Subsynchronous resonance risk quantitative evaluation method based on electrical damping at modal frequency
A subsynchronous resonance, electrical damping technology, applied in design optimization/simulation, special data processing applications, complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve problems such as inability to comprehensively analyze the degree of system risk, large workload, and small scale
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
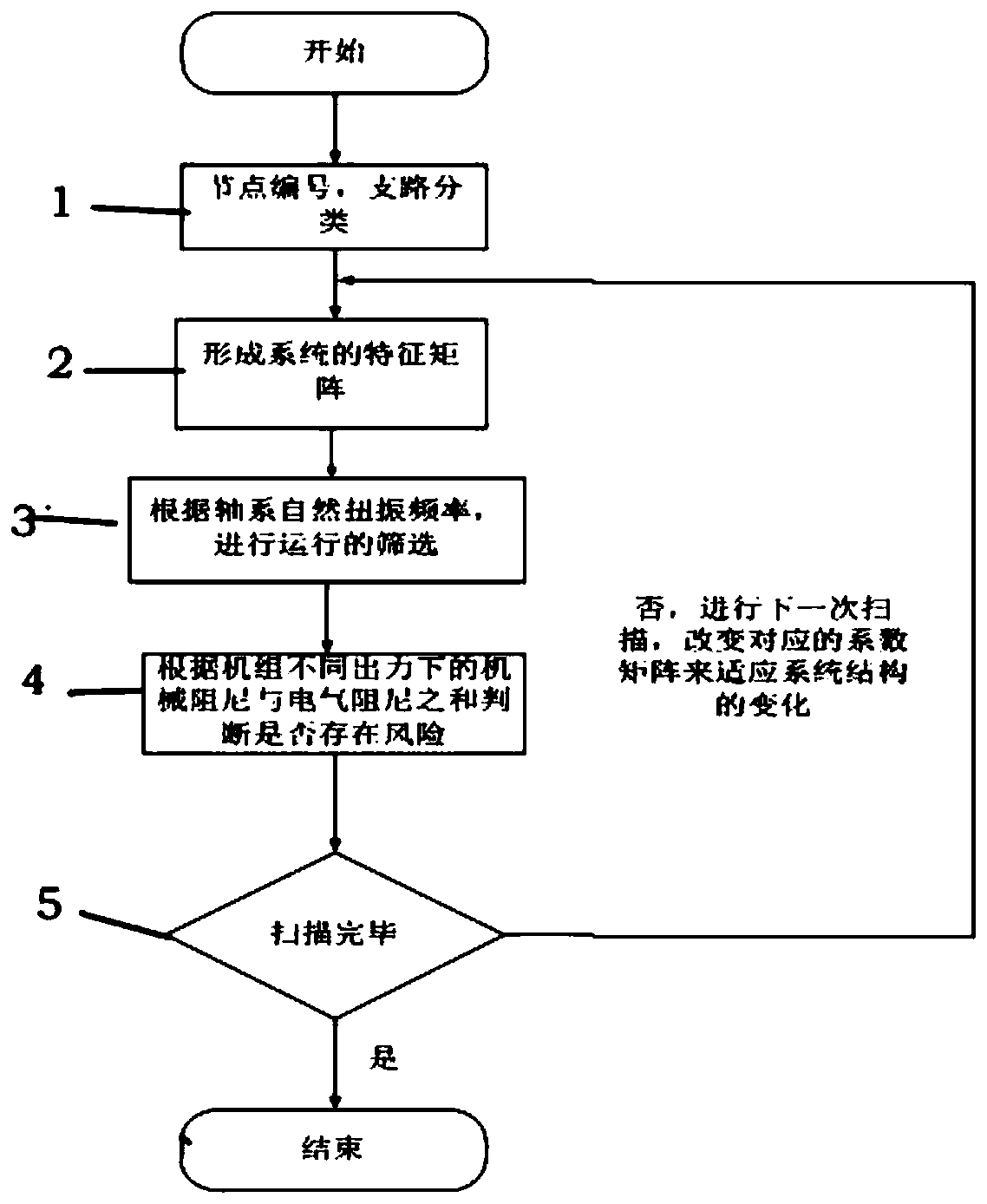
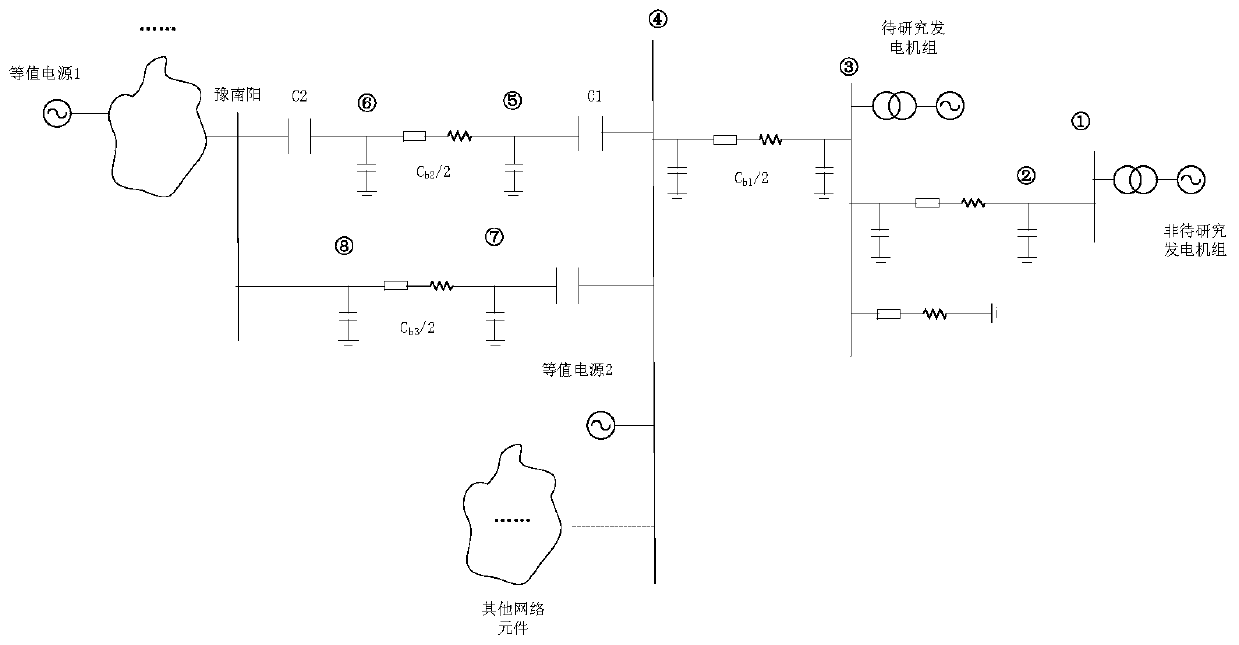
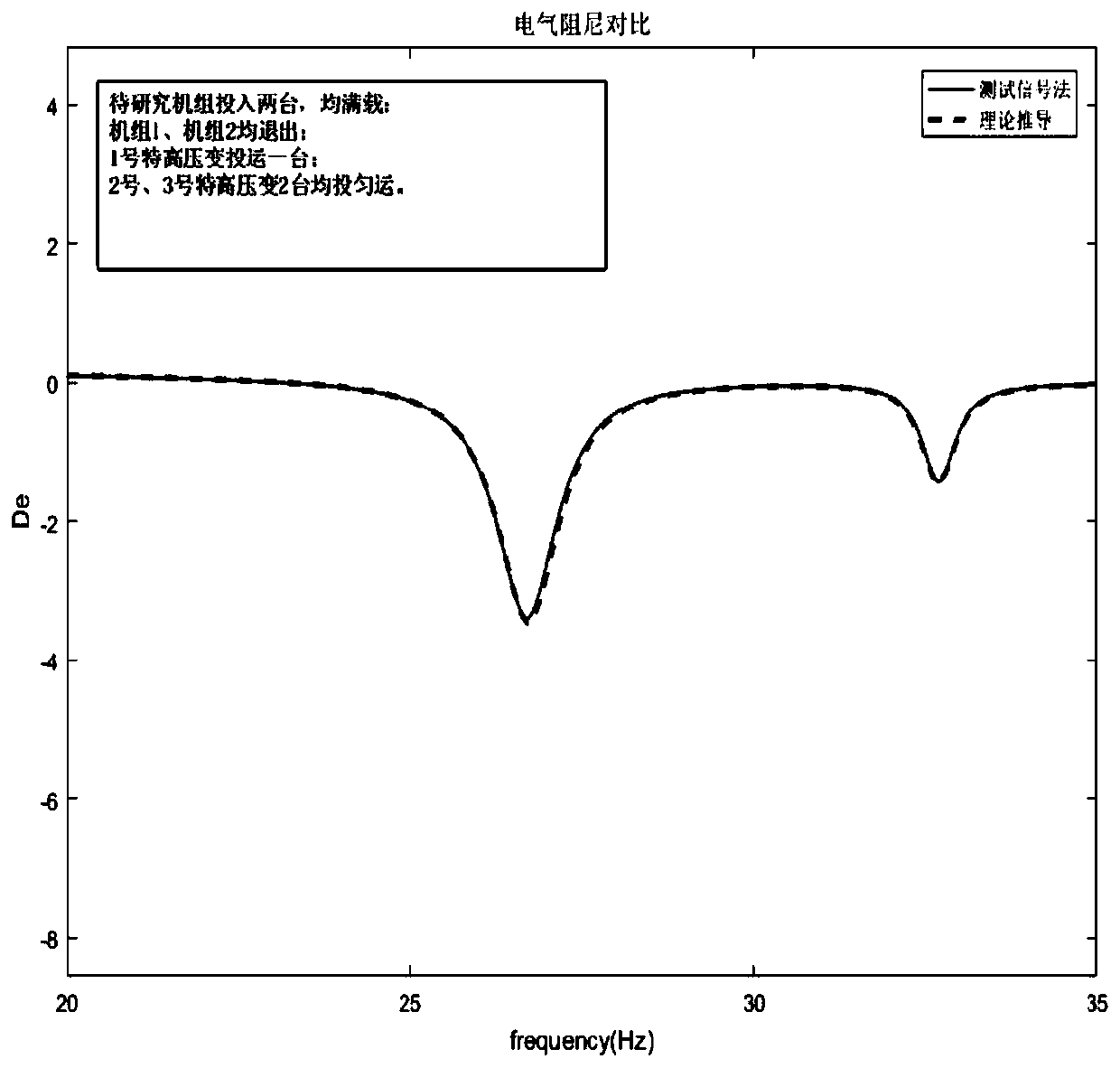
[0118] In order to verify the correctness of the subsynchronous resonance risk assessment method for synchronous generating units connected to complex AC grids with series compensation, the method and accuracy of the present invention will be further described in conjunction with a domestic actual project. The grid structure system is as follows Figure 5 As shown, in this system, the shafting natural torsional vibration frequency of the unit similar to the researched unit has a large difference from the shafting natural torsional vibration frequency of the researched unit, so the unit can be set at a fixed frequency of subtransient reactance The line length has been marked in the figure, and the line parameters of the system are shown in Table 1. The three natural torsional vibration modal frequencies of the unit to be studied are 21.38Hz, 26.5Hz, and 56.64Hz, respectively, and the first two frequency components are The main concern is the subsynchronous oscillator frequency c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com