Method for accurately controlling and repairing cutting length in optical fiber welding process
A technology of cutting length and precise control, applied in the coupling of optical waveguides, optics, light guides, etc., can solve the problems of scrapped optical fibers, the blade of the optical fiber cleaver is not adjusted properly, and the optical fibers cannot meet the requirements, and achieves safe and convenient use. Avoid equipment scrap, good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
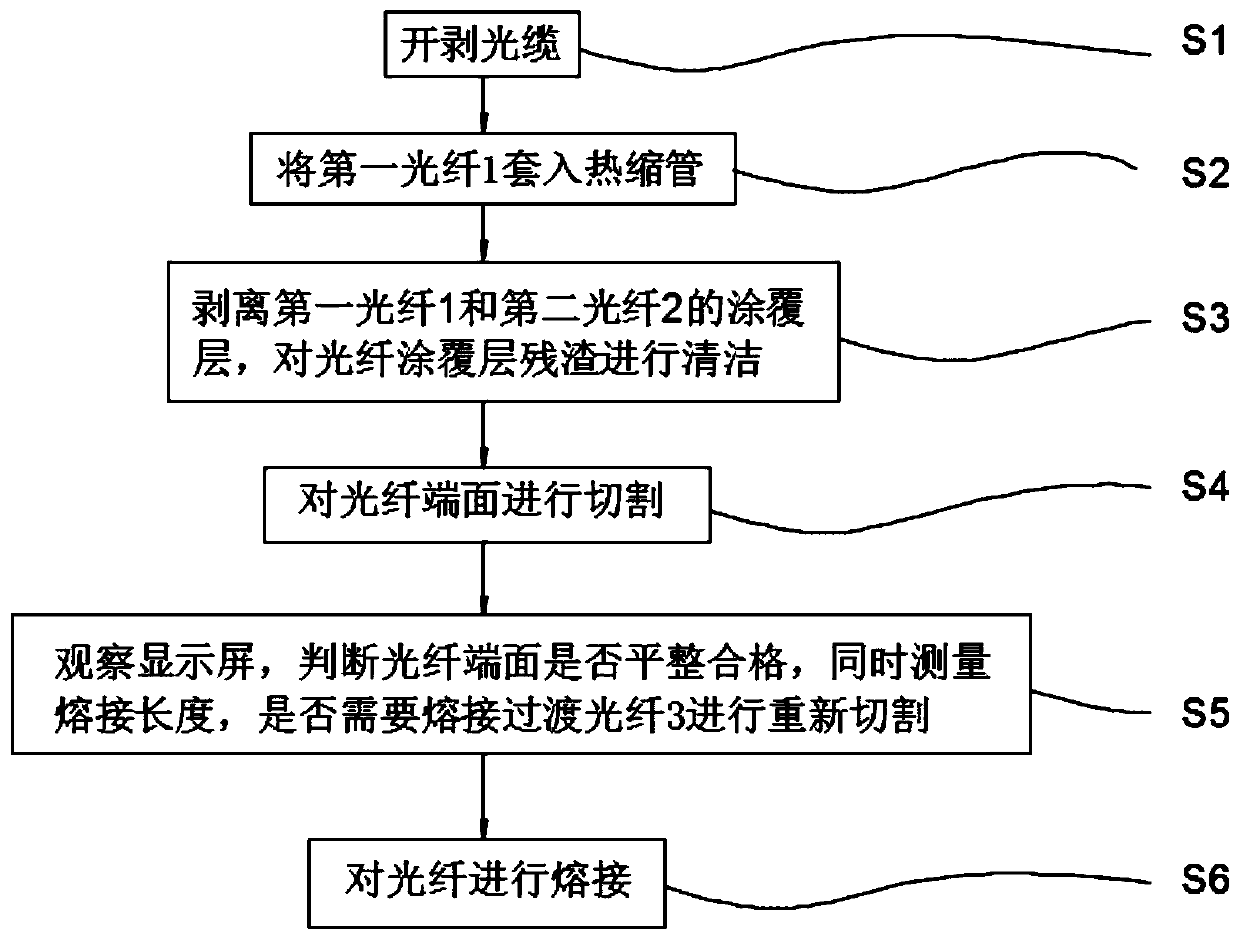
[0035] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 , a method for precisely controlling and repairing the cutting length in the process of optical fiber fusion, the method includes the following steps:
[0036] S1, stripping the optical cable;
[0037] S2. Insert the first optical fiber 1 into the heat shrinkable tube;
[0038] S3, peeling off the coating layer of the first optical fiber 1 and the second optical fiber 2, and cleaning the residue of the optical fiber coating layer;
[0039] S4, cutting the end face of the optical fiber;
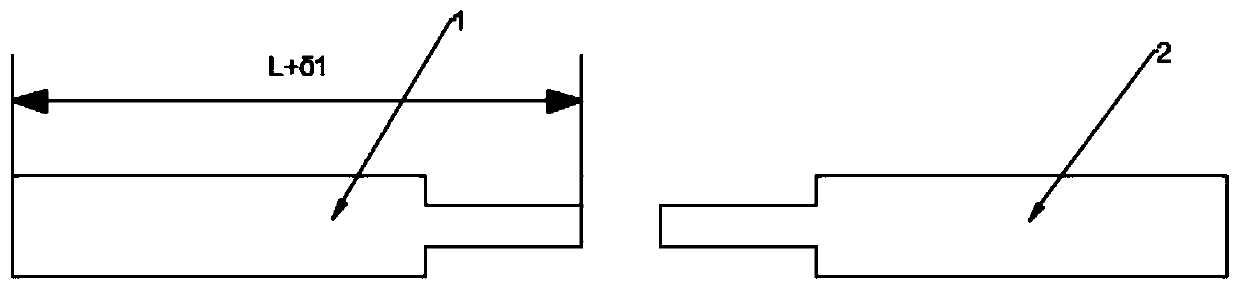
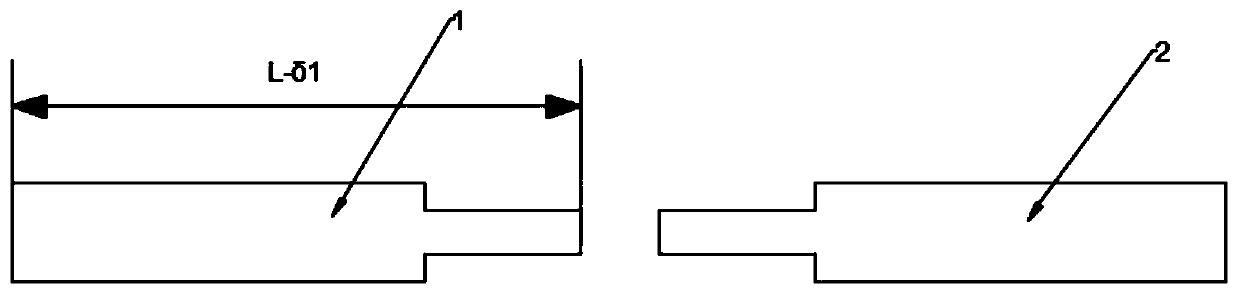
[0040] S5. Observe the display screen to determine whether the end face of the optical fiber is flat and qualified, and measure the length of the fusion splicing at the same time, whether it is necessary to re-cut the fusion splicing transition optical fiber 3;
[0041] S6. Splicing the optical fibers.
[0042] In step S1, after the optical cable is stripped, the optical cable needs to be fixed in the splice box, and inserted into the splice box, and the fi...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2: as figure 1 , a method for precisely controlling and repairing the cutting length in the process of optical fiber fusion, the method includes the following steps:
[0056] S1, stripping the optical cable;
[0057] S2. Insert the first optical fiber 1 into the heat shrinkable tube;
[0058] S3, peeling off the coating layer of the first optical fiber 1 and the second optical fiber 2, and cleaning the residue of the optical fiber coating layer;
[0059] S4, cutting the end face of the optical fiber;
[0060] S5. Observe the display screen to determine whether the end face of the optical fiber is flat and qualified, and measure the length of the fusion splicing at the same time, whether it is necessary to re-cut the fusion splicing transition optical fiber 3;
[0061] S6. Splicing the optical fibers.
[0062] In step S1, after the optical cable is stripped, the optical cable needs to be fixed in the splice box, and inserted into the splice box, and the fi...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Embodiment 3: as figure 1 , a method for precisely controlling and repairing the cutting length in the process of optical fiber fusion, the method includes the following steps:
[0076] S1, stripping the optical cable;
[0077] S2. Insert the first optical fiber 1 into the heat shrinkable tube;
[0078] S3, peeling off the coating layer of the first optical fiber 1 and the second optical fiber 2, and cleaning the residue of the optical fiber coating layer;
[0079] S4, cutting the end face of the optical fiber;
[0080] S5. Observe the display screen to determine whether the end face of the optical fiber is flat and qualified, and measure the length of the fusion splicing at the same time, whether it is necessary to re-cut the fusion splicing transition optical fiber 3;
[0081] S6. Splicing the optical fibers.
[0082] In step S1, after the optical cable is stripped, the optical cable needs to be fixed in the splice box, and inserted into the splice box, and the fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com