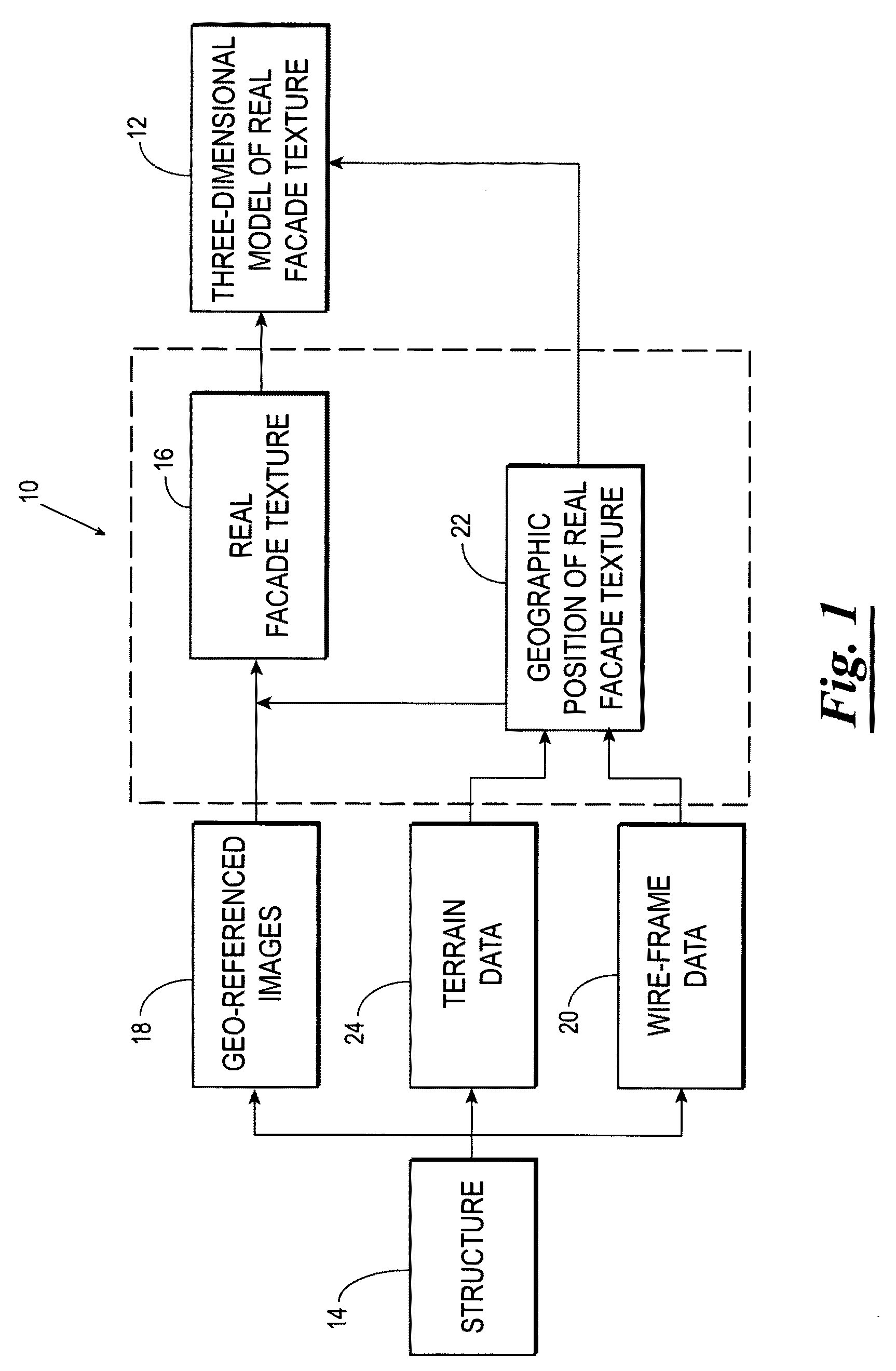
Systems and methods for rapid three-dimensional modeling with real facade texture
Owner:PICTOMETRY INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
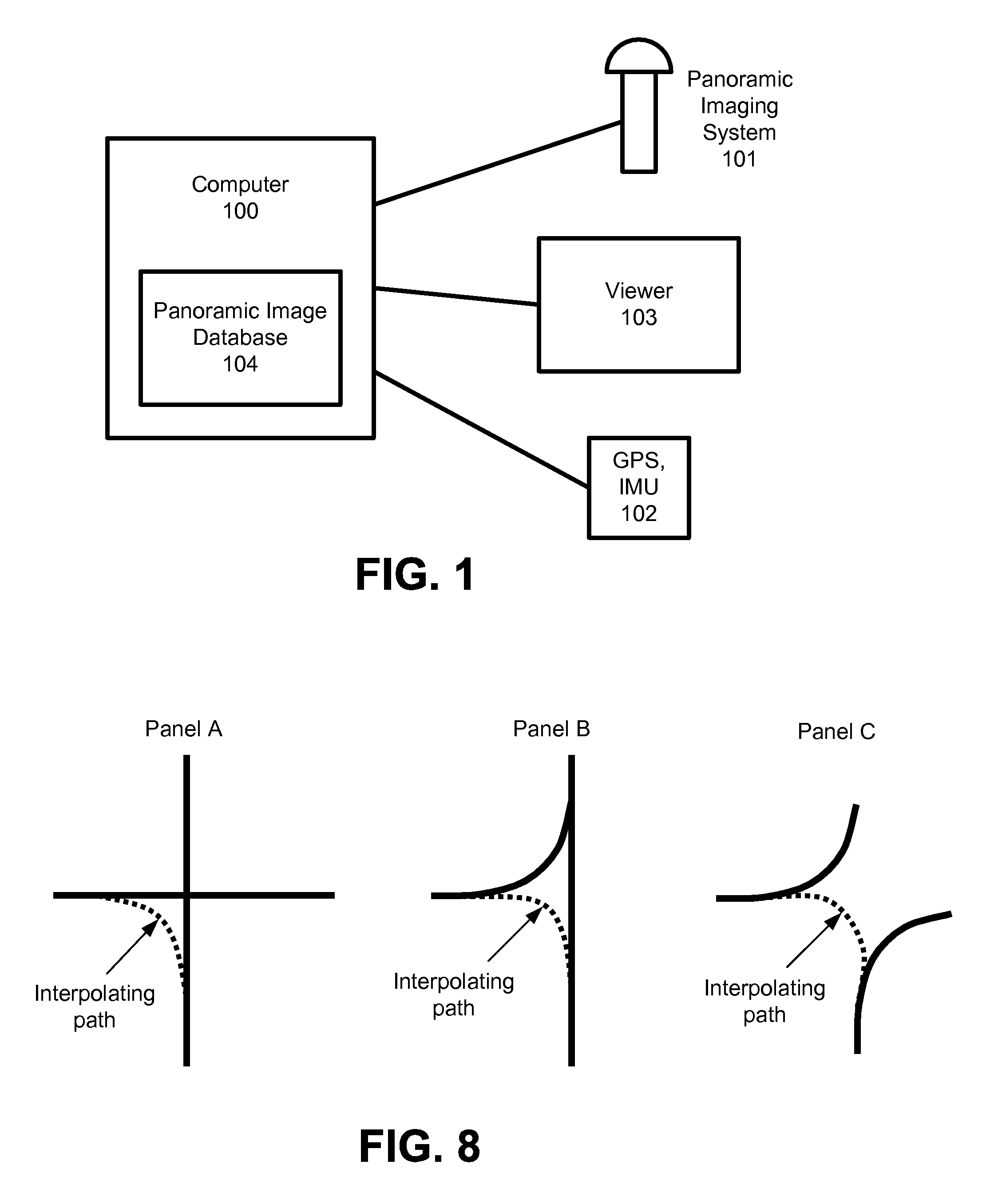
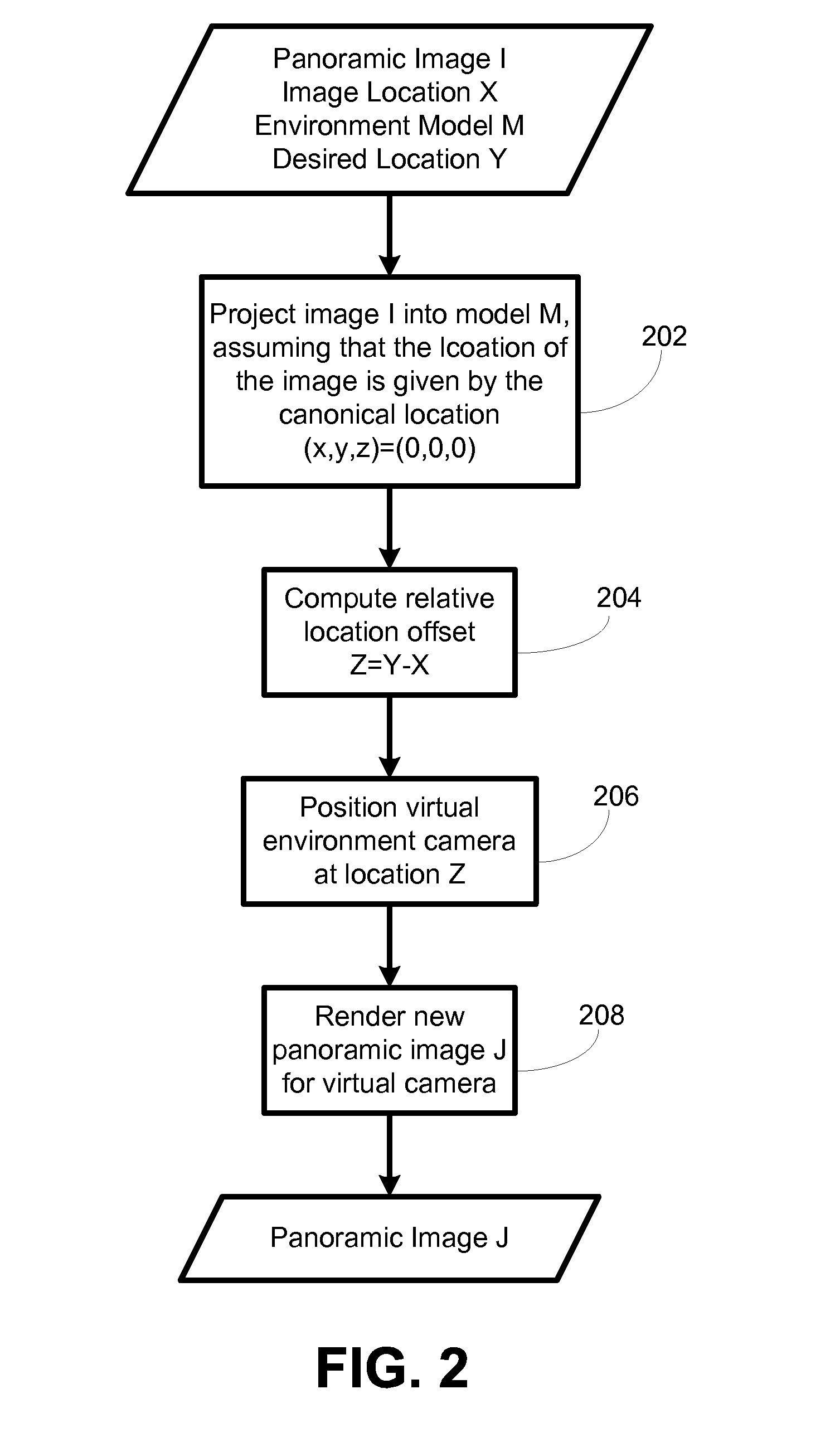
System and process for synthesizing location-referenced panoramic images and video
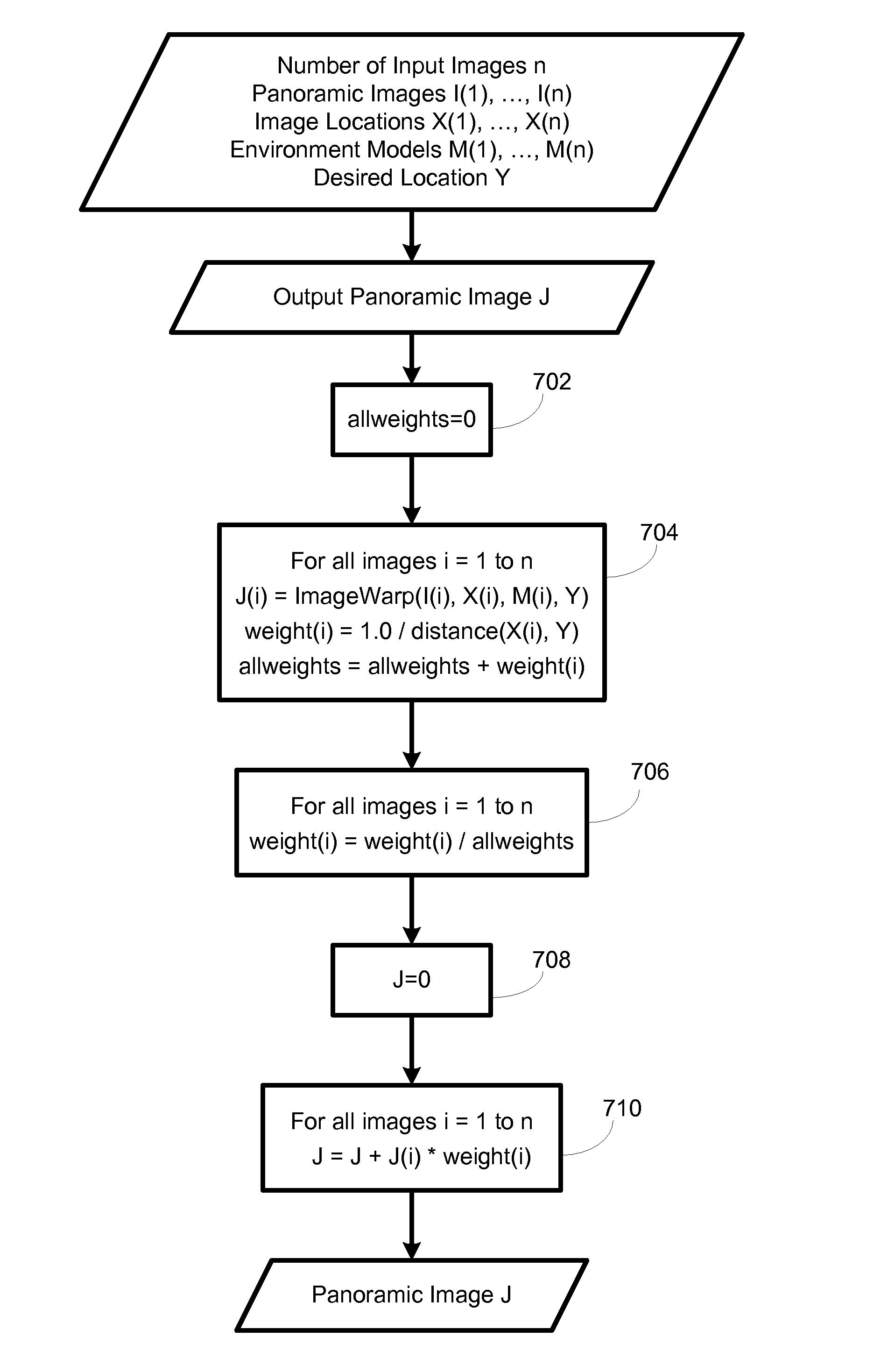
ActiveUS20080106593A1Bridging the gapImprove viewing experienceGeometric image transformationTelevision systemsViewpointsPanorama
A system and process of morphing location-referenced panoramic images into views at nearby locations. When using panoramic images in an interactive tour, a user might desire to see the environment from viewpoints for which no panoramic images are available. This invention makes this possible. It enables a user to experience views from arbitrary locations in the environment, so as long as one or more panoramic images are available at nearby locations. In particular, this invention makes it possible to combine two non-overlapping geo-referenced panoramic video streams into a new video stream which seamlessly transitions between these streams. When used in a client-server architecture, this invention also makes it possible for the server to transmit a sparse sequence of panoramic images, and provide the user with a dense panoramic video stream, by synthesizing the missing panoramic images. Said system and process is also applicable to incomplete panoramic images, photographs, and video.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
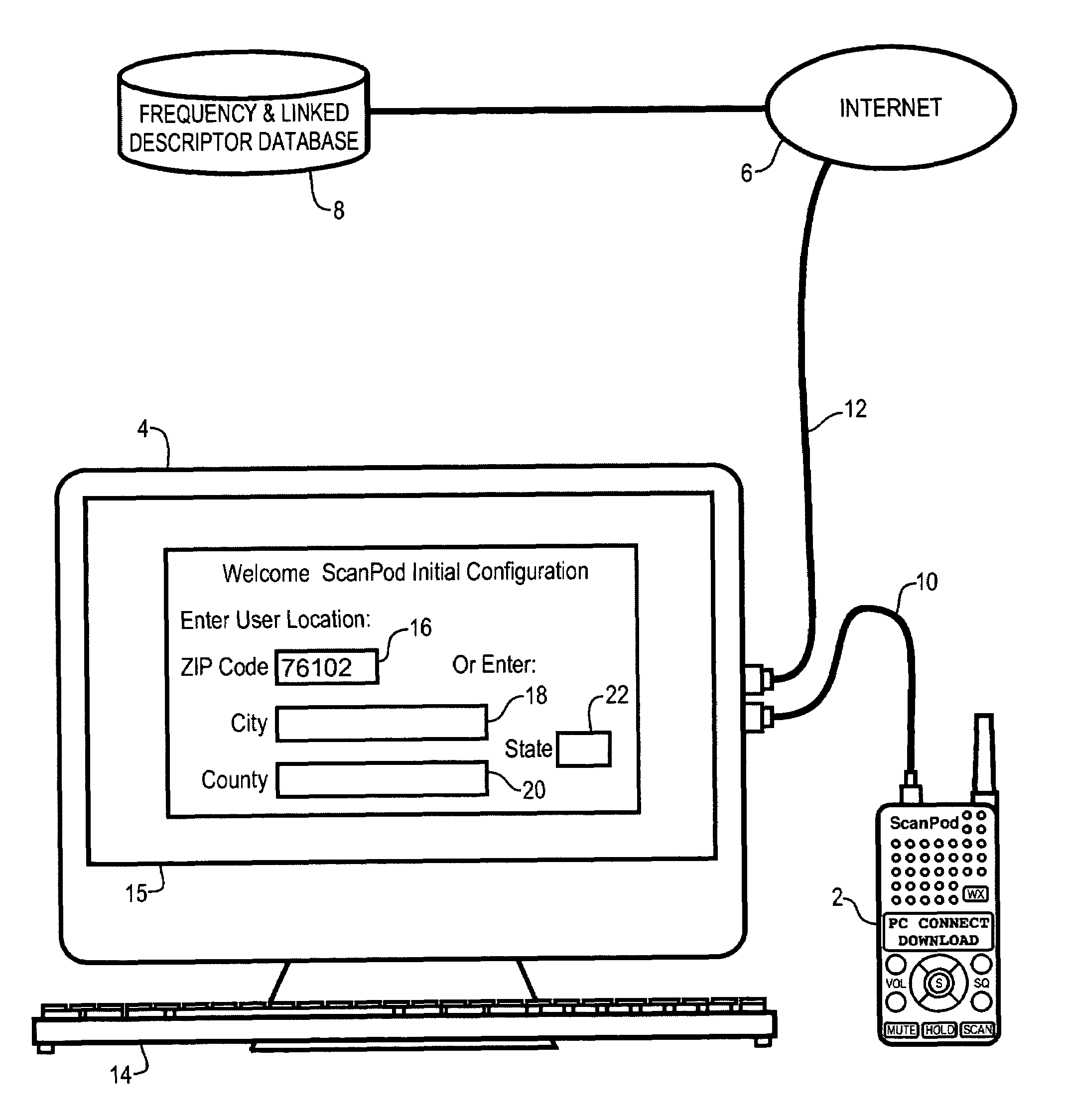
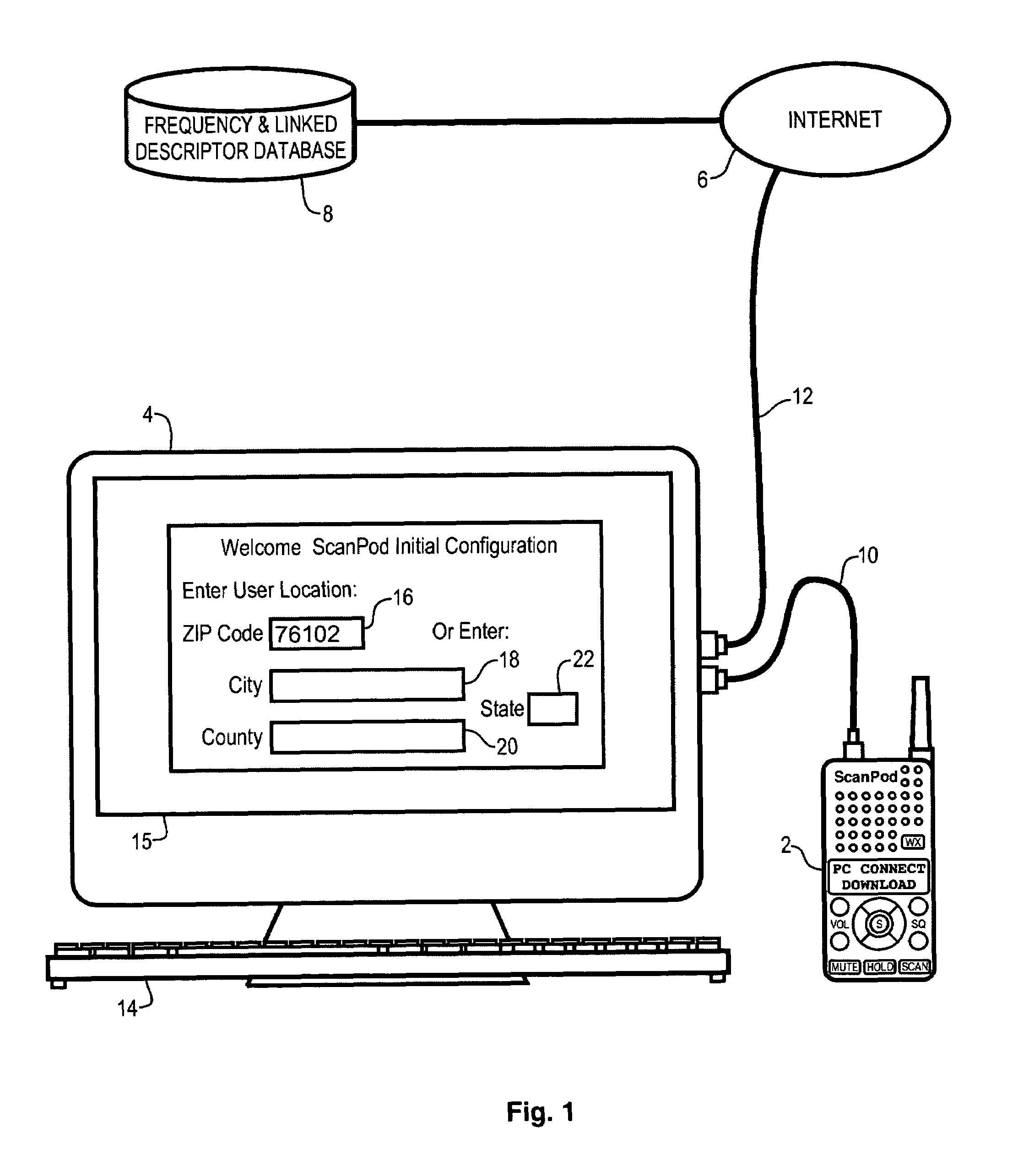
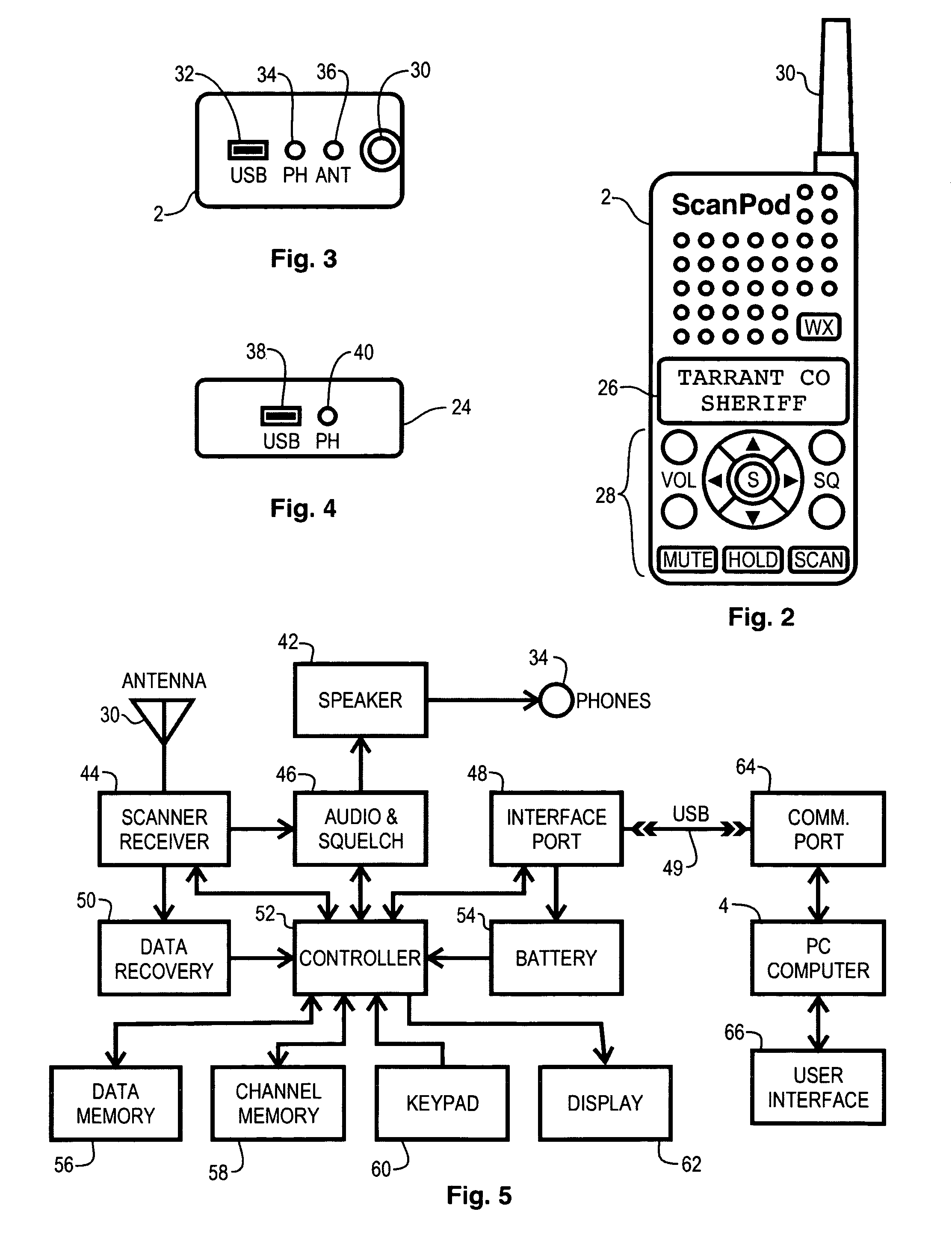
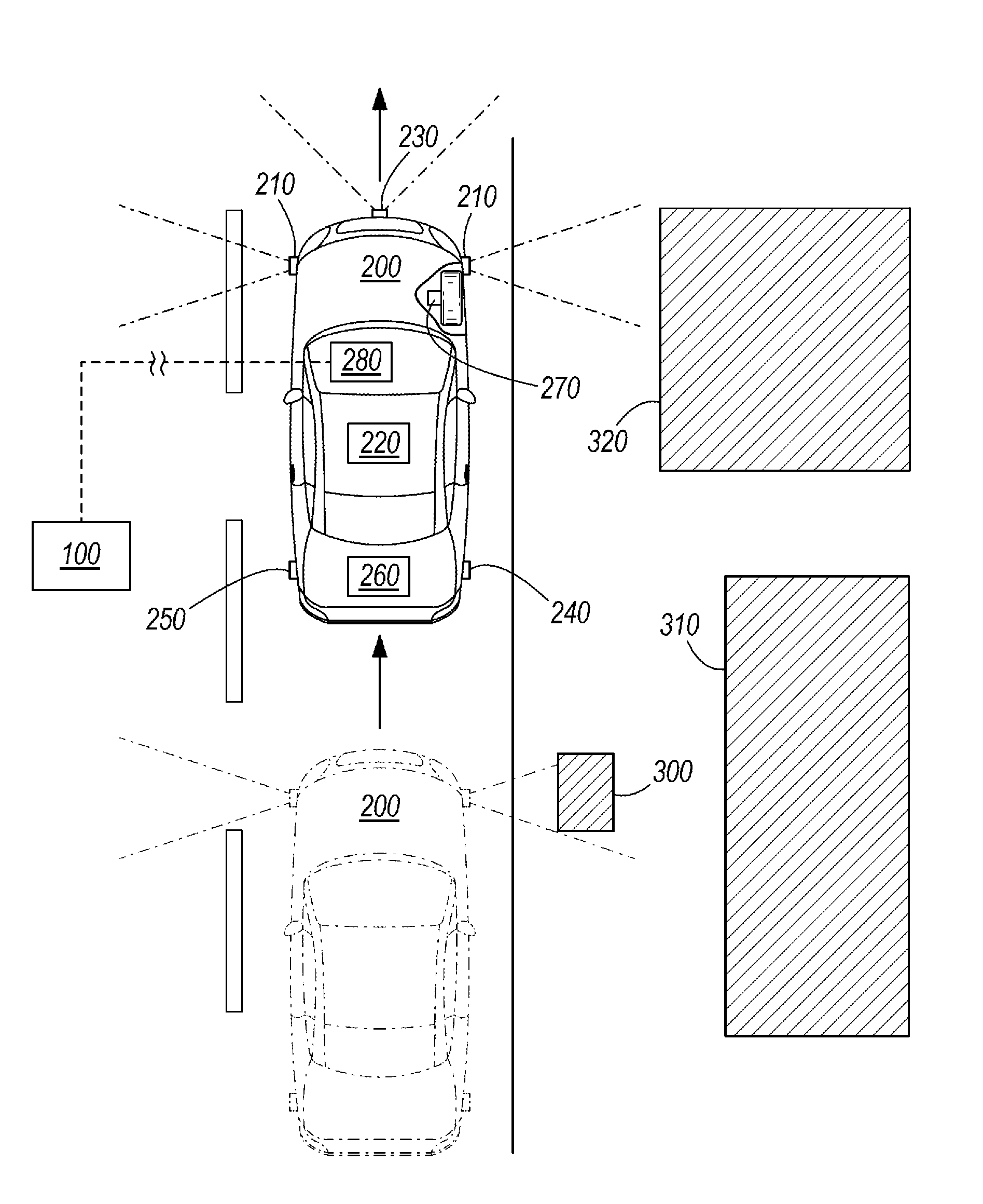
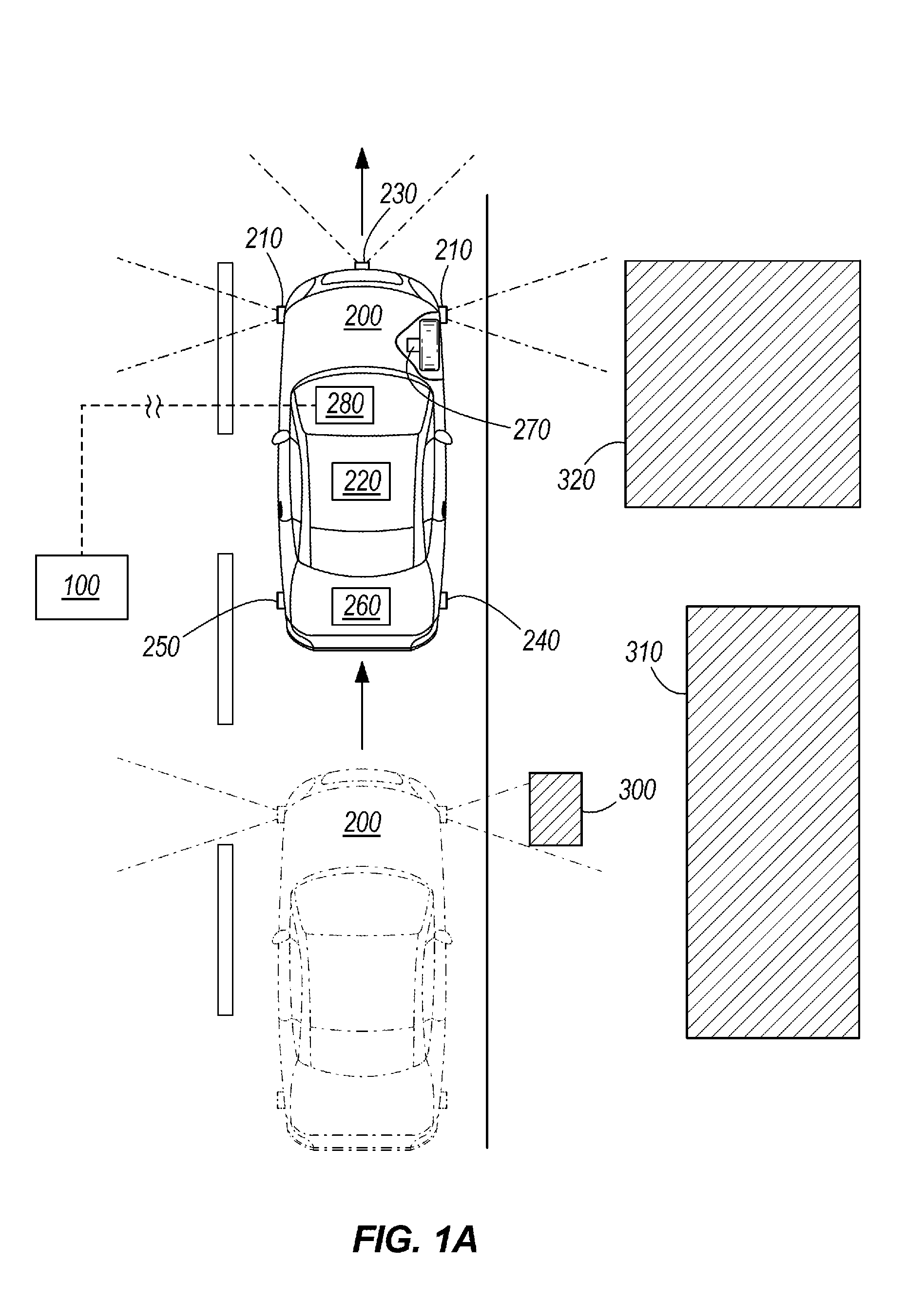
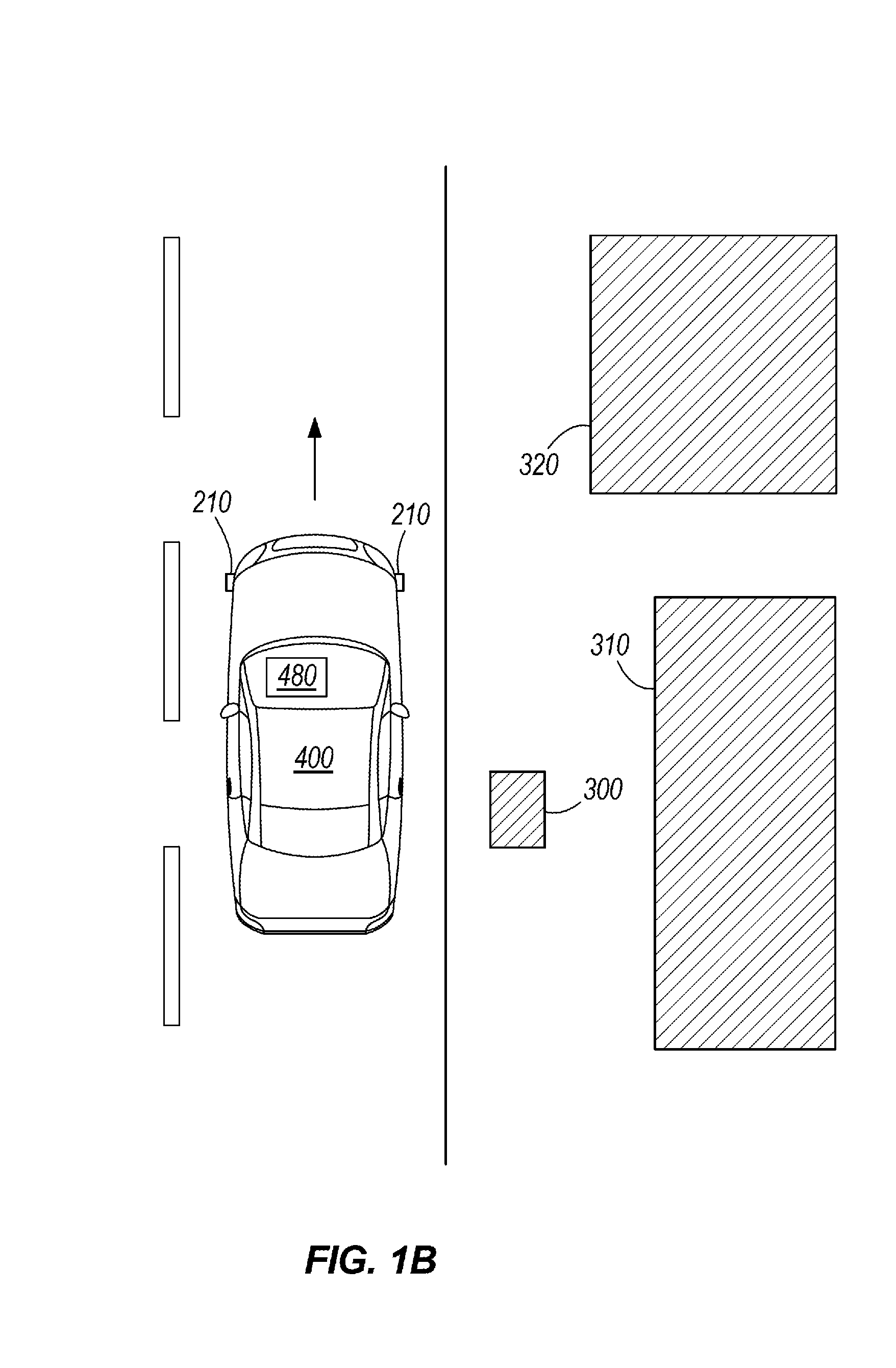
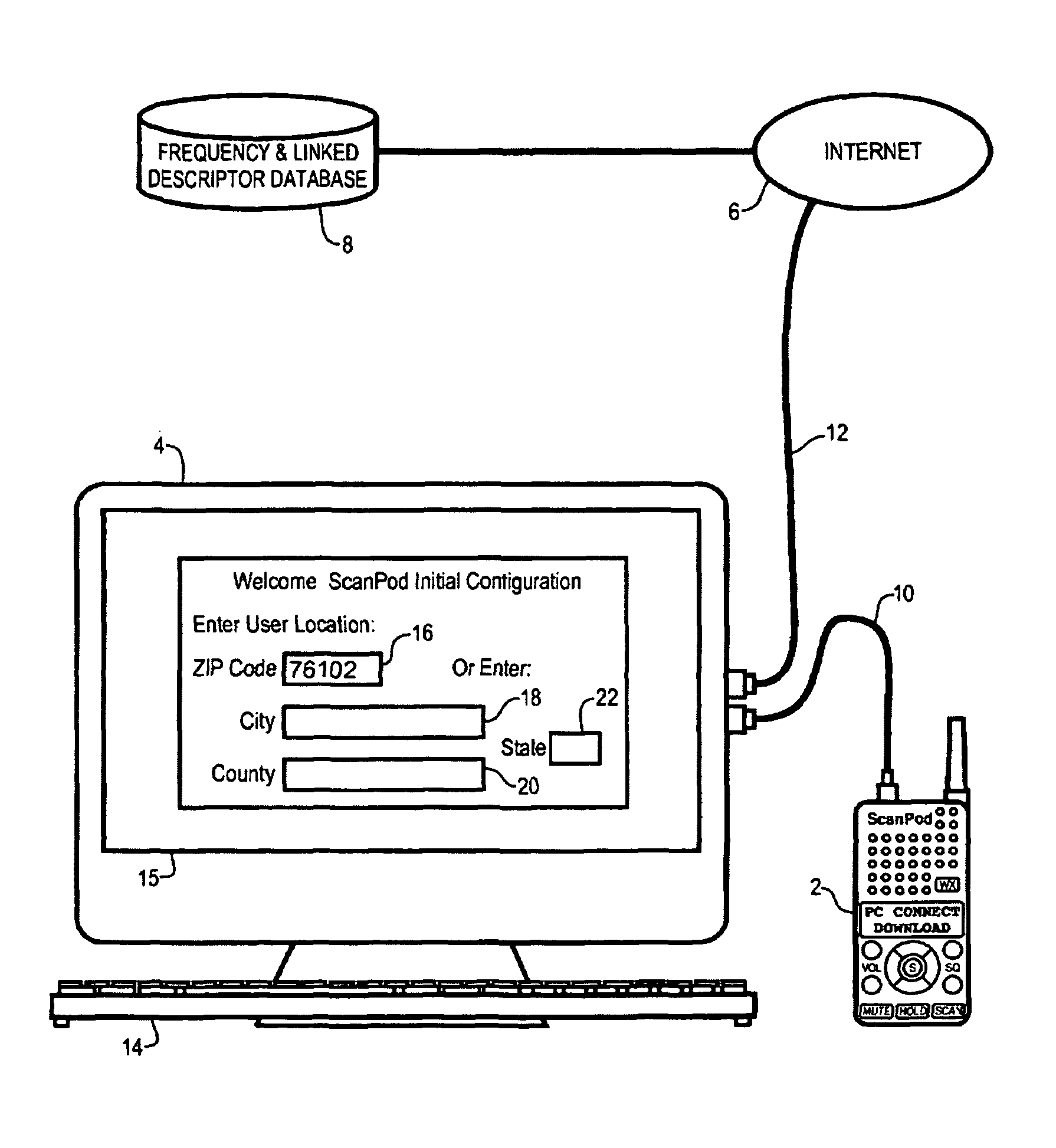
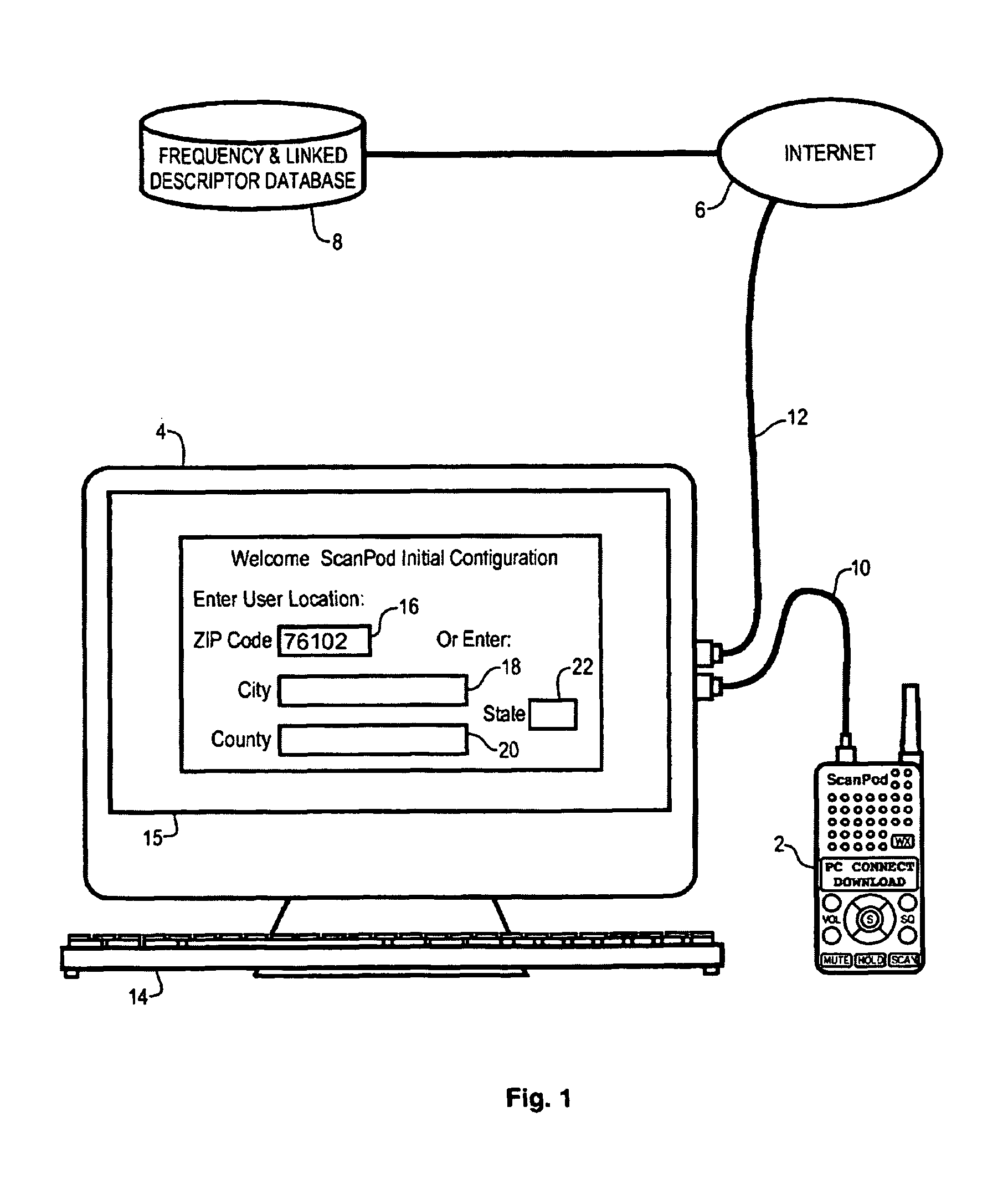
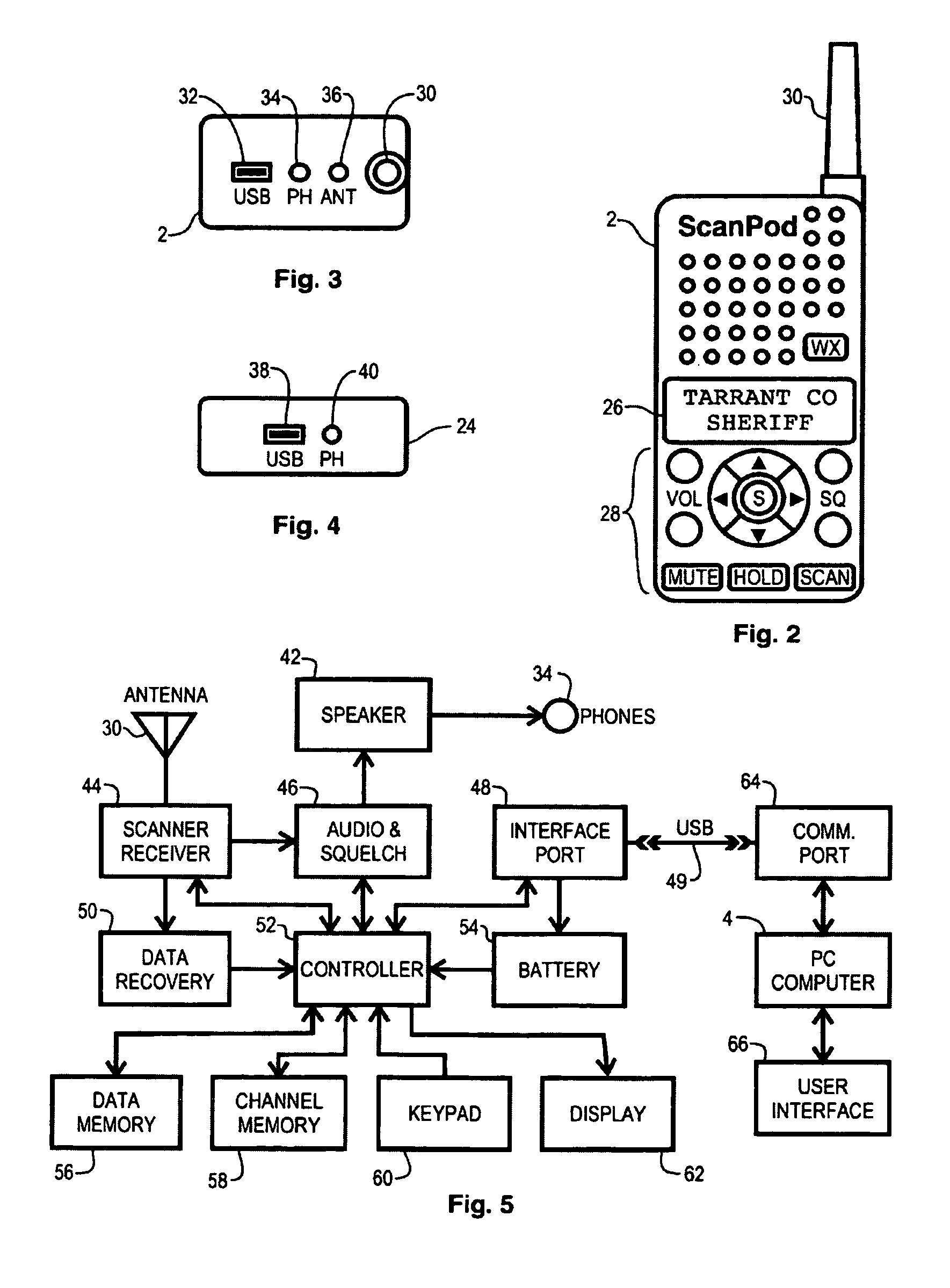
Radio scanner programmed from frequency database and method
A scanning radio and method using a receiver, a channel memory and a display in conjunction with a frequency and linked descriptor database. The frequency and linked descriptor database is queried using a geographic reference to produce a list of local radio channels that includes a list of frequencies with linked descriptors. The list of radio channels is transferred into the channel memory of the scanner, and the receiver is sequentially tuned to the listed frequencies recalled from the list of radio channels while the corresponding linked descriptors are simultaneously displayed.
Owner:GENERAL WIRELESS IP HLDG +1
Text display of geo-referenced information based on relative distance to a user location
A system, method, and computer readable medium are provided for displaying geographically referenced information. In one example, a method includes causing a display of search results from a search of geographically referenced information (e.g., point-of-interest locations, geo-tagged objects, other users, and so on), the display comprising text associated with each of the search results, where the text varies for at least one of the search results based on the distance of the search results from a user location. For example, text associated with relatively close search results displayed more prominently than relatively distant search results. The method may further include generating presentation data according to a display scheme for displaying search results and communicating the presentation data to a user device. The method may vary the text based on at least one of font size, font style, color, shading, three-dimensional height, associated features, animation, combinations thereof, and the like.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Methods and systems for precise vehicle localization using radar maps
ActiveUS20130103298A1High resolutionPrecise positioningSatellite radio beaconingComplex mathematical operationsRadarGeoreference
A method for determining a location of a vehicle. The method includes steps of acquiring a plurality of sensor data from a radar sensor associated with the vehicle; obtaining an approximate location of the vehicle using a GPS unit; comparing the sensor data to a database of geo-referenced sensor data; and based on the comparison, determining a location of the vehicle.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Radio scanner programmed from frequency database and method
InactiveUSRE44142E1Television system detailsBroadcast transmission systemsTelecommunicationsDisplay device
A scanning radio and method using a receiver, a channel memory and a display in conjunction with a frequency and linked descriptor database. The frequency and linked descriptor database is queried using a geographic reference to produce a list of local radio channels that includes a list of frequencies with linked descriptors. The list of radio channels is transferred into the channel memory of the scanner, and the receiver is sequentially tuned to the listed frequencies recalled from the list of radio channels while the corresponding linked descriptors are simultaneously displayed.
Owner:GENERAL WIRELESS OPERATIONS +1
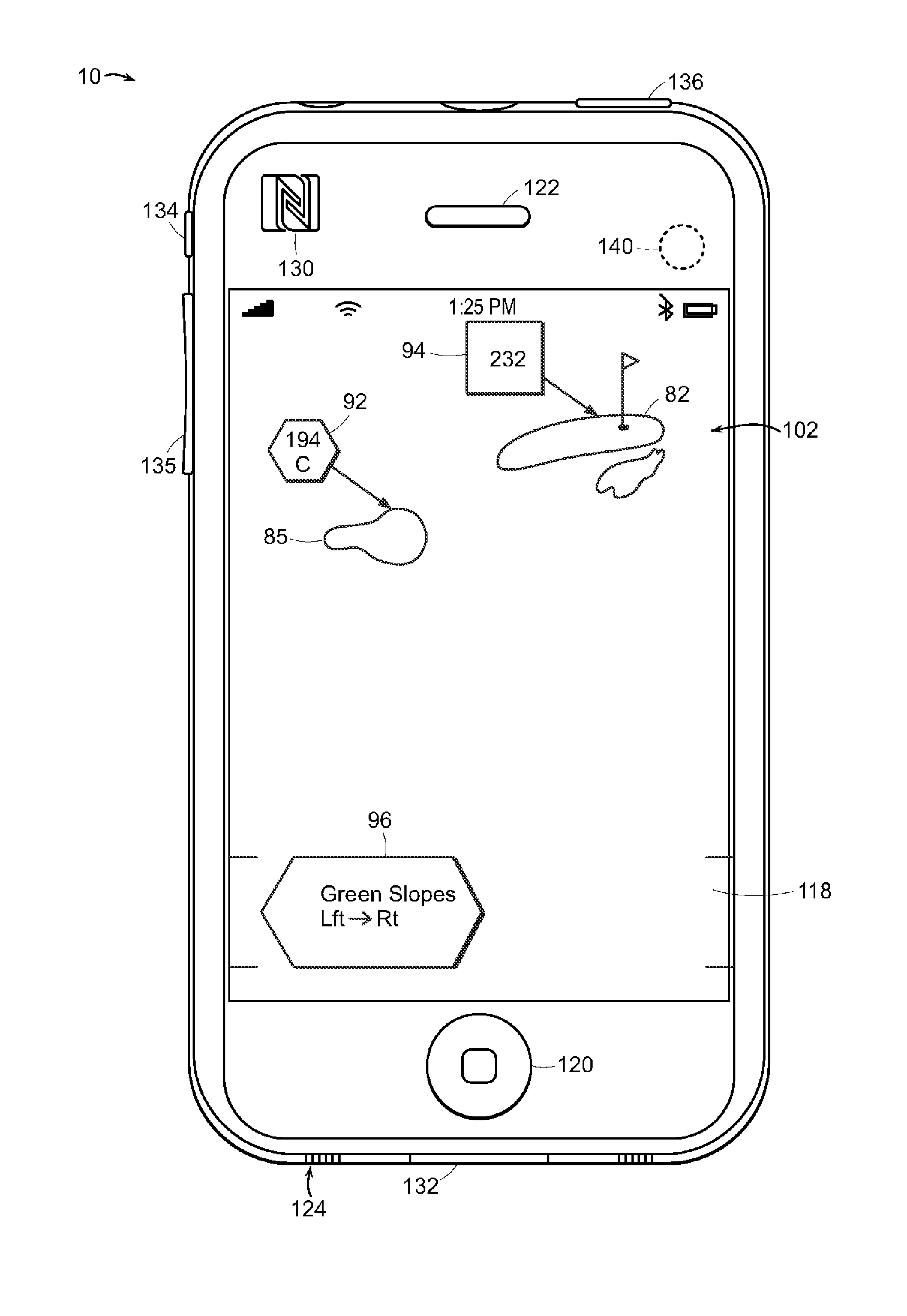
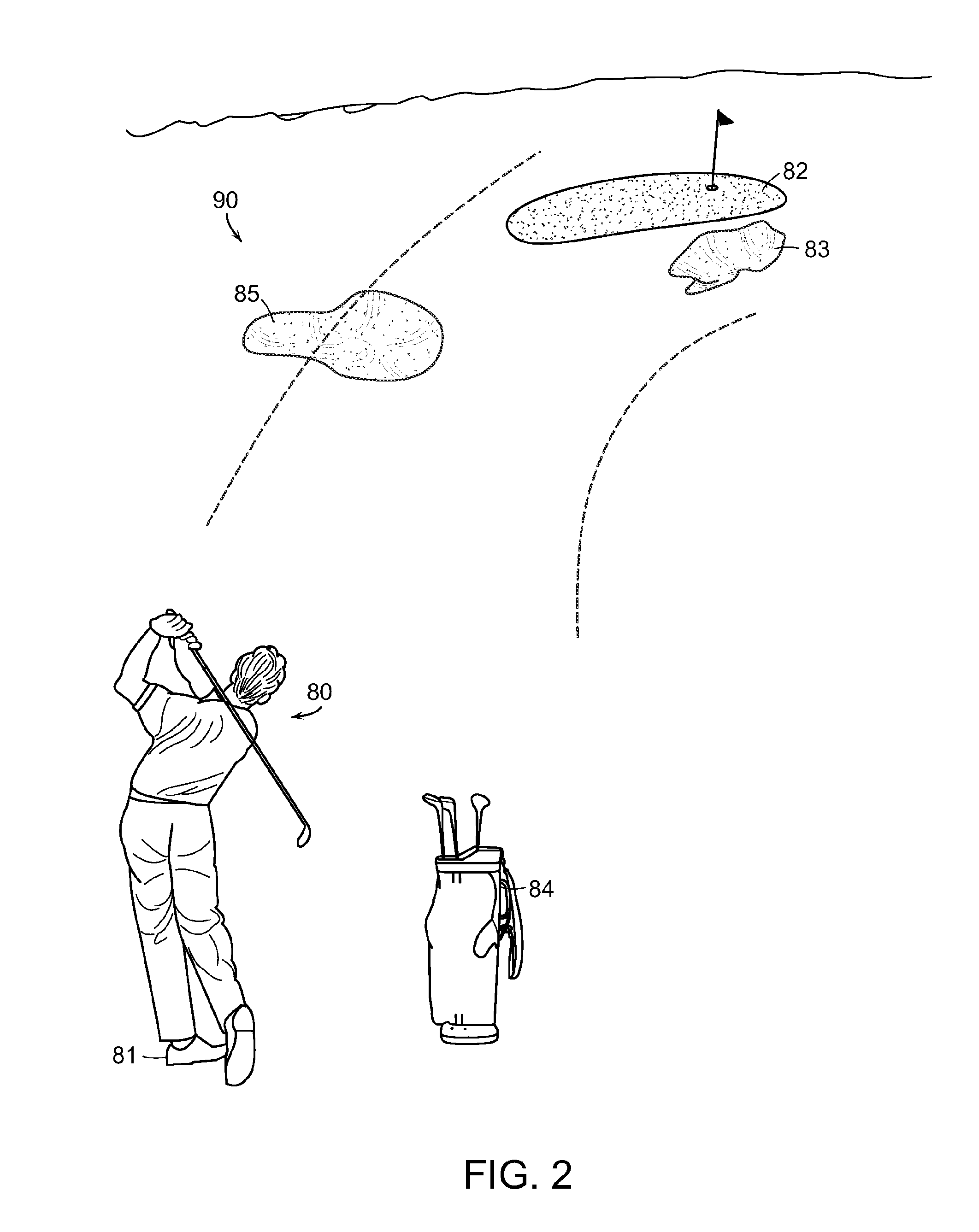
System and Method for Viewing Golf Using Virtual Reality
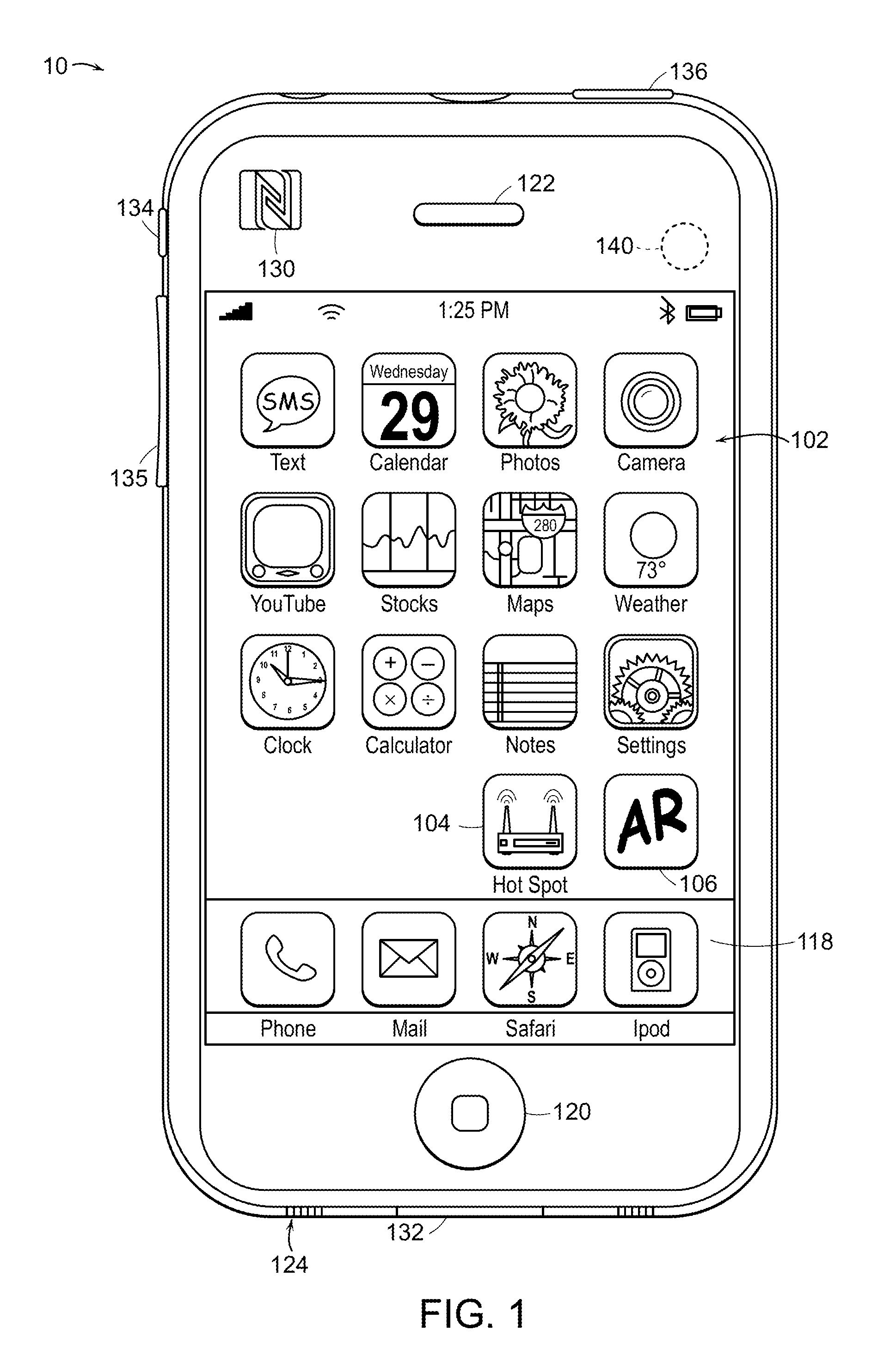
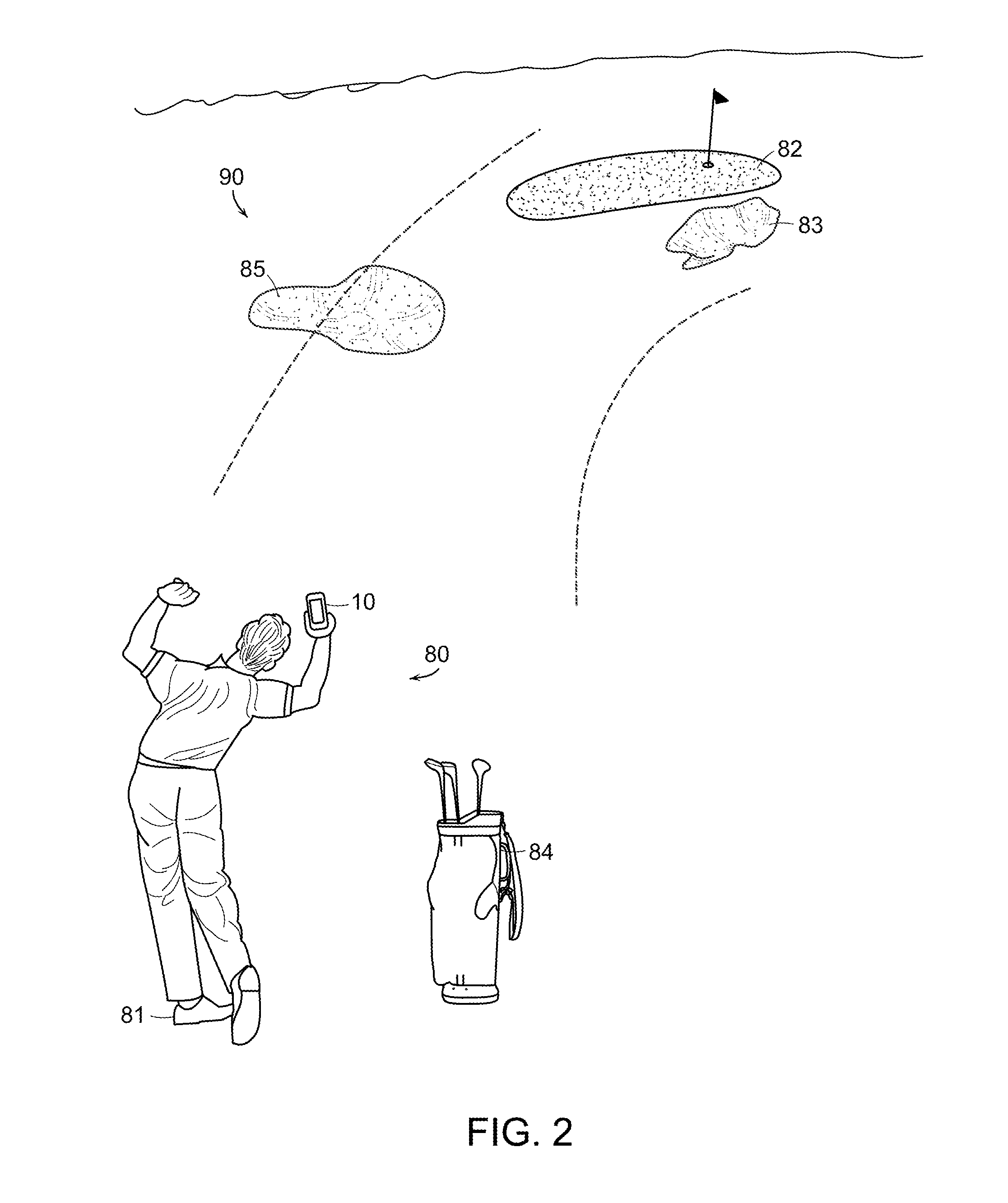
ActiveUS20120007885A1Improve experienceGood awareness of situationCathode-ray tube indicatorsSatellite radio beaconingGolf course turfComputer graphics (images)
A system and method for viewing artificial reality (AR) messages on a golf course, where the messages are geo-referenced artificial reality words or symbols to indicate distances, tips, targets or other information to the golfer. Typically, the AR messages are geo-referenced to a fixed location on the golf hole, such as a hazard or green. Using the spectator's chosen location as the viewing origin, an artificial reality message or object is inserted into the golfer's perspective view of the golf hole. Outings and contests can be held even if the matches are separated by hours or days, and outcomes and information published to select groups or individuals.
Owner:SPATIAL REALITY LLC
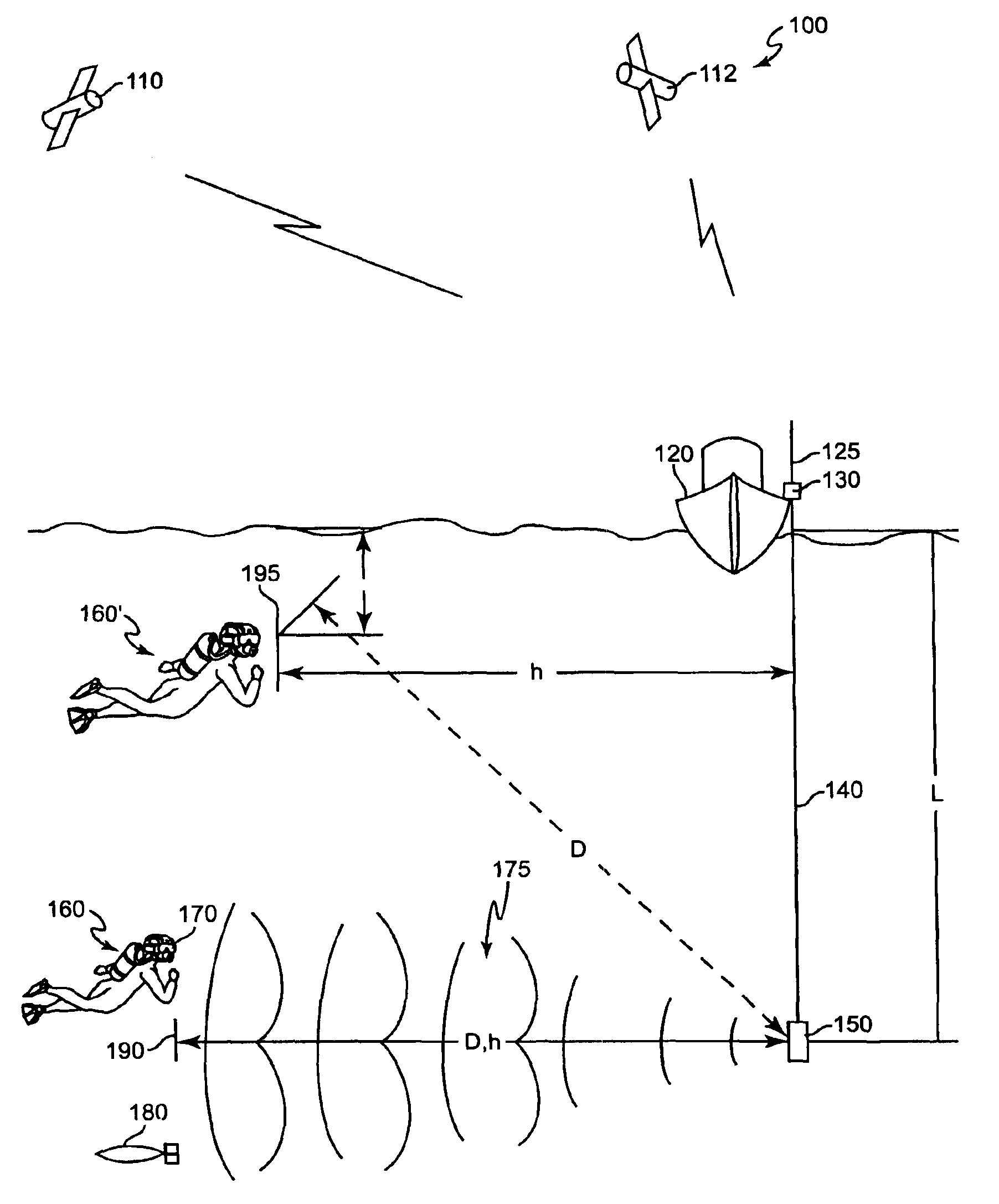
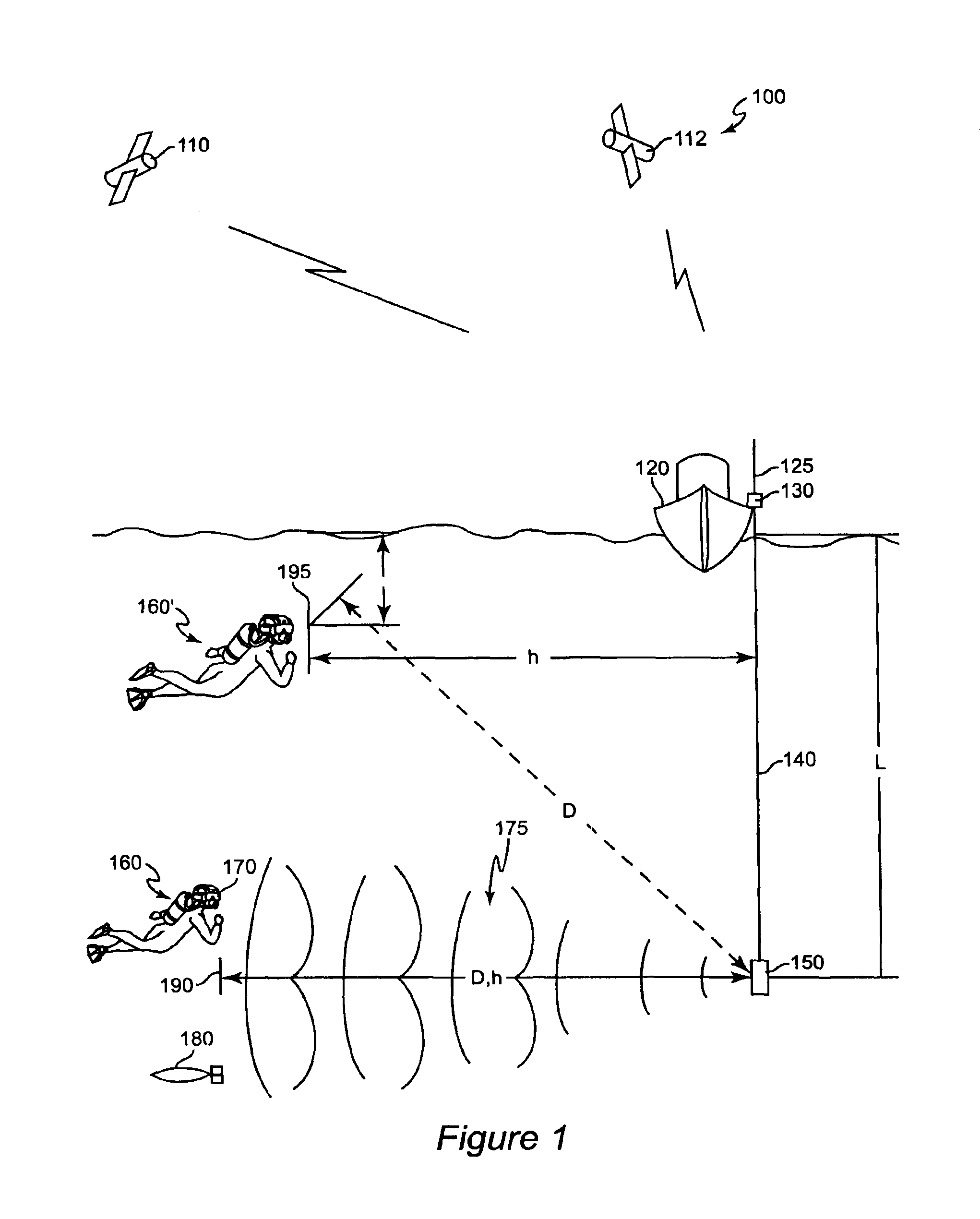
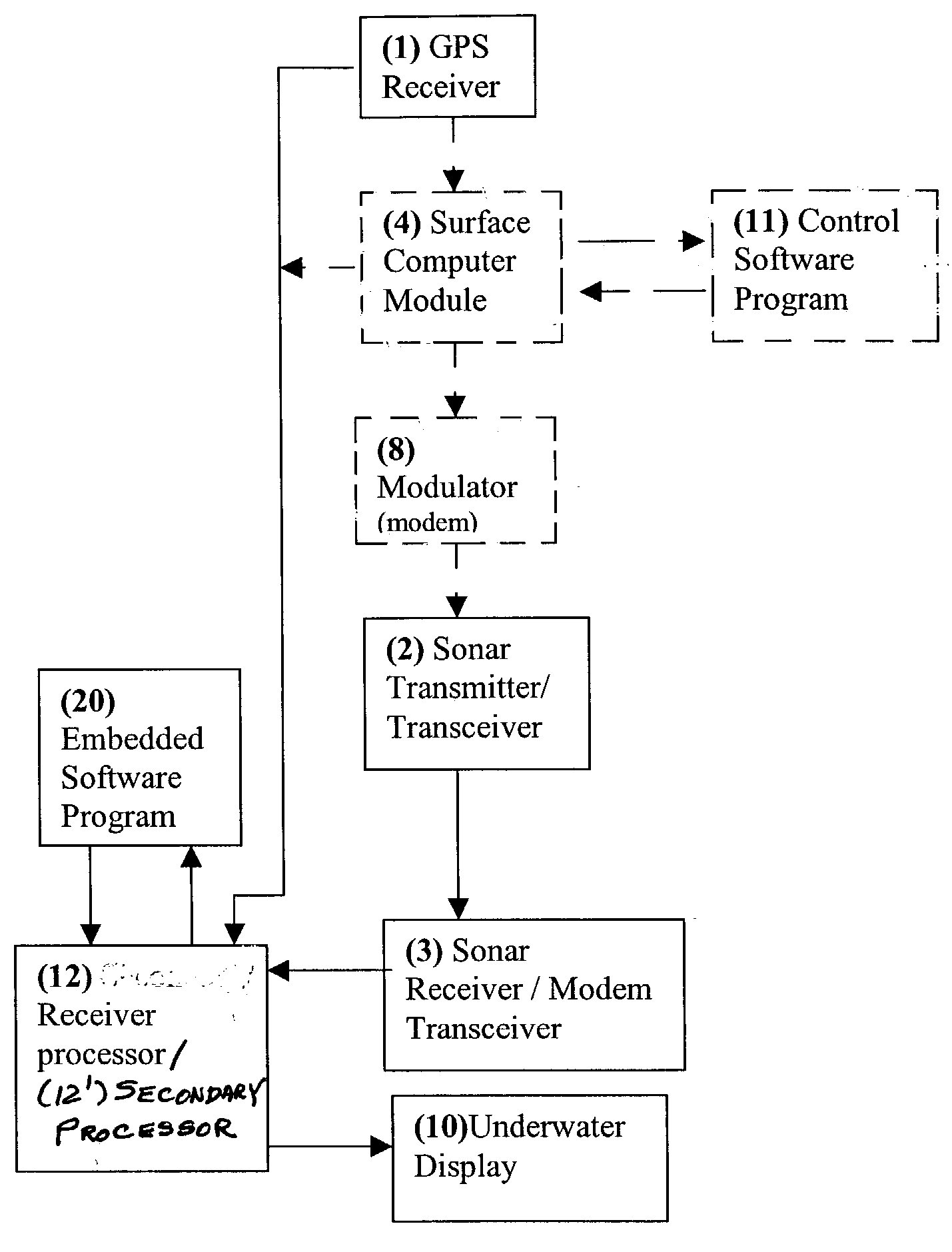
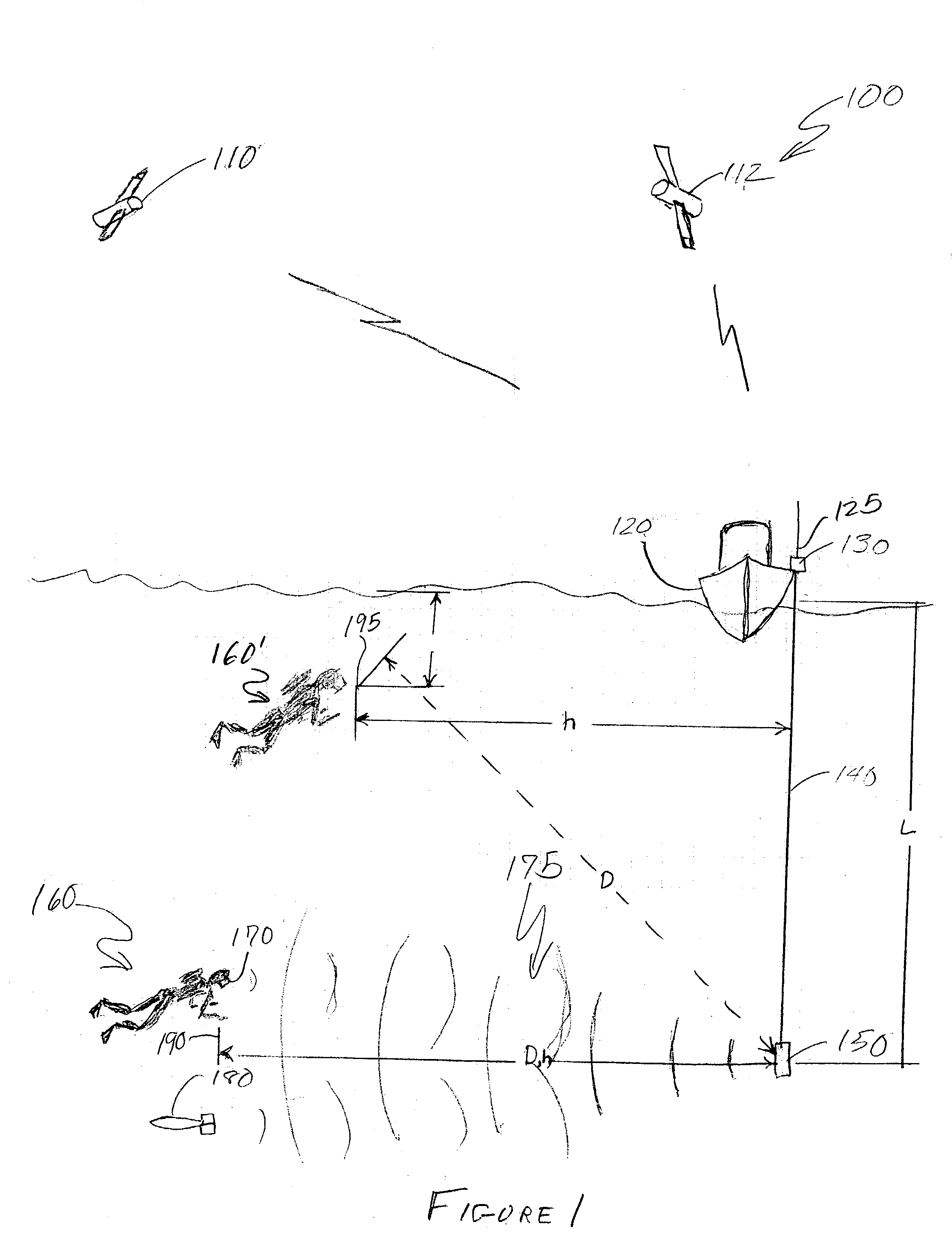
Method for determining, recording and sending GPS location data in an underwater environment
InactiveUS6941226B2Accurately and effectively employingDigital data processing detailsPosition fixationSonarGps receiver
Underwater position determination is provided by combining sonar-derived ranging data between a sonar receiver and a sonar transmitter with GPS position data to provide geographically-referenced position data accurately representing the position of a sonar receiver carried or worn by a diver or submersible vehicle. Function and accuracy enhancements are provided to compensate for diver and sonar transmitter and depth difference and differences of sonar signal propagation speed as well as several techniques of compensation for change of position of the GPS receiver and for logging diver and / or vehicle path.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Method for determining, recording and sending GPS location data in an underwater environment
InactiveUS20040068371A1Accurately and effectively employingSpeed controllerInstruments for road network navigationSonarGps receiver
Underwater position determination is provided by combining sonar-derived ranging data between a sonar receiver and a sonar transmitter with GPS position data to provide geographically-referenced position data accurately representing the position of a sonar receiver carried or worn by a diver or submersible vehicle. Function and accuracy enhancements are provided to compensate for diver and sonar transmitter and depth difference and differences of sonar signal propagation speed as well as several techniques of compensation for change of position of the GPS receiver and for logging diver and / or vehicle path.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
GPS-Based Location and Messaging System and Method
ActiveUS20080259096A1Easy to displayPrecise positioningData processing applicationsCathode-ray tube indicatorsGeolocationGeoreference
A system and method for viewing a target in a background from a user's perspective. In one form, the views are selectable by the user on, for example, a GPS equipped cell phone, to include a view from the participant's position, zoom, pan, and tilt views, or views from another geographic location, giving increased situational awareness and identification of the target. Other information can be conveyed, such as messages or advertisements, on a billboard, which may be a geo-referenced area on or near the target. Preferably, an orientation mechanism shows when the device is correctly pointed to a target.
Owner:SPATIAL REALITY LLC
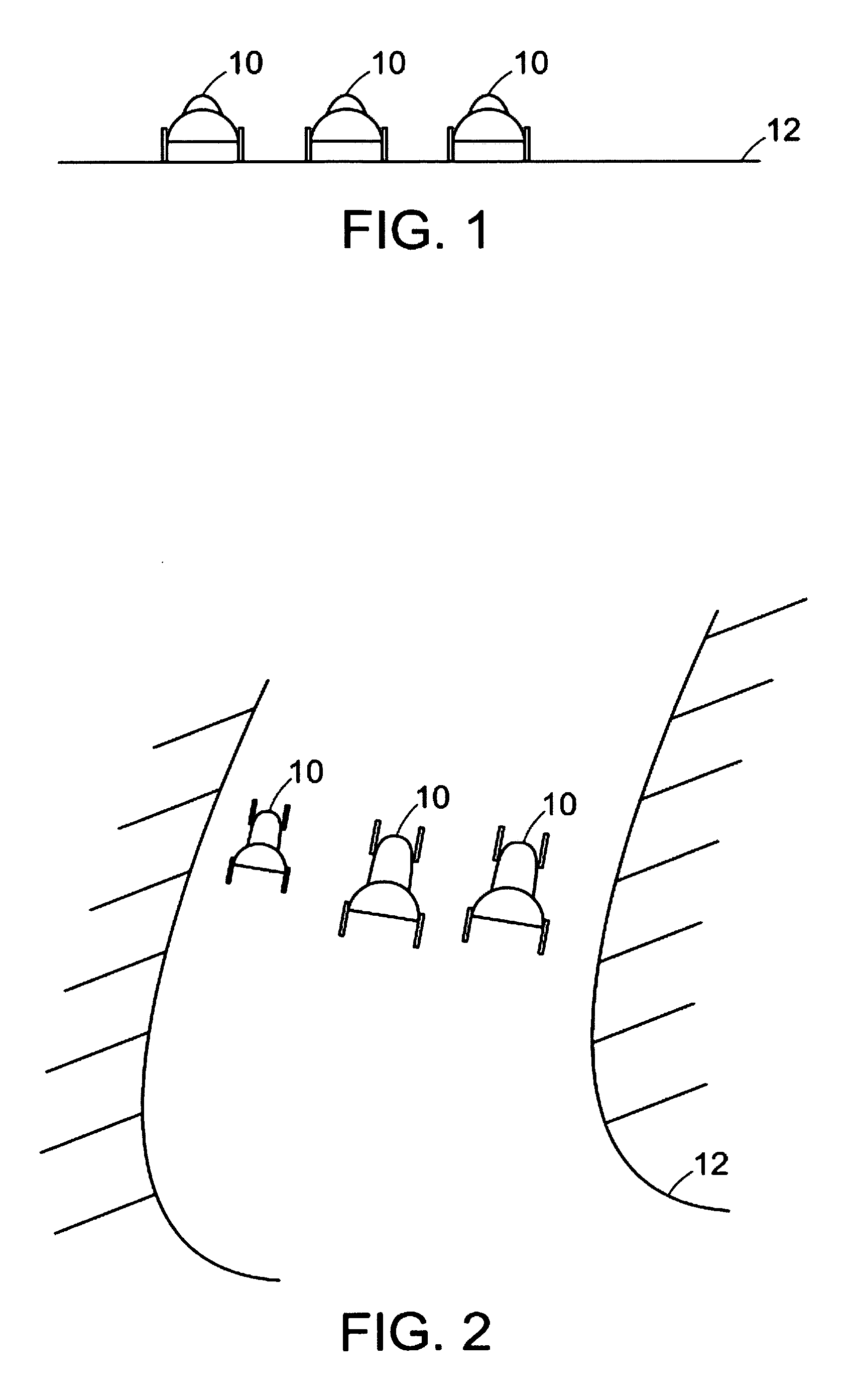
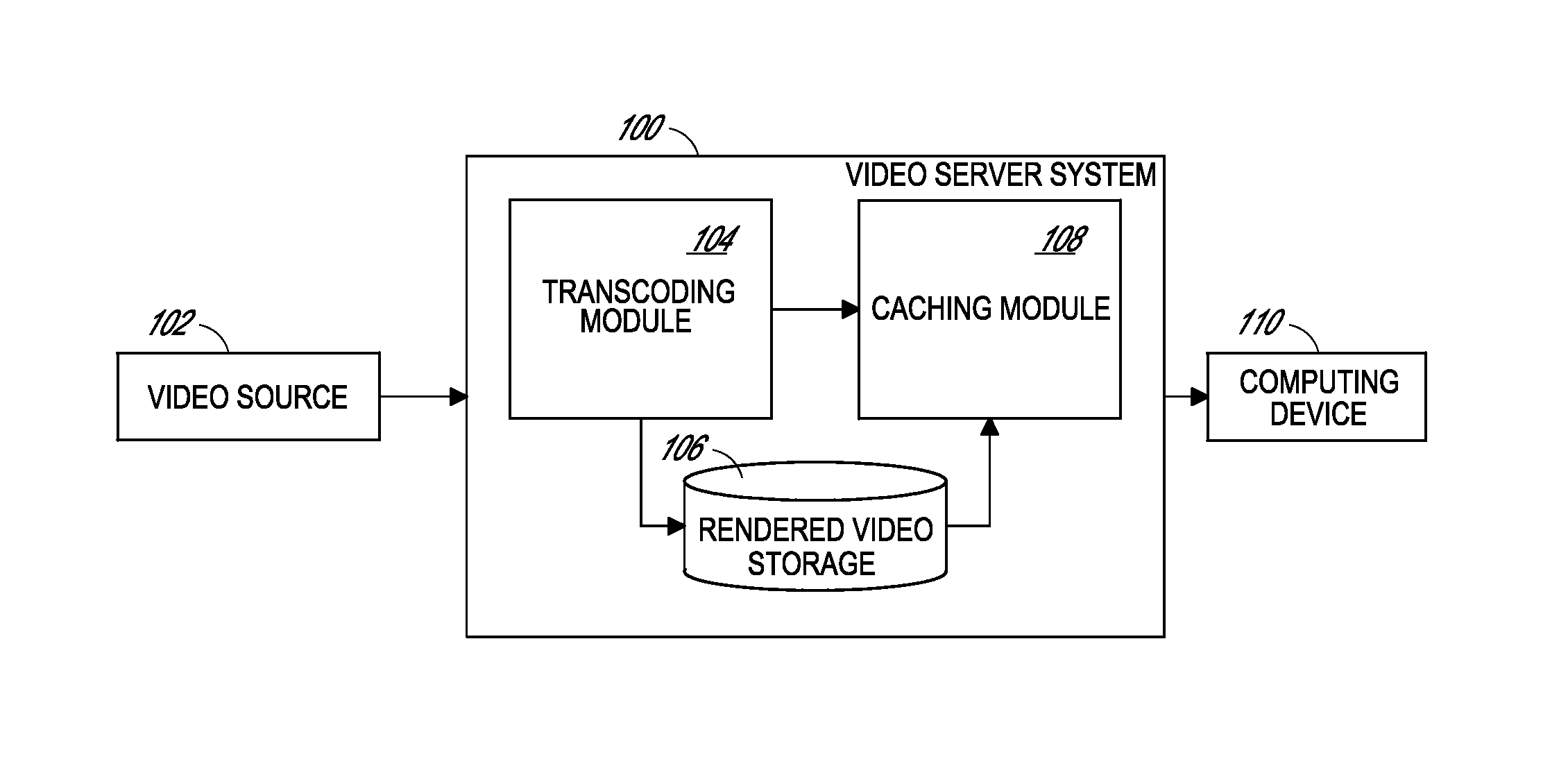
Multi-resolution pyramid for georeferenced video
ActiveUS20140059166A1High spatialHigh temporal resolutionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionImage resolutionComputer graphics (images)
Examples of systems and methods for delivering overhead video to a computing device are provided. Delivering the overhead video can include generating multiple versions of the overhead video having respective resolutions, bitrates, or frame rates. The system can then generate georeferenced video data for each version by incorporating georeferencing coordinates and time synchronization information. The georeferenced video data can be stored in transcoded video files. In response to a request from a computing device for video data of a geographical region, the system can transmit a primary video stream comprising georeferenced video data of a relatively high quality and a secondary video stream comprising georeferenced video data of a relatively low quality, wherein the primary video stream includes the geographical region and the secondary video stream includes a proximal geographical region.
Owner:PLANET LABS PBC
System and method for managing facility content and equipment information
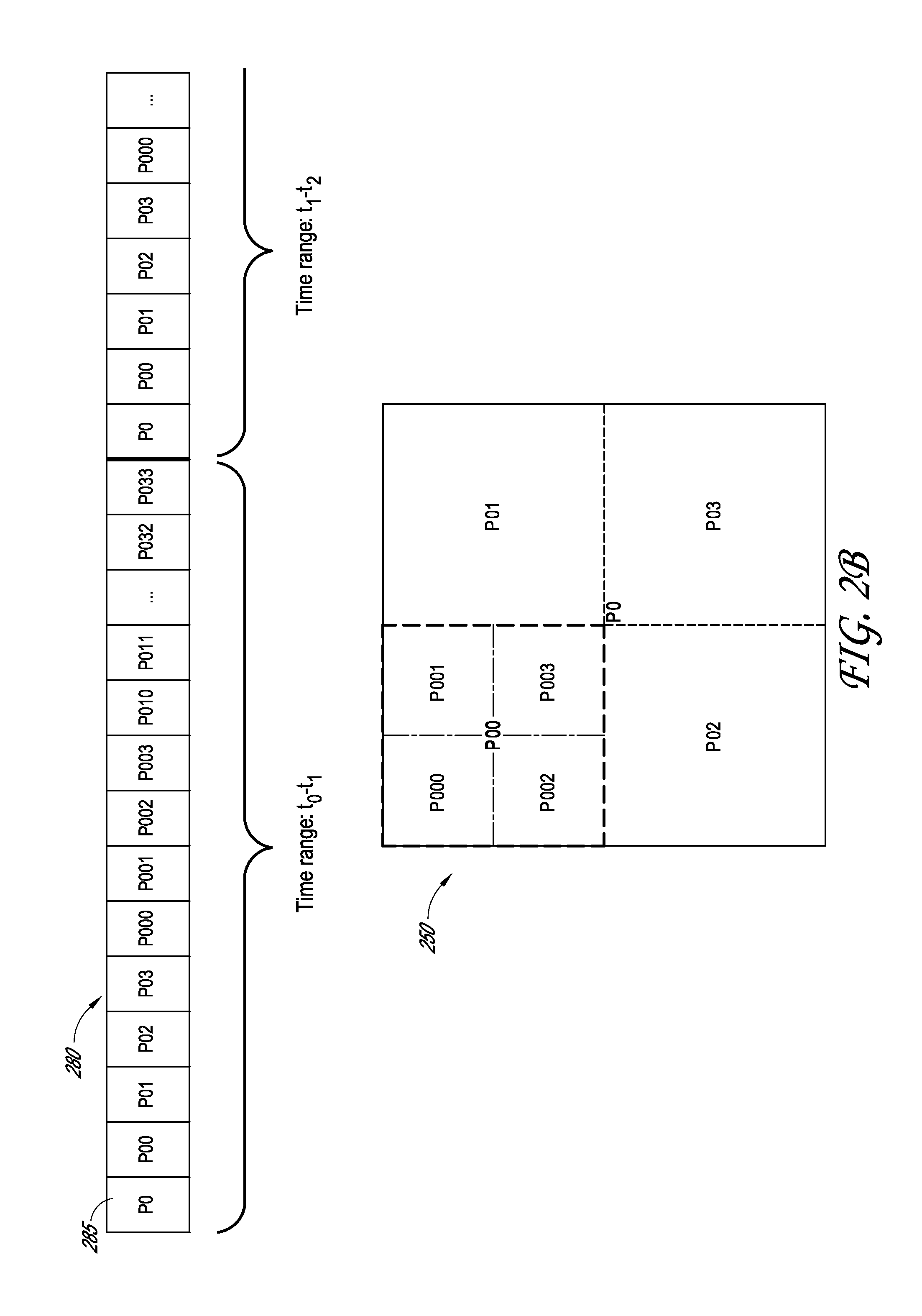
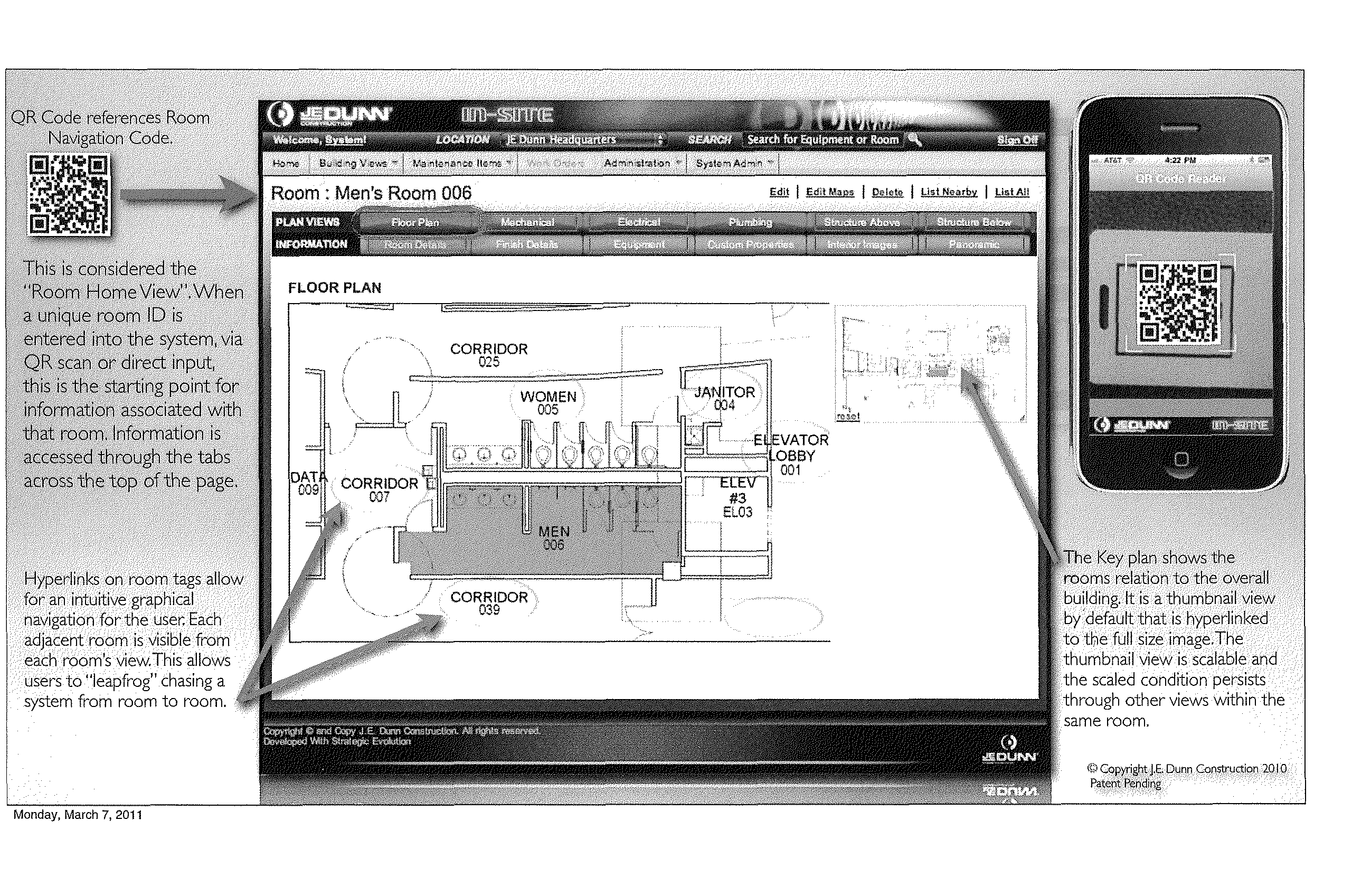
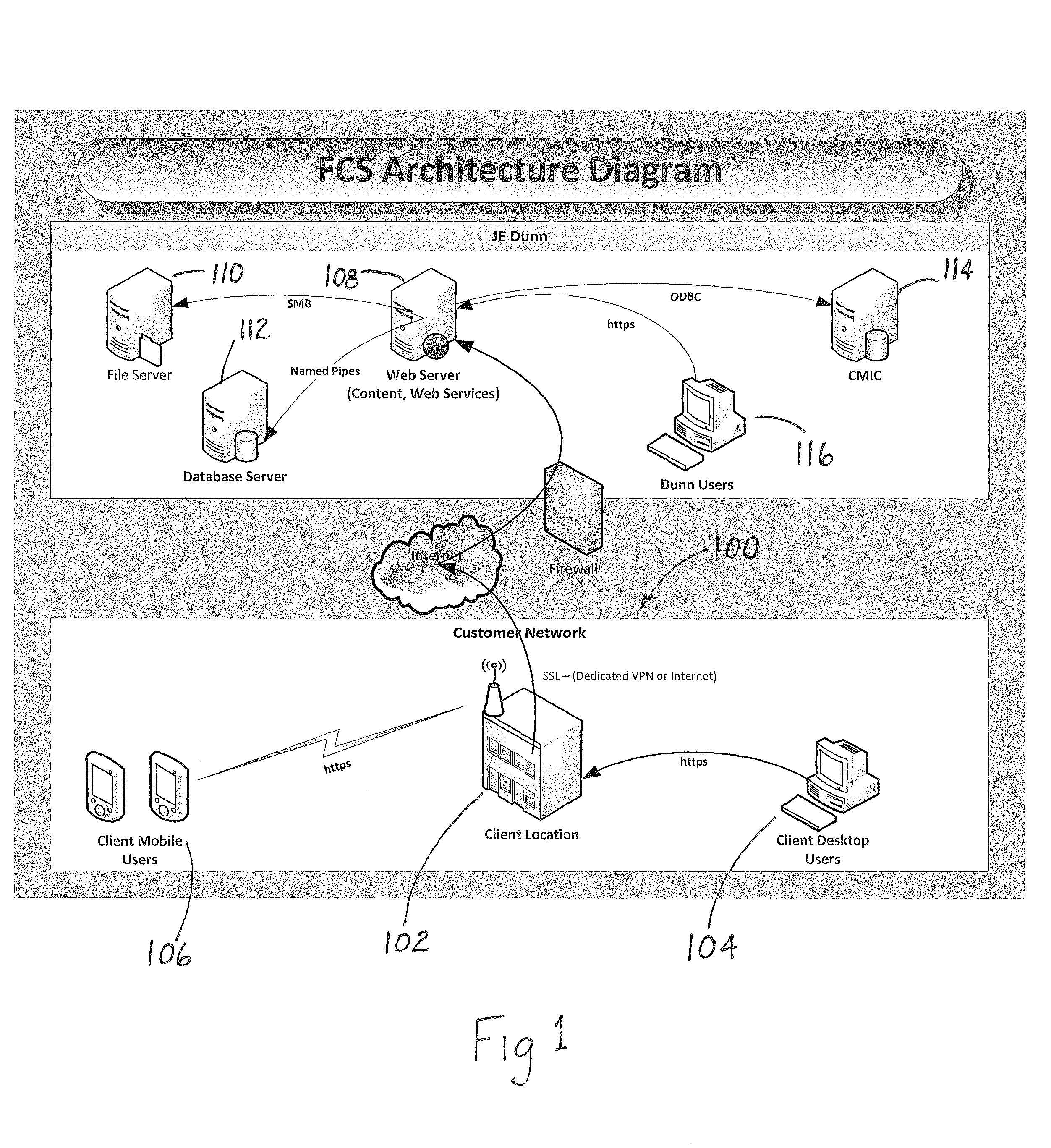
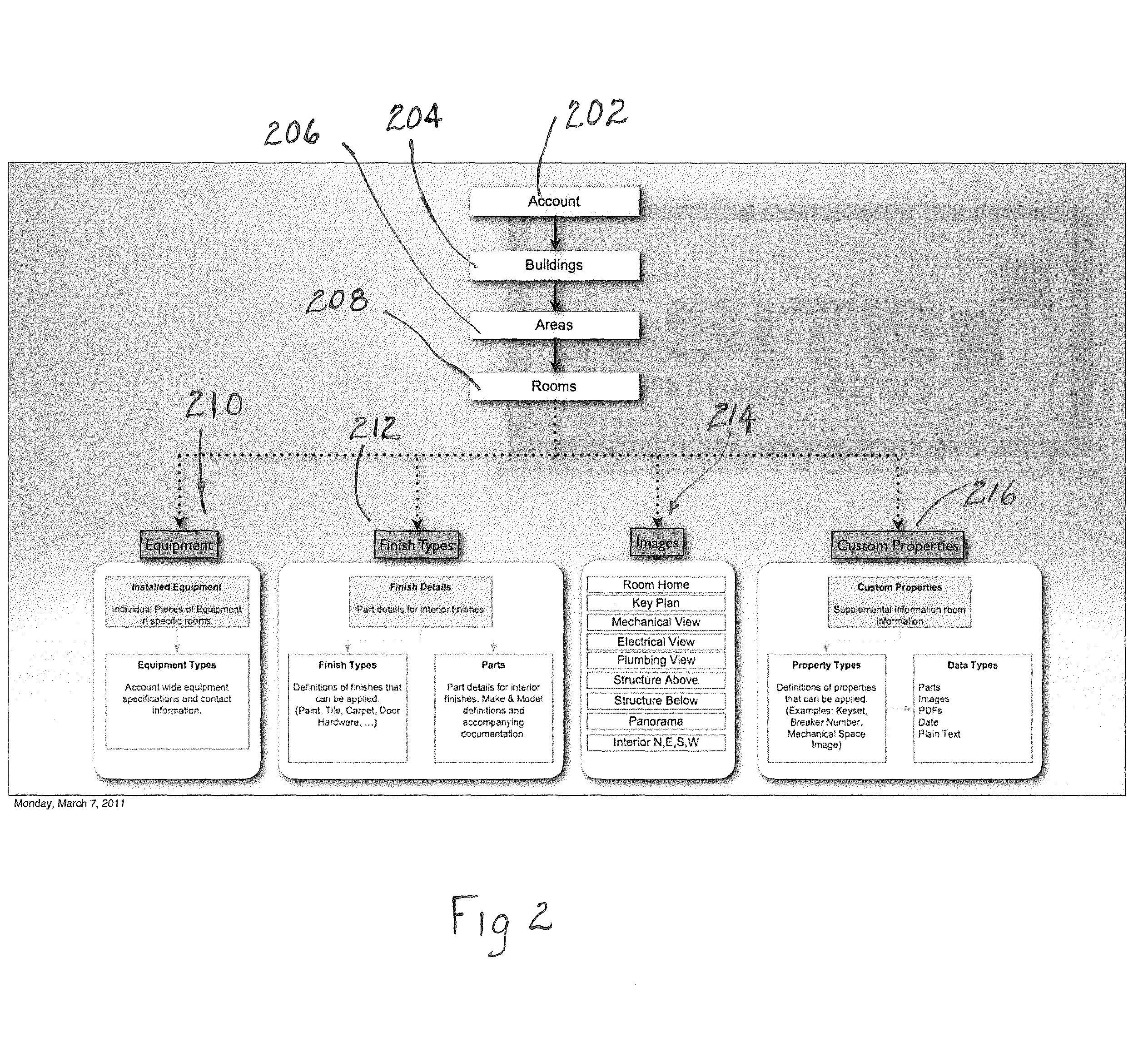
A system and method that provides a unique building maintenance tool which leverages the information collected during the design and construction phase of the building lifecycle. User access BIMs, Revit schedules and other data sources within the unique construction process to provide clients with a post occupancy view previously unobtainable. The solution provides for simple integration with external data sources through data file import or direct integration. The intent of the data integration model is to reduce costs of ongoing implementations providing a scalable model. Mobile access to information is a central component of customer appeal and will be a focal point of the design process. With the present invention mobile users can use mobile devices to scan 2 dimensional barcodes or QR Codes or other georeferencing technologies including RFIDs, thereby using the mobile device as the primary navigation portal to room and equipment information and images. The present invention provides building management functionality by leveraging extracted building data of a database constructed from construction process data as a basis for data organization, which includes detailed equipment specifications.
Owner:SITE 10 01 INC
Method and System for Visualization Enhancement for Situational Awareness
InactiveUS20150121222A1Instruments for road network navigationRecording carrier detailsComputer graphics (images)Engineering
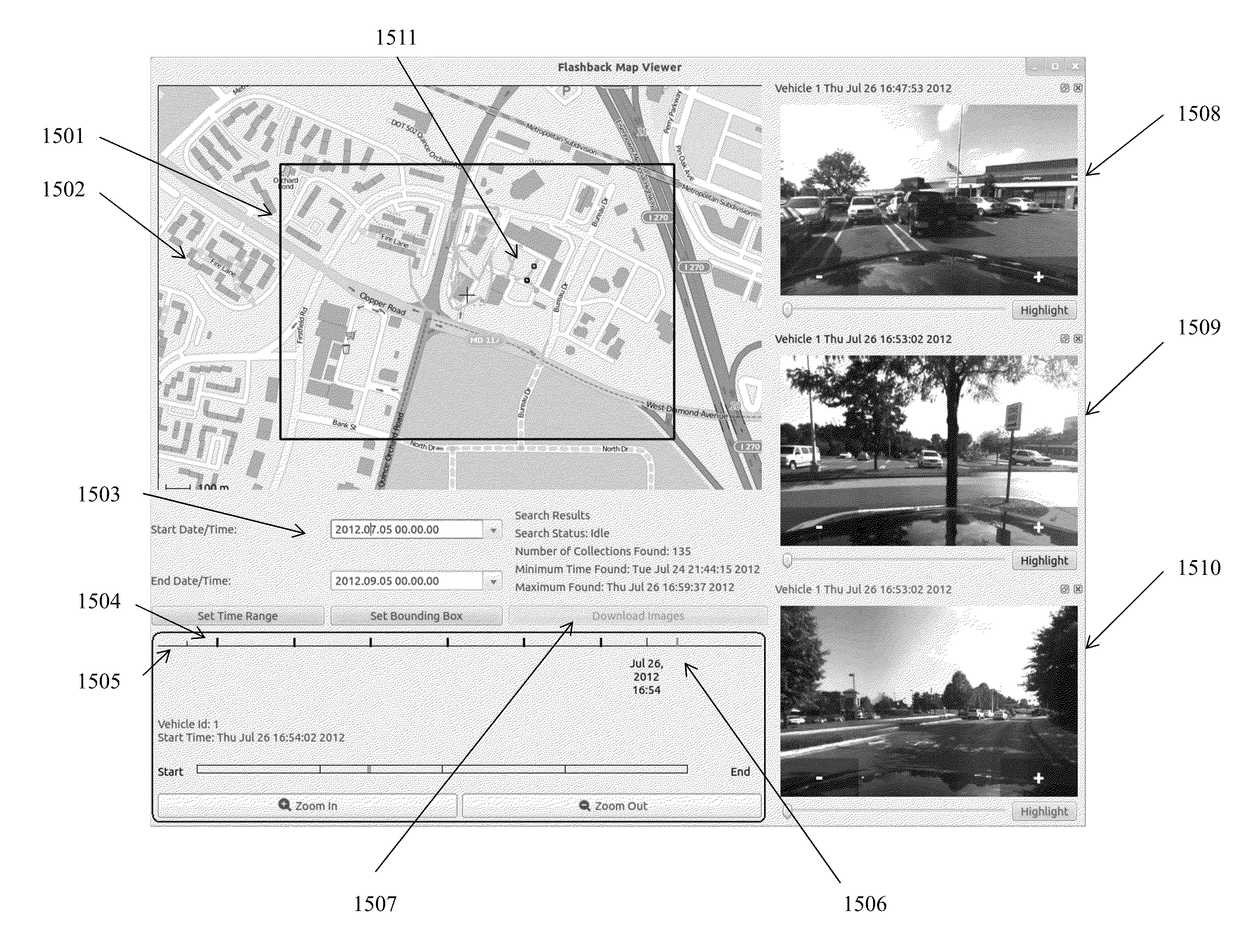
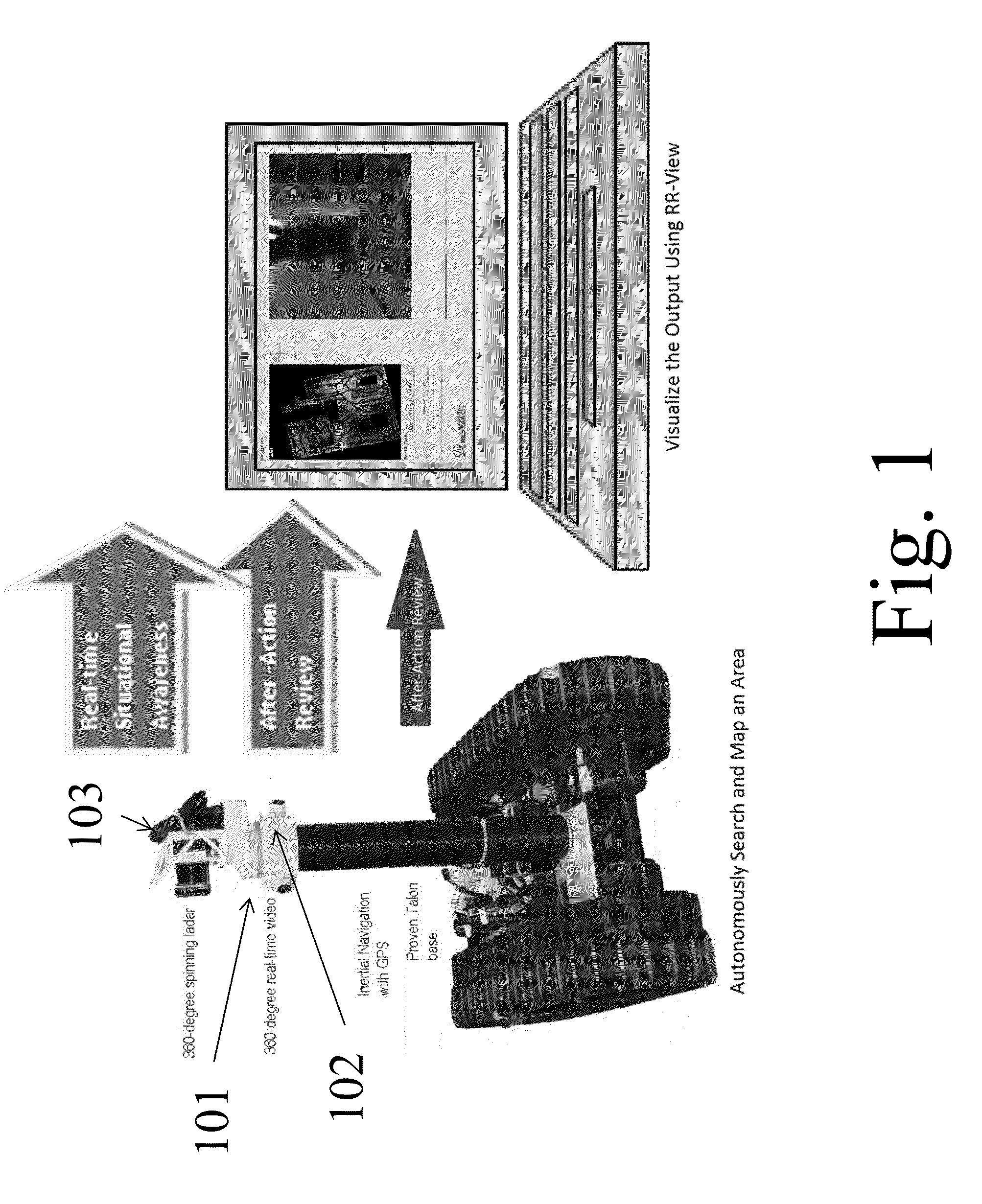
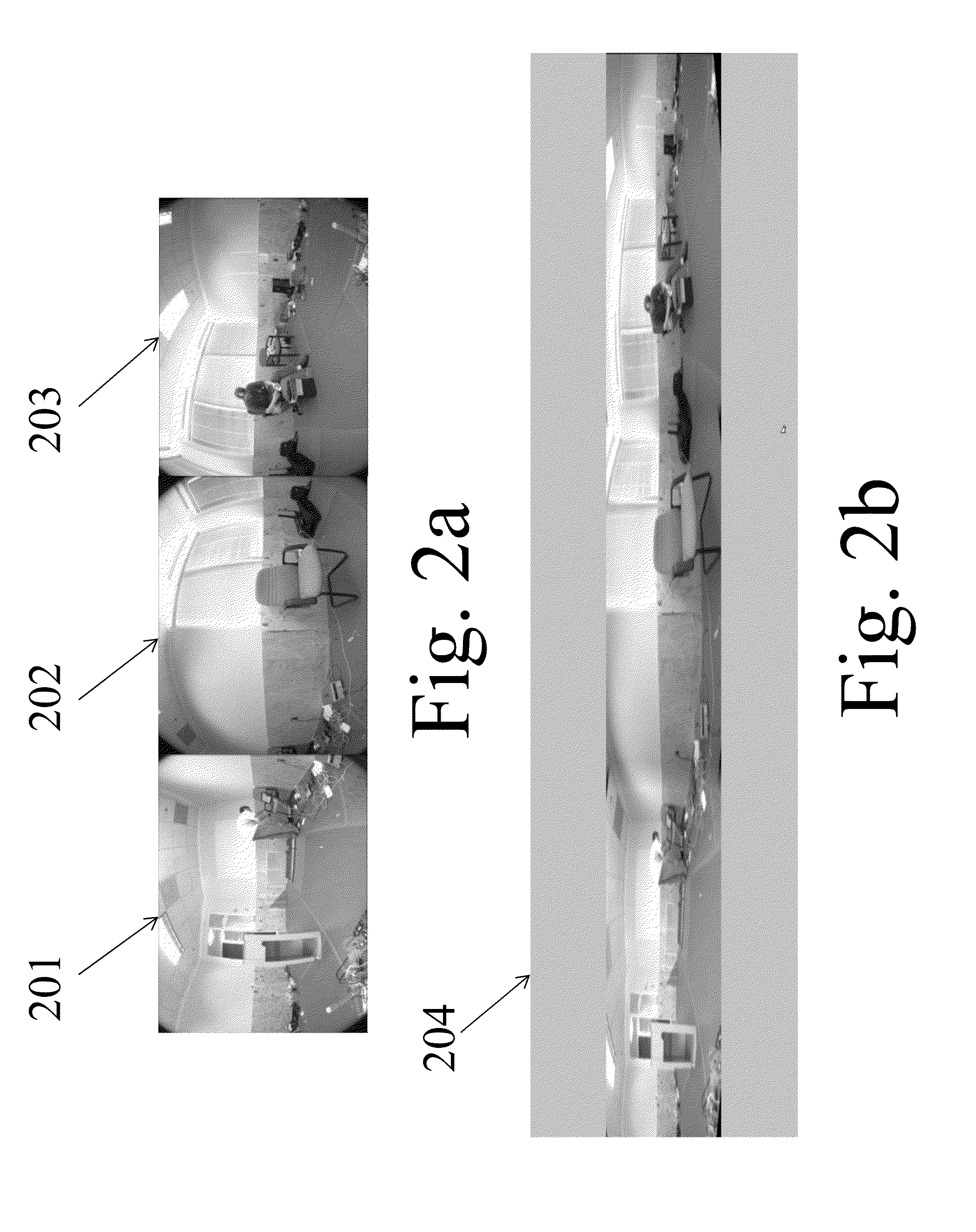
An after-action, mission review tool that displays camera and navigation sensor data allowing a user to pan, tilt, and zoom through the images from front and back cameras on an vehicle, while simultaneously viewing time / date information, along with any available navigation information such as the latitude and longitude of the vehicle at that time instance.Also displayed is a visual representation of the path the vehicle traversed; when the user clicks on the path, the image is automatically changed to the image corresponding to that position. If aerial images of the area are available, the path can be plotted on the geo-referenced image.
Owner:ROBOTIC RES OPCO LLC
Augmentation of a dynamic terrain surface
In one embodiment, an augmented view is generated that accounts for dynamically changing terrain surface at a site. A sensor captures live georeferenced terrain surface topography for the site. A camera captures an image of the site. Further, a tracking system determines a georeferenced camera pose of the camera. An augmented reality application aligns a georeferenced three-dimensional (3-D) model for the site with the live georeferenced terrain surface topography. Then, using at least the captured image, the georeferenced camera pose, the georeferenced 3-D model and live georeferenced terrain surface topography, the augmented reality application creates an augmented view of the site that shows graphical representations of subsurface features. At least a portion of the graphical representations are dynamically conformed to the contours of the terrain surface in the image based on the live georeferenced terrain surface topography. The graphical representations may include virtual excavation and / or virtual paint markings.
Owner:BENTLEY SYST INC
Geospatial modeling system for images and related methods
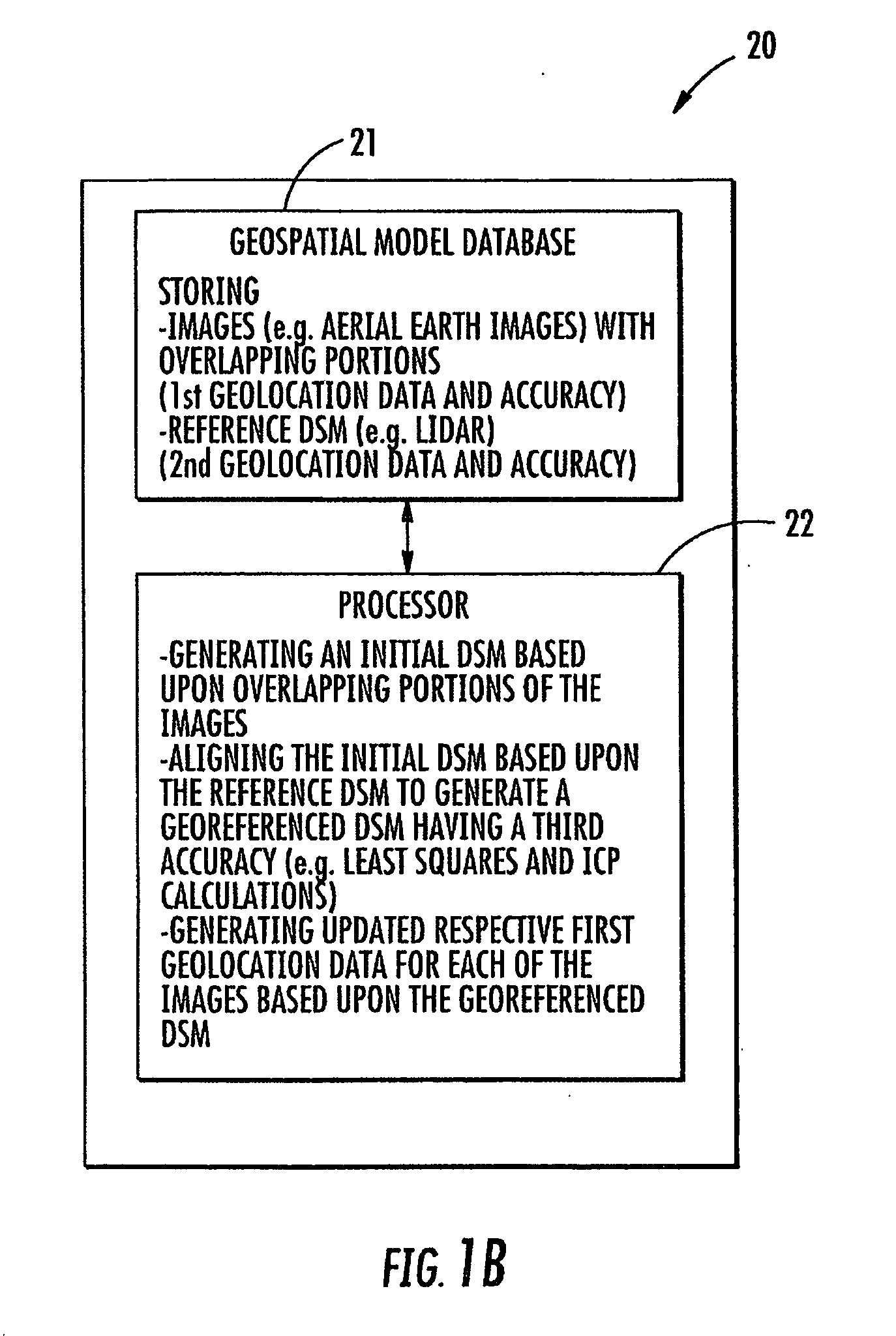
InactiveUS20100118053A1Precise processAccurate dataImage enhancementImage analysisGeolocationDigital surface
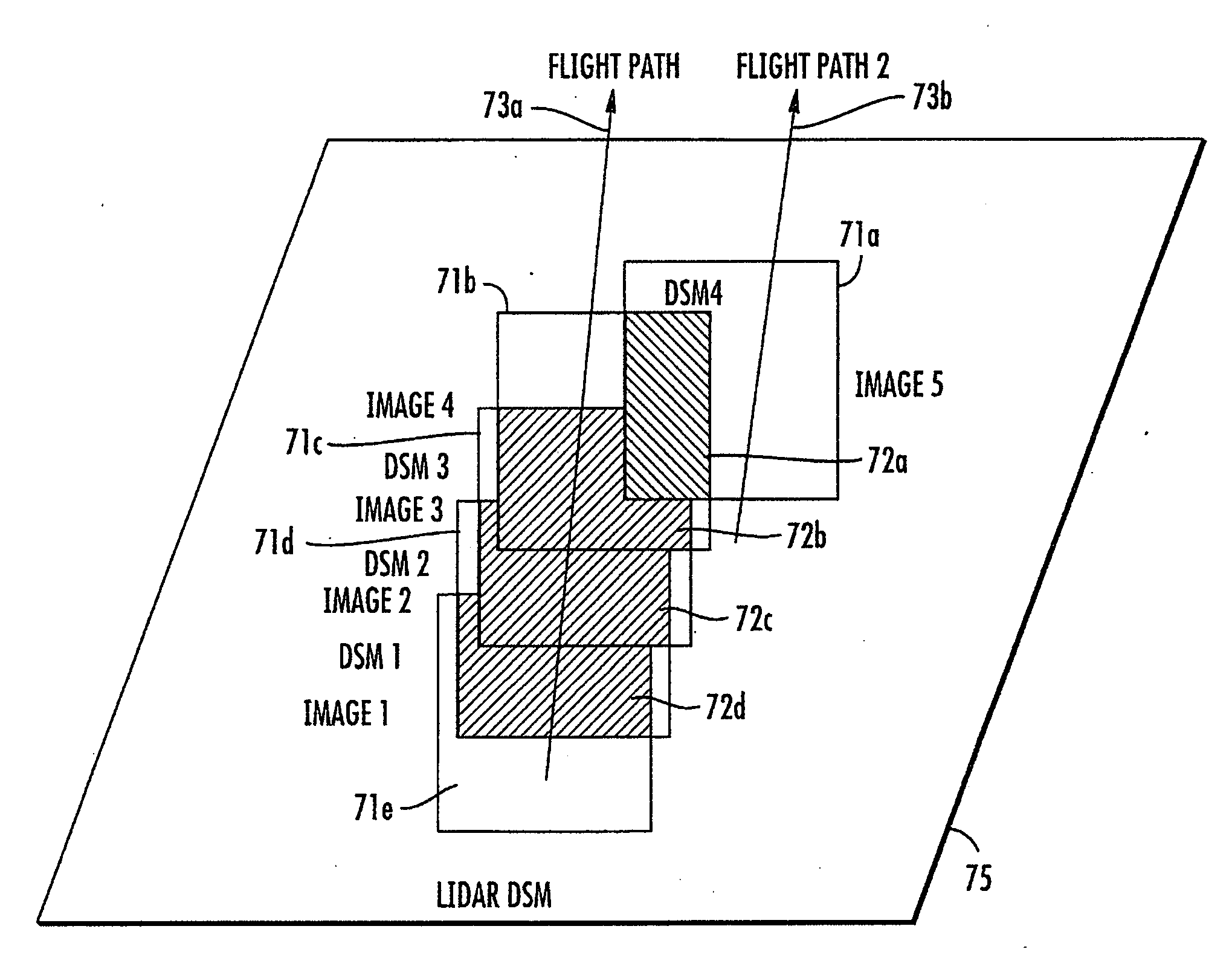
A geospatial modeling system may include a geospatial model database for storing images of a geographical area and a reference digital surface model (DSM) of the geographical area. The images each have associated with them respective first geolocation data with a first accuracy. The reference DSM may include second geolocation data with a second accuracy being greater than the first accuracy. The geospatial modeling system may further include a processor cooperating with the geospatial model database for generating an initial DSM based upon overlapping portions of the images, and aligning the initial DSM based upon the reference DSM to generate a georeferenced DSM having a third accuracy greater than the first accuracy.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
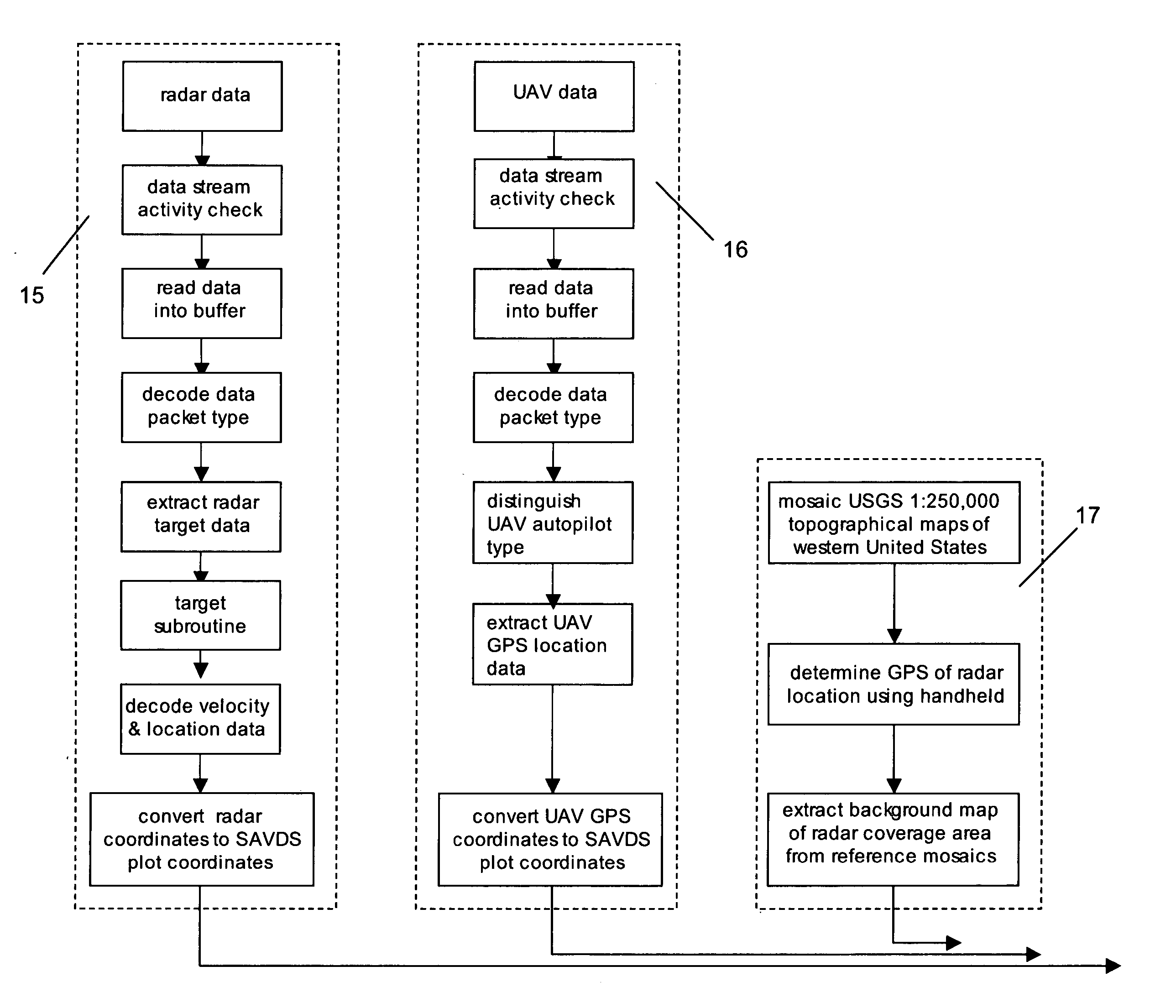
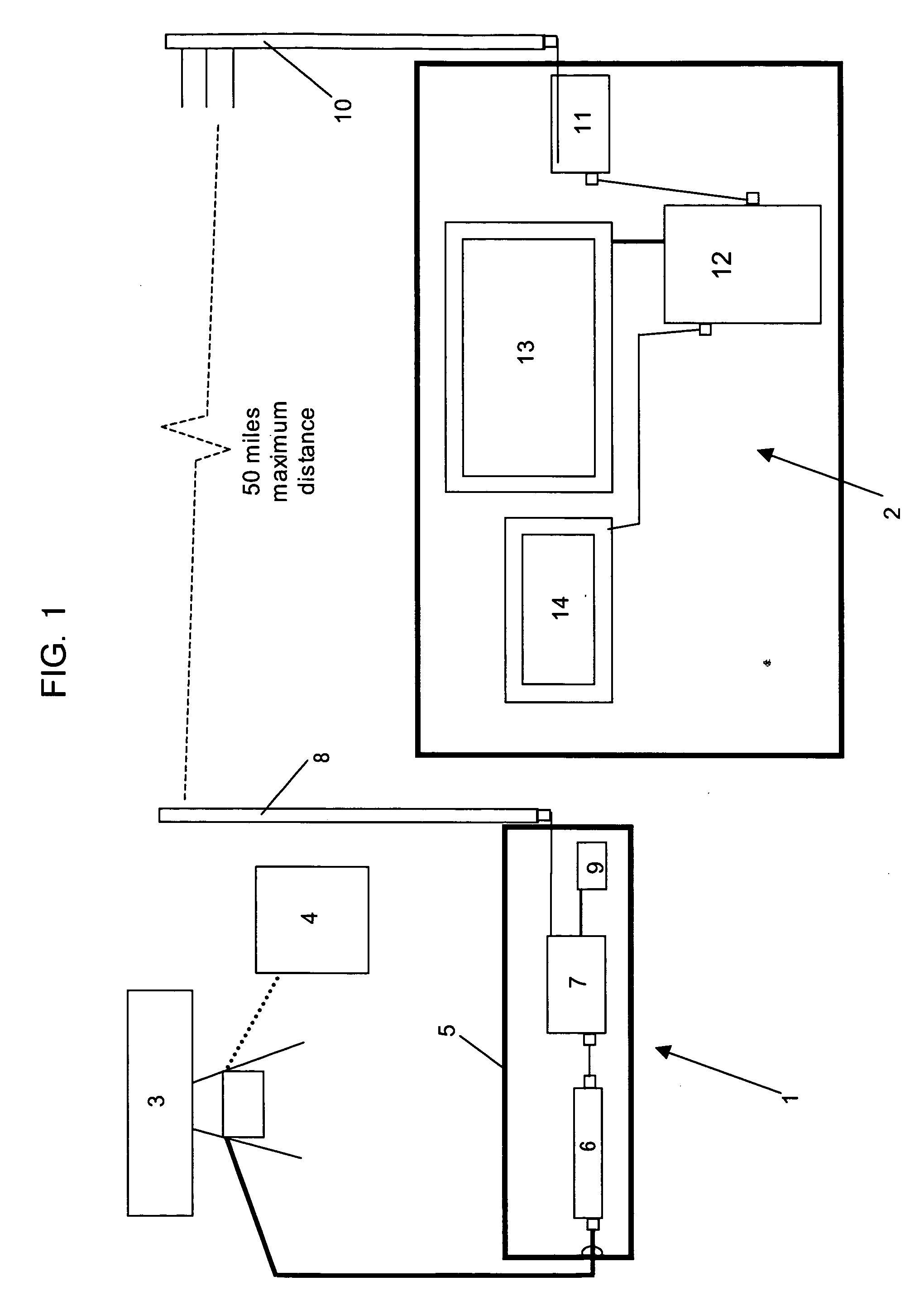
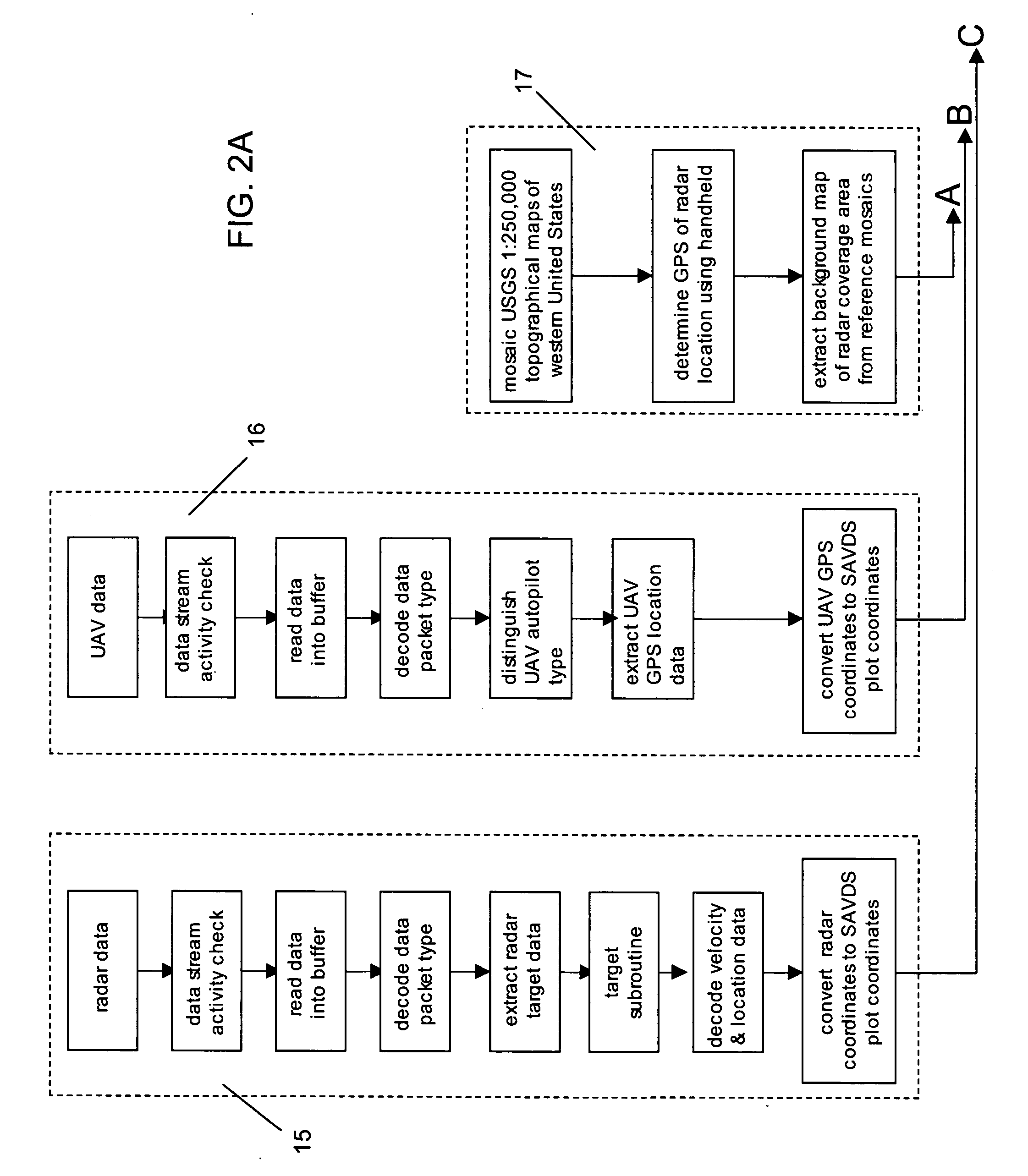
Ground-based Sense-and-Avoid Display System (SAVDS) for unmanned aerial vehicles
InactiveUS20060253254A1Limited resolutionHigh-resolution displayAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficGround based radarSense and avoid
The present invention is a Sense-and-Avoid Display System (SAVDS) that integrates data from a ground-based short-range tracking radar with positional data from a global positioning system (GPS) element in the flight management autopilot system in the unmanned aerial vehicle. Using a high-resolution display, the SAVDS shows the GPS location of the unmanned aerial vehicle in relation to other aircraft operating in the same airspace. With the SAVDS co-located on the same tabletop as the computer controlling the unmanned aerial vehicle, the SAVDS operator can instruct the unmanned aerial vehicle pilot to change the heading of the vehicle until any potential aircraft conflict is abated. Ground-based radar data and GPS data are integrated and displayed with georeferenced base maps that provide collision avoidance information, and provide a means for tracking the UAV relative to geographic waypoints.
Owner:HERWITZ STANLEY R
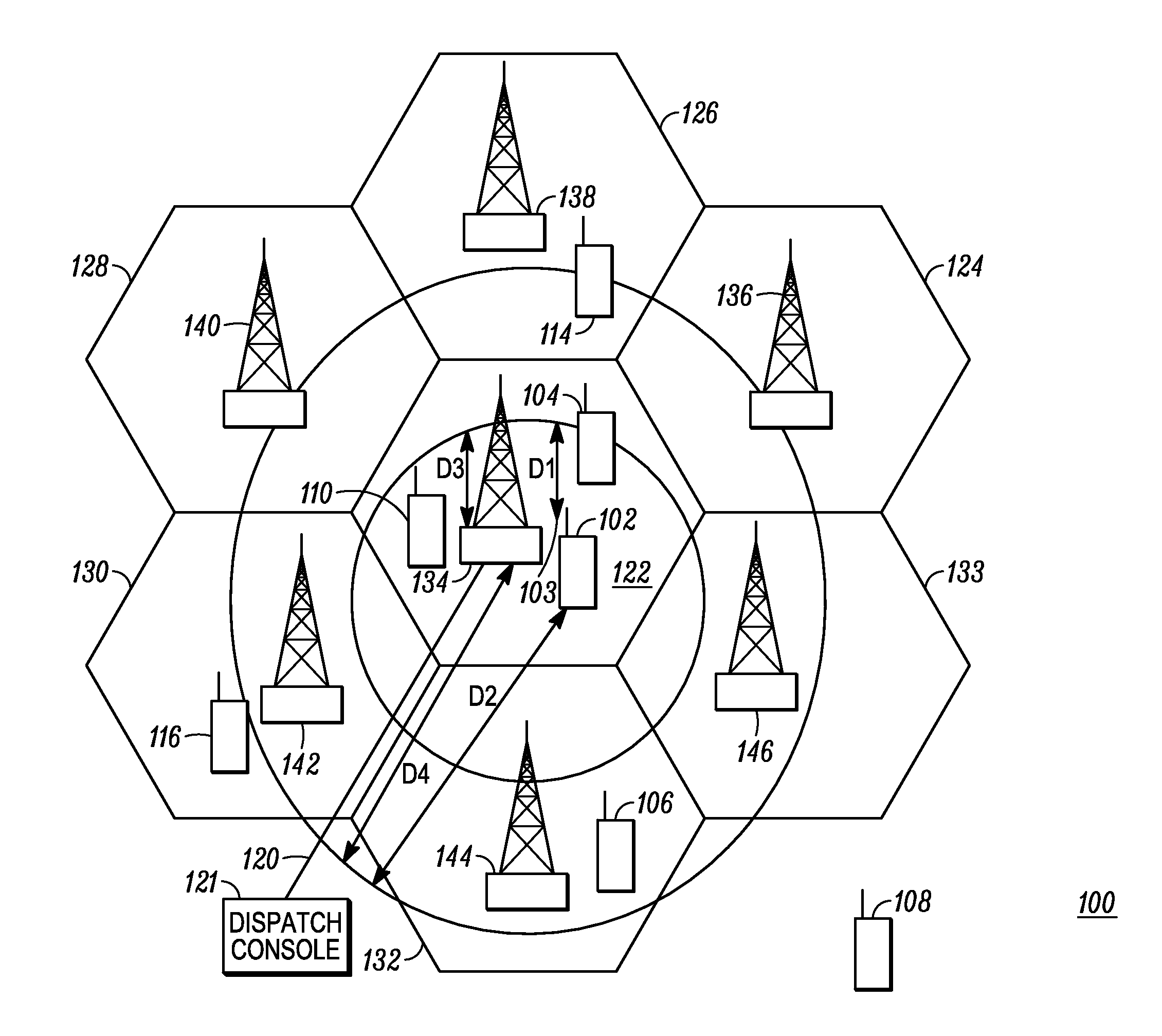
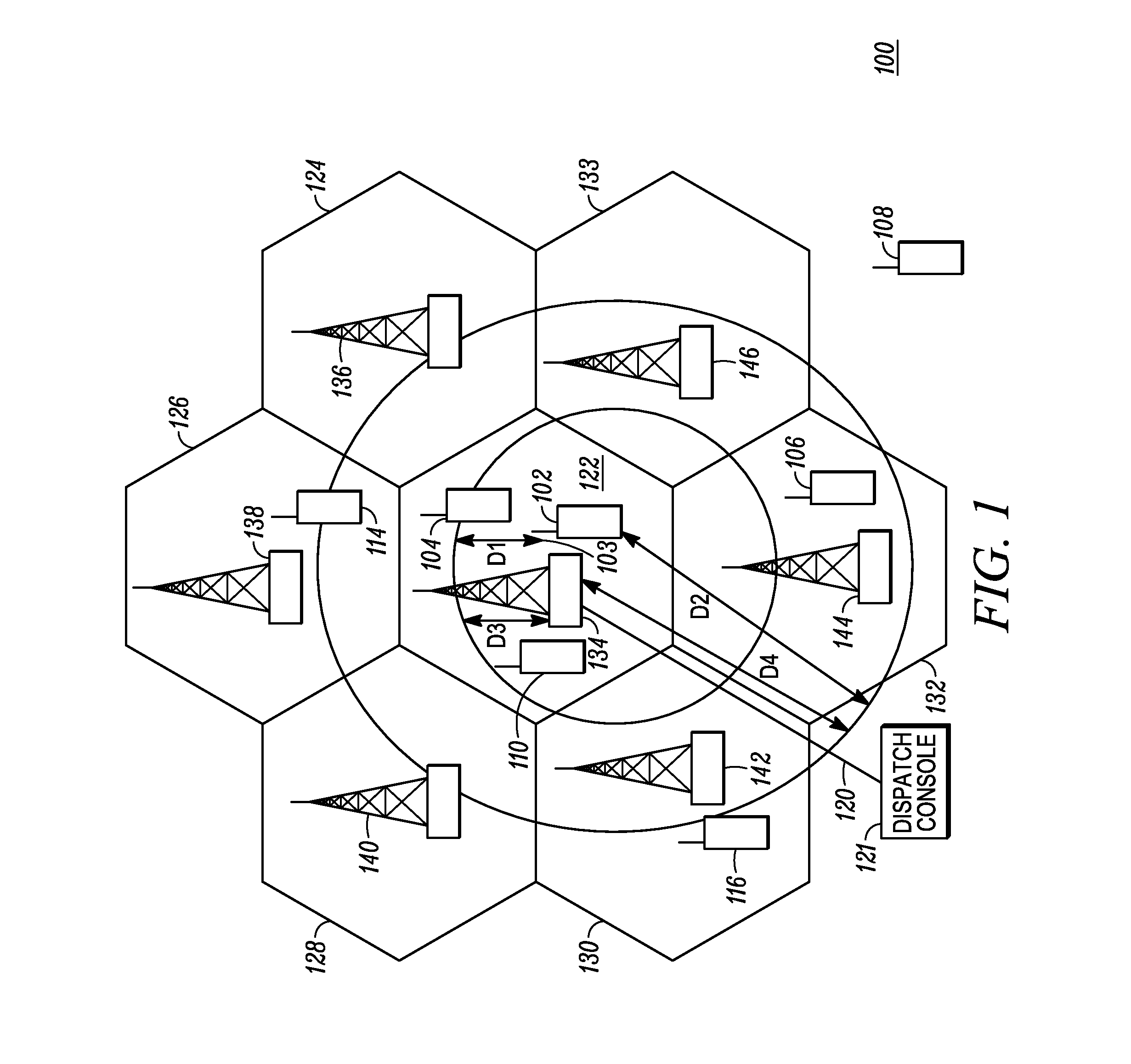
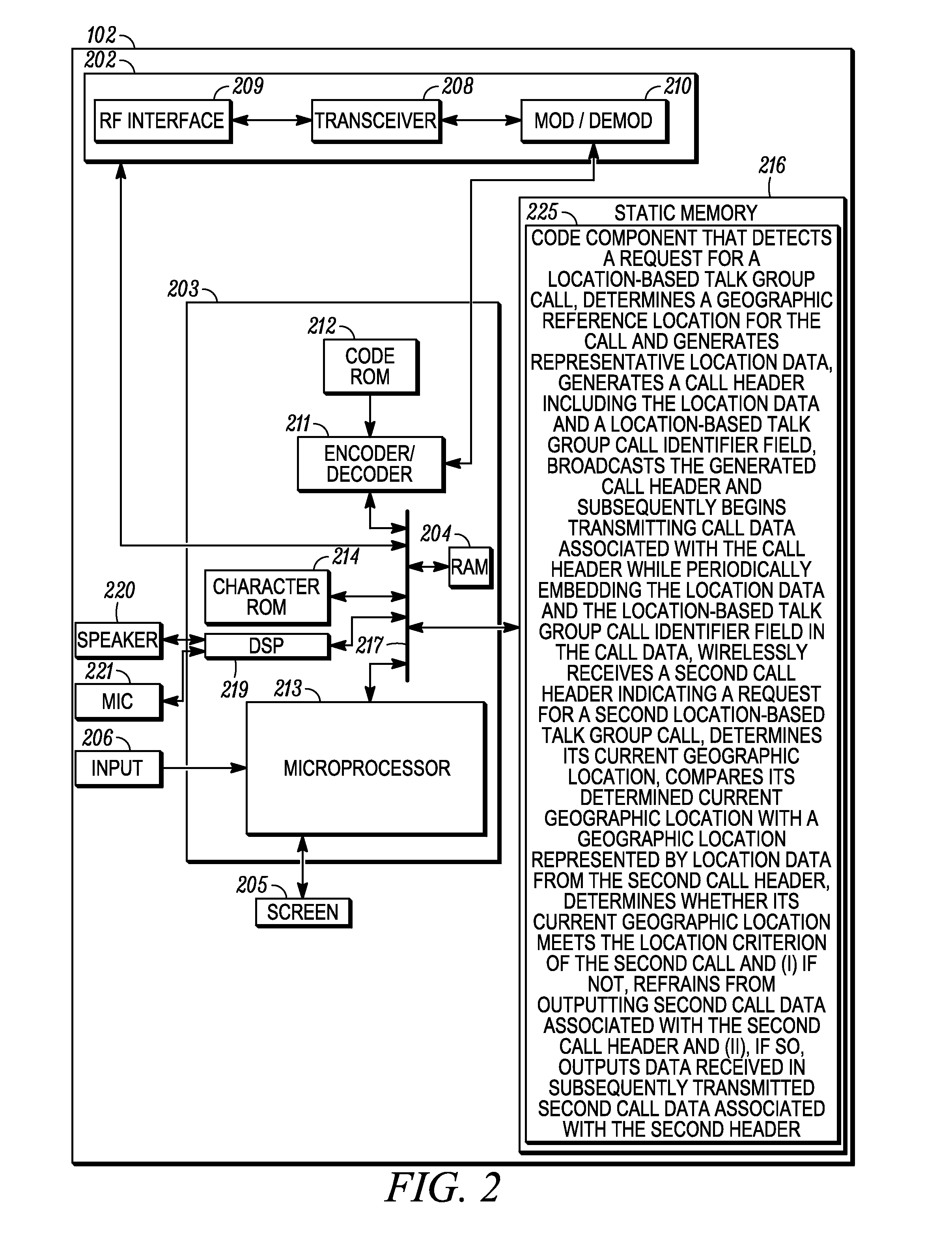
Method and device for automatic creation of a location-based talk group call with reduced messaging overhead
Disclosed is a method of automatic establishment of a location-based talk group call with reduced messaging overhead. The initiating device may be a subscriber unit (SU). The SU determines a geographic reference location and generates location data representative of the location. The SU broadcasts a location-based talk group call header including the location data and including a location-based talk group call identifier field set to cause other SUs receiving the call header to receive and output subsequent data associated with the call header responsive to determining that its current geographic location satisfies the location criterion of the call. The location criterion may be fully determined by the initiating SU and specified in the call header, and may take the form of a specified radius that extends from the geographic reference location represented in the call header.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
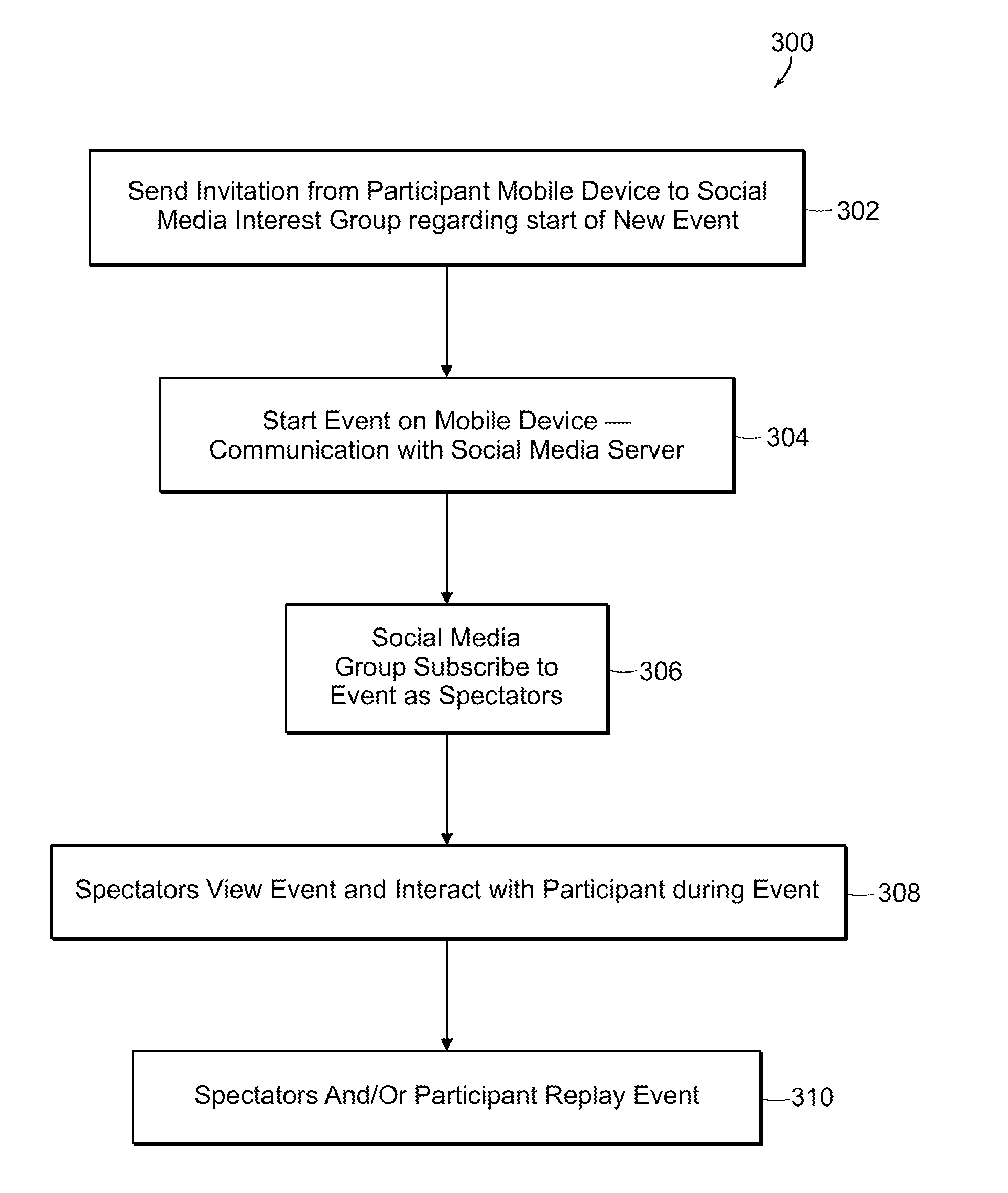
System and Method for Creating Content for an Event Using a Social Network
ActiveUS20120331058A1Enhance and expand and spectator experienceDiscounts/incentivesServices signallingVirtual goodsComputer science
A system and method for creating content such as artificial reality (AR) messages at an event, particularly among members on a social network, thereby enhancing and expanding the event experience. Typically, a participant shares an event with spectators, such as friends or a subset of friends in the participant's social network. The AR message may include geo-referenced artificial reality words, products or symbols and appear in a perspective view of the event to the participant or spectators. In addition to creating an active gallery for an event, messages, audio and video can be exchanged among participants and spectators, and virtual goods, money, bets, applause, other feedback, and donations exchanged.
Owner:SPATIAL REALITY LLC
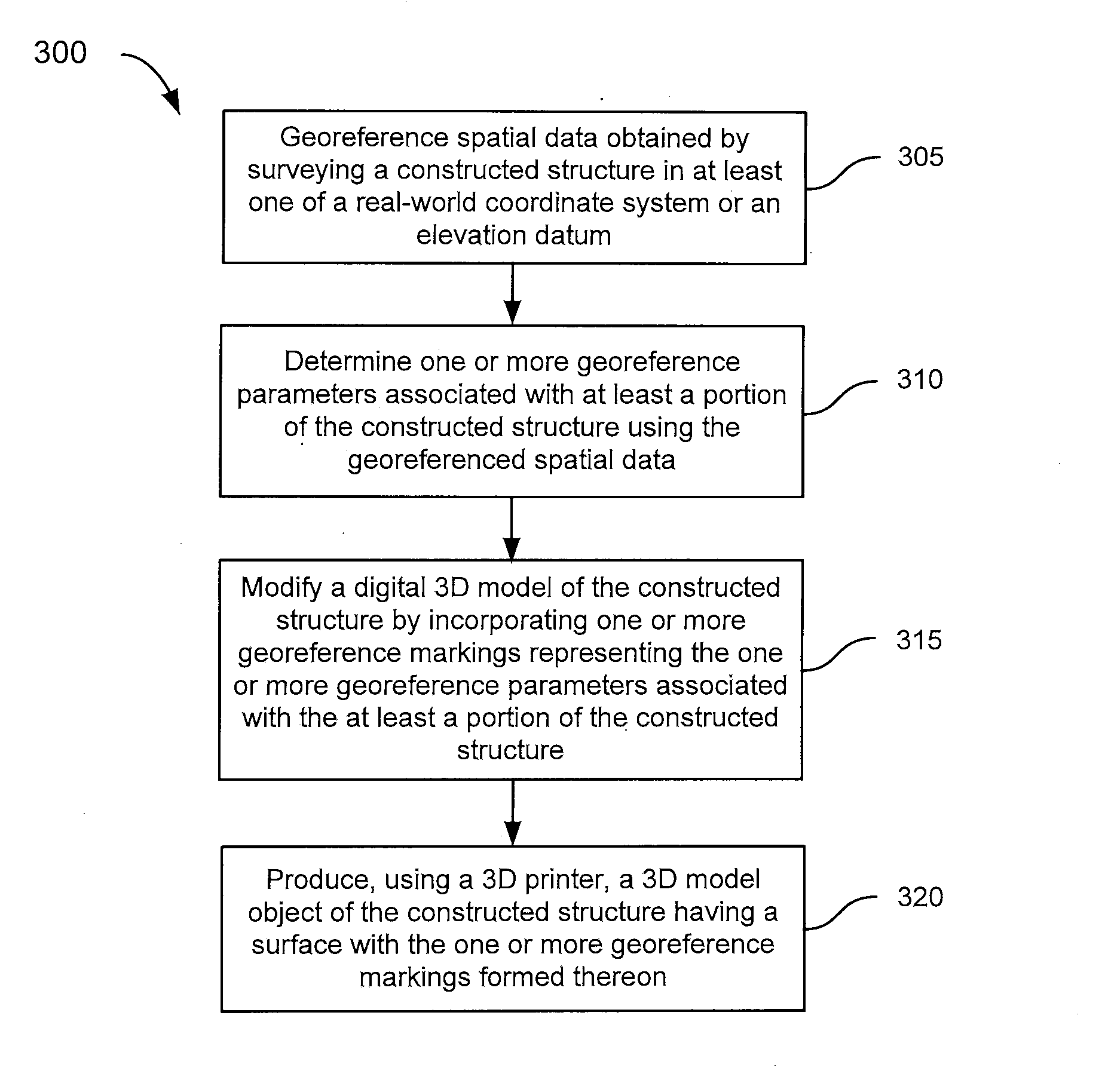
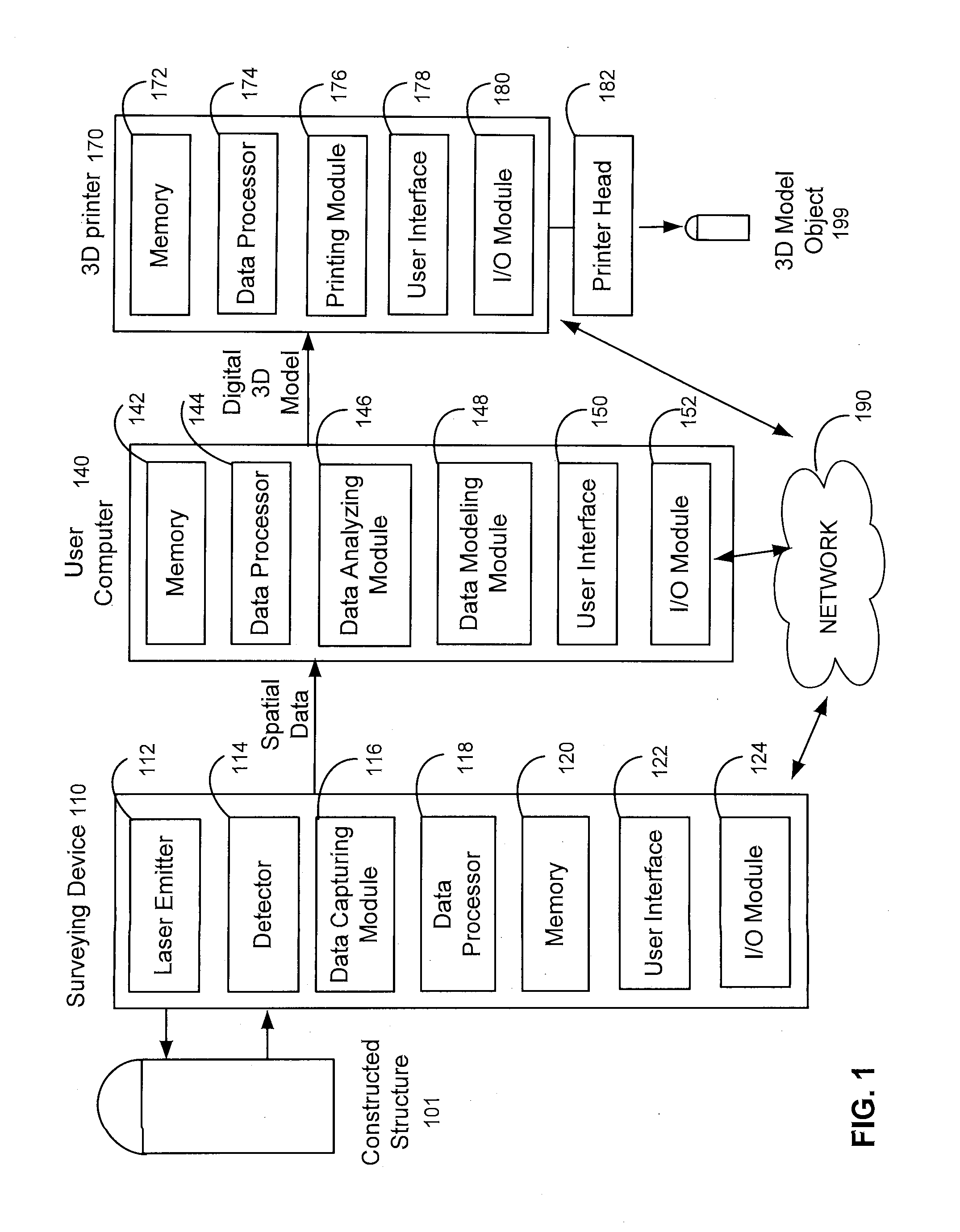
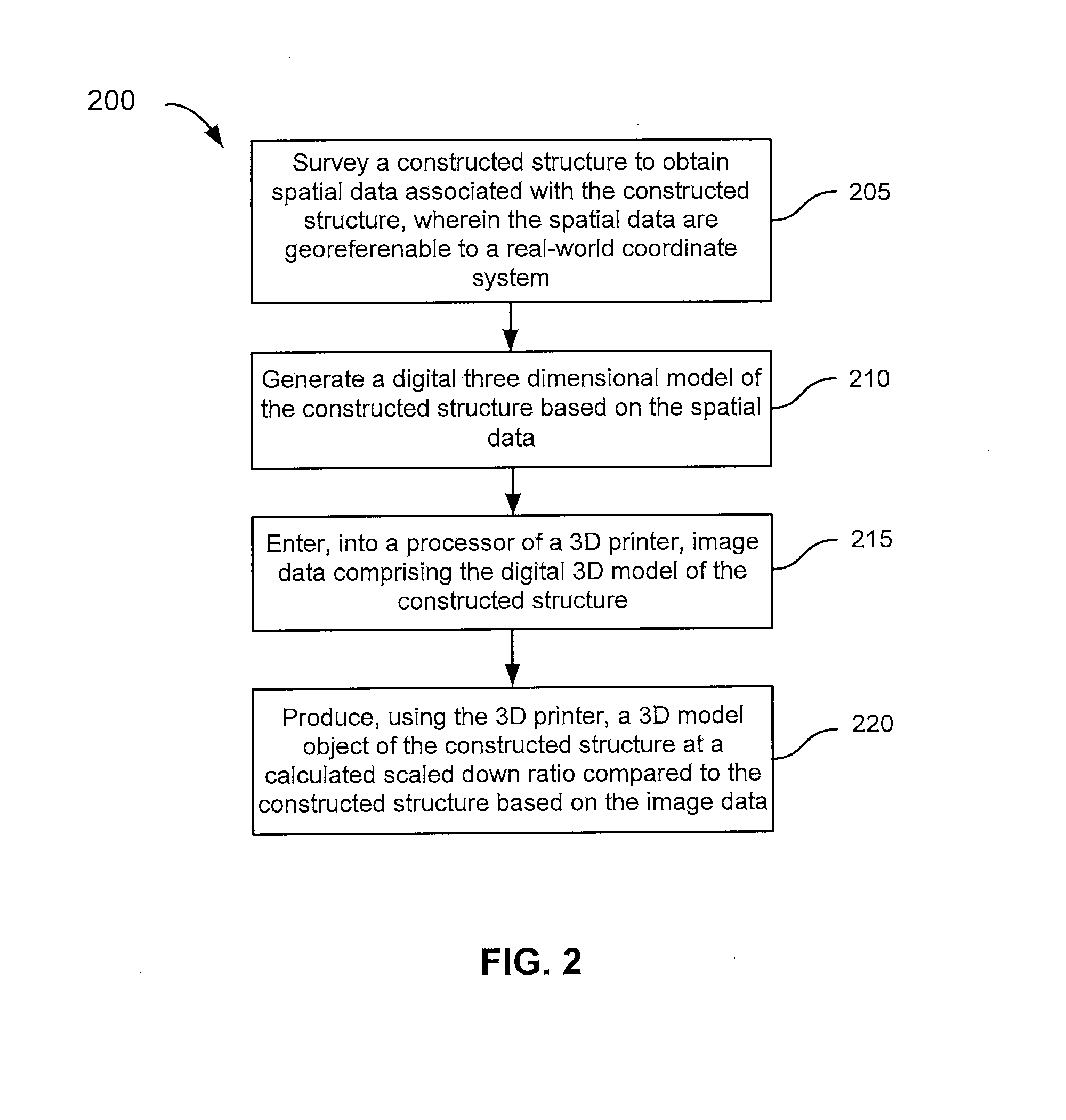
Three Dimensional Model Objects
Embodiments of the present invention provide a three dimensional model object, a method of producing the three dimensional model object, and a kit comprising the three dimensional model object and a scaled measurement device. The method in accordance with the present invention includes surveying a constructed structure which is georeferenceable in the real world, obtaining spatial data associated with the constructed structure, generating a digital three dimensional model of the constructed structure in a computer, and producing a physical model object with accurately surveyed as-built data of the constructed structure. The physical model object of the constructed structure can incorporate, on its surface, surveyed and measured useful real world intelligence, such as dimensions, georeference data, or orientation, associated with the constructed structure.
Owner:F3 & ASSOC
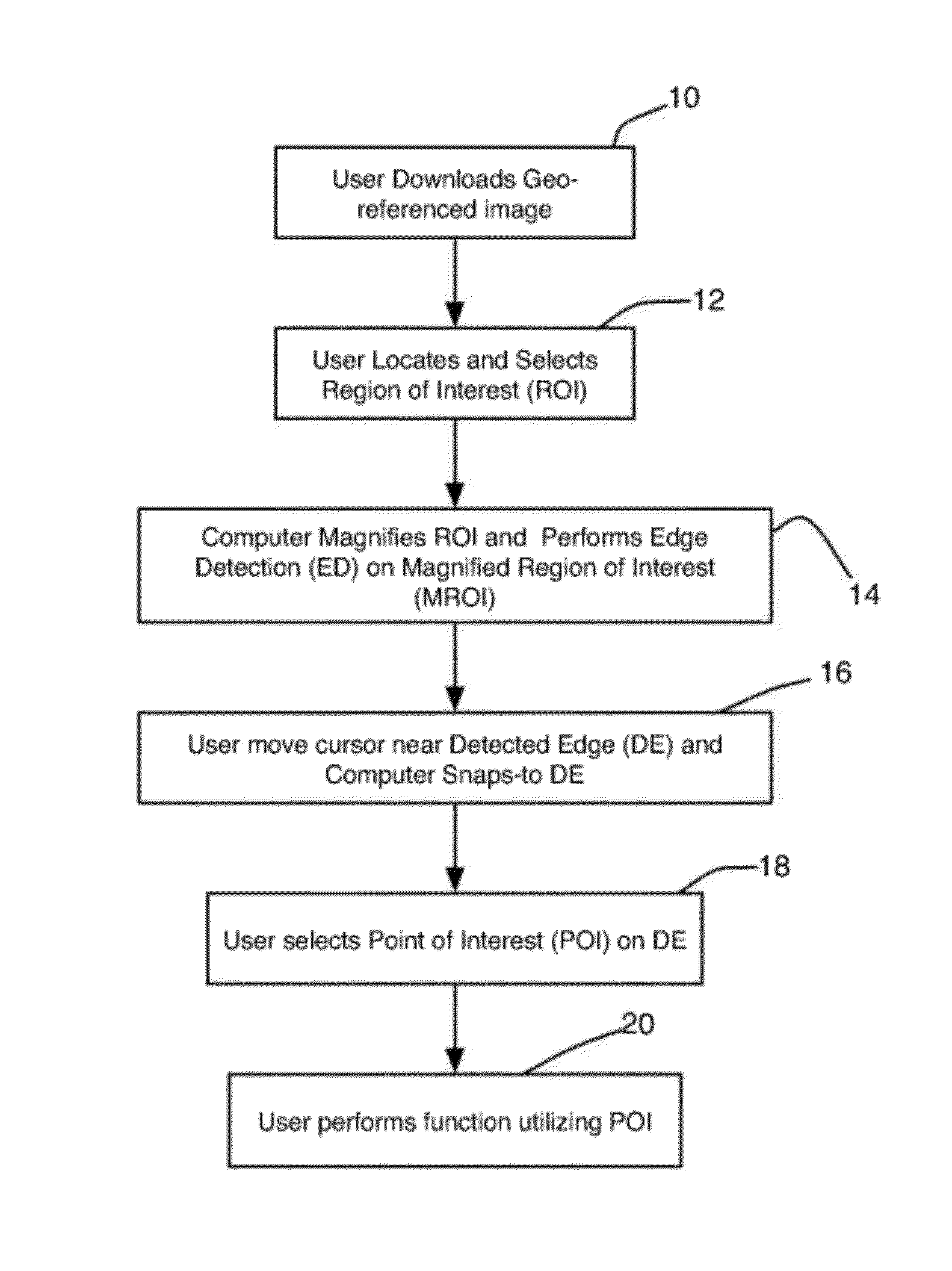
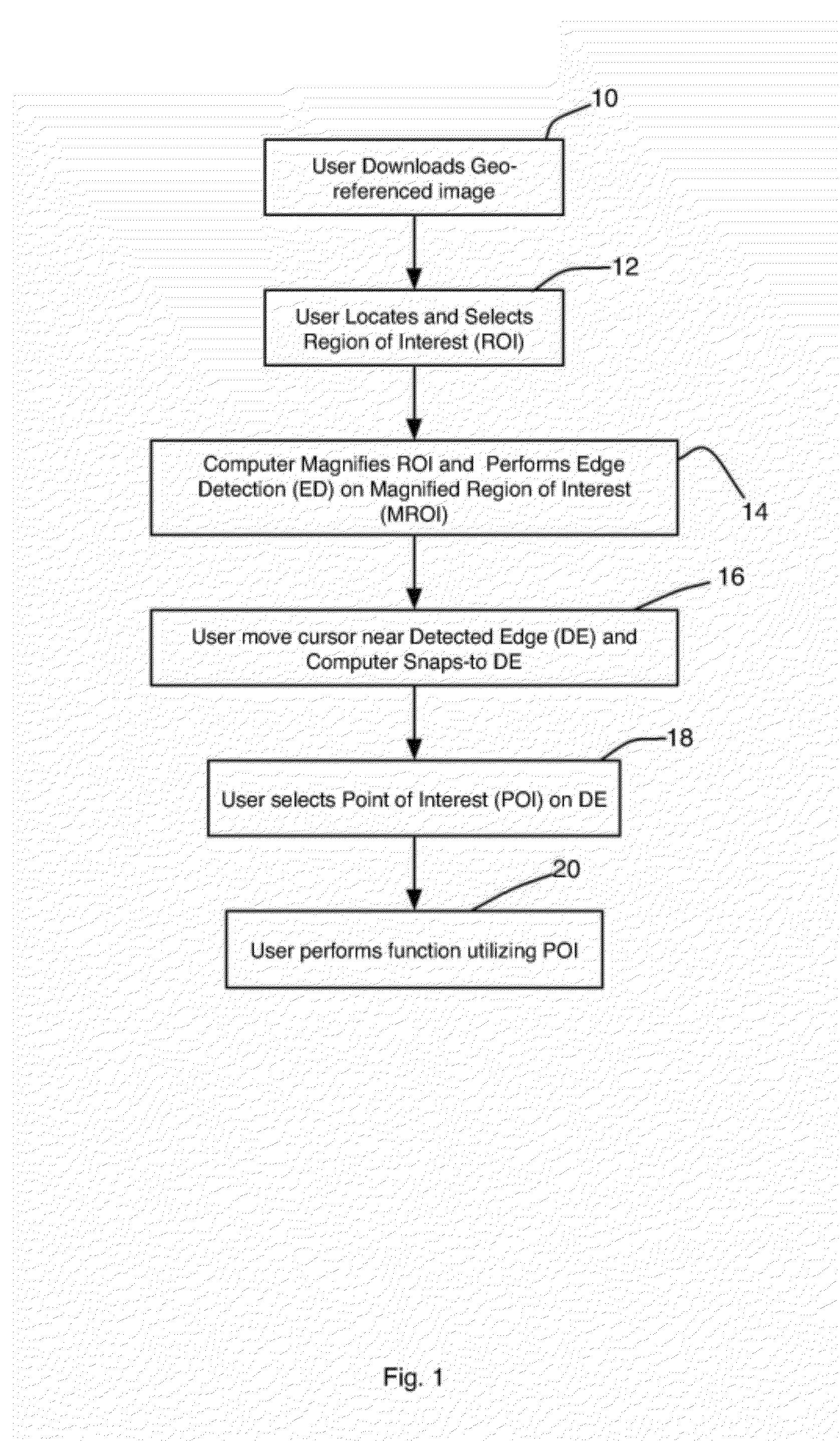
Systems and methods for processing images with edge detection and snap-to feature
A method for creating image products includes the following steps. Image data and positional data corresponding to the image data are captured and processed to create geo-referenced images. Edge detection procedures are performed on the geo-referenced images to identify edges and produce geo-referenced, edge-detected images. The geo-referenced, edge-detected images are saved in a database. A user interface to view and interact with the geo-referenced image is also provided such that the user can consistently select the same Points of Interest between multiple interactions and multiple users.
Owner:PICTOMETRY INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Vision system and method of analyzing an image
ActiveUS20120114178A1Improve robustnessIncrease speedCharacter and pattern recognitionNavigation instrumentsComputer visionVisual perception
A vision system comprises a camera that captures an image and a processor coupled to process the received image to determine at least one feature descriptor for the image. The processor includes an interface to access annotated map data that includes geo-referenced feature descriptors. The processor is configured to perform a matching procedure between the at least one feature descriptor determined for the at least one image and the retrieved geo-referenced feature descriptors.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Systems and methods for rapid three-dimensional modeling with real façade texture
Owner:PICTOMETRY INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com