In-situ ecological restoration method for water body bottom mud
A technology of ecological restoration and sediment, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc. High degree of automation and the effect of reducing heavy metal content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] An in-situ ecological restoration method for bottom mud of a water body is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0033] S1. Based on the rectangular metal mesh frame and the modified nano-magnetic iron oxide contained in the rectangular metal mesh frame, the adsorption treatment of heavy metals in the sediment is realized;
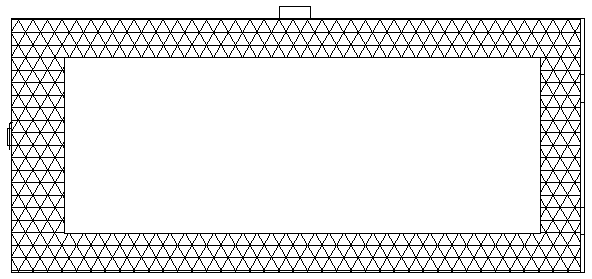
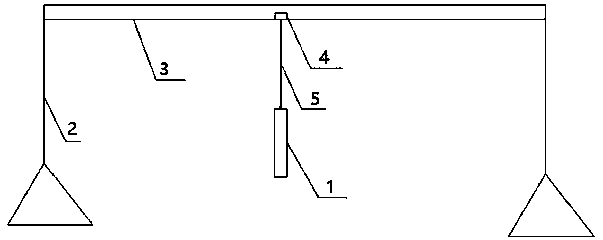
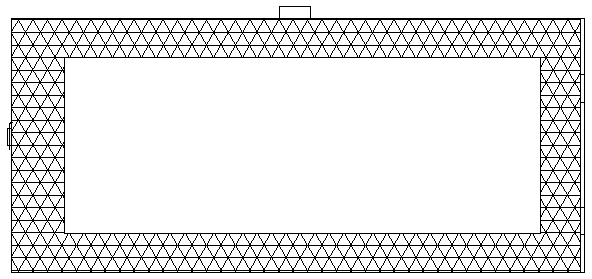
[0034] S11. Complete the installation of the supporting mechanism, and arrange it according to a certain threshold value. The threshold value must at least satisfy that two adjacent rectangular metal mesh frames will not affect each other during work; the rectangular metal mesh frame is pressed by a driving mechanism and a supporting mechanism. A certain threshold is arranged in the river, and the lower bottom of the rectangular metal mesh frame is always located in the sediment; the driving mechanism includes a slider, a slider driving device, and an electric telescopic rod, and the supporting mechanism includes supporting frames...
Embodiment 2
[0044] An in-situ ecological restoration method for bottom mud of a water body is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0045] S1. Based on the rectangular metal mesh frame and the modified nano-magnetic iron oxide contained in the rectangular metal mesh frame, the adsorption treatment of heavy metals in the sediment is realized;
[0046] S11, complete the installation of the supporting mechanism; the rectangular metal mesh frame is arranged in the river by a certain threshold through a driving mechanism and a supporting mechanism, and the lower bottom edge of the rectangular metal mesh frame is always located in the bottom mud; the driving mechanism includes a sliding block, slider driving device, and electric telescopic rod. The support mechanism includes support frames erected on both sides of the river, and a cross bar erected between the two support frames. The chute of the block drive device, the rectangular metal screen frame is fixed to the slider t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com