Battery management system and method thereof
A battery management system and battery management technology, applied in the field of management systems, can solve the problems of shortening battery life, consuming a lot of energy, increasing volume, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] In order to make the structural features of the present invention and the achieved effects have a further understanding and recognition, preferred embodiments and detailed descriptions are specially used, which are described as follows:
[0058] Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail by illustrating various embodiments of the present invention by means of drawings. Inventive concepts may however be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as limited to the illustrative embodiments set forth herein.
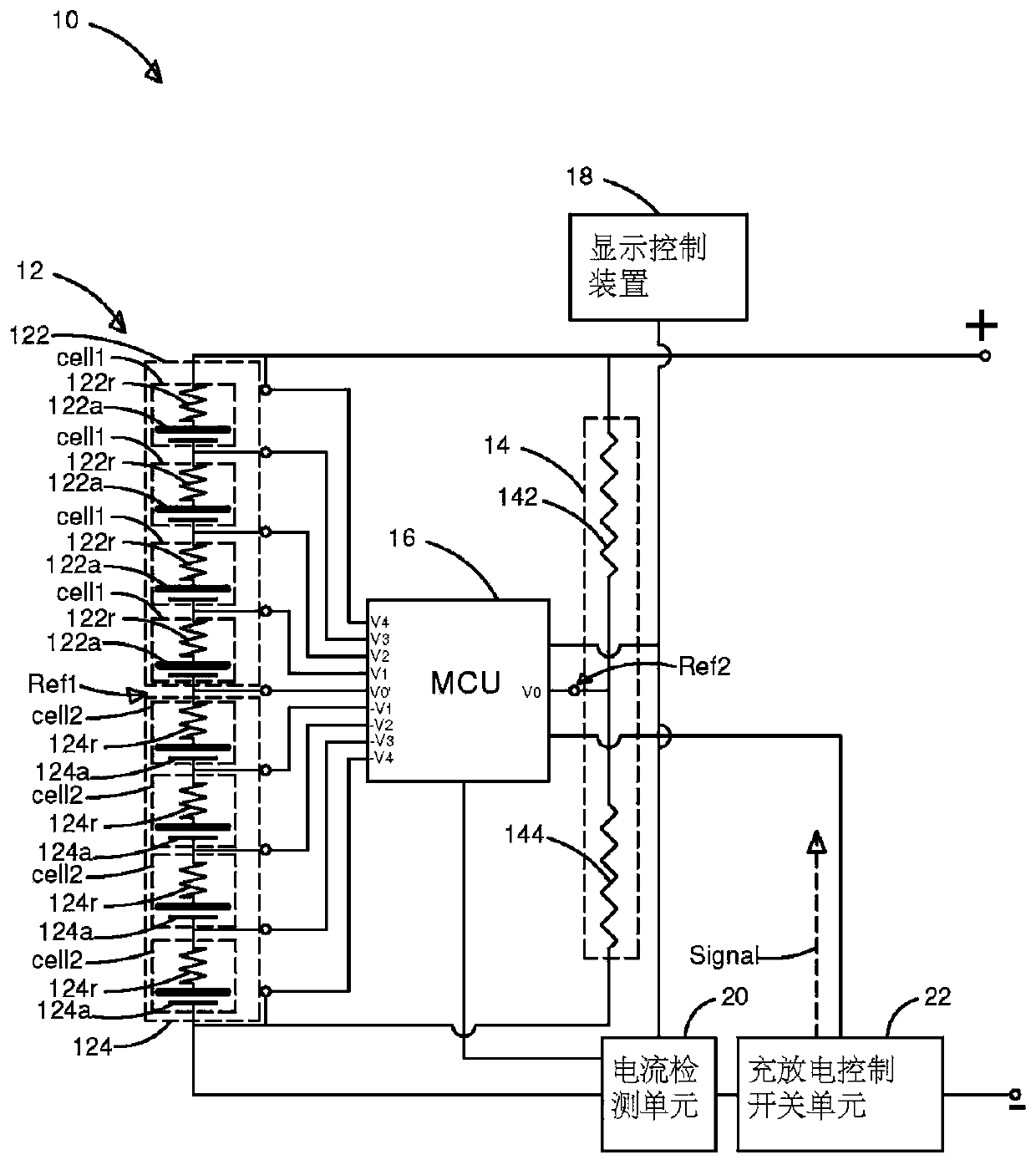
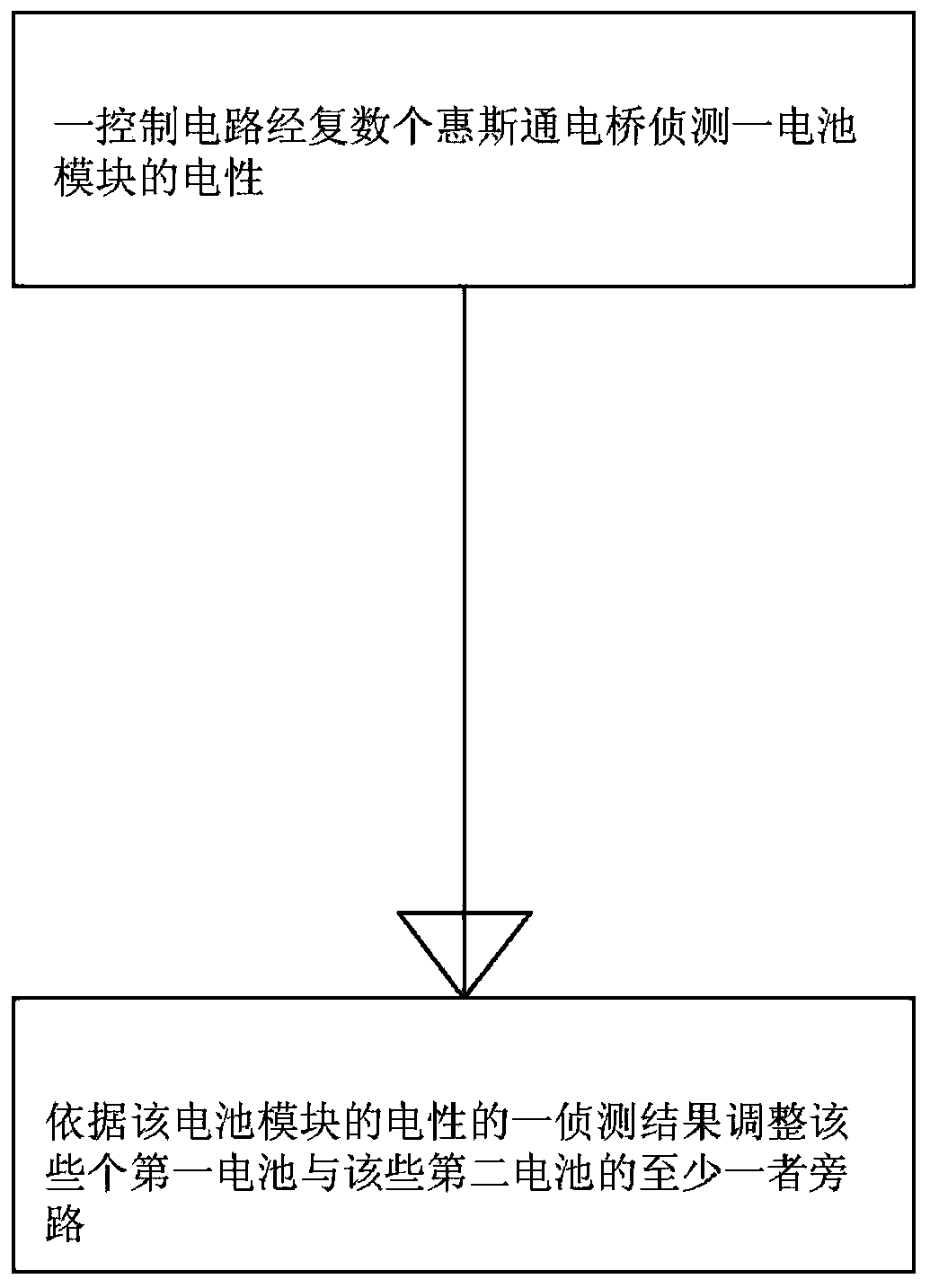
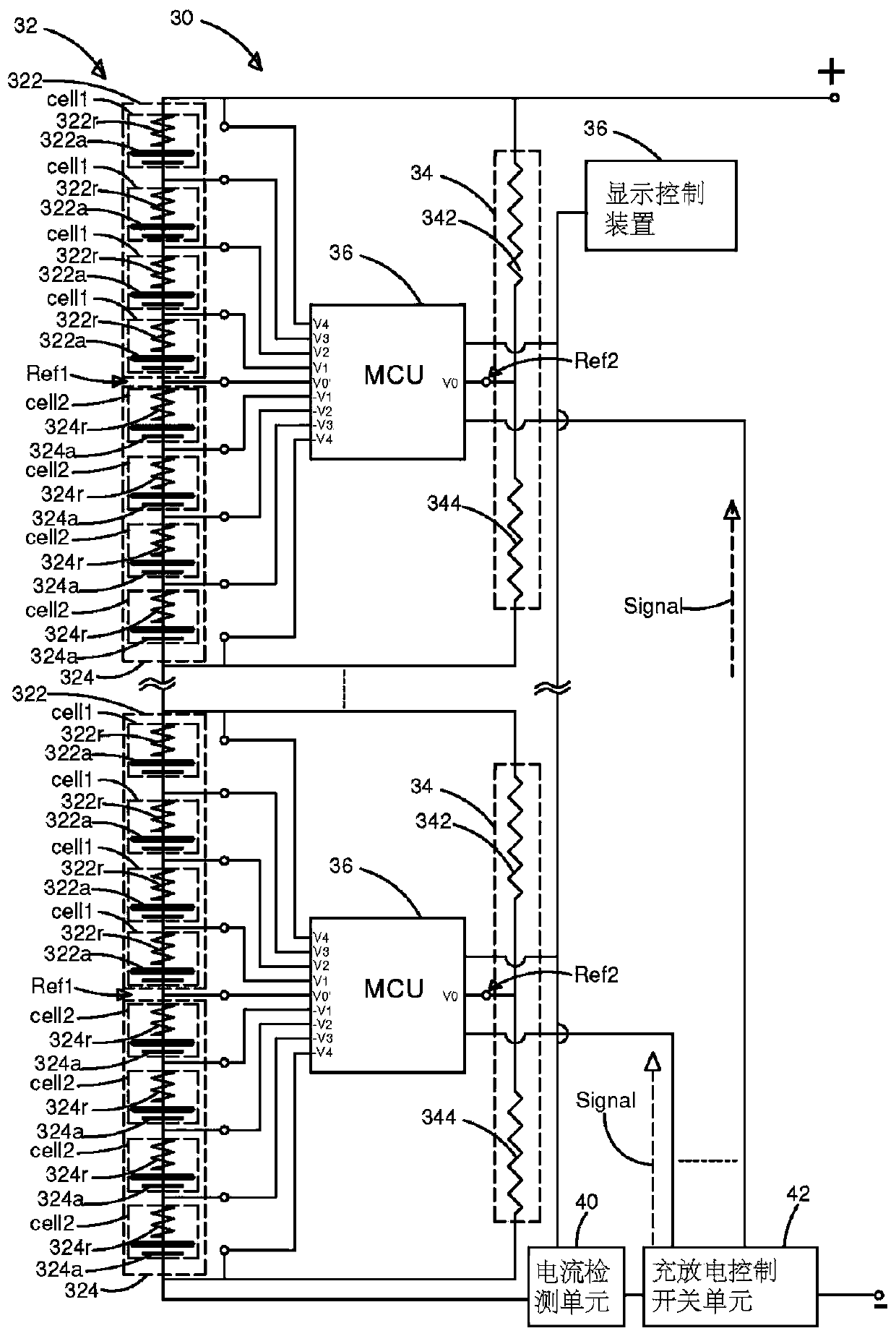
[0059] The present invention breaks the conventional way that each battery in the battery module is equipped with a control circuit to detect the electrical properties of the battery, thus providing a battery management method, the user can switch the detected battery through a single control circuit through the Wheatstone bridge measured battery.
[0060] First, see figure 1 , which is a system diagram of an embodiment of the p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com