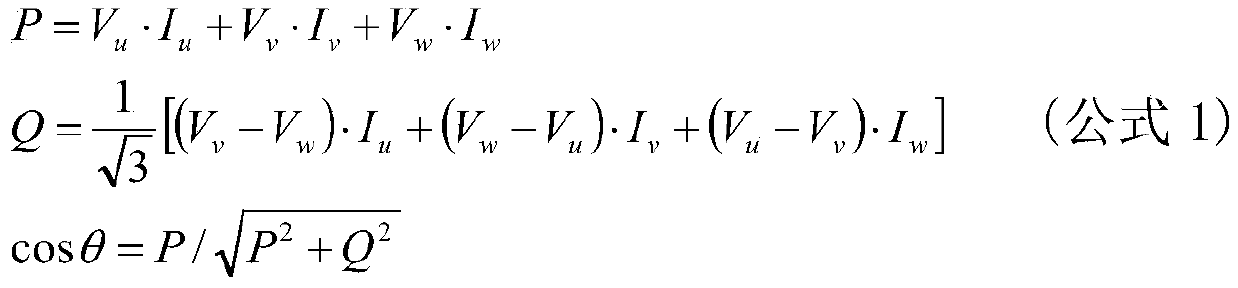Permanent magnet synchronous motor static state rotor position identification method
A permanent magnet synchronous motor and rotor position technology, which is applied in the control of generators, motor control, motor generator control, etc., can solve the problems of small calculation amount of detection data, long time, small motor reversal angle, etc., and achieve start-up response High speed, low process noise, and improved reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The present invention will be preferably described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
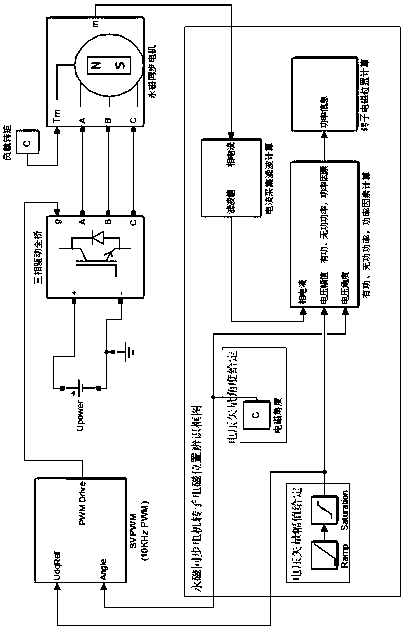
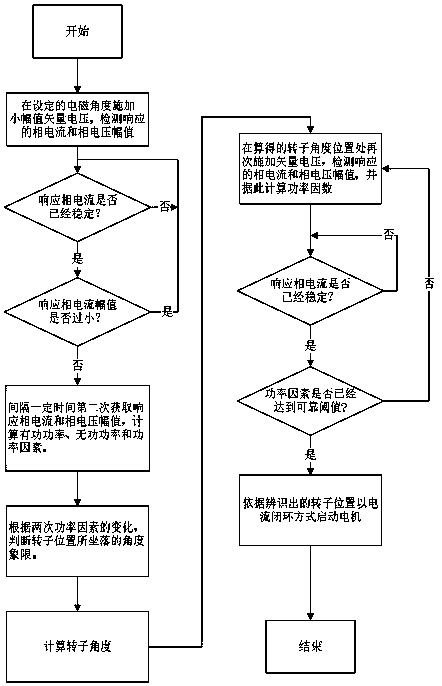
[0018] Such as figure 2 As shown, an embodiment of the rotor position identification method of the permanent magnet synchronous motor in the static state of the present invention includes the following steps:
[0019] Step 1: applying a driving voltage with a small amplitude to the set electromagnetic angle. The electromagnetic angle is the parameters of each phase of the three-phase full-bridge driver (voltage, current, flux linkage, etc.), in the agreed motor analysis coordinate system (it is agreed that the U phase is used as the zero angle of the coordinate system, the V phase is located at 120 degrees, and the W phase is located at 240 degrees. degrees) and the angle between the resultant vector and the 0 degree angle. The amplitude of the small-amplitude driving voltage is set by the detection current and the motor line resistance, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com