Intestinal barrier function-enhancing composition
A technology of intestinal barrier function and composition, applied to the application of improving intestinal barrier function, improving intestinal barrier function, and the field of intestinal barrier function improving enhancer of gallic acid, which can solve the problem of unfavorable economy or safety and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving intestinal barrier function and enhancing the effect of improving intestinal barrier function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0113] Using gallic acid as a sample, the effect of improving intestinal barrier function in Caco-2 cells was evaluated by the above evaluation method. Gallic acid (Nacalai Tesque Co., Ltd.) was added so that the concentration in the test solution would be 100 μM (μmol / L).
[0114] As a reference, 100 μM quercetin (Funakoshi Co., Ltd.) was added to the test solution instead of gallic acid, and the intestinal barrier function improving effect was similarly evaluated. For quercetin, a tight junction barrier function improving action has been reported (Non-Patent Document 1).
[0115] As a result, the TEER reduction inhibition rate was 86.5% for gallic acid and 75.0% for quercetin. It has been confirmed that gallic acid at 100 μM has a 1.15-fold higher inhibition rate of TEER reduction than quercetin at the same concentration.
Embodiment 2
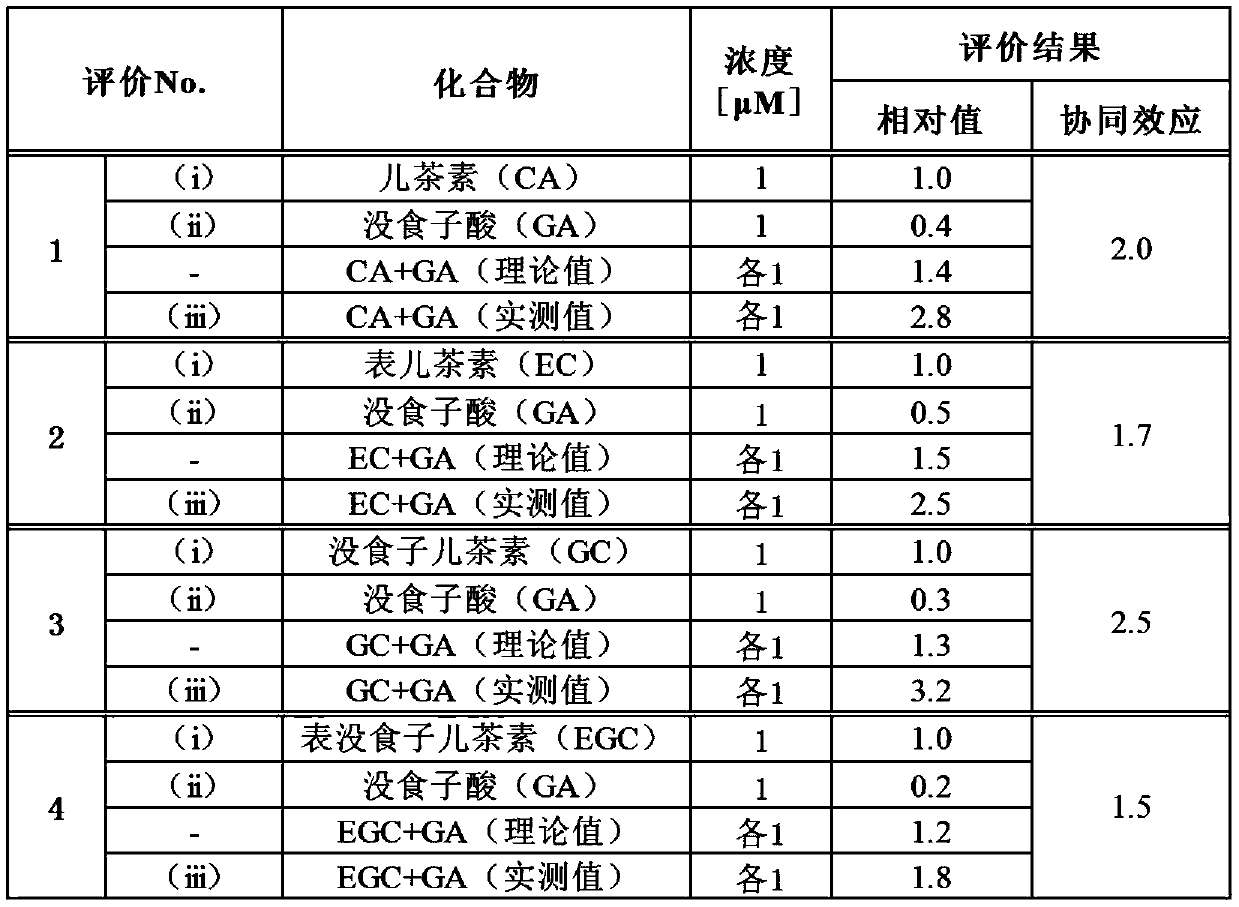
[0117] In evaluations 1 to 4, gallic acid and the following phenolic compounds were used as samples.
[0118] Evaluation 1: Catechin (CA) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.)
[0119] Evaluation 2: Epicatechin (EC) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.)
[0120] Evaluation 3: Gallocatechin (GC) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.)
[0121] Evaluation 4: Epigallocatechin (EGC) (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.)
[0122] The phenolic compounds used in Example 2 are flavanols.
[0123] In evaluations 1 to 4, for the samples shown in (i) to (iii) in each evaluation system, the TEER decrease inhibition rate (%) in Caco-2 cells was evaluated by the evaluation method described above.
[0124] (i) Phenolic compounds (CA, EC, GC or EGC) (1 μM)
[0125] (ii) Gallic acid (GA) (1 μM)
[0126] (iii) Combined use of phenolic compound (1 μM) and gallic acid (1 μM) (phenolic compound + GA)
[0127] The sample was added to the test liquid so that the concentration in the test liquid ...
Embodiment 3
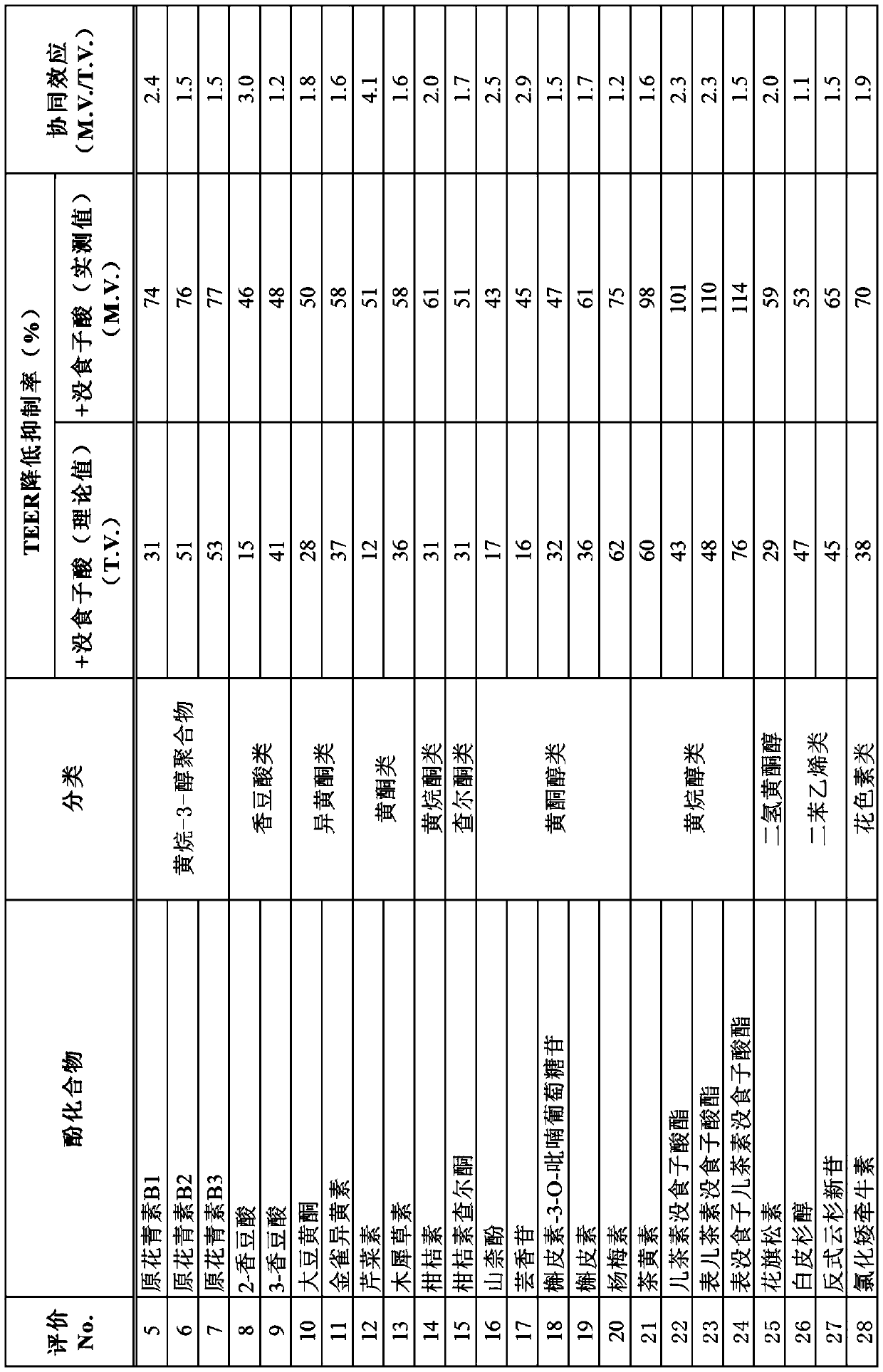
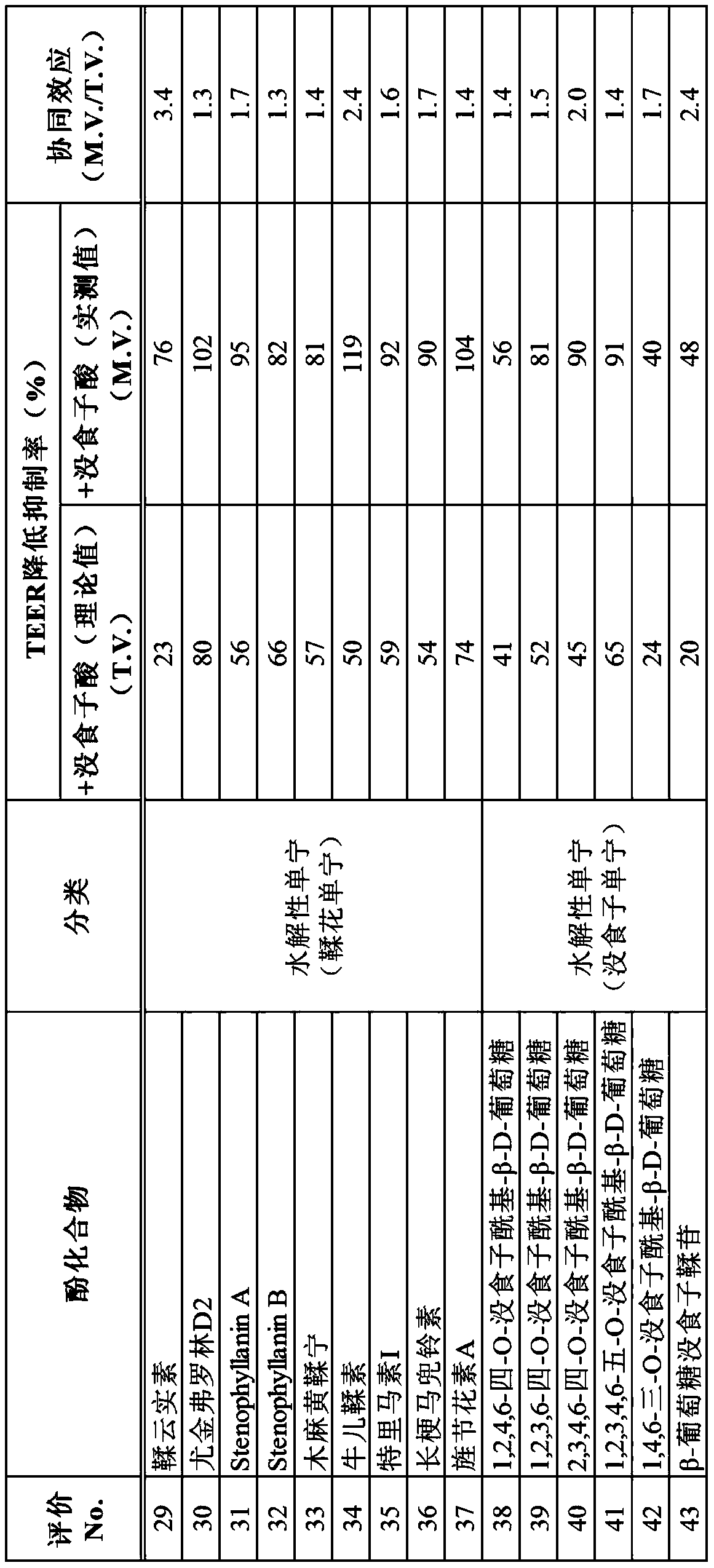
[0138] Using the above-mentioned evaluation method using Caco-2 cells, gallic acid and the phenolic compounds shown in Tables 2 to 3 were used as samples to evaluate intestinal barrier function improvement effects (Evaluations 5 to 43).
[0139] In the same manner as in Example 2, the following (i) to (iii) were used as samples in each evaluation system, and the TEER decrease inhibition rate (%) was evaluated.
[0140] (i) Phenolic compounds (10 μM for compounds shown in Table 2; 1 μM for compounds shown in Table 3)
[0141] (ii) Gallic acid (10 μM in the evaluation system of the compounds shown in Table 2; 1 μM in the evaluation system of the compounds shown in Table 3)
[0142] (iii) Combined use of phenolic compound and gallic acid (10 μM in the evaluation system of the compounds shown in Table 2; 1 μM in the evaluation system of the compounds shown in Table 3)
[0143] The sample was added to the test liquid so that the concentration in the test liquid became the above-me...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com