Porous meniscus substitute modeling and preparation method thereof
A modeling method and meniscus technology, applied in the field of bionic materials, can solve the problems of limited biomechanical properties, single pore structure, unfavorable implant fixation, etc., and achieve the effects of short preparation time, rapid prototyping, and avoiding stress concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A method for preparing a porous meniscus substitute model, the steps are as follows:
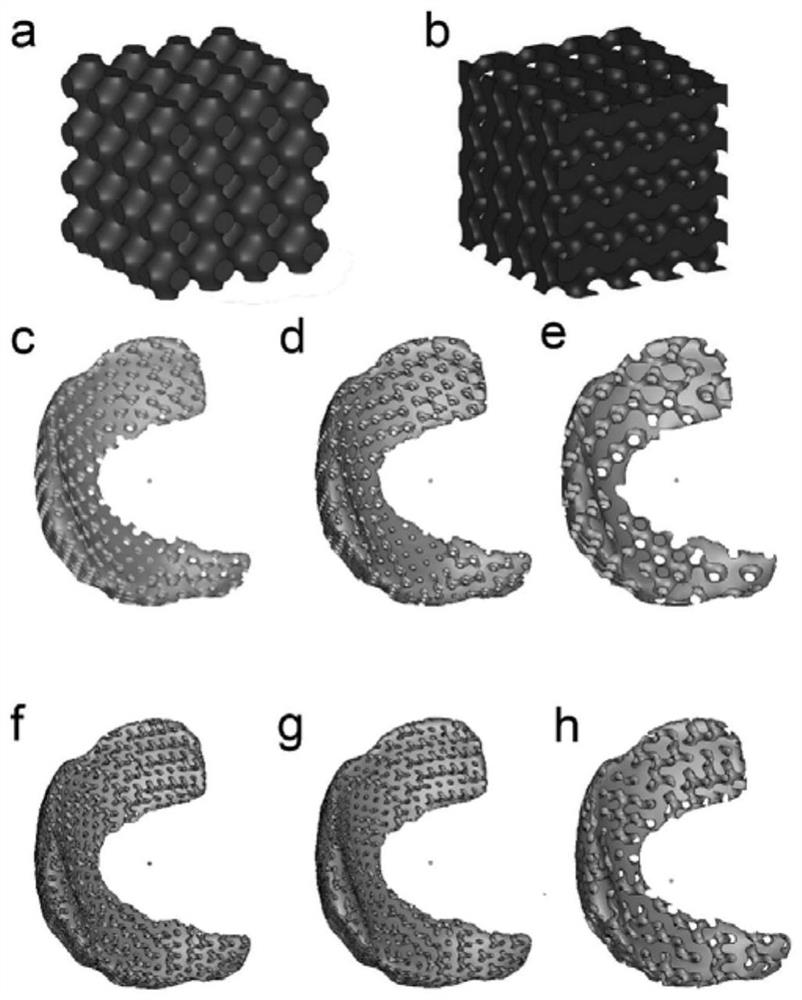
[0034] (1) Use CT to scan the meniscus of the patient, and perform image processing on the scanned image to obtain a meniscus model that matches the patient. The image processing steps are as follows: Because the distance between the meniscus and the surrounding tissue is very close, it is difficult to directly perform Contour extraction, so first binarize the image, then use the median filter to remove the noise doped in the process of CT image acquisition and digitization, and then use the edge detection method to perform edge detection and contour extraction on the filtered image. The batch-processed images are imported into Mimics software, and the curve profile is fitted to finally obtain a meniscus model that matches the patient (the 3D reconstruction model of human meniscus tissue after CT scan image processing is shown in figure 2 );
[0035] (2) Obtain the relevant peak str...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The preparation method of the porous meniscus substitute model in this example is the same as in Example 1, the difference is that the specific process of the parametric modeling method is as follows: the irregular Gyroid structure is generated by the triple periodic (TPMS) primitive parameter modeling method As a porous structure, adjust the pore shape, pore diameter and porosity of the porous meniscus substitute model by adjusting the construction parameters of the Gyroid structural surface. Gyroid surfaces see figure 1 b, The original porous structure can be generated by finding the ϕ = 0 isosurface of the TPMS equation as follows. This surface is the boundary between solid and void material phases.
[0045] (Ⅱ)
[0046] In formula (II), the pore size and surface structure are controlled by the parameters a, b and c in the above function. The porosity is controlled by the parameter d. An area of Φ≥0 indicates a solid, and an area of Φ<0 indicates a pore. (...
Embodiment 3
[0053] The design method of the porous meniscus substitute model in this embodiment is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
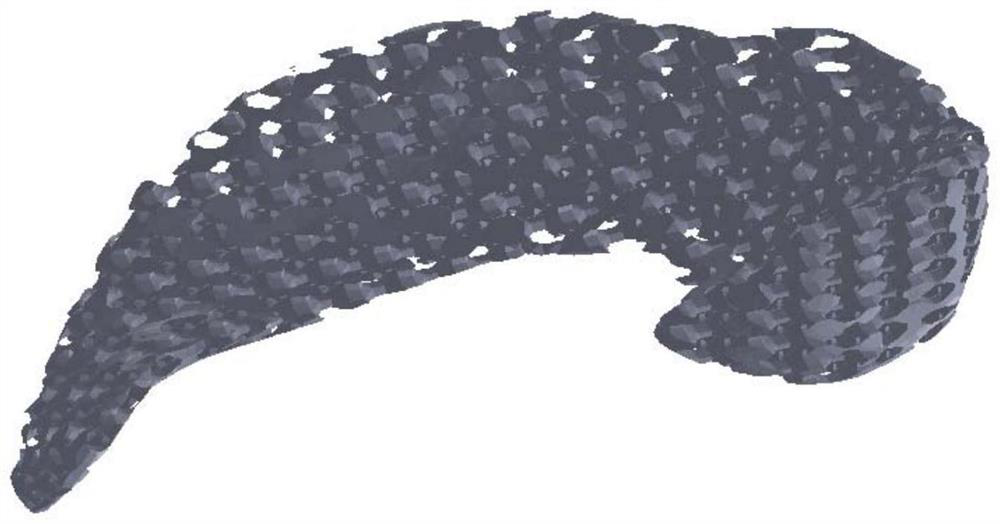
[0054] When using the prepared porous meniscus substitute model to prepare the porous meniscus substitute, the method adopted in this embodiment is the 3D printing method, using double nozzle printing, and filling the hydrogel through the 3D printer. In this embodiment, the hydrogel is poly Oxyethylene polyoxypropylene ether block copolymer, the support material is polycarbonate polyurethane (PCU) particles.
[0055] The specific steps are as follows: slice the porous meniscus substitute model to obtain the printing path of the 3D printer (the slice process is to use related software, this embodiment is Simplify 3D, set the diameter of the nozzle to 0.4 mm, the height of the printing layer to 0.3 mm, The filling rate is 20%, the printing speed is 2 mm / s, and the support filling angle is 45°. The porous meniscus substitute is sliced to obtain the printing...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Shear stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com