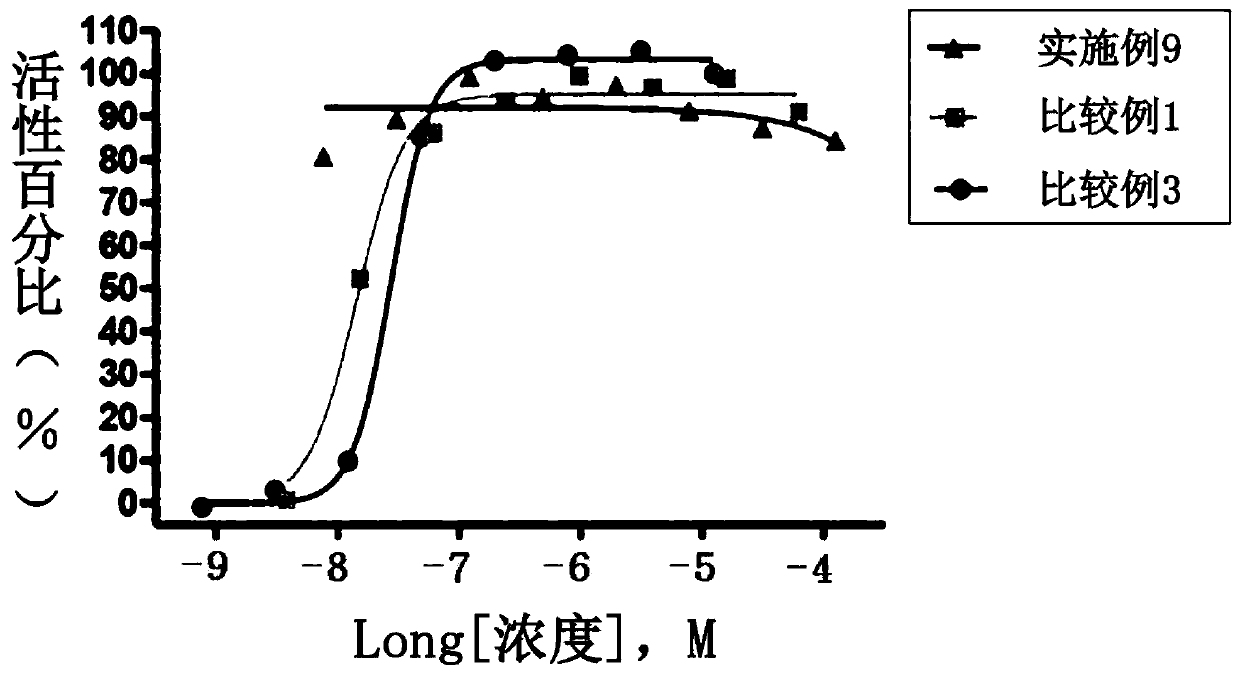
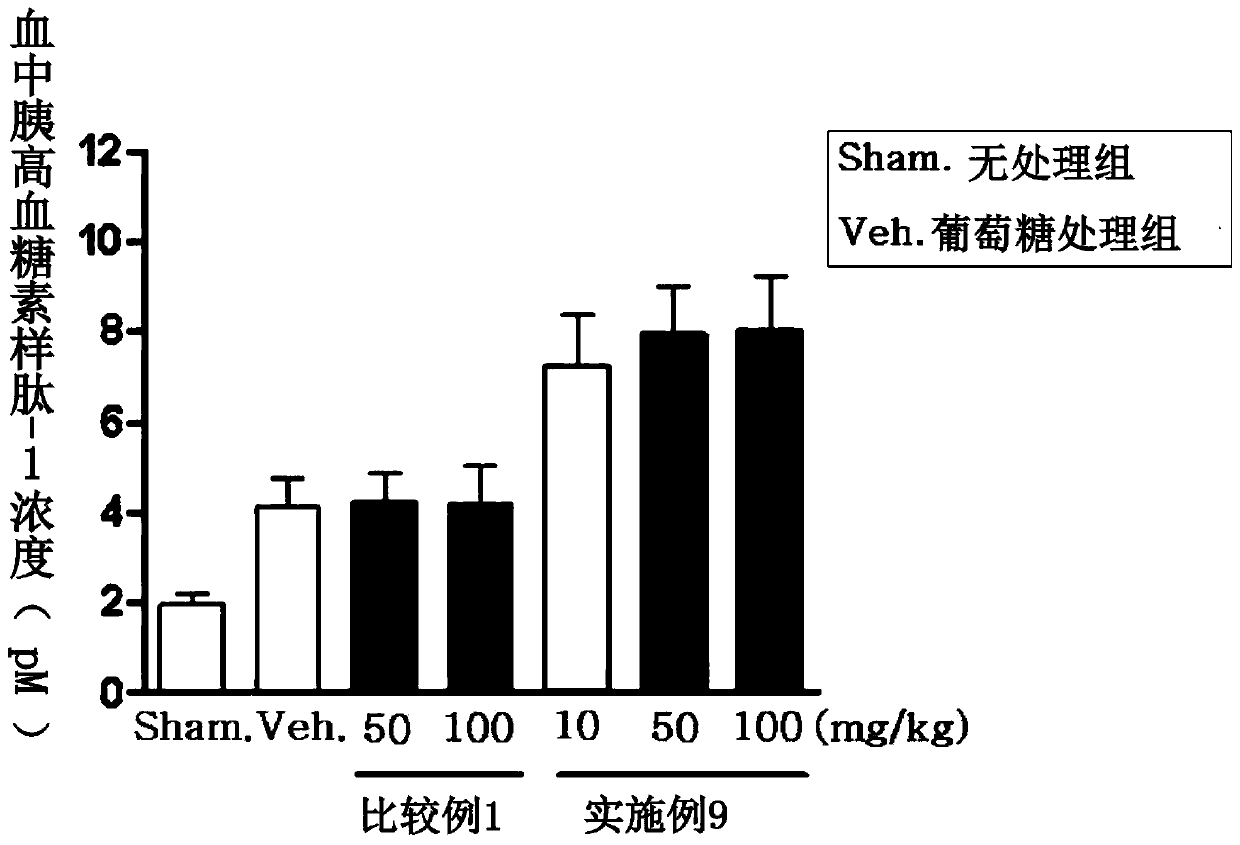
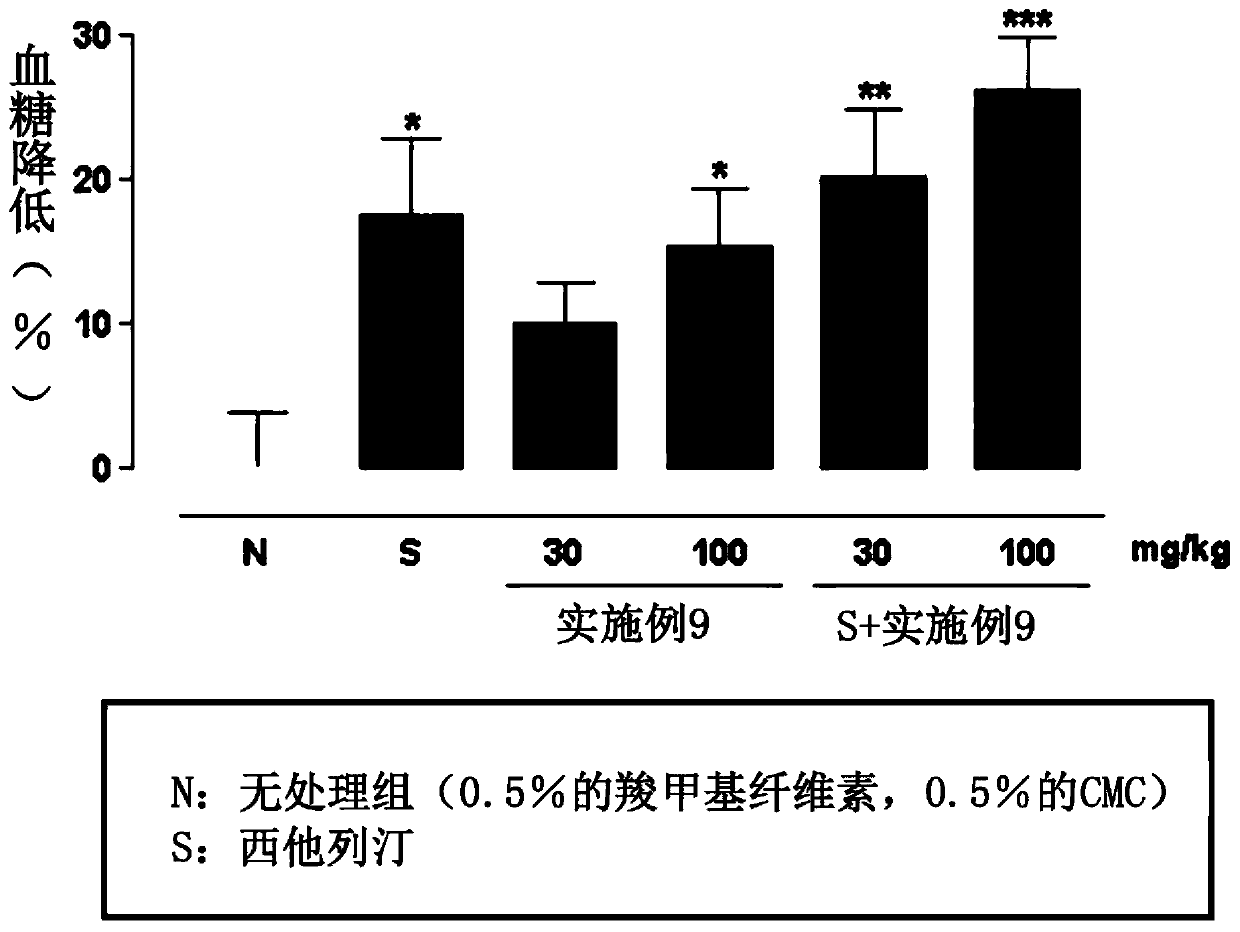
Composite preparation for preventing or treating metabolic diseases
A metabolic disease and inhibitor technology, applied in the field of compound preparations for the prevention or treatment of metabolic diseases, can solve the problems of low therapeutic responsiveness and achieve excellent blood sugar lowering effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0120] The preparation method of the compound represented by Chemical Formula 1 of the present invention is as follows.
[0121] Preparation method 1
[0122] As shown in the following reaction formula 1, the preparation method of the compound represented by chemical formula 1 of the present invention comprises: step 1, making the compound represented by chemical formula 2 and the compound represented by chemical formula 3 undergo condensation reaction to prepare the compound represented by chemical formula 4 the compound; and step 2, performing a reduction reaction on the compound represented by Chemical Formula 4 prepared in the above Step 1 to prepare the compound represented by Chemical Formula 1.
[0123] Reaction 1:
[0124] (In the above reaction formula 1, R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , R 4A , R 4B , R 5 , A, E, n and X are the same as defined in the above chemical formula 1; Y is C 1-10 straight-chain or side-chain alkyl).
[0125] Hereinafter, the preparation method of...
preparation example 1
[0204] Preparation of 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-hexenoic acid ethyl ester
[0205]
[0206] Under a nitrogen atmosphere, inject 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-hex-4-enoic acid (20.0 g) and ethanol (200 mL) into a 250 mL flask, and after stirring to complete the dissolution, slowly Sulfuric acid (9.6 mL) was instilled dropwise. Then, reflux stirring was performed for 6 hours or more, and when the reaction was completed, distilled water (150 mL) was slowly dripped, and then ethyl acetate (200 mL) was injected to perform extraction. The extracted layers were dried under reduced pressure to obtain the target compound (19.5 g, 85.7%).
[0207] 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ7.25(2H, d), 6.78(2H, d), 4.95(1H, s), 4.14(2H, m), 4.04(1H, m), 2.68(2H, m), 1.84(3H, d), 1.29 (3H,t).
preparation example 2
[0208] Preparation of (S)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-hexenoic acid ethyl ester
[0209]
[0210] Under a nitrogen atmosphere, (S)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-hex-4-enoic acid (20.0 g) and ethanol (200 mL) were injected into a 250 mL flask, and after dissolution was completed by stirring, Sulfuric acid (9.6 mL) was slowly dripped at room temperature. After that, reflux stirring was performed for 6 hours or more, and when the reaction was completed, distilled water (150 mL) was slowly dripped, followed by extraction with ethyl acetate (200 mL). The extracted layers were dried under reduced pressure to obtain the target compound (21.2 g, 93.2%).
[0211] 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ7.25(2H, d), 6.78(2H, d), 4.95(1H, s), 4.14(2H, m), 4.04(1H, m), 2.68(2H, m), 1.84(3H, d), 1.29 (3H,t).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com