Code conversion method and apparatus, code recording medium, code recording apparatus and code reproducing apparatus
A technology of code conversion and equipment, applied in the direction of code conversion, analog-to-digital converter, individual digital conversion, etc., which can solve the problems of uneven characteristics of recording media, reduction of reproduction signal S/N ratio and reproduction error, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
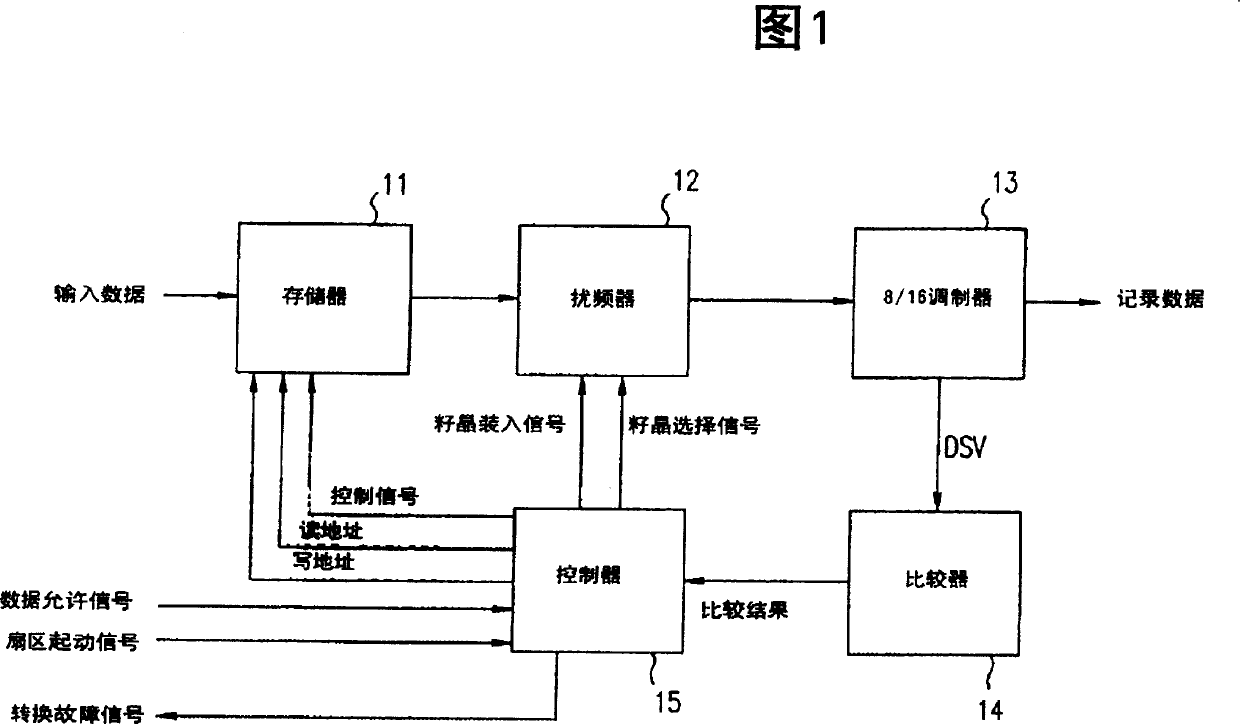
[0097]Fig. 1 shows a transcoding apparatus in a first example of the present invention. In FIG. 1, the memory 11 stores input main data words, and can store main data words of at least two sectors. When the main data word stored in the memory 11 is input to the scrambler 12, the scrambler 12 scrambles the input main data word, and outputs the scrambled main data word to the 8 / 16 modulator 13 . The 8 / 16 modulator 13 modulates the scrambled main data word by pit position modulation (PPM), thereby generating a main data word (16 bits) from the scrambled main data word (8 bits). Afterwards, the 8 / 16 modulator 13 also modulates the 16-bit main data word by pulse width modulation (PWM), thereby generating a 16-bit output main data word from the 16-bit main data word and outputting the 16-bit output main data word . When the DSV obtained by the 8 / 16 modulator 13 is input to the comparator 14, the comparator determines whether the variation (or differential value) of the DSV exceed...
example 2
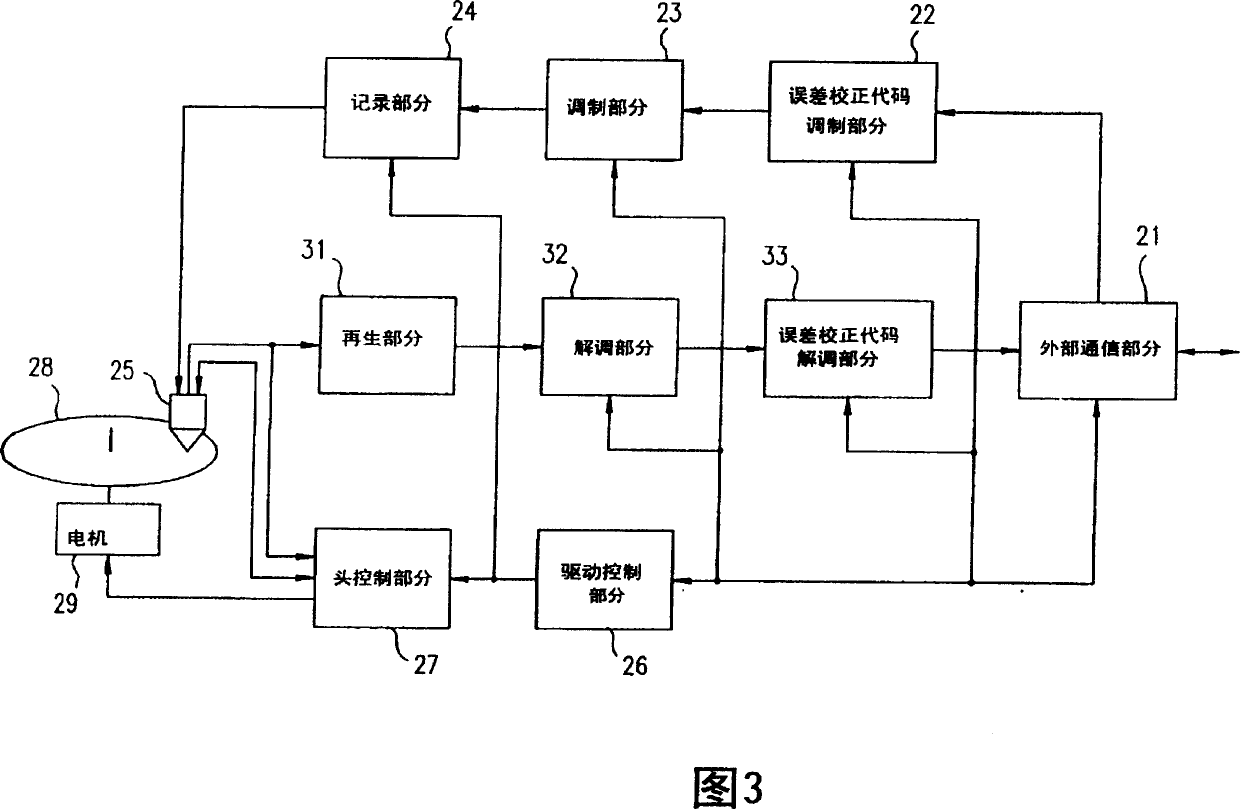
[0131] Fig. 4 shows a code conversion apparatus in a second example of the present invention. This second transcoding device differs from the first transcoding device in that a sector counter 41 is additionally provided to the device shown in FIG. The scrambler switching section 42 restarts scrambling and modulation on a sector basis when DSV has diverged, and selectively changes the scrambling method only in a frame in which the DSV has been caused to diverge.
[0132] When a sector start signal is required or a sector for reading main data is started from the memory 11, the sector counter 41 counts the frames of the sector according to a bit clock or a word clock, and detects from the top of the frame which is currently blocked by a scrambler. The position of the frame processed by the frequency converter conversion section 42 and the 8 / 16 modulator 13 or the position of the current frame, and then notifies the comparator 14 and the controller 15 of the frame position.
[0...
example 3
[0153] Fig. 7 shows a code conversion apparatus in a third example of the present invention. The transcoding apparatus of this third example differs from that of the first example in that an output control section 48 for interrupting or outputting through the 8 / 16 modulator 13 is additionally provided to the apparatus shown in FIG.
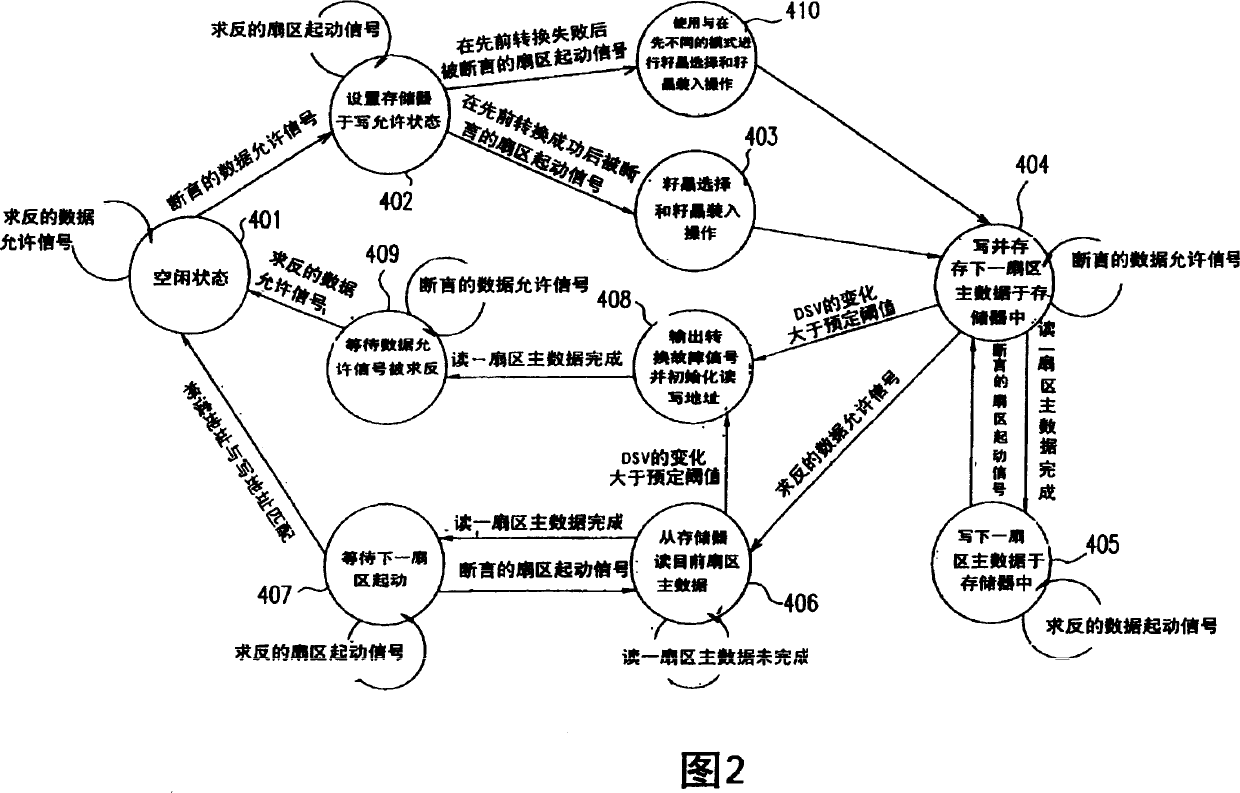
[0154] In this example, the controller 15 negates an output enable signal to the output control section 48, thereby interrupting the output of the 8 / 16 modulator 13 through the output control section 48, when the data enable signal is required in this state , the controller 15 sets the memory 11 in a write-enabled state, thereby inputting and storing one sector of main data into the memory 11. Next, the controller 15 starts reading a sector of main data from the memory 11 and supplies the read main data word to the scrambler 12 when a sector start signal is requested. Controller 15 also applies to the scrambler 12 a seed select signal and a seed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com