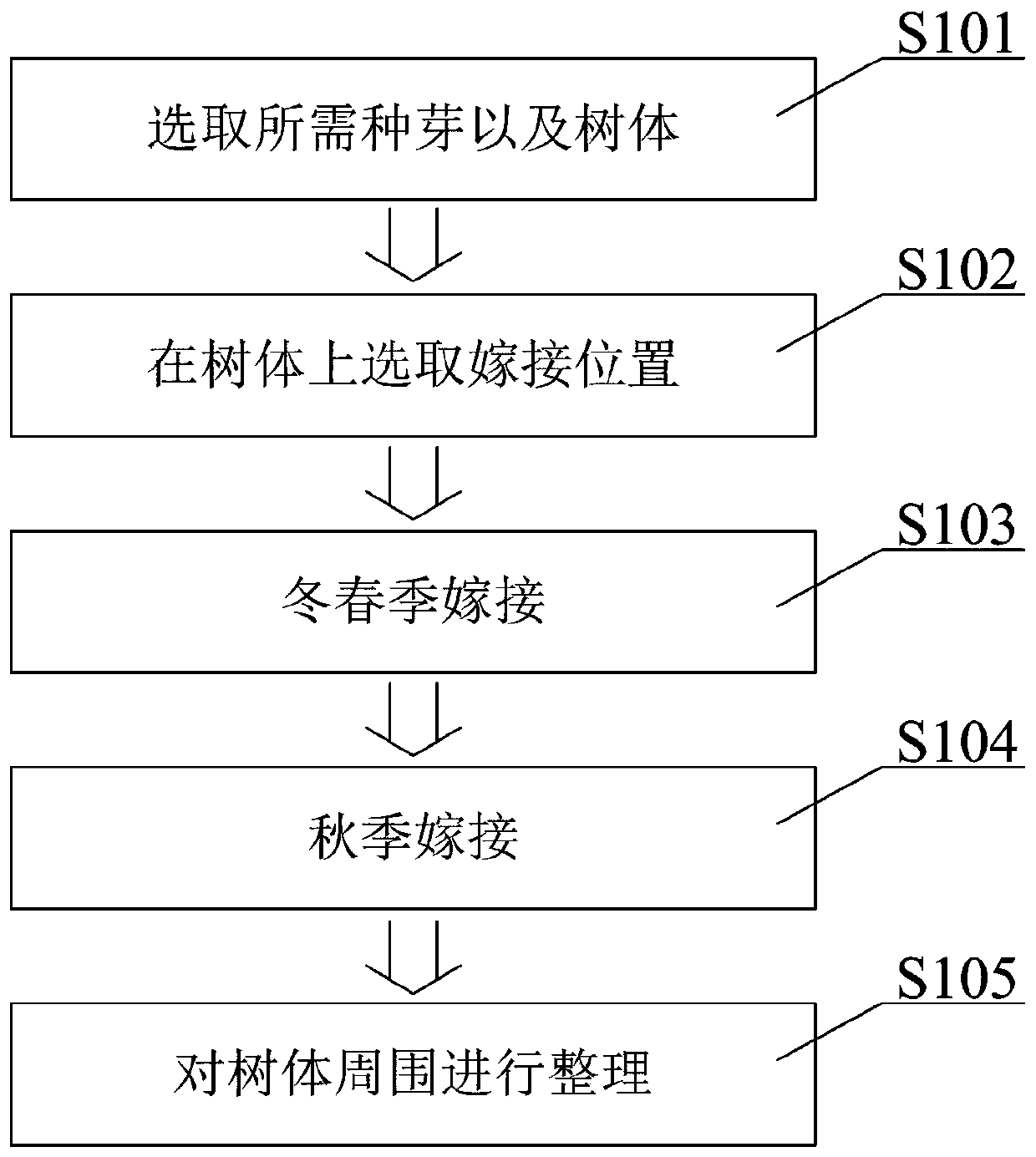
Minimally invasive bud grafting and head changing method for kiwi trees
A kiwifruit and bud grafting technology, applied in the field of kiwifruit minimally invasive budding transfer method, can solve the problems of poor fruit quality, low yield, weakened tree vigor, etc., and achieve the effects of high grafting survival rate, strong tree vigor growth, and prevention of diseases and insect pests.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
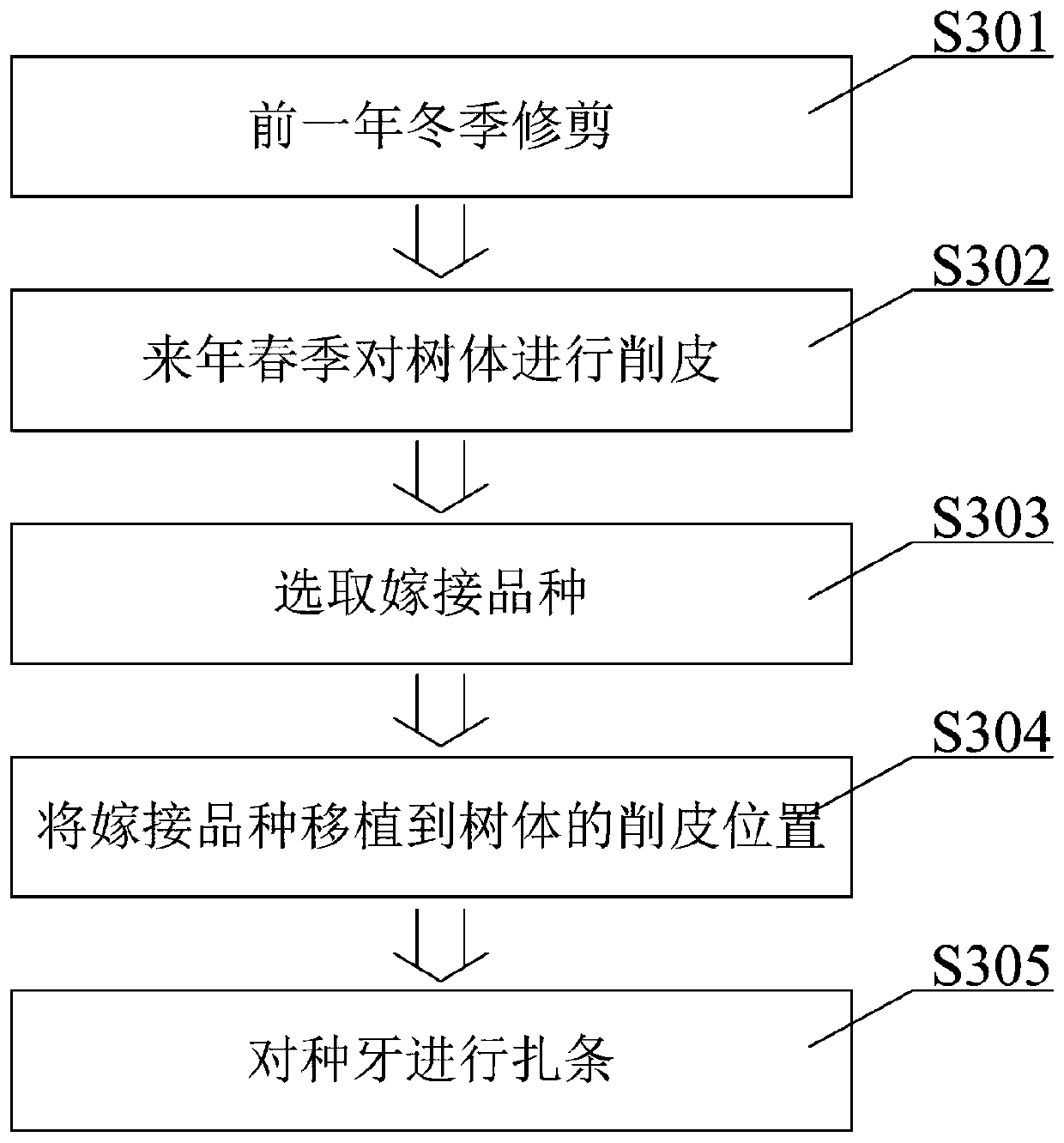
[0060]Embodiment 1: choose full seed buds and kiwifruit old trees, choose the grafting position on the tree body, use the main rod, main vine, branch or fruiting mother branch as the grafting position according to the needs of the use, when pruning in the winter of the previous year Cut off the front branches at the first three centimeters to five centimeters of the grafting site. In the next spring, use a grafting knife to cut a knife with a width of 10 millimeters to 20 millimeters until the xylem, and then cut it upward from the bottom 8 millimeters to 15 millimeters to reach the xylem grafting. Peel the buds according to their size, connect the new varieties (new and excellent varieties to be grafted) stably, select plump buds, first cut the buds flat to reach 8mm to 15mm xylem, and then cut upwards from the bottom of the buds to reach the xylem 8 mm to 15 mm, remove the entire woody bud piece, inlay the cut off bud piece in the part where the rootstock is to be grafted aft...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2: choose full seed buds and kiwifruit old trees, choose the grafting position on the tree body, use main pole, main tendril, pole or fruiting mother branch as grafting position according to the needs of use, when pruning in the winter of the previous year Cut off the front branches at the first three centimeters to four centimeters of the grafting site. In the next spring, use a grafting knife to cut a knife with a width of ten millimeters to fifteen millimeters until it reaches the xylem, and then cut it upward from the bottom eight millimeters to twelve millimeters to reach the xylem grafting. Peel the buds according to their size, connect the new varieties (new and excellent varieties to be grafted) stably, select plump buds, cut the buds flat to reach 8 mm to 13 mm xylem, and then cut upwards from the buds to reach the xylem 8 mm to 12 mm, remove the entire woody bud piece, inlay the cut off bud piece on the part of the rootstock to be grafted after the s...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Embodiment 3: choose full seed buds and kiwifruit old trees, choose grafting positions on the tree body, use main bar, main vine, branch or fruiting mother branch as grafting positions according to the needs of use, when pruning in the winter of the previous year Cut off the front branches at the first 4 cm to 5 cm of the grafting site. In the next spring, use a grafting knife to cut 12 mm to 20 mm wide until the xylem, and then cut upwards from the bottom 10 mm to 15 mm to reach the xylem. The size of the grafted buds is peeled off, and the new varieties (new and excellent varieties to be grafted) are stably grafted. Select plump buds, first cut a knife on the buds to reach the xylem by 10 mm to 15 mm, and then make a knife from the bottom of the buds to reach the xylem. The xylem is 10 mm to 15 mm, remove the entire woody bud piece, and inlay the cut bud piece on the part after grafting and skinning of the rootstock to be jointed, and tie the tree body tightly with pla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com