Additive substrate plane distortion compensating method
A distortion compensation and planar technology, which is applied in the field of electromechanical methods, can solve problems such as high cost, initial deposition layer warping, and complex drive mechanism, so as to reduce material and processing costs, cancel substrate leveling operations, and have high technical feasibility Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
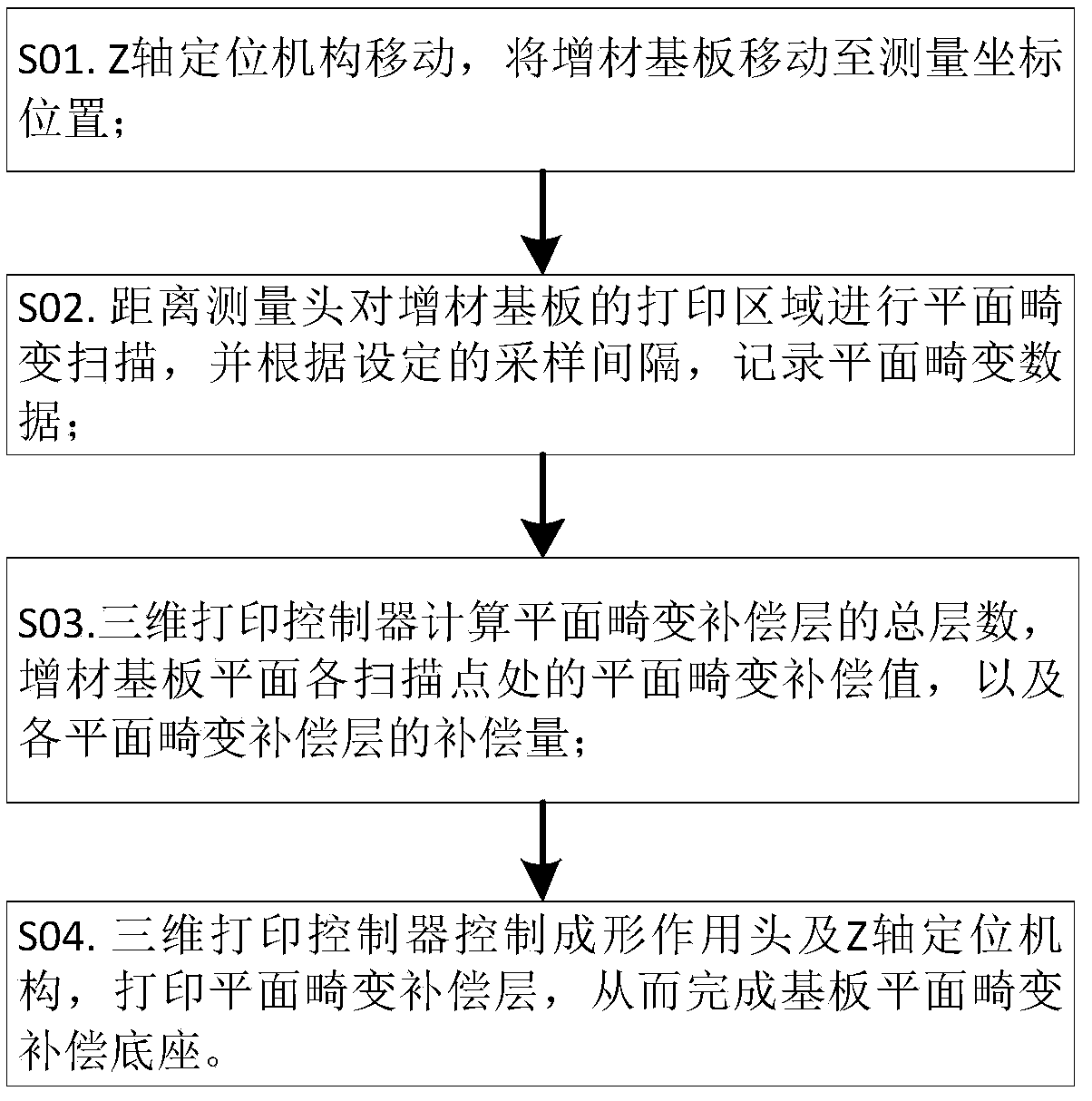
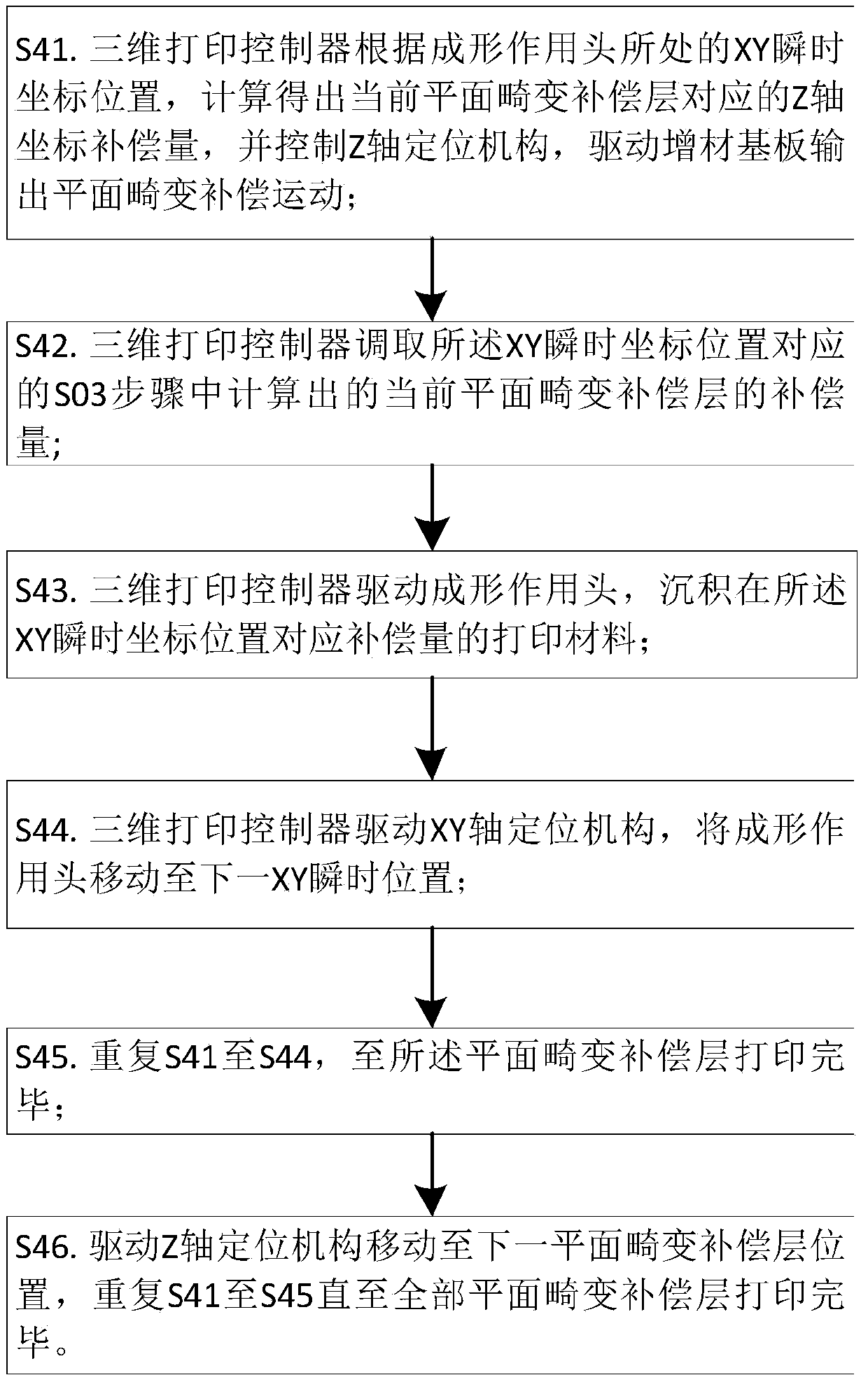
[0032] The embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
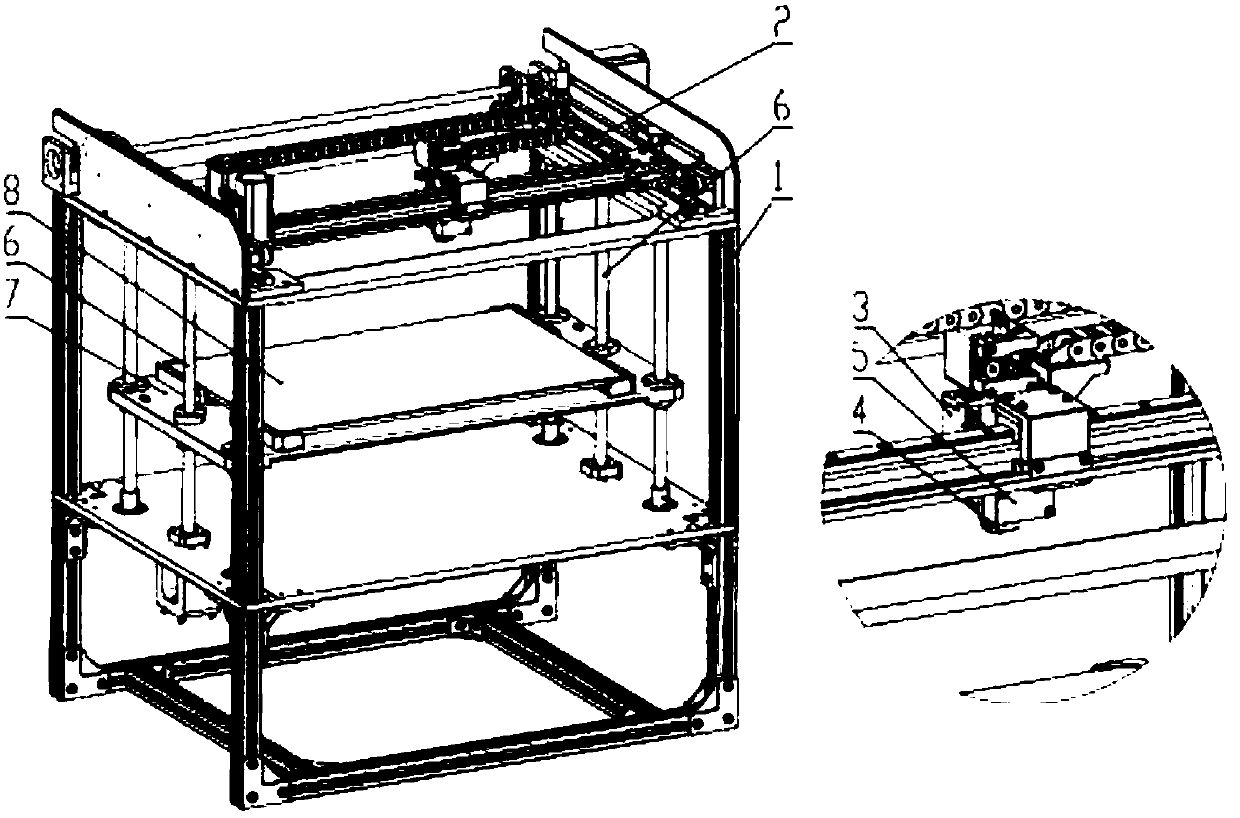
[0033] In order to realize the method for compensating the plane distortion of the additive substrate of the present invention, the corresponding printing device is such as figure 1 As shown, the printing device includes a rigid support 1, an XY-axis positioning mechanism 2, a Z-axis positioning mechanism 6, a first moving platform 3, a second moving platform 7, a forming head 4, a distance measuring head 5, an additive substrate 8, a three-dimensional Print controller 11, where:
[0034] The XY axis positioning mechanism 2 is located on the top of the rigid support 1, and there is a first mobile platform 3 on the XY axis positioning mechanism 2; the first mobile platform 3 has a shaping head 4 and a distance measuring head 5, wherein the The shaping head 4 and the distance measuring head 5 use the XY-axis positioning mechanism 2 to perform planar motio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com