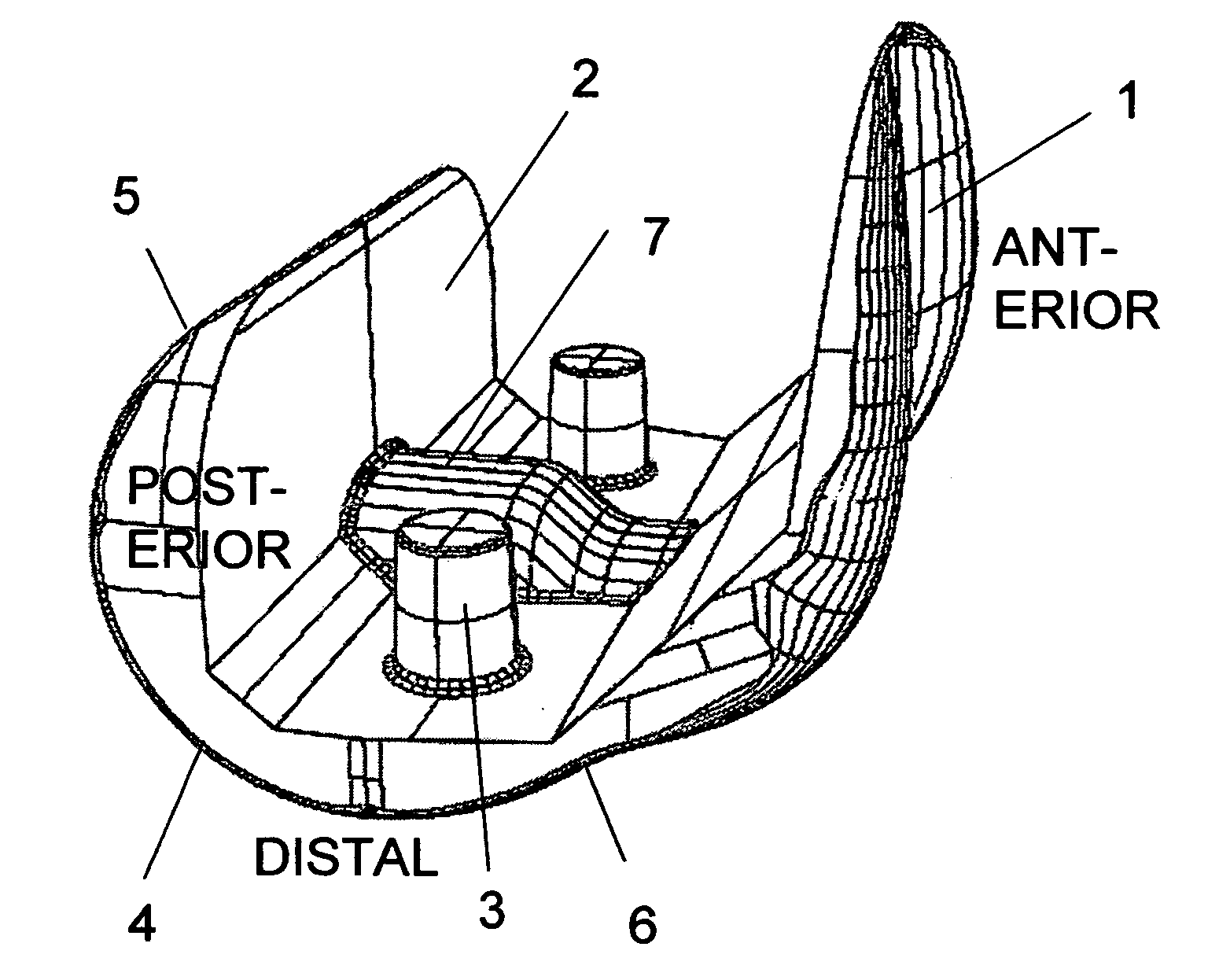
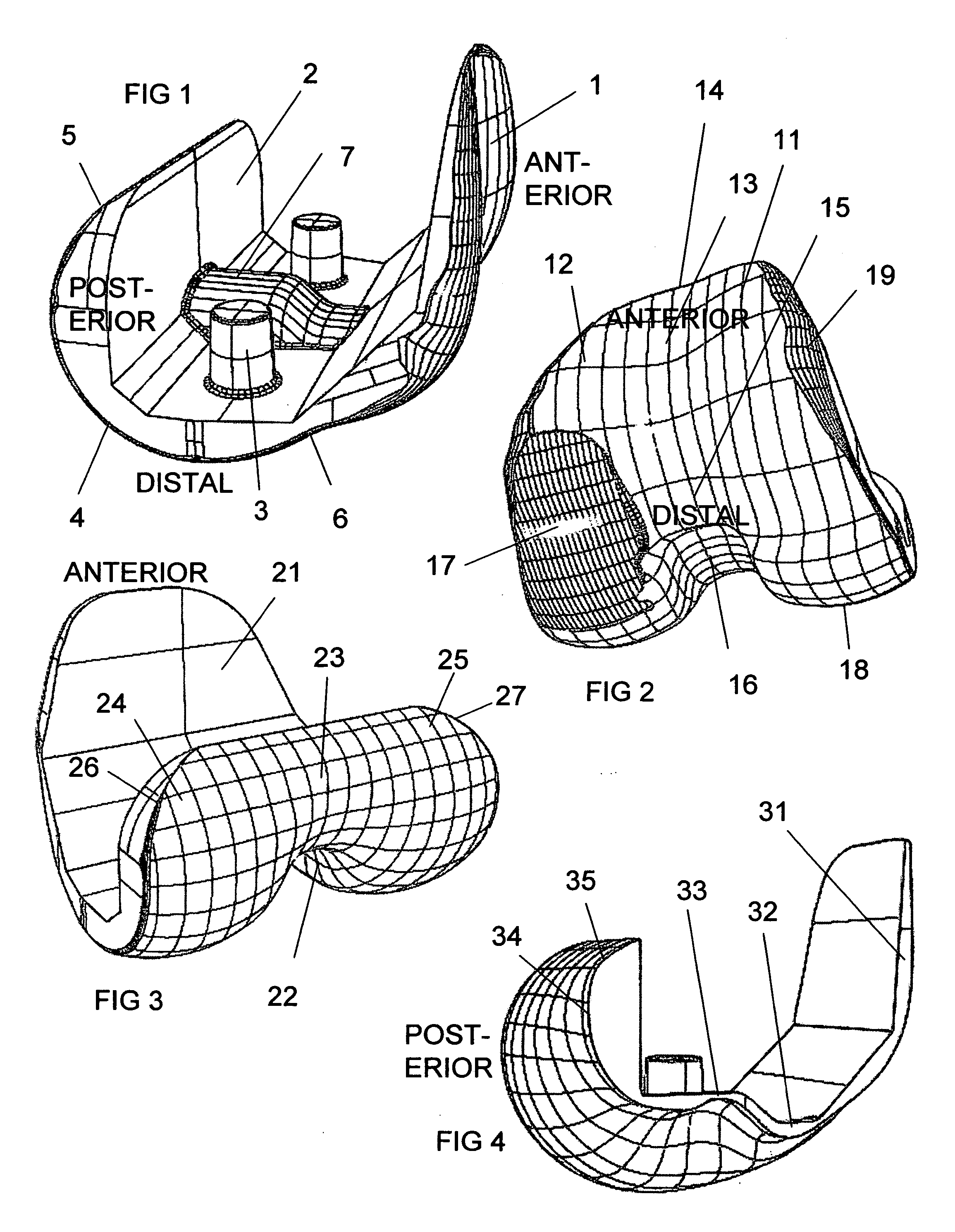
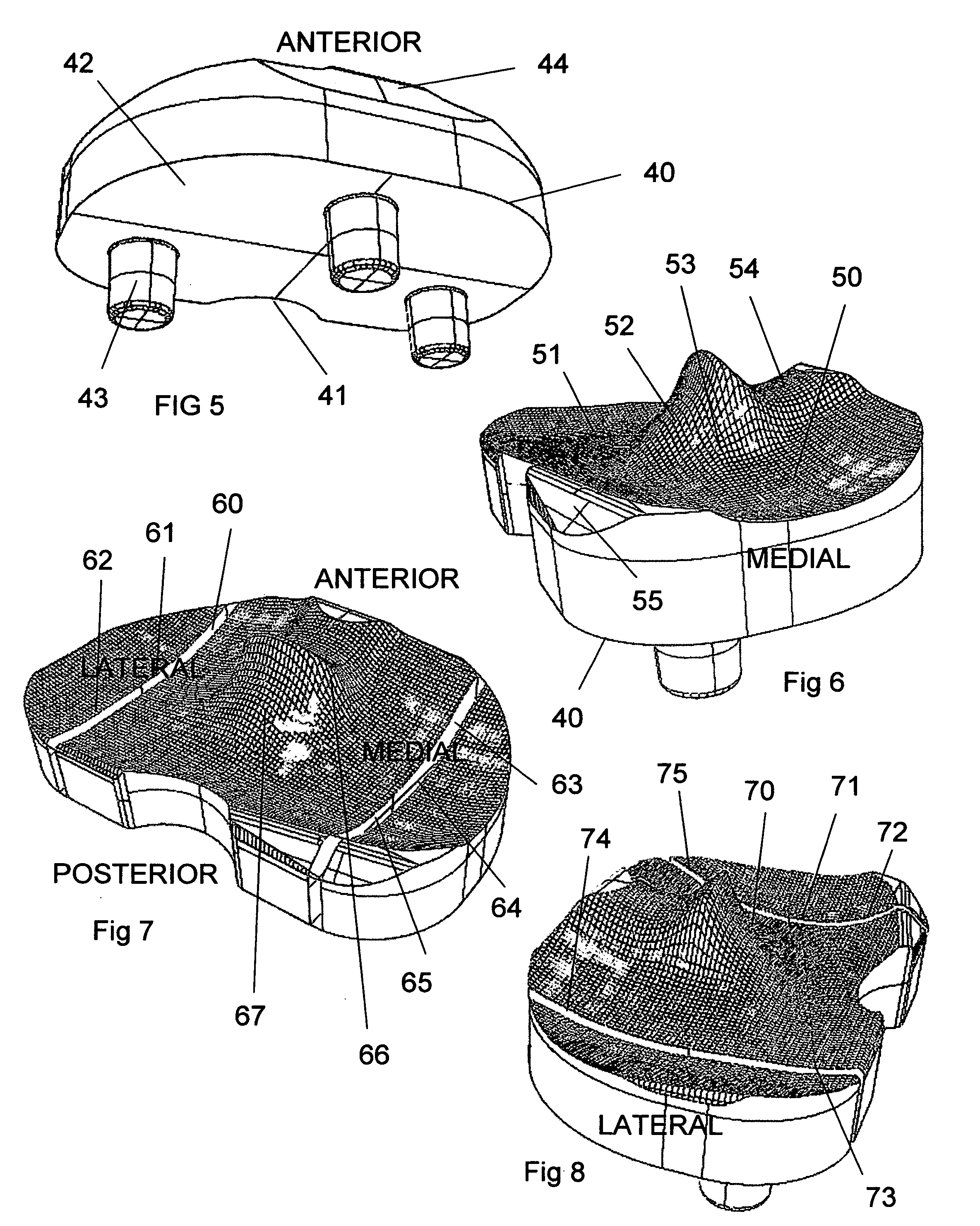
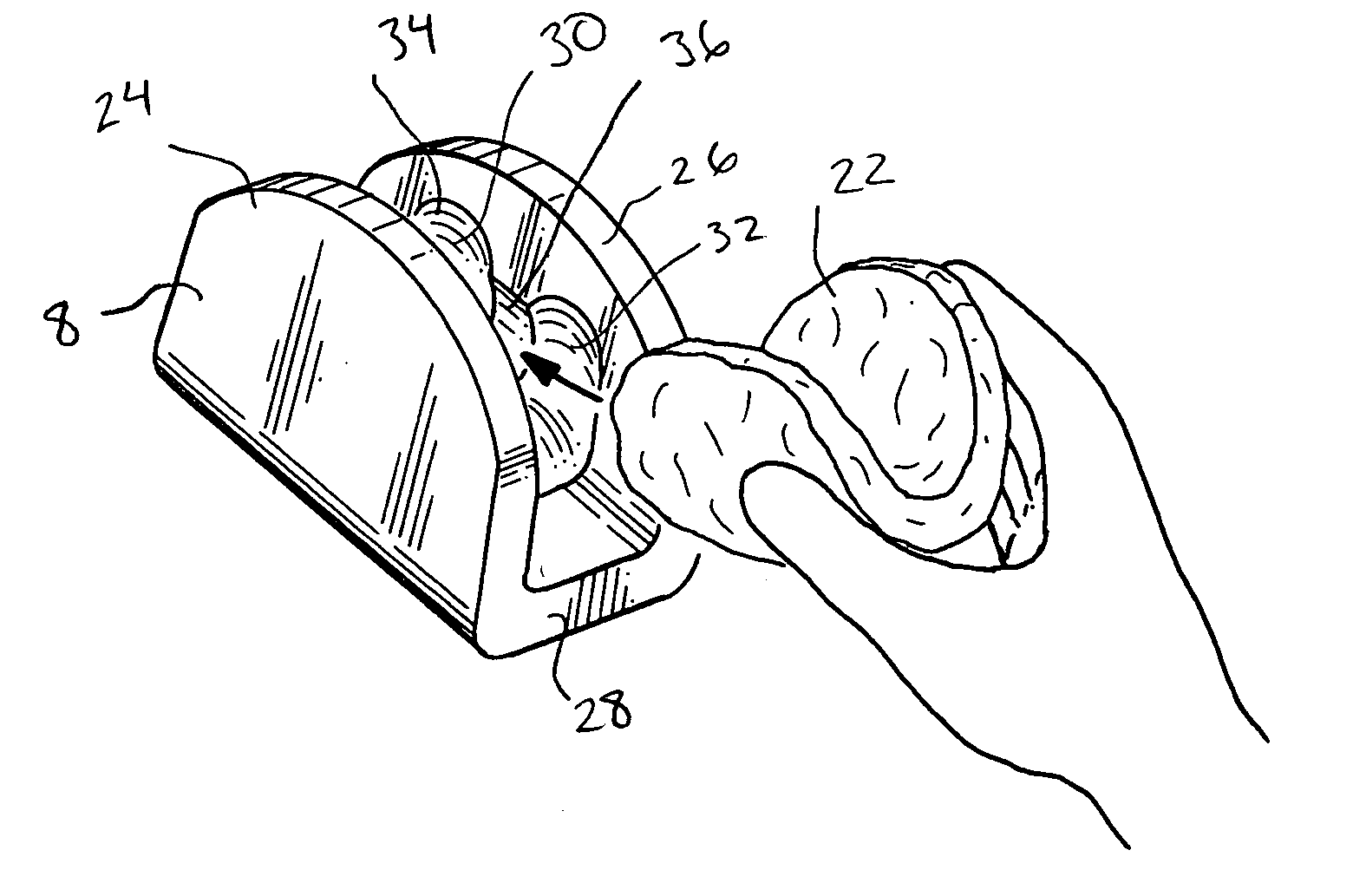
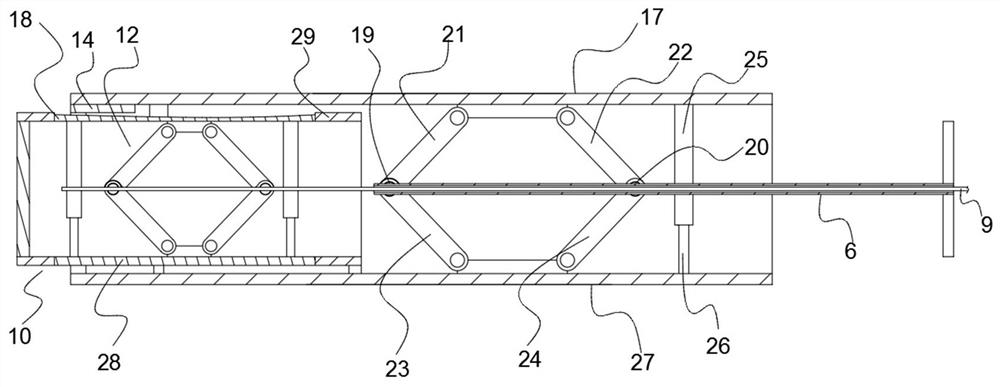
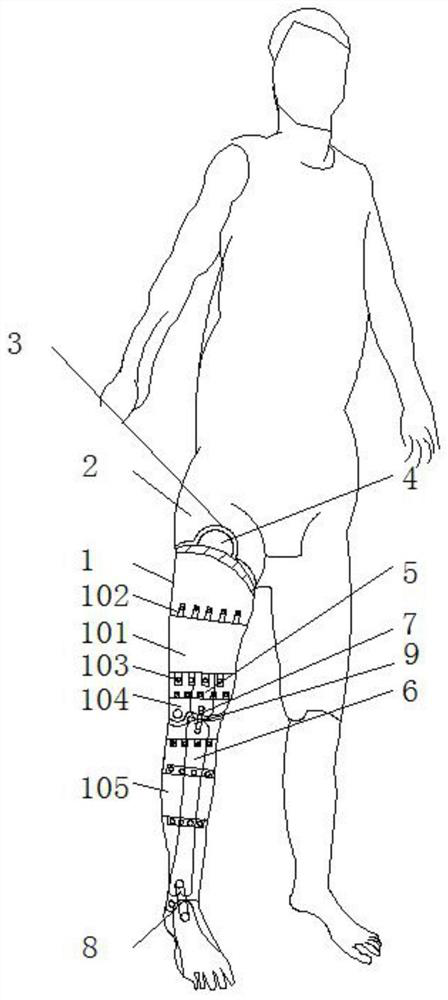
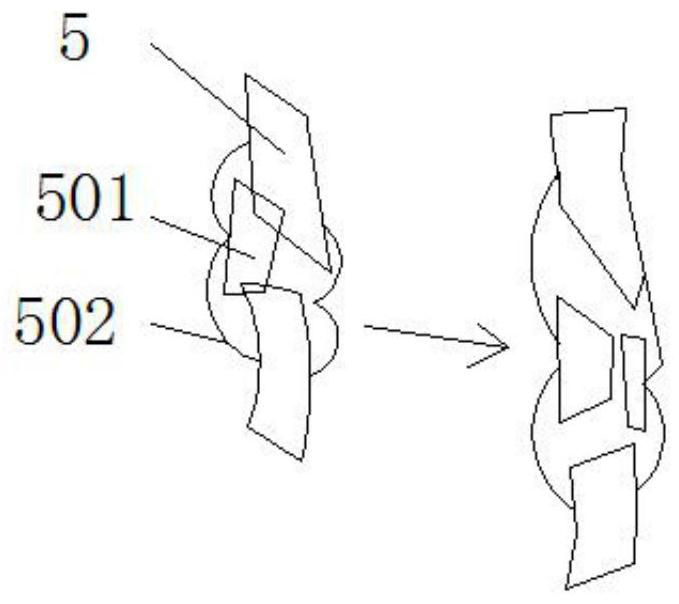
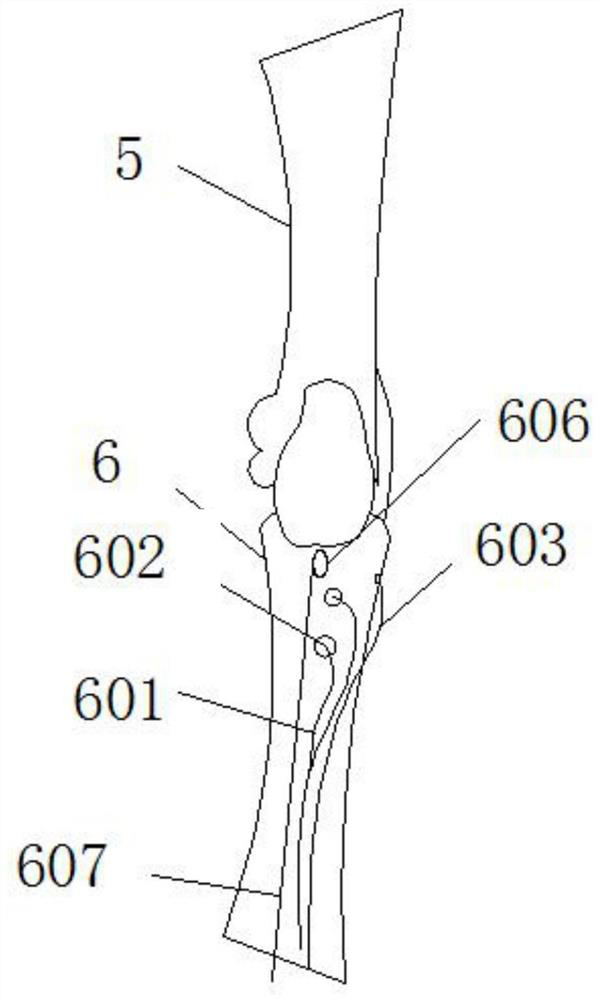
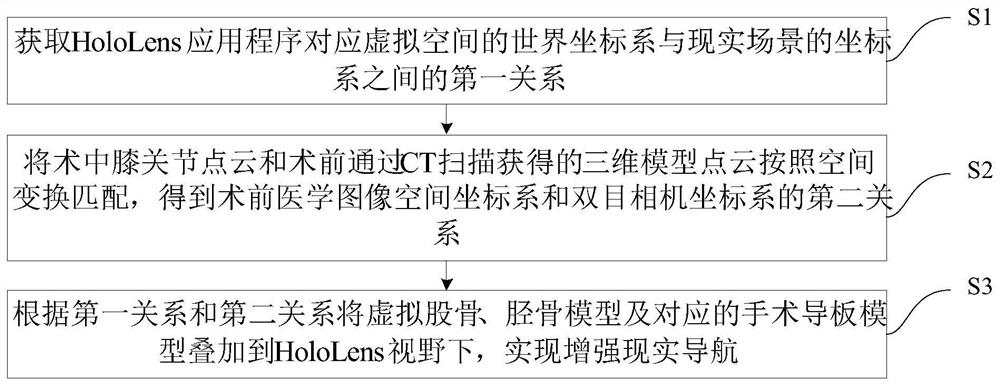
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Femur tibia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
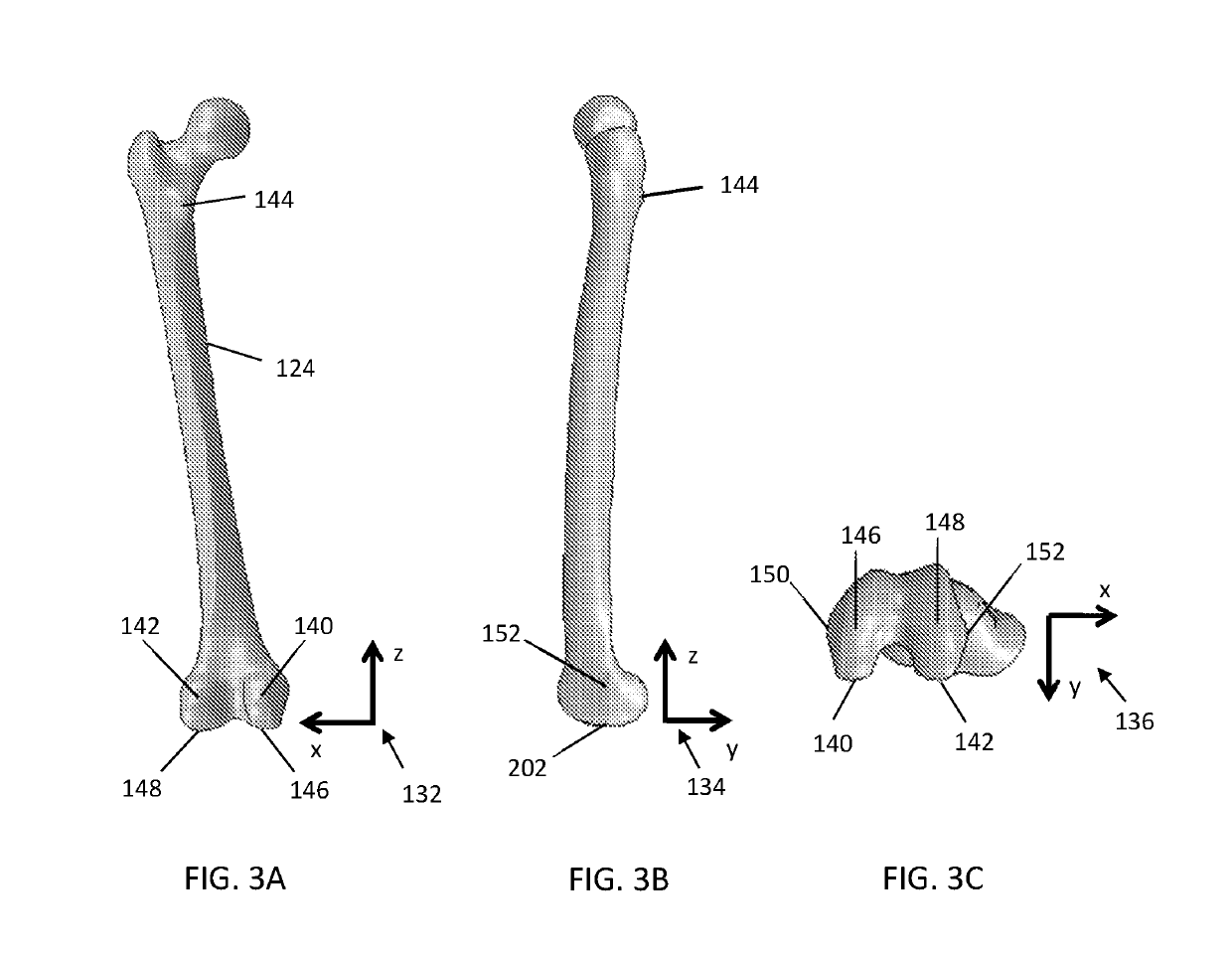
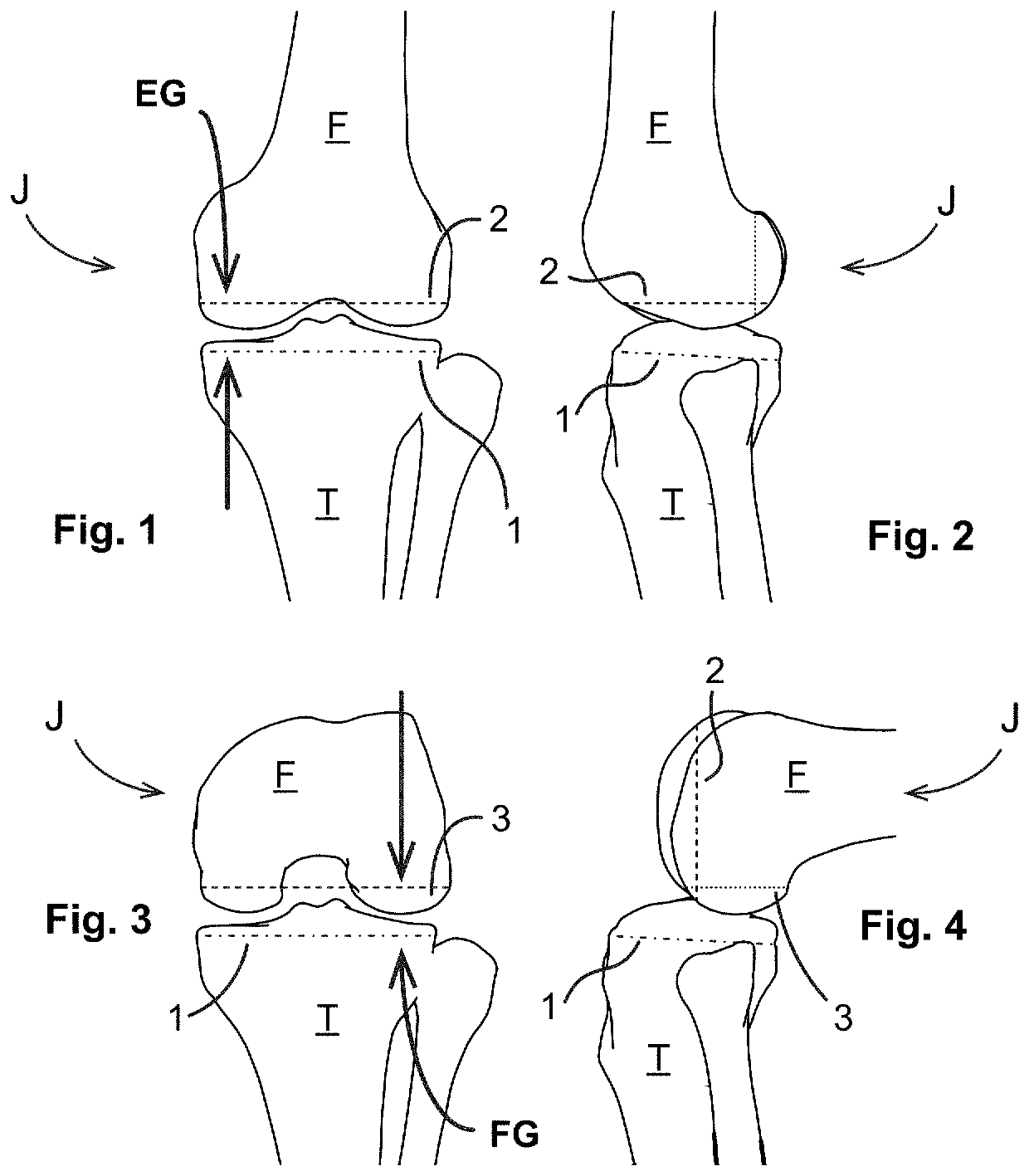
The head of the femur rests inside the acetabulum in the pelvic bone; together, they form the hip joint. The distal end of the femur joins with the tibia and the patella to form the knee joint. The femur, or thigh bone, is the longest, heaviest, and strongest bone in the body.
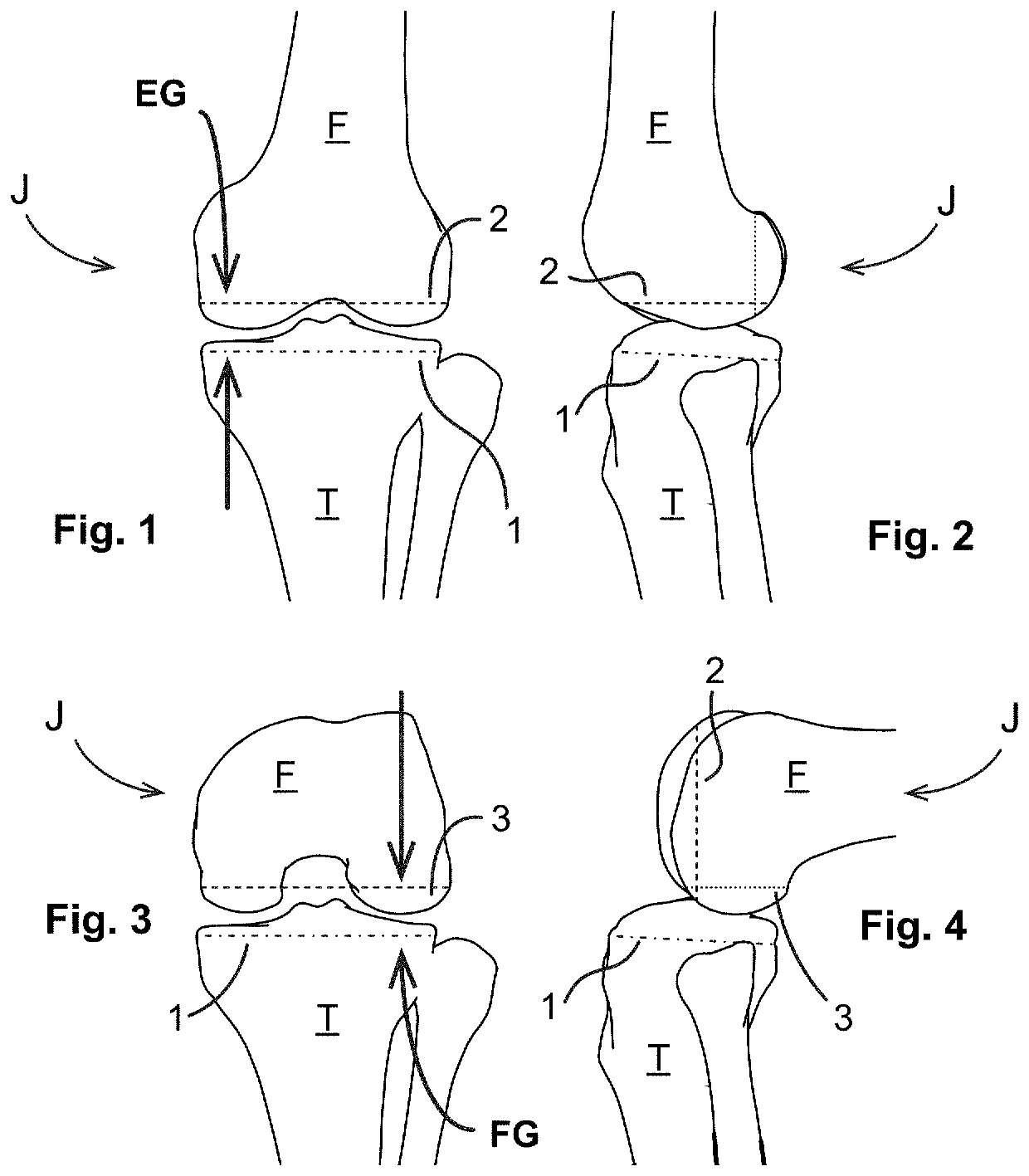
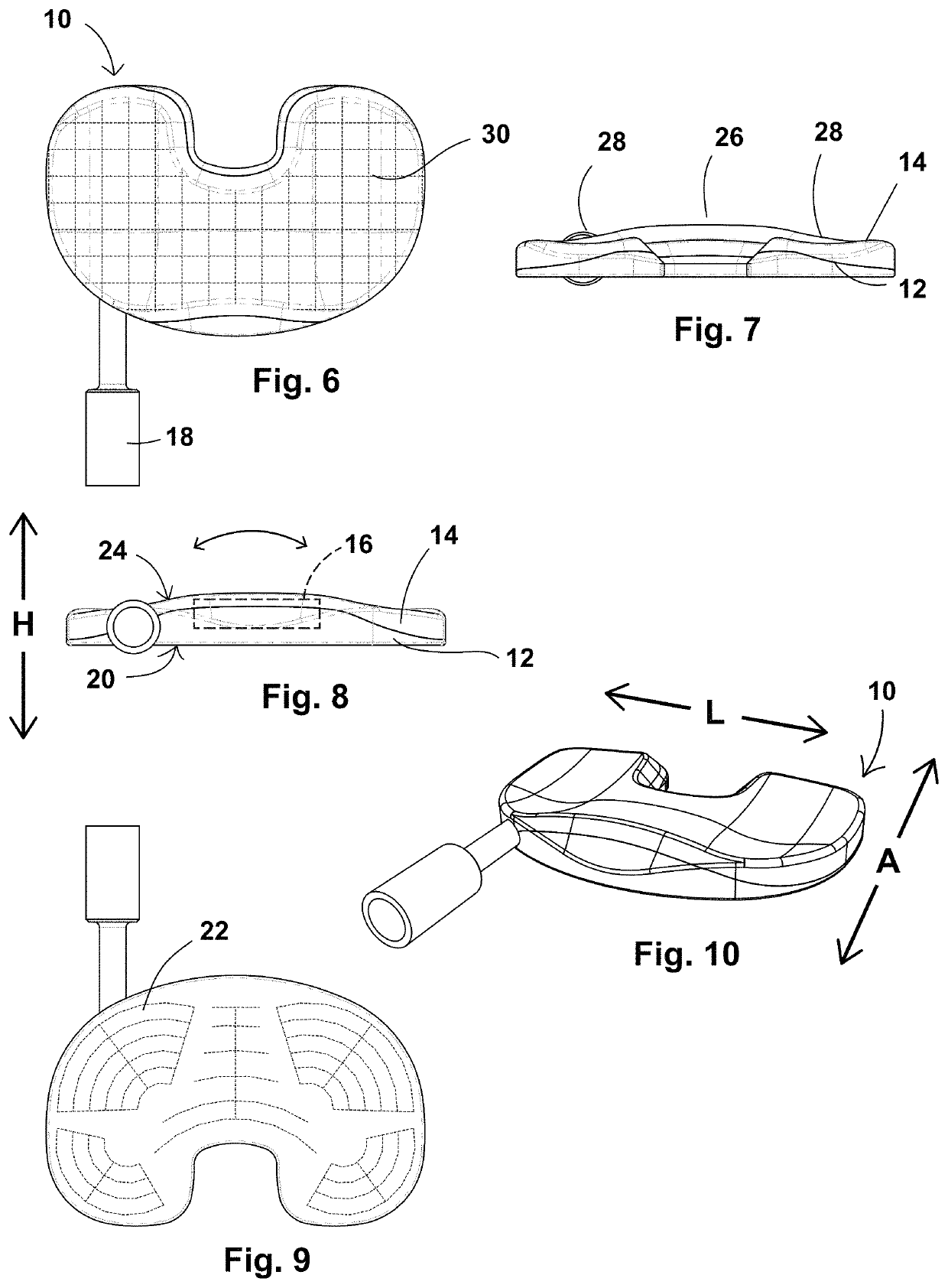
Surface guided knee replacement
InactiveUS20070135925A1Reduce consistencyAvoid large displacementJoint implantsKnee jointsGonial angleTibial surface
An artificial knee joint that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the motion and stability characteristics of the anatomic knee. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, more so on the lateral side than on the medial side. This is accomplished by the interaction of a projecting tibial post inside a cupola in the center of the femoral component, and by the saggital radius on the medial side being smaller than that on the lateral side. The prevention of anterior sliding of the femur on the tibia in early flexion is accomplished by the interaction between a distal-anterior recess on the medial side of the femur and an apposing raised pad on the tibial surface. Rotational laxity at all angles is allowed by the presence of only one recess pad and by non-conforming femoral-tibial surfaces on the lateral side.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Total knee joint mold and methods
ActiveUS20050107885A1Easy to disassembleIncrease success rateSurgical adhesivesBone implantKnee JointFemoral component
In one embodiment, a method for treating an infected implant area of a knee joint comprises surgically accessing the implant area, and inserting a tibial component into the tibia using an antibiotic-impregnated material. A femoral component is formed that is configured to interact with the tibial component by stable knee joint articulation and motion. The femoral component is formed of an antibiotic-impregnated material using a mold. The femoral component is attached to the femur using an antibiotic-impregnated material, and the tibial component is interfaced with the femoral component to form a stable temporary knee joint capable of reducing the spread of infection while permitting movement of the knee joint.
Owner:EVANS RICHARD P +1
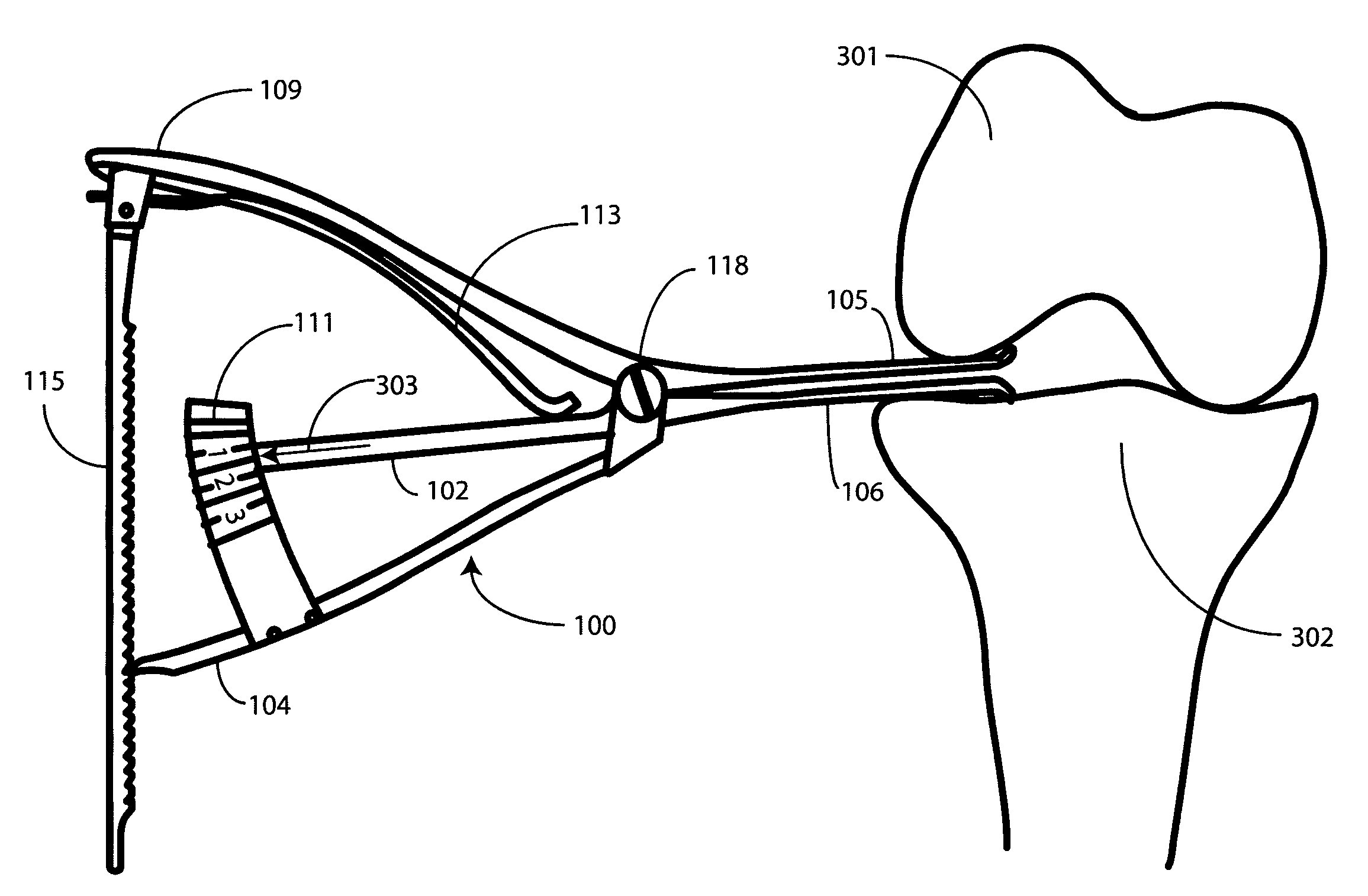
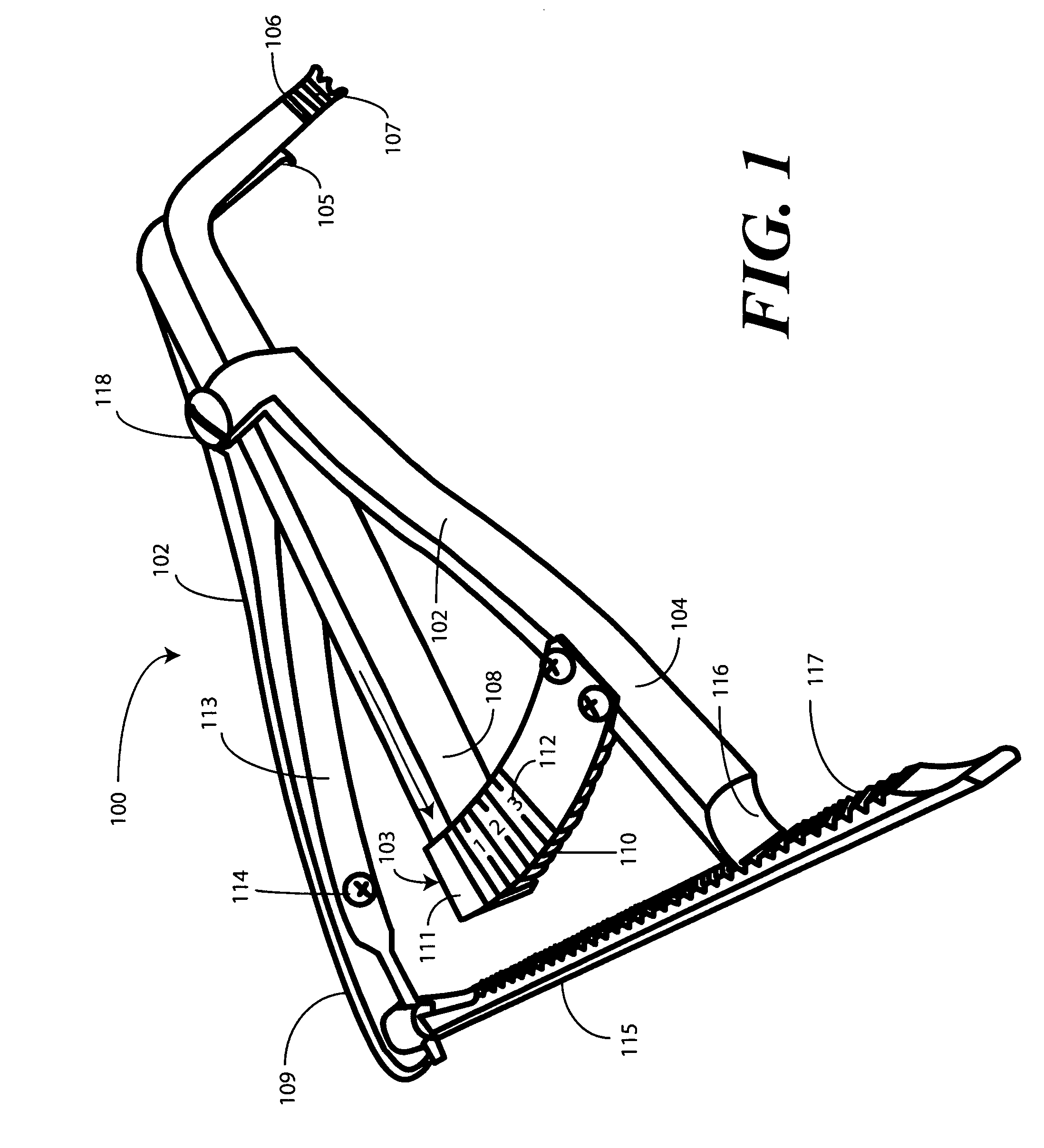
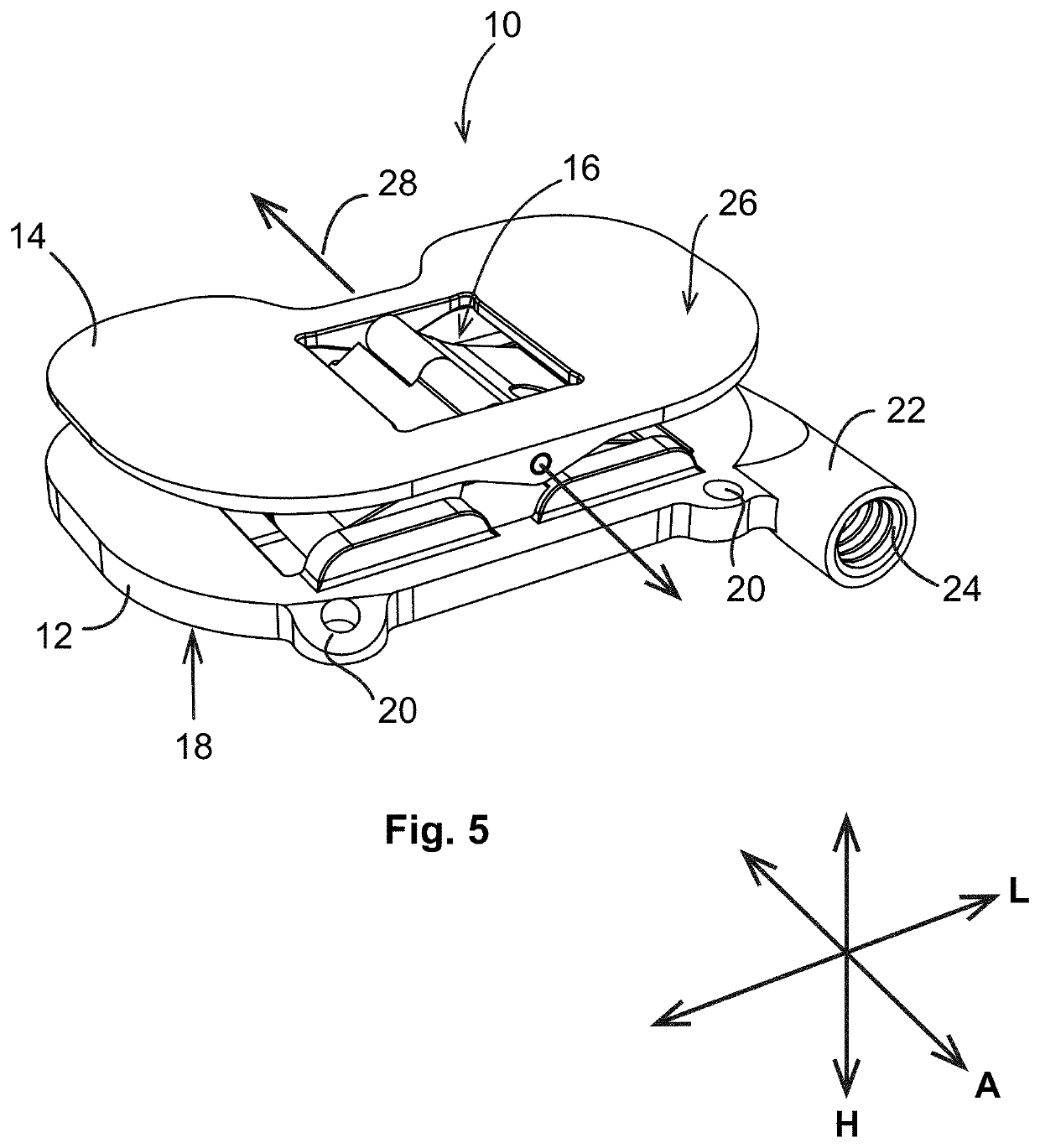
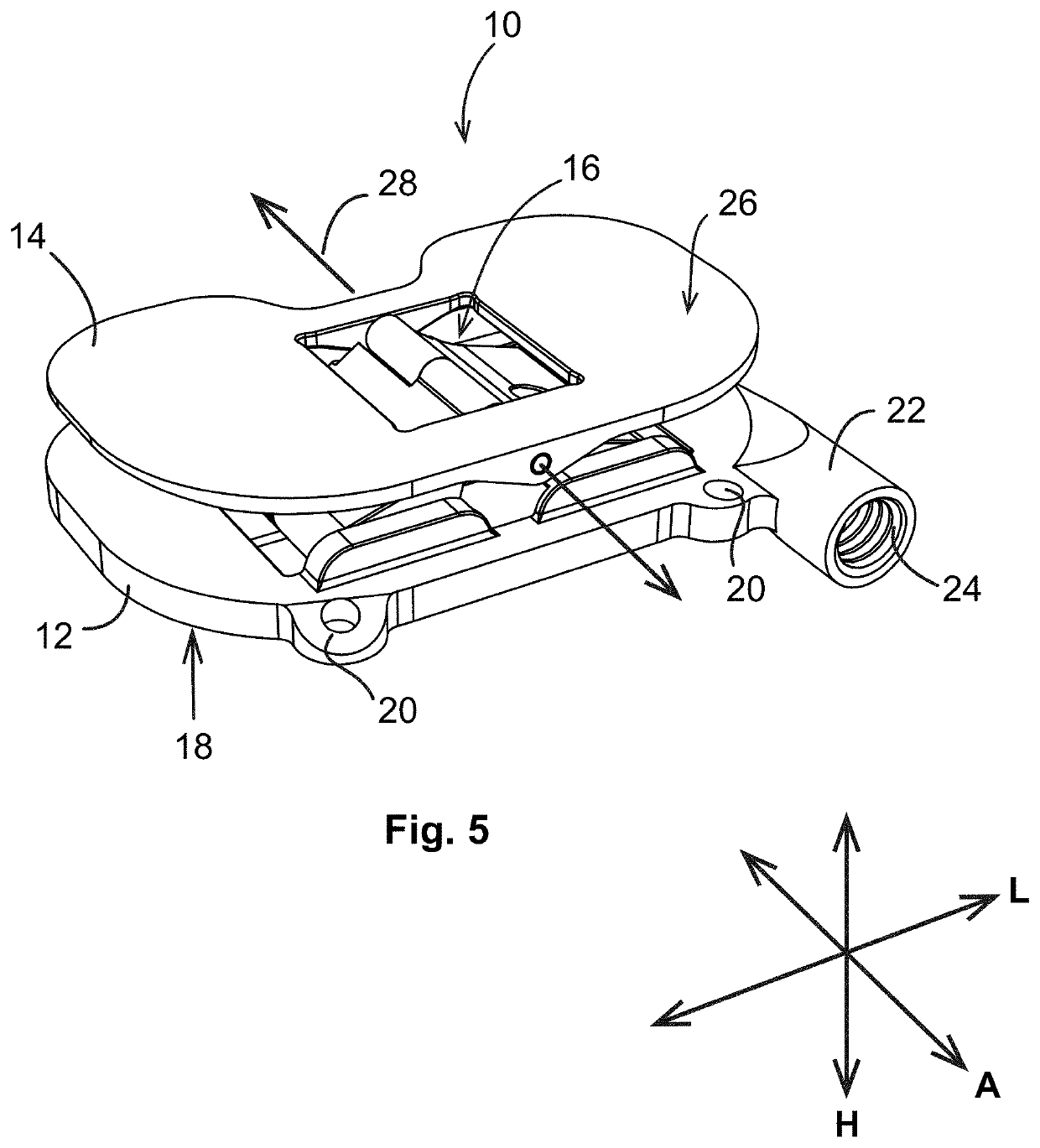
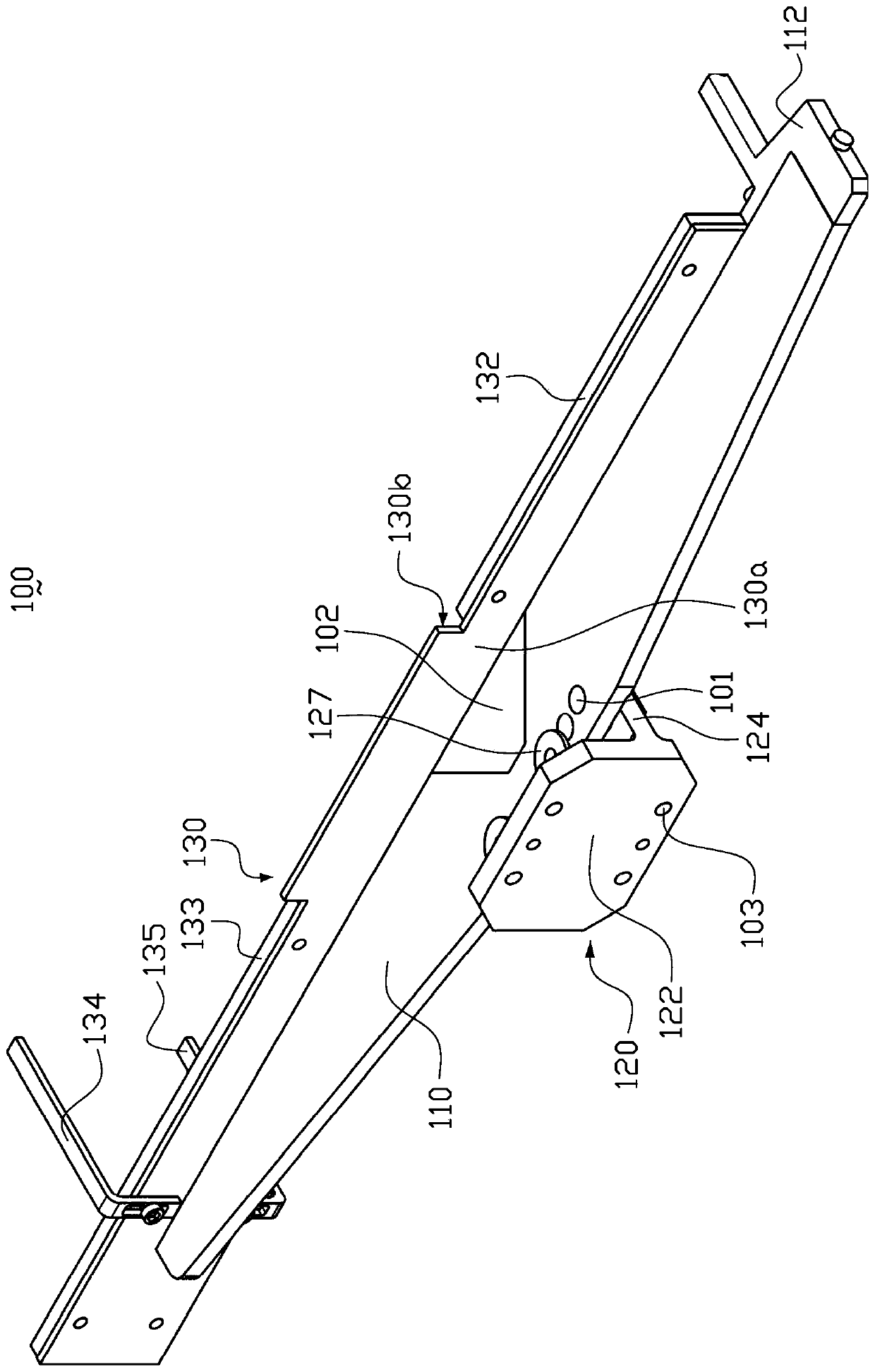
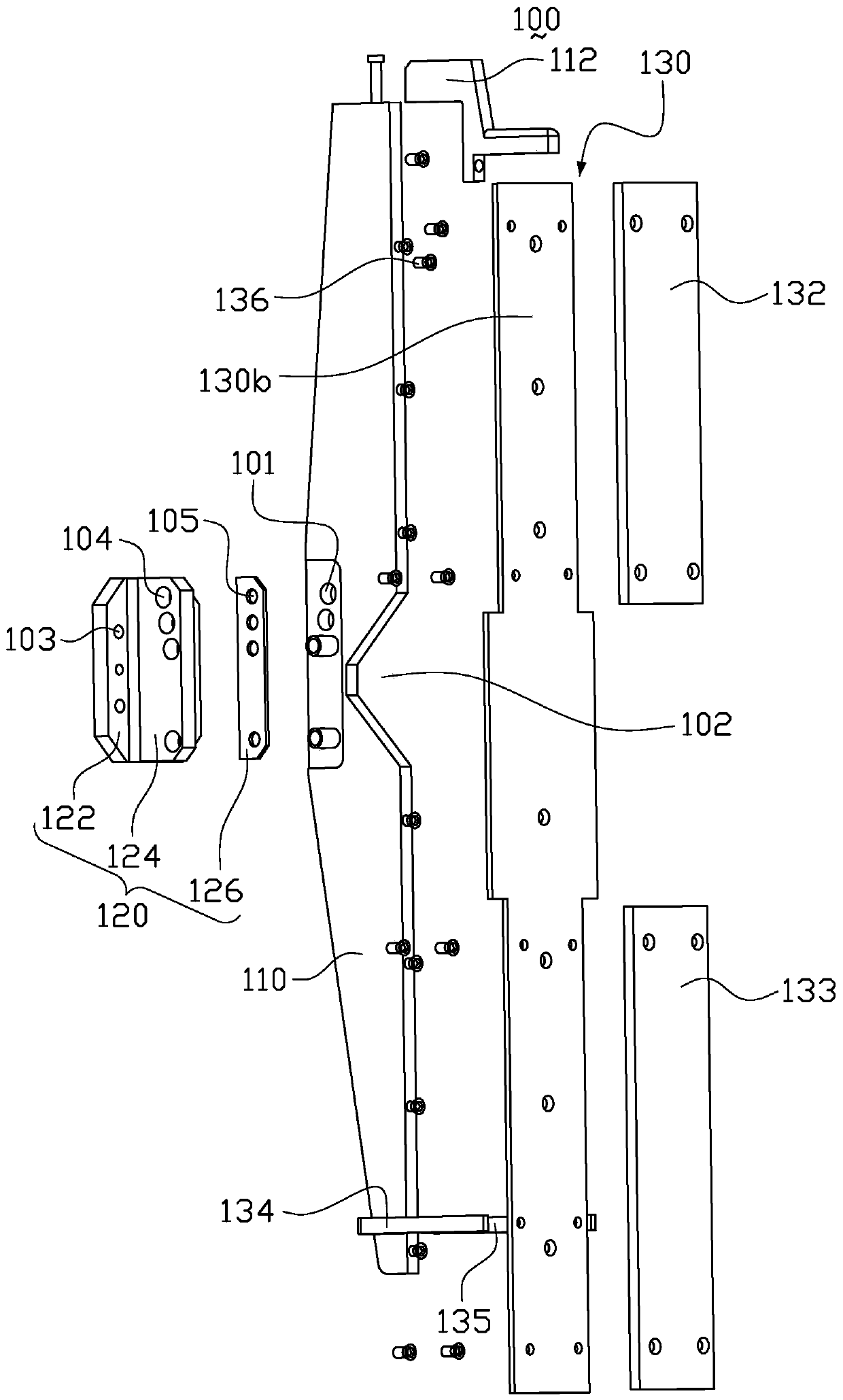
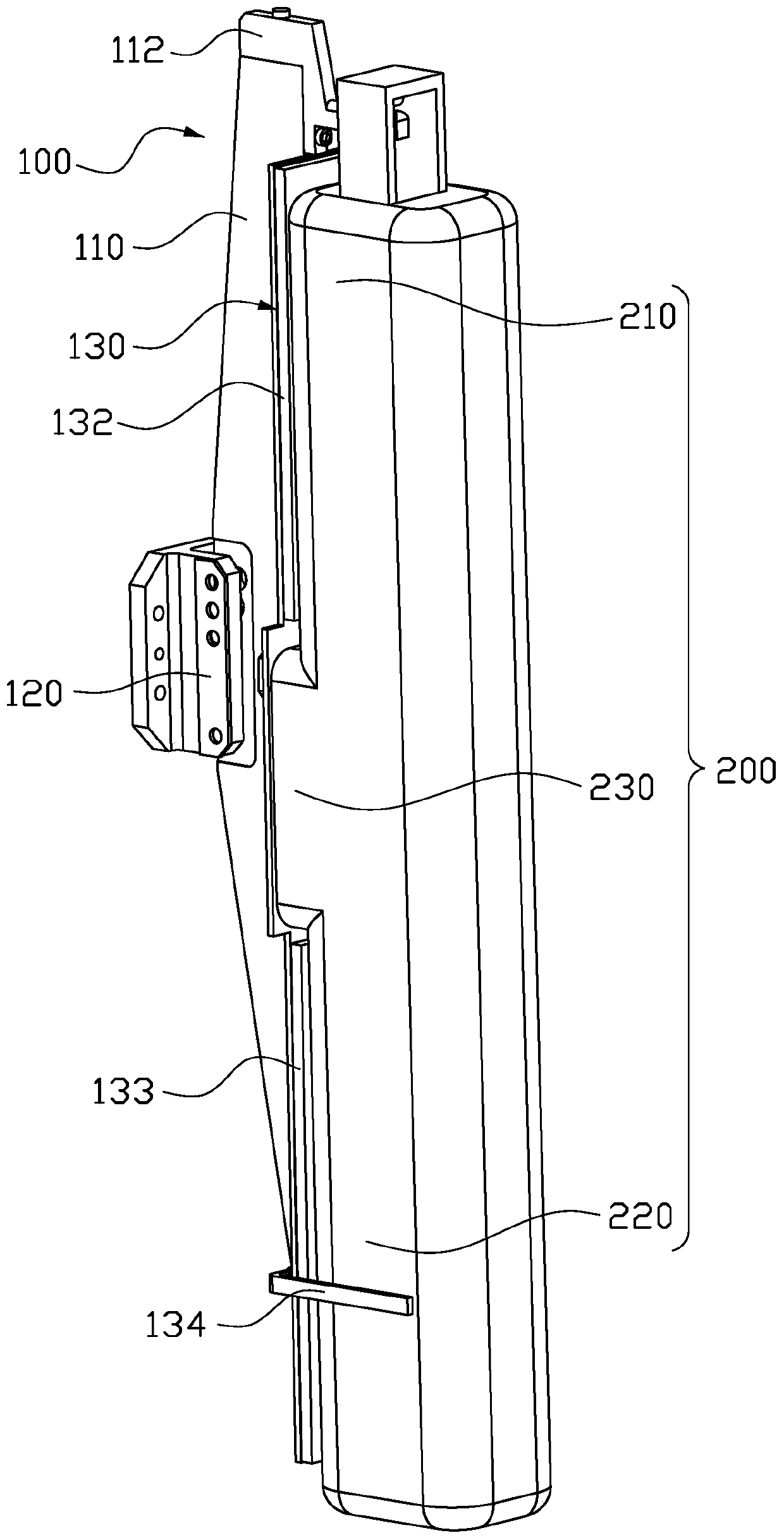
Femoral Tibial Spreader with Tensor Measurement
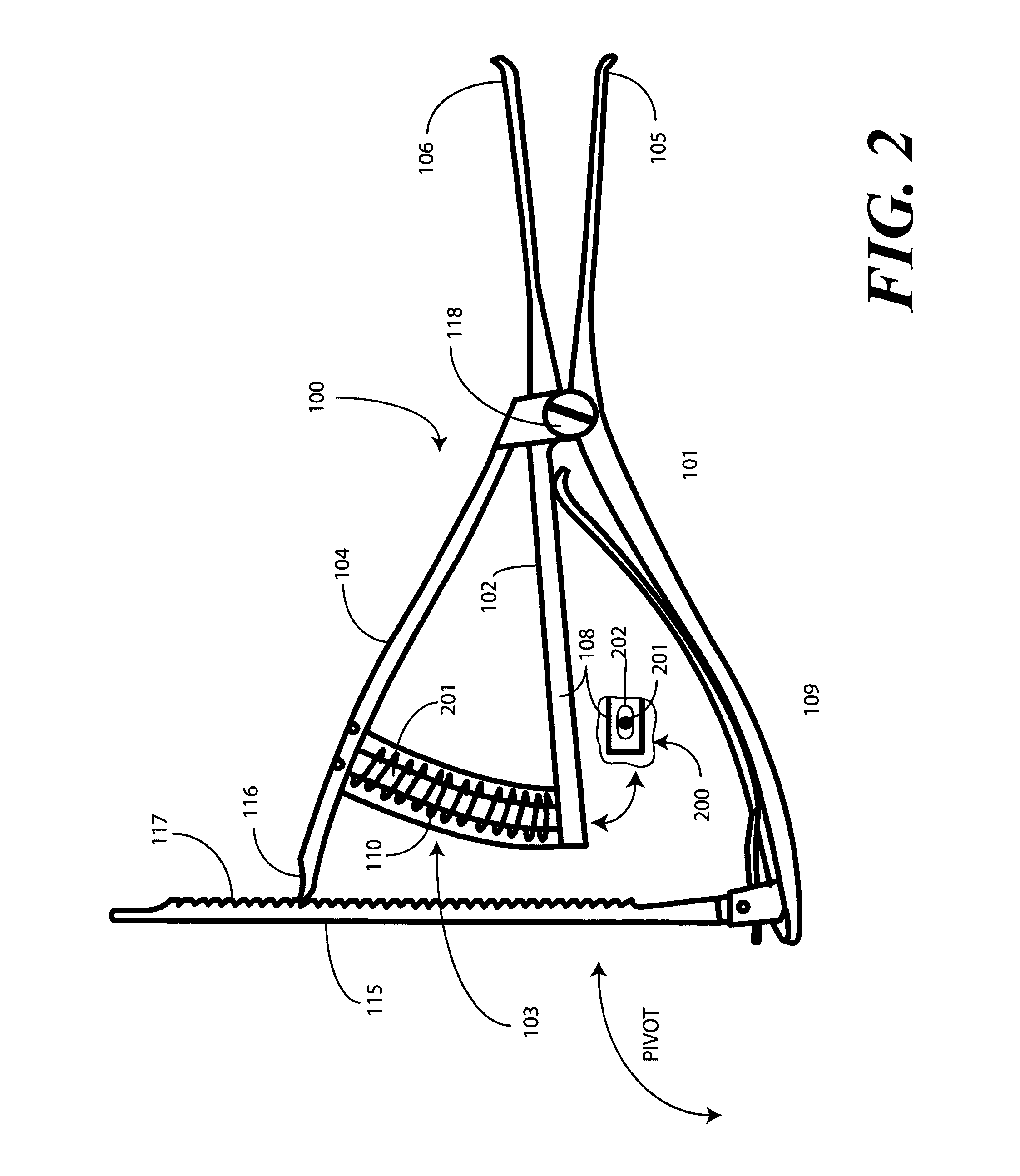
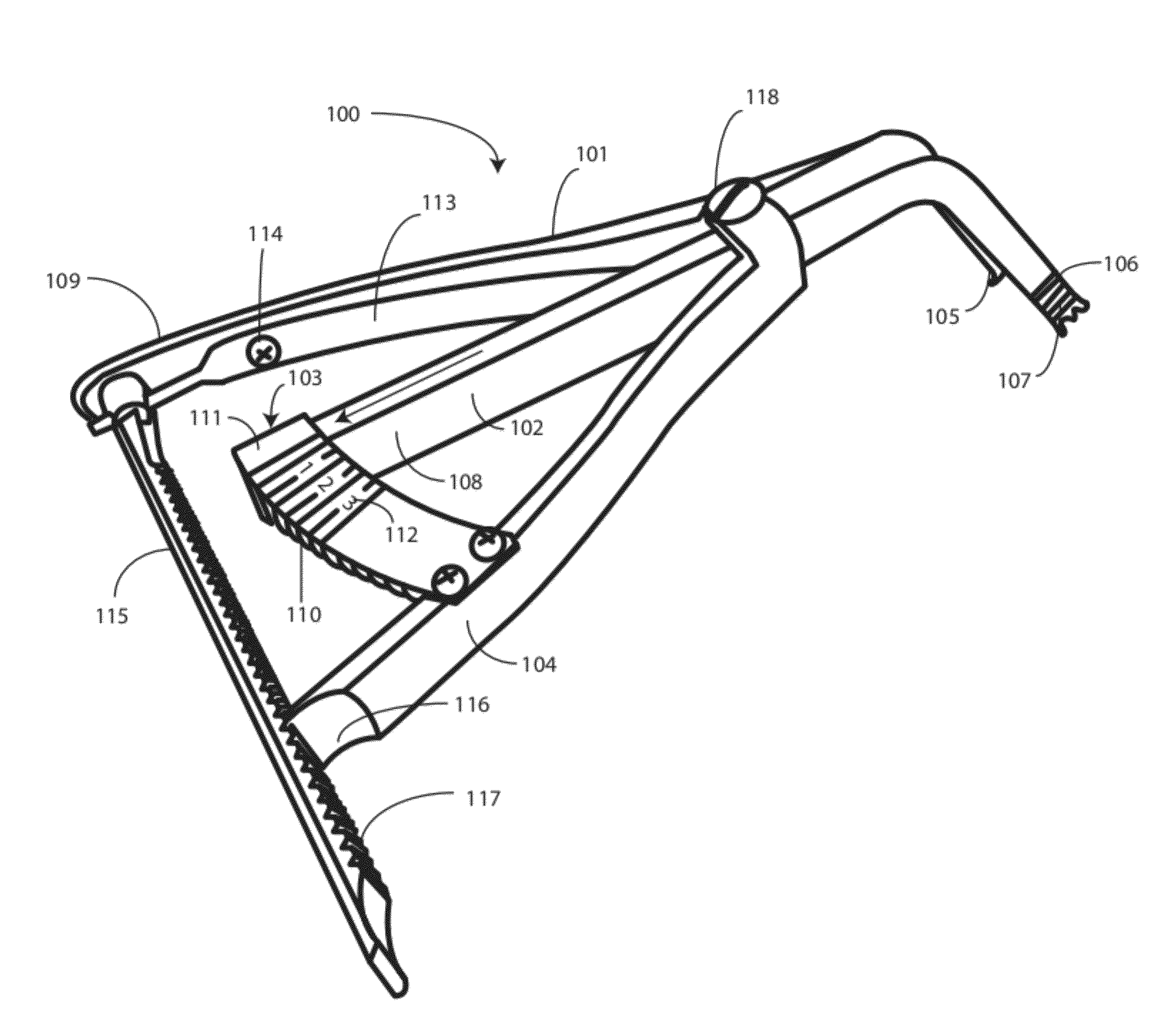
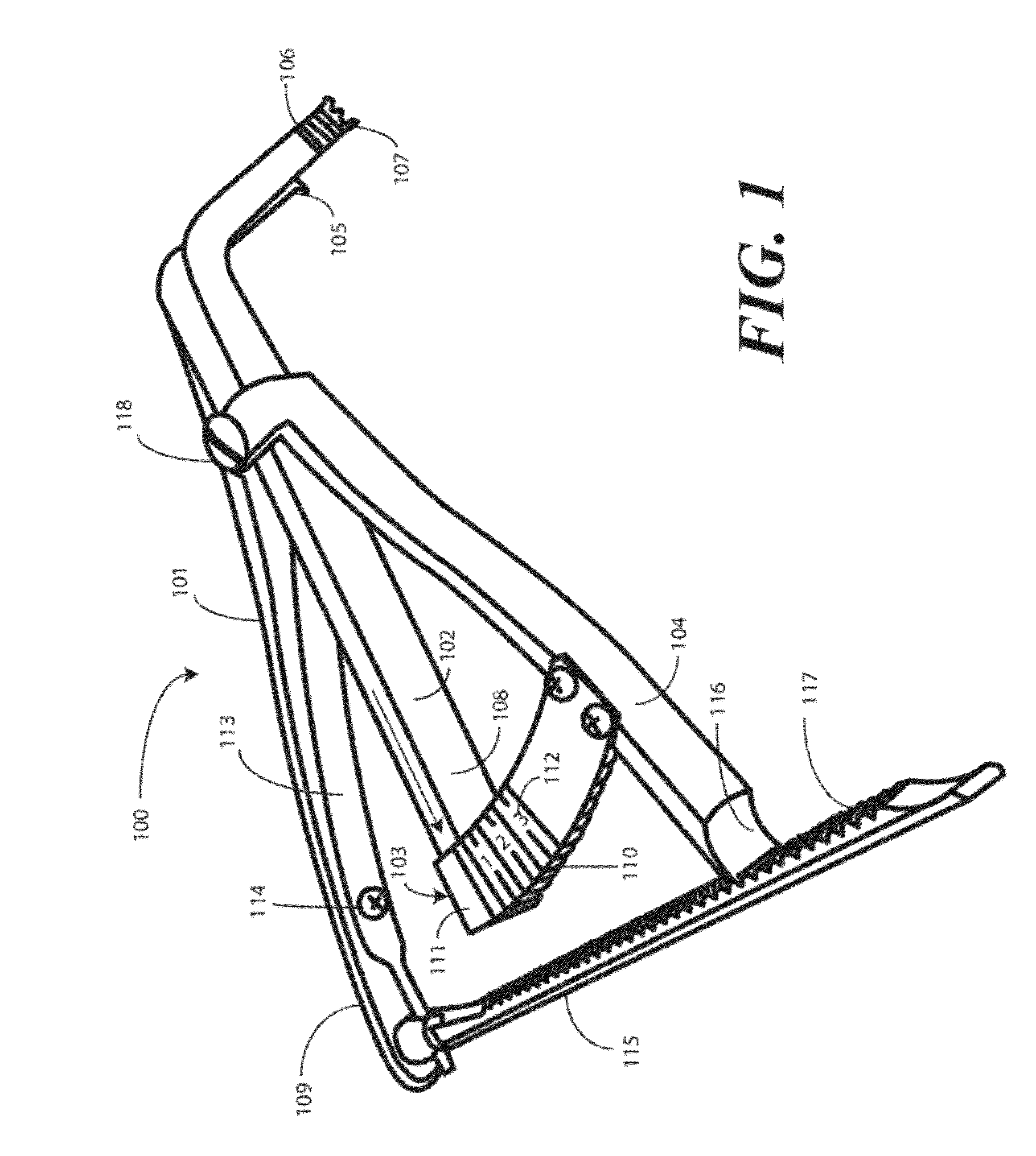
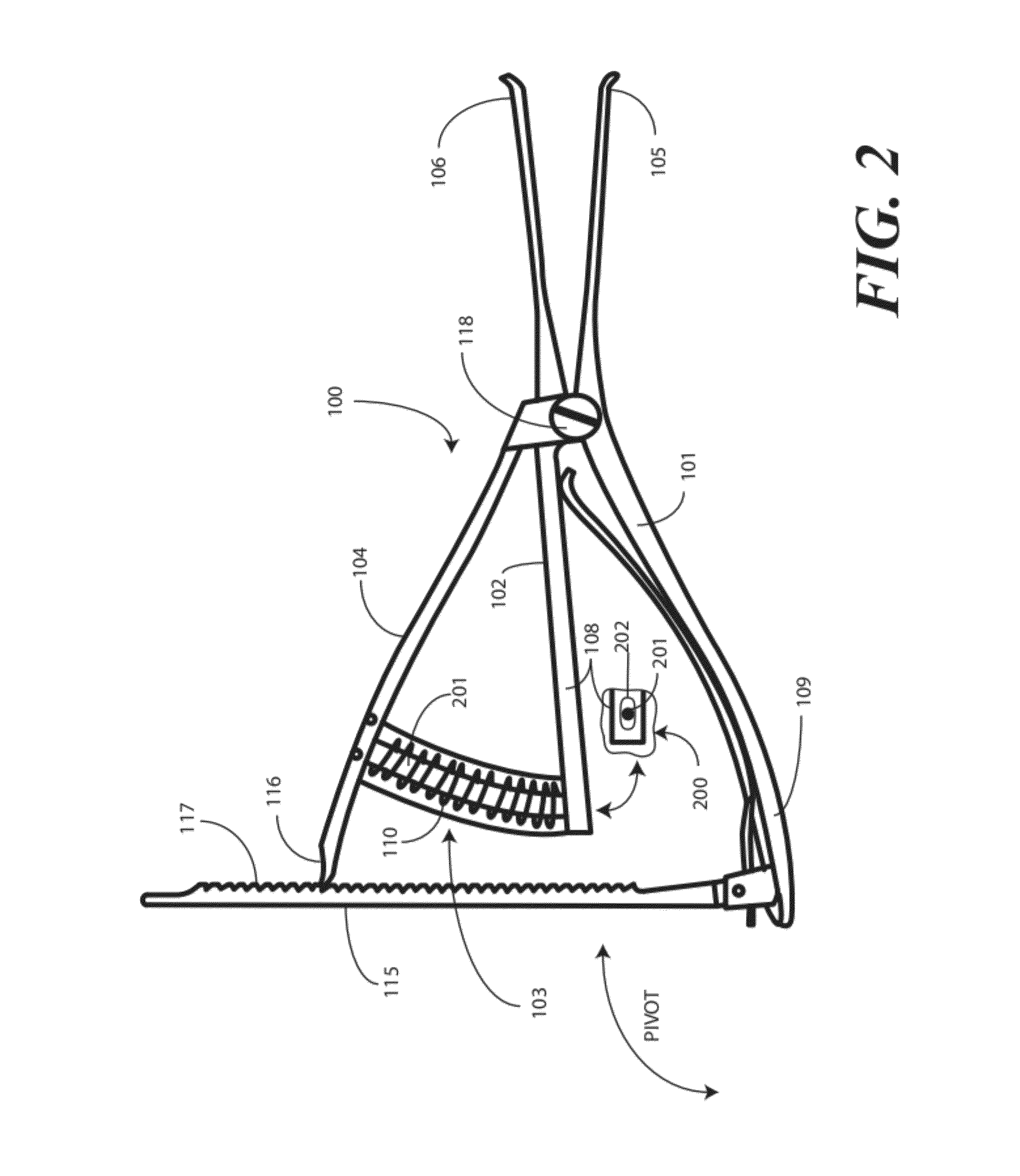
A femoral tibial spreader (100) for spreading adjacent bones includes a radial measurement gauge (111) for providing incidia corresponding to an amount of force being applied to the forward ends (105,106) of the femoral tibial spreader (100). The femoral tibial spreader (100) may be used, for example, to separate the femur (301) and tibia (302) during knee surgery. The radial measurement gauge (111) may be used to determine an amount of force being applied to the femur (301) and tibia (302), for example, by the medial and arterial ligaments. Two handle members (104,109) are squeezed together, which causes the forward ends (105,106) to open. A biasing member (110) allows a measurement extension (108) to pivot towards a handle member under tension, thereby providing a measurement of force applied by the ligaments.
Owner:INNOMED INC
Femoral tibial spreader with tensor measurement
A femoral tibial spreader (100) for spreading adjacent bones includes a radial measurement gauge (111) for providing incidia corresponding to an amount of force being applied to the forward ends (105,106) of the femoral tibial spreader (100). The femoral tibial spreader (100) may be used, for example, to separate the femur (301) and tibia (302) during knee surgery. The radial measurement gauge (111) may be used to determine an amount of force being applied to the femur (301) and tibia (302), for example, by the medial and arterial ligaments. Two handle members (104,109) are squeezed together, which causes the forward ends (105,106) to open. A biasing member (110) allows a measurement extension (108) to pivot towards a handle member under tension, thereby providing a measurement of force applied by the ligaments.
Owner:INNOMED INC
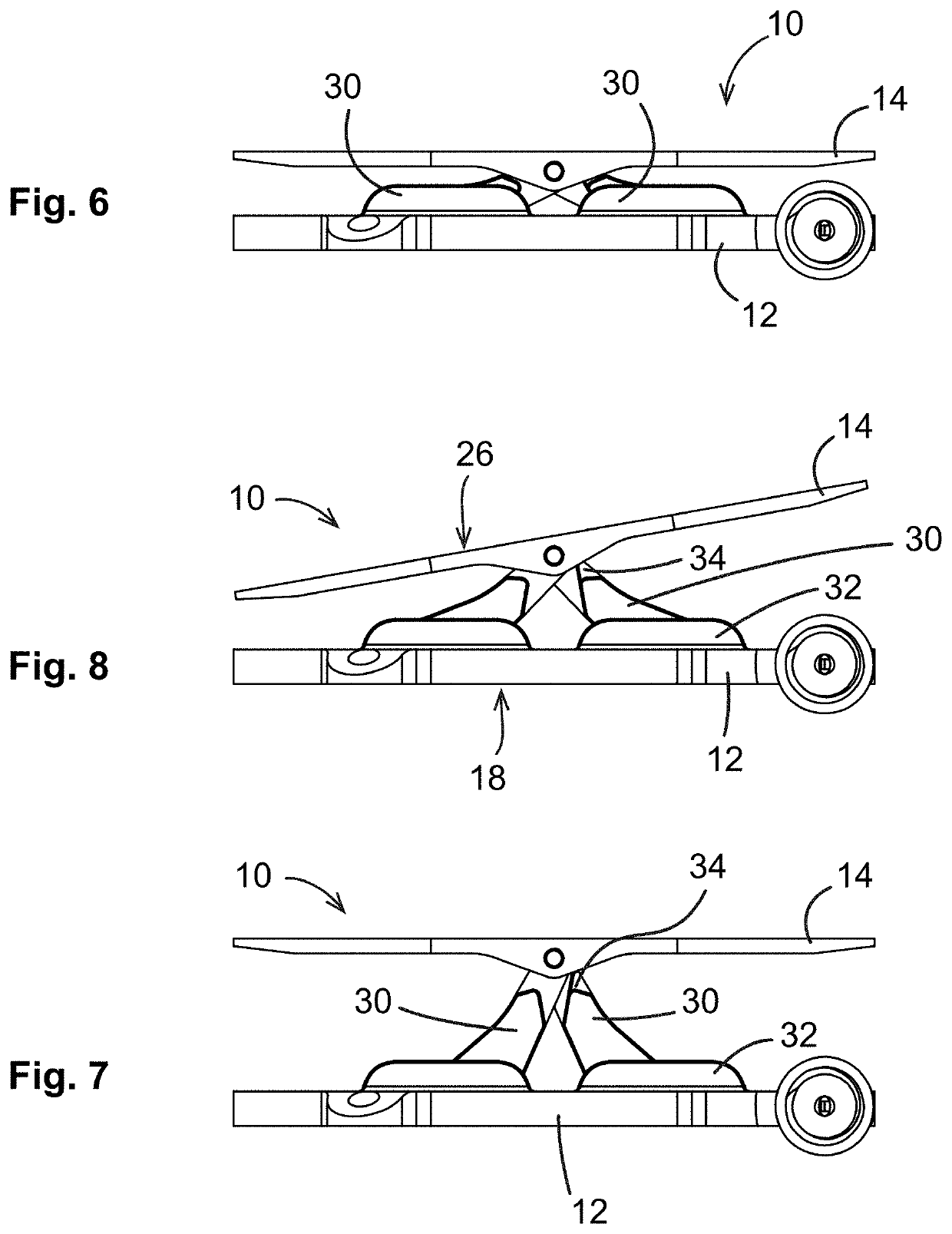
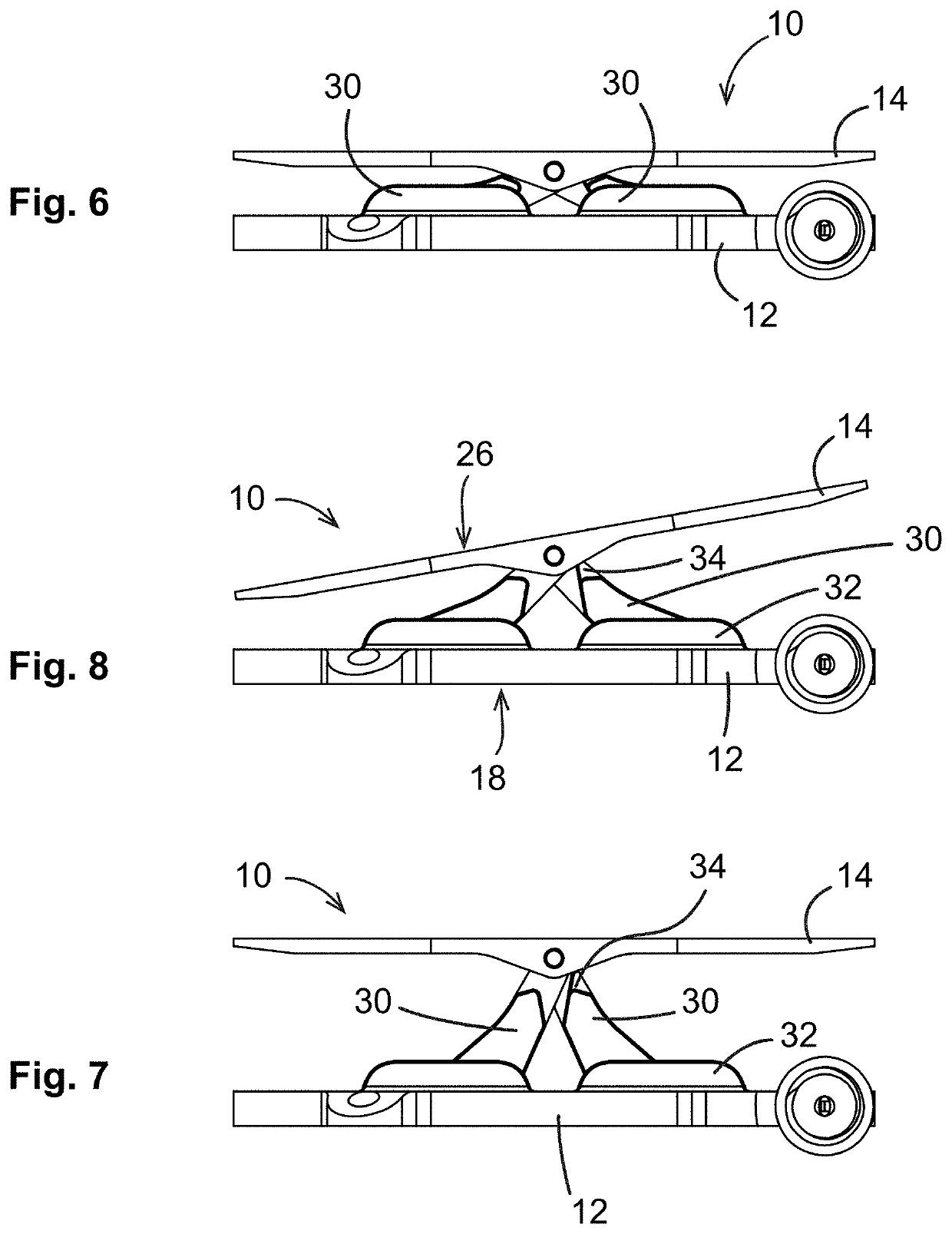
Knee flexion and extension gap tensioning and measuring method
A method for imparting tension across a human knee joint which includes a femur bone, a tibia bone, a patella bone, a patellar tendon, and ligaments, wherein the ligaments and patellar tendon are under anatomical tension to connect the femur and tibia together, creating a load-bearing articulating joint. The method includes: providing a tensioning device, including: a baseplate; a top plate; and a linkage interconnecting the baseplate and the top plate and operable to move the tensioning device between retracted and extended positions, wherein the top plate is pivotally connected to the linkage so as to be able to freely pivot about a pivot axis; positioning the tensioning device between the femur and the tibia; applying an actuating force to the linkage to move the tensioning device towards the extended position, so as to impart a controlled separating force driving the femur and tibia apart to extend the ligaments.
Owner:LITTLE ENGINE LLC
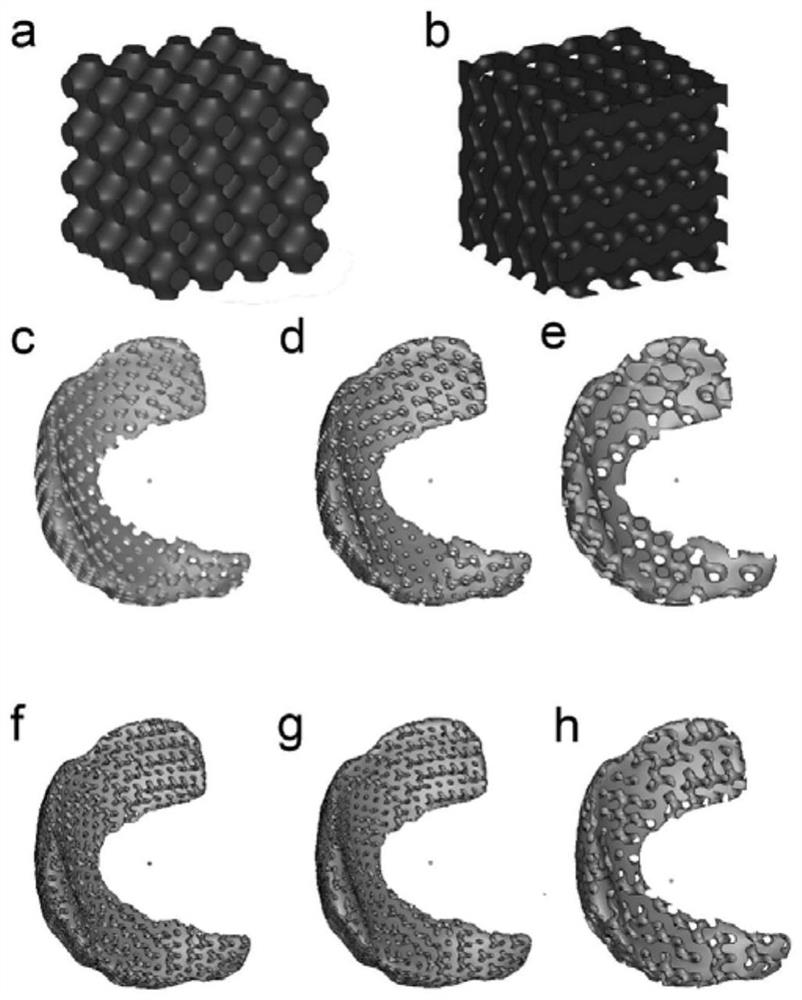
Porous meniscus substitute modeling and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111728742AAvoid narrow situationsReduced stress limitJoint implantsKnee jointsMeniscal tissueKnee Joint
The invention provides a porous meniscus substitute modeling and a preparation method thereof. The modeling method comprises the following steps: scanning the meniscus part of a patient by using CT, performing image processing on a scanned image to obtain a meniscus model matched with the patient, performing parameter acquisition on the concentrated compression stress, shear stress and stress distribution of the femur, tibia and meniscus part of the patient at the meniscus, and setting the pore shape, pore diameter and porosity of the pores in the porous meniscus substitute by adopting a parametric modeling mode to obtain a final meniscus substitute model. The model is subjected to a 3D printing or injection molding process to obtain the porous meniscus substitute. The porous meniscus substitute prepared by the invention can be matched with the meniscus of the user, is favorable for rapid formation of meniscus tissues after transplantation, and has the biomechanical properties meetingthe requirements of knee joint parts; and in addition, through the cooperation of hydrogel and a porous scaffold, the effects of transmitting load, absorbing oscillation and improving the joint stability of the meniscus substitute can be greatly improved.
Owner:蒋青 +4
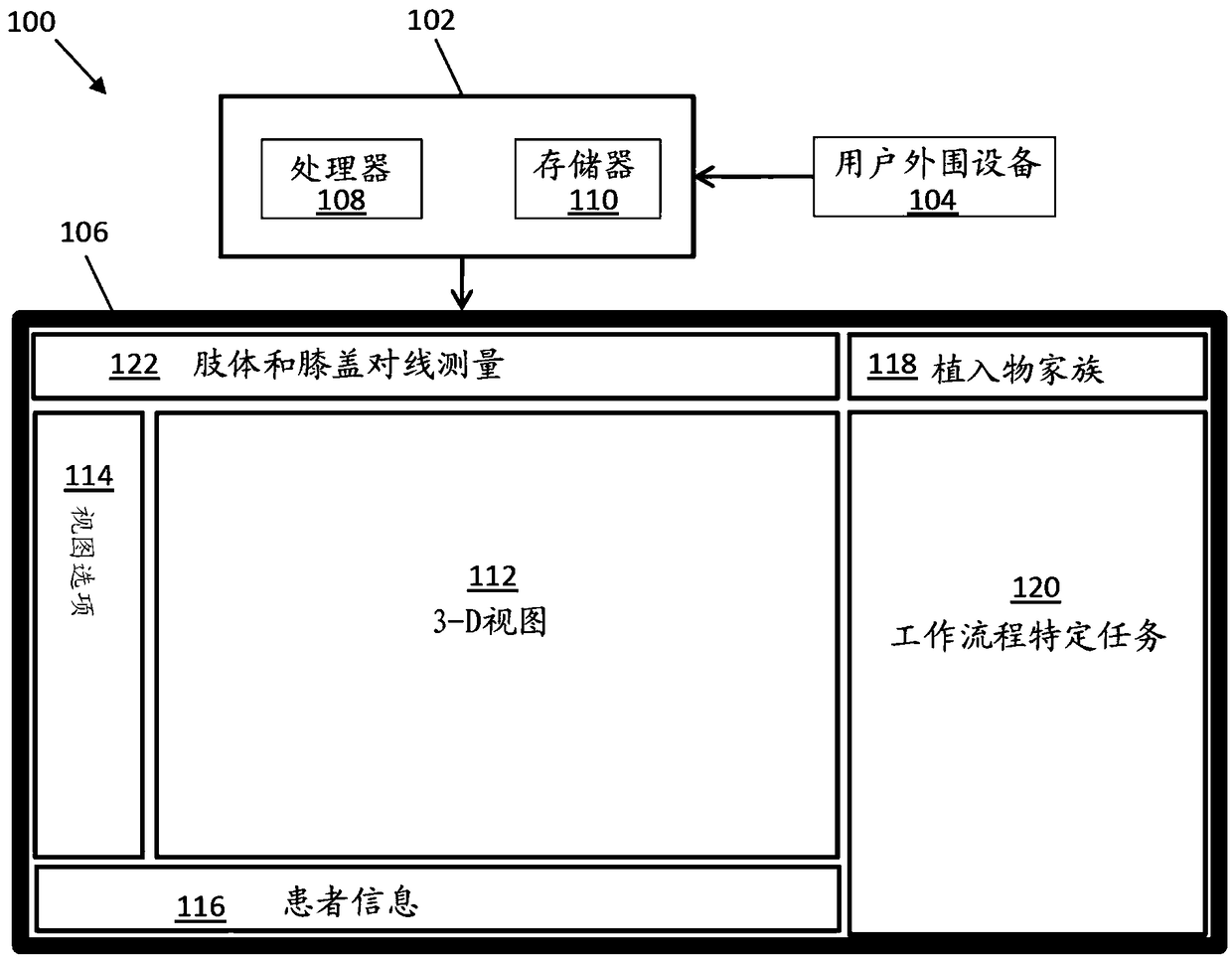
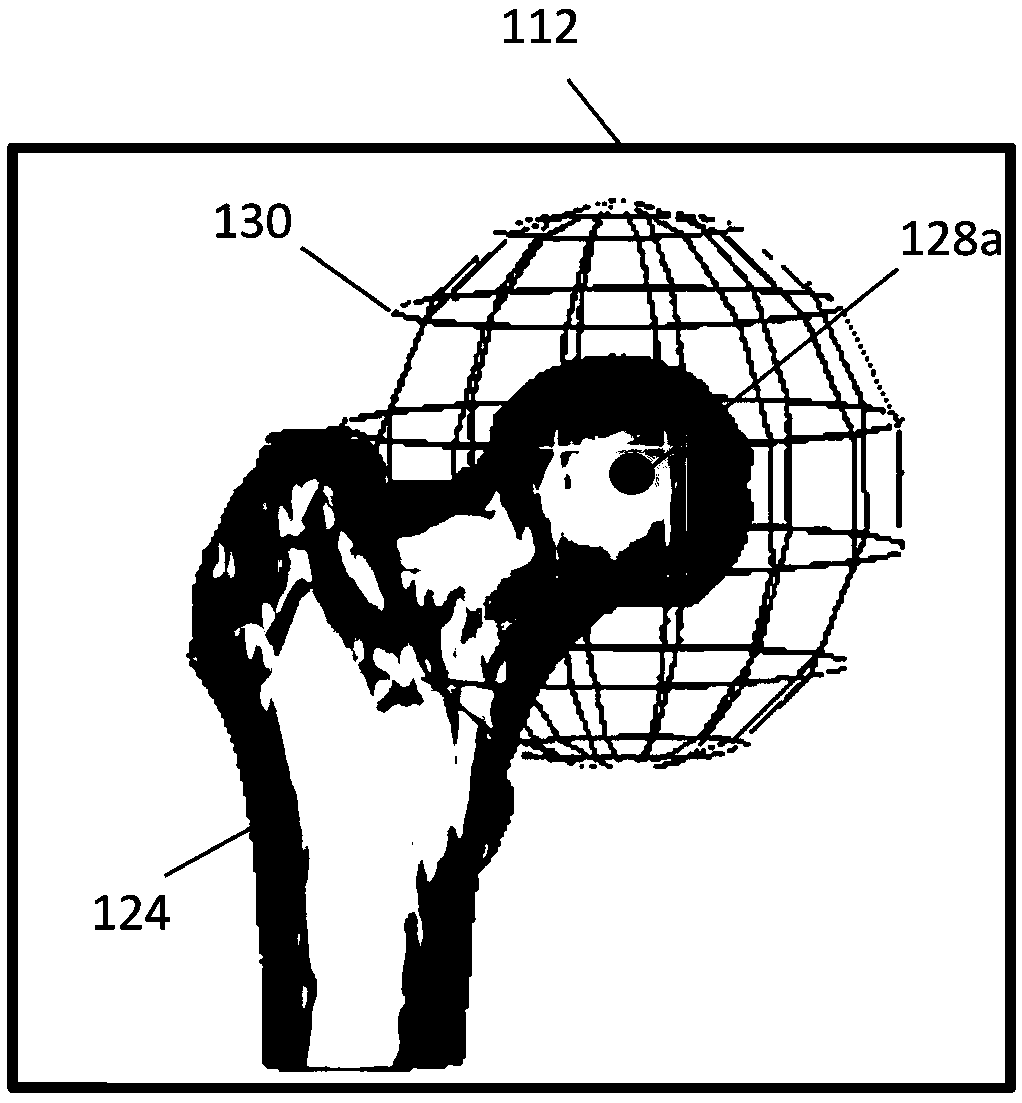
Automated arthroplasty planning
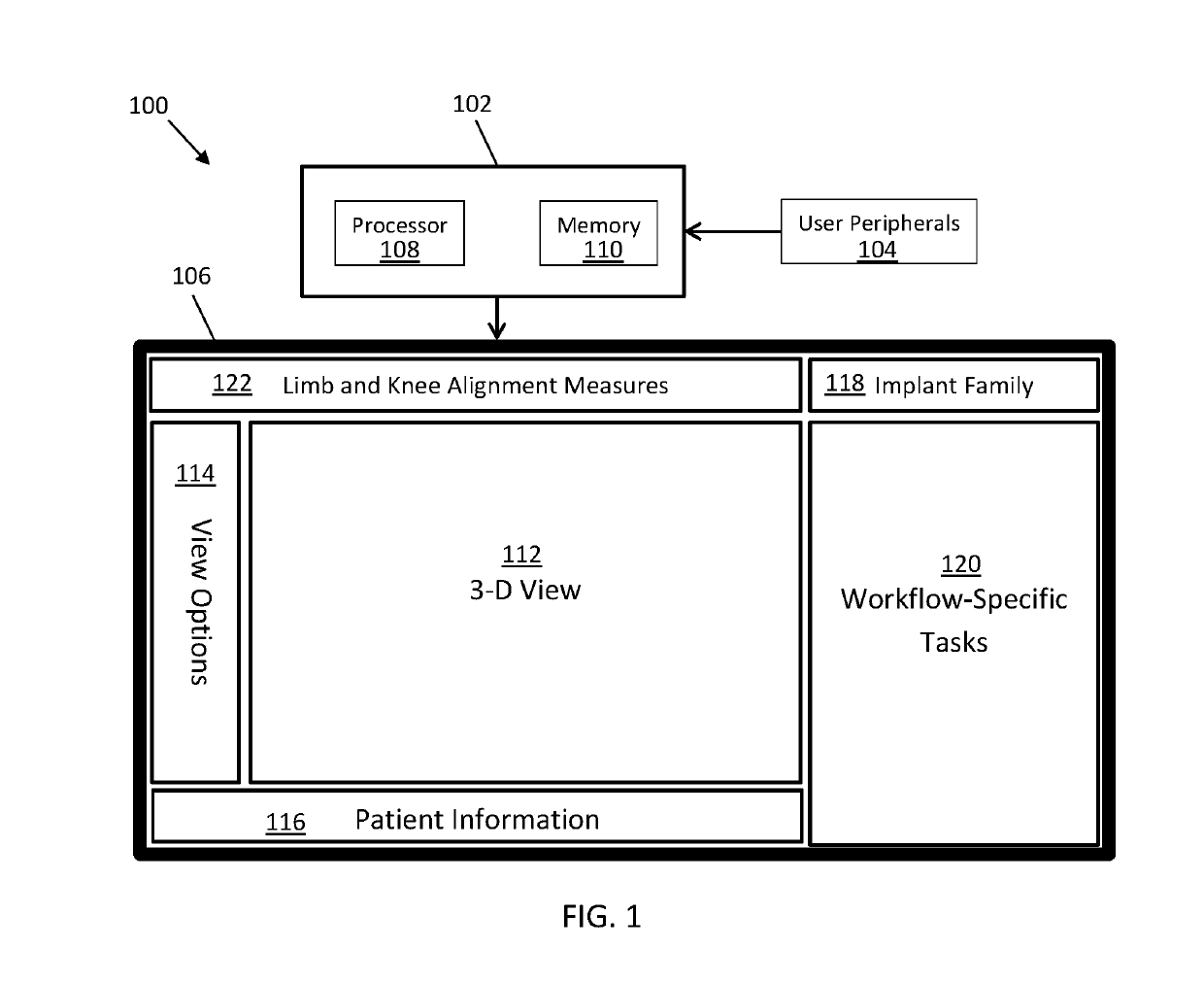
Systems and methods are provided to aid in planning at least a portion of a total knee arthroplasty procedure. The system and method automatically aligns the implant components and the bones according to a desired clinical alignment goal with minimum user input. The system and method further allows the user to adjust the position and orientation of the femur, tibia, or implant in a clinical direction regardless of a pre-adjusted position and orientation of the femur, tibia, or implant. The graphical user interface is provided that includes a three-dimensional (3-D) view window, a view options window, a patient information window, an implant family window, a workflow-specific tasks window, and a limb and knee alignment measures window.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
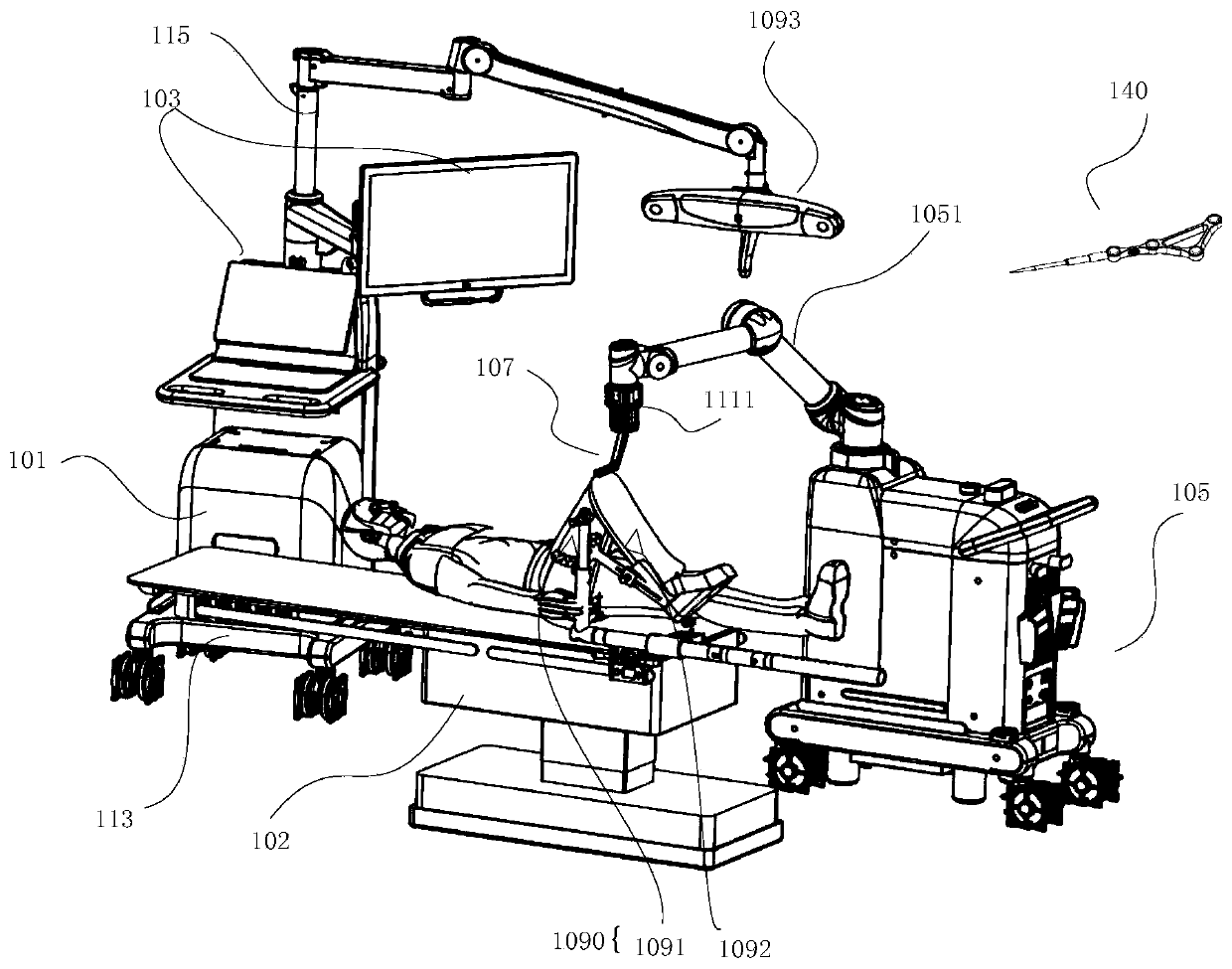
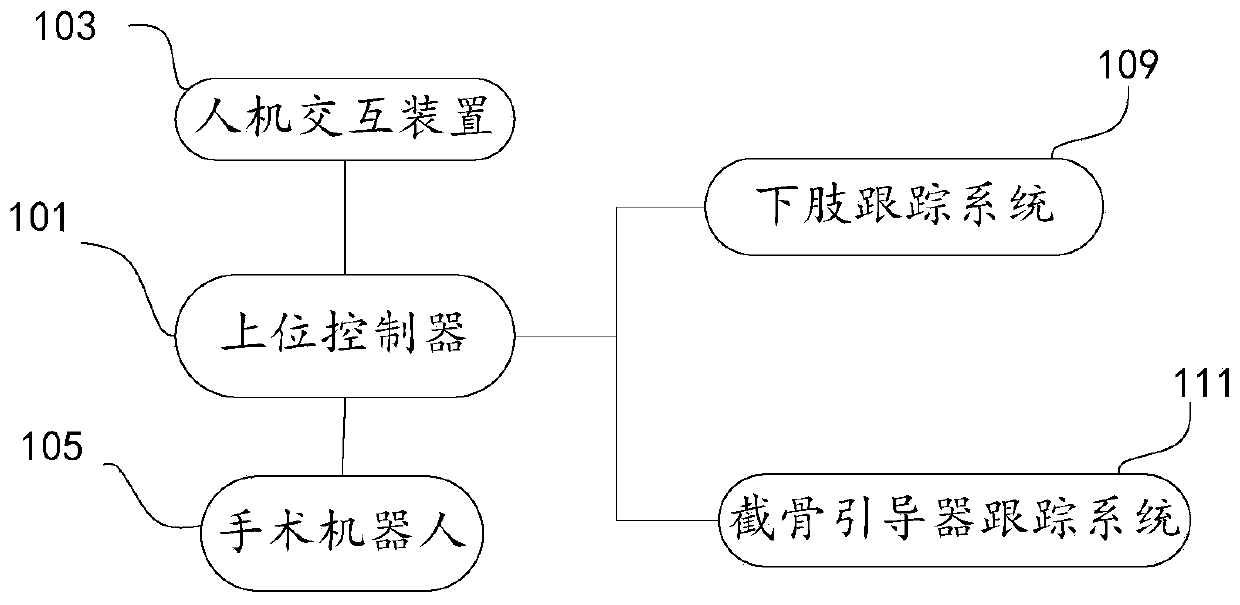
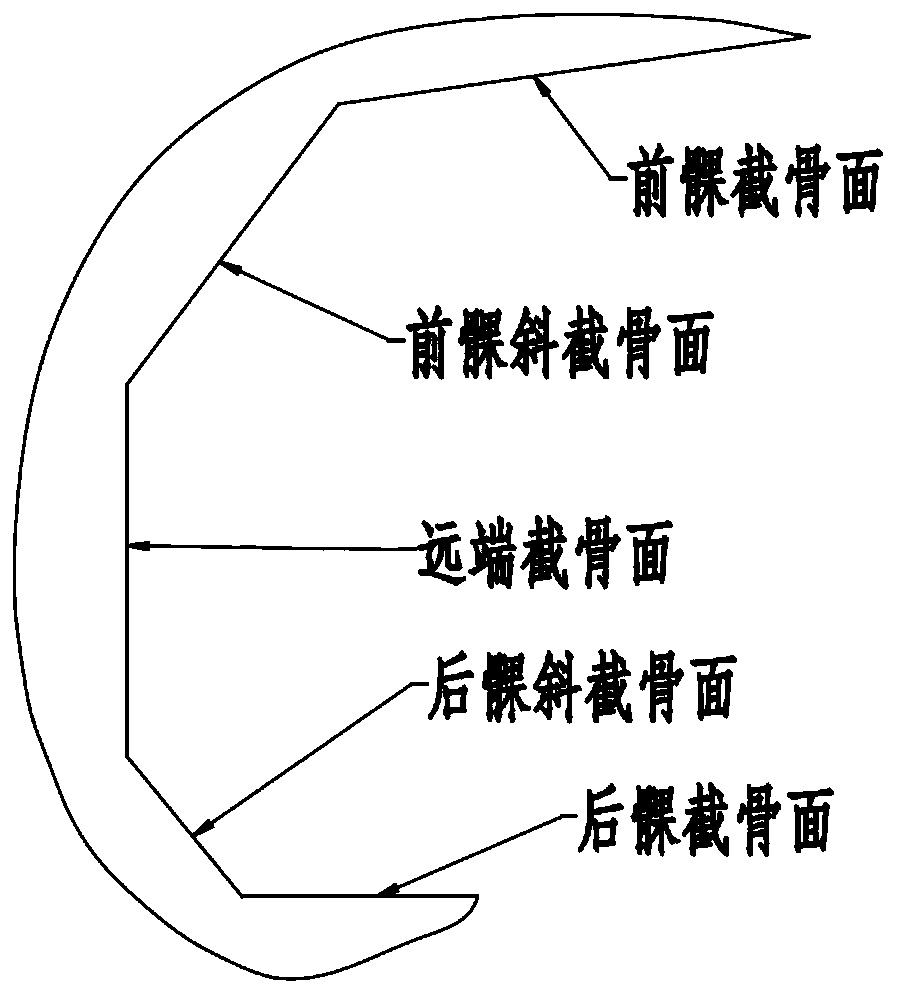
Osteotomy execution system, positioning, control and simulation execution methods and electronic equipment
ActiveCN111345896ASurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingTotal knee replacement surgeryKnee Joint
The invention provides an osteotomy execution system, a positioning method, a control method and a simulation execution method for primary total knee replacement surgery operation. The osteotomy execution system for the primary total knee replacement surgery operation comprises: a man-machine interaction device; a surgical robot which comprises a mechanical arm; an osteotomy guider which is fixedto the operation end of the mechanical arm and used for positioning and guiding an osteotomy tool during osteotomy operation of total knee replacement, wherein the osteotomy guider is provided with athrough groove for containing the osteotomy tool; a lower limb tracking system which is used for acquiring position data of thighbone and tibia; an osteotomy guider tracking system which is used for acquiring position data of the osteotomy guider; and an upper controller which is in communication connection with the man-machine interaction device, the surgical robot, the lower limb tracking systemand the osteotomy guider tracking system. The system provided by the invention can improve the execution effect and efficiency of the joint replacement surgery operation.
Owner:BEIJING TINAVI MEDICAL TECH
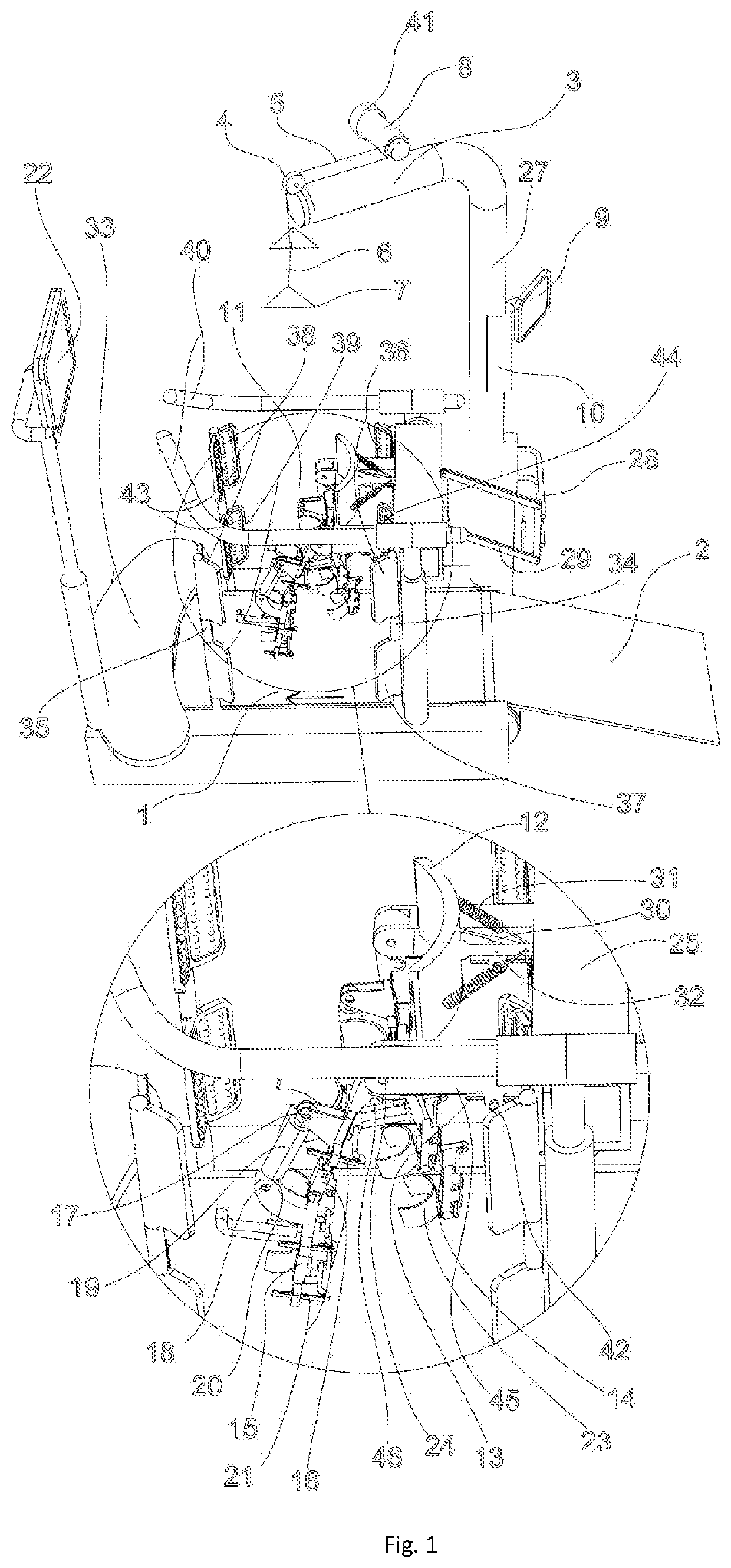
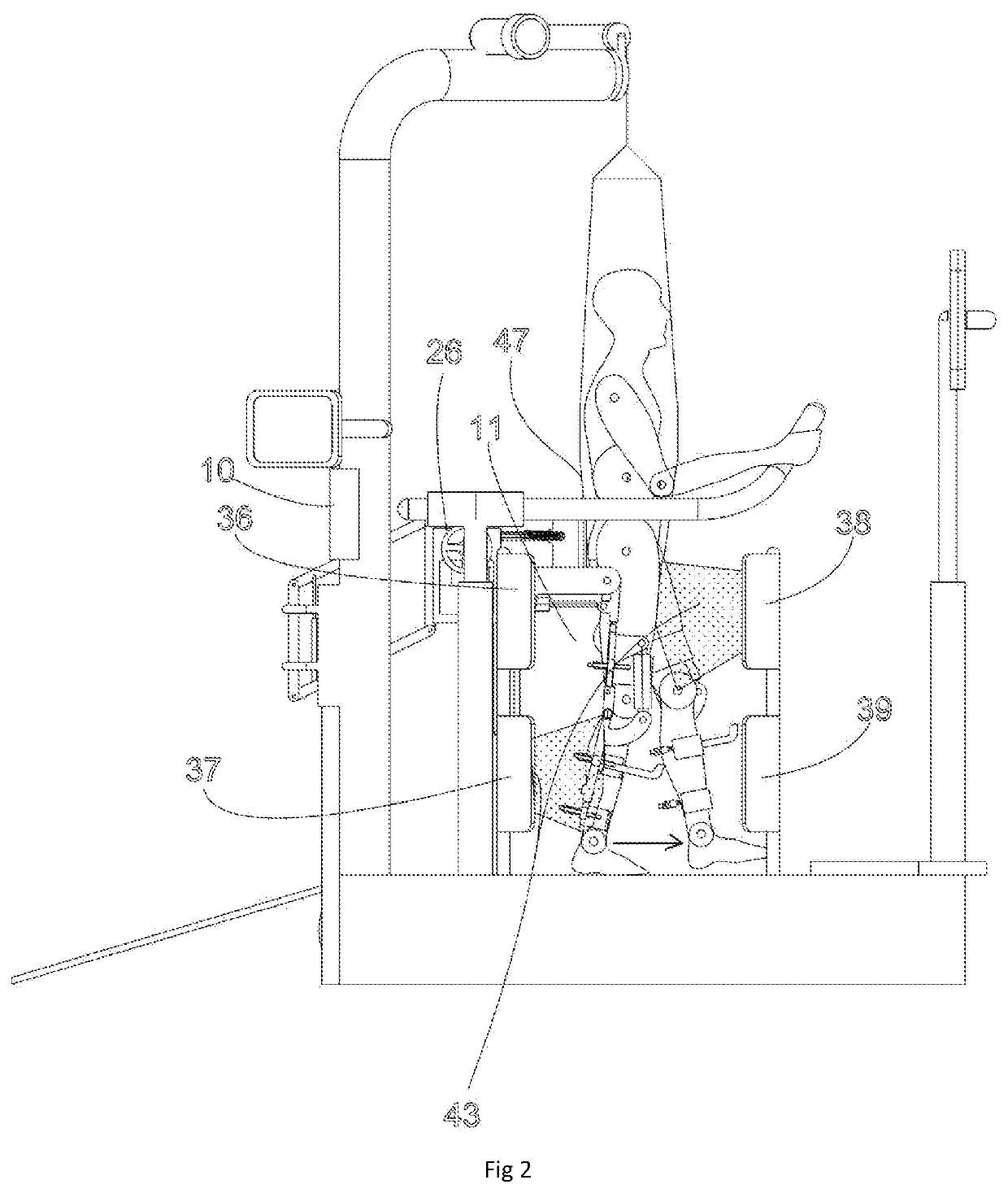
Knee rehabilitation machine with multi-position synchronous force application
PendingCN110840643AInstability CorrectionEliminate discomfortChiropractic devicesVibration massagePhysical medicine and rehabilitationKnee rehabilitation
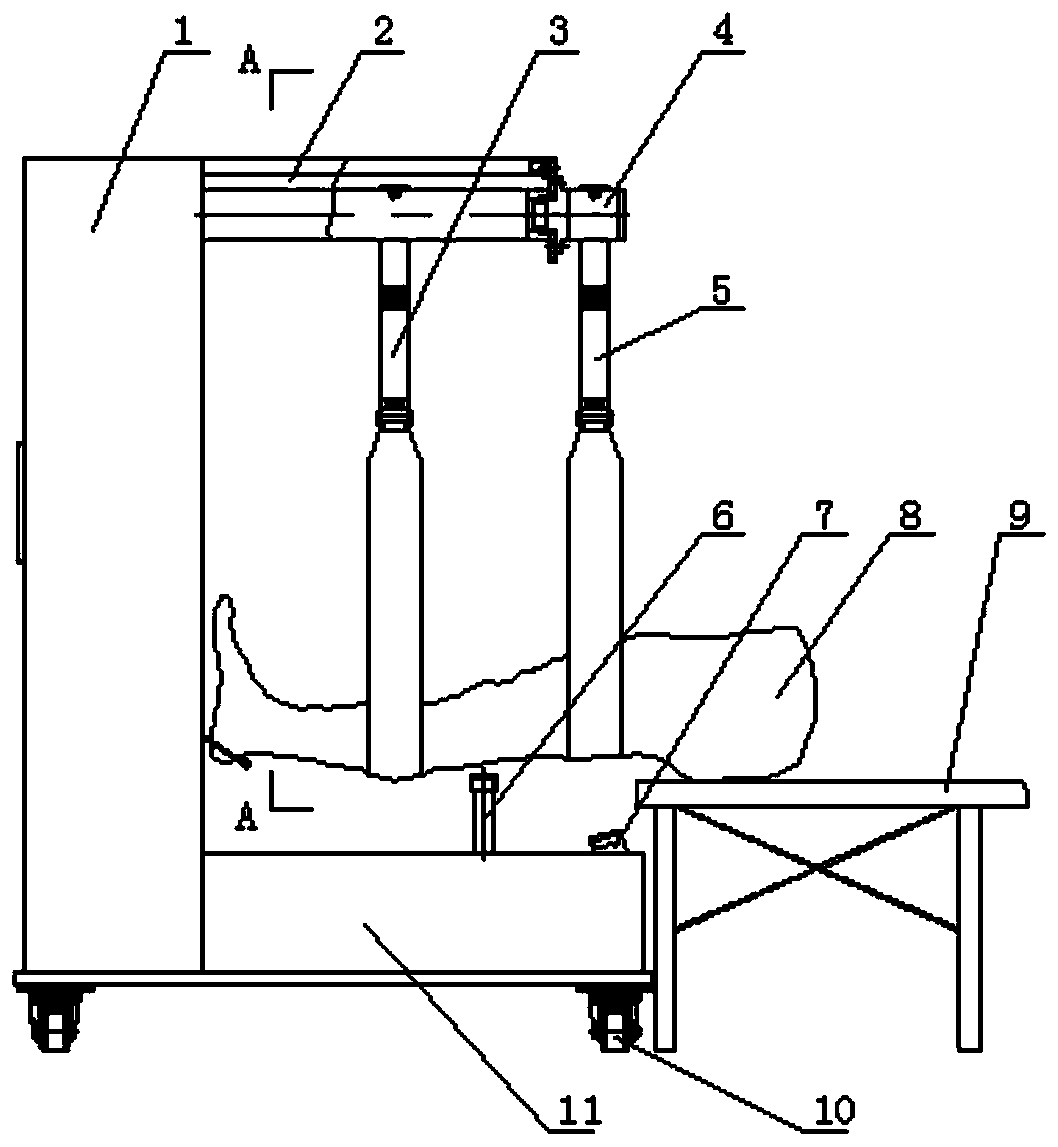
The invention relates to a knee rehabilitation machine with multi-position synchronous force application, which comprises a bottom box, a vertical box and a suspension box; the vertical box is vertically arranged at one end of the bottom box, the suspension box is transversely and fixedly arranged at the upper end of the vertical box, a pressing unit rocker mechanism is fitted in the bottom box, and a transmission mechanism for a vibration unit, a traction unit and a pressing unit are fitted in the vertical box. The traditional Chinese medicine method for correcting the instability state of knee joint is simulated, synchronous scientific force application adjustment is carried out on the relationship between the femur and the tibia through suspension, traction, torsion, pressing and vibration with controllable strength, angle and distance, the femur and the tibia are restored to the normal natural states by means of the memory of the human body, the instability state of the knee jointis corrected, various discomforts caused by the instability state is eliminated, and the occurrence of knee joint diseases is prevented.
Owner:费璟昊
Knee flexion and extension gap tensioning and measuring method
A method for imparting tension across a human knee joint which includes a femur bone, a tibia bone, a patella bone, a patellar tendon, and ligaments, wherein the ligaments and patellar tendon are under anatomical tension to connect the femur and tibia together, creating a load-bearing articulating joint. The method includes: providing a tensioning device, including: a baseplate; a top plate; and a linkage interconnecting the baseplate and the top plate and operable to move the tensioning device between retracted and extended positions, wherein the top plate is pivotally connected to the linkage so as to be able to freely pivot about a pivot axis; positioning the tensioning device between the femur and the tibia; applying an actuating force to the linkage to move the tensioning device towards the extended position, so as to impart a controlled separating force driving the femur and tibia apart to extend the ligaments.
Owner:LITTLE ENGINE LLC
Automated arthroplasty planning
InactiveCN108697471AMedical simulationSurgical systems user interfacePhysical medicine and rehabilitationGraphical user interface
Systems and methods are provided to aid in planning at least a portion of a total knee arthroplasty procedure. The system and method automatically aligns the implant components and the bones accordingto a desired clinical alignment goal with minimum user input. The system and method further allows the user to adjust the position and orientation of the femur, tibia, or implant in a clinical direction regardless of a pre-adjusted position and orientation of the femur, tibia, or implant. The graphical user interface is provided that includes a three- dimensional (3-D) view window, a view optionswindow, a patient information window, an implant family window, a workflow-specific tasks window, and a limb and knee alignment measures window.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
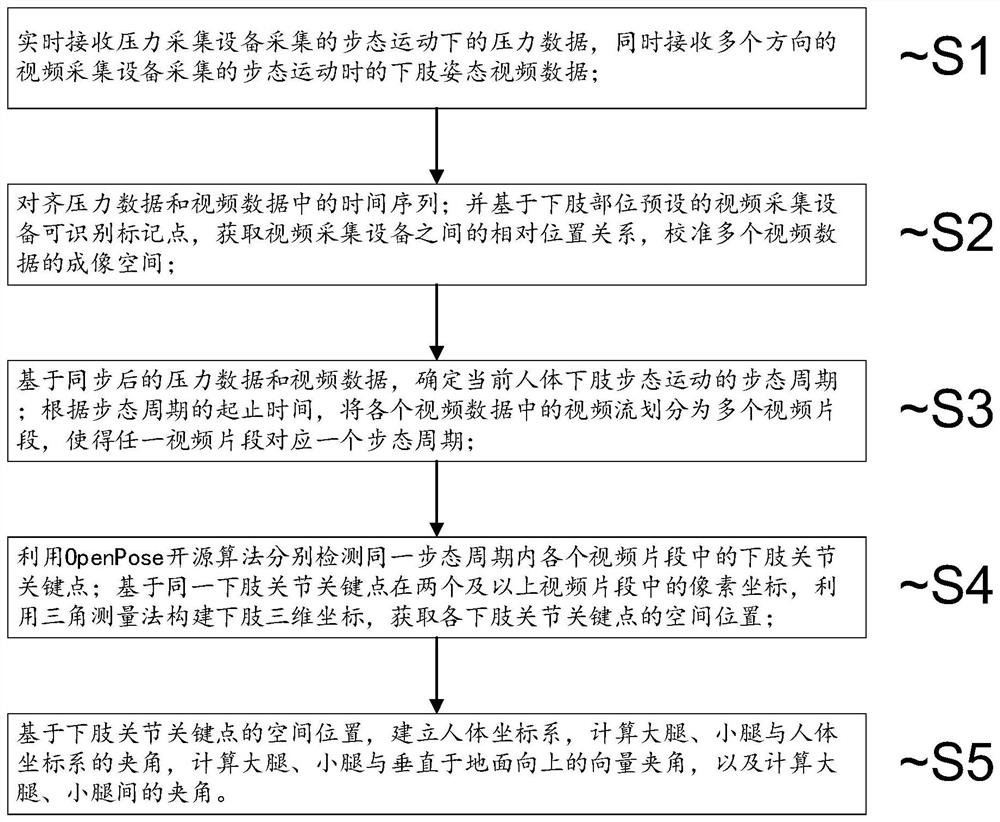
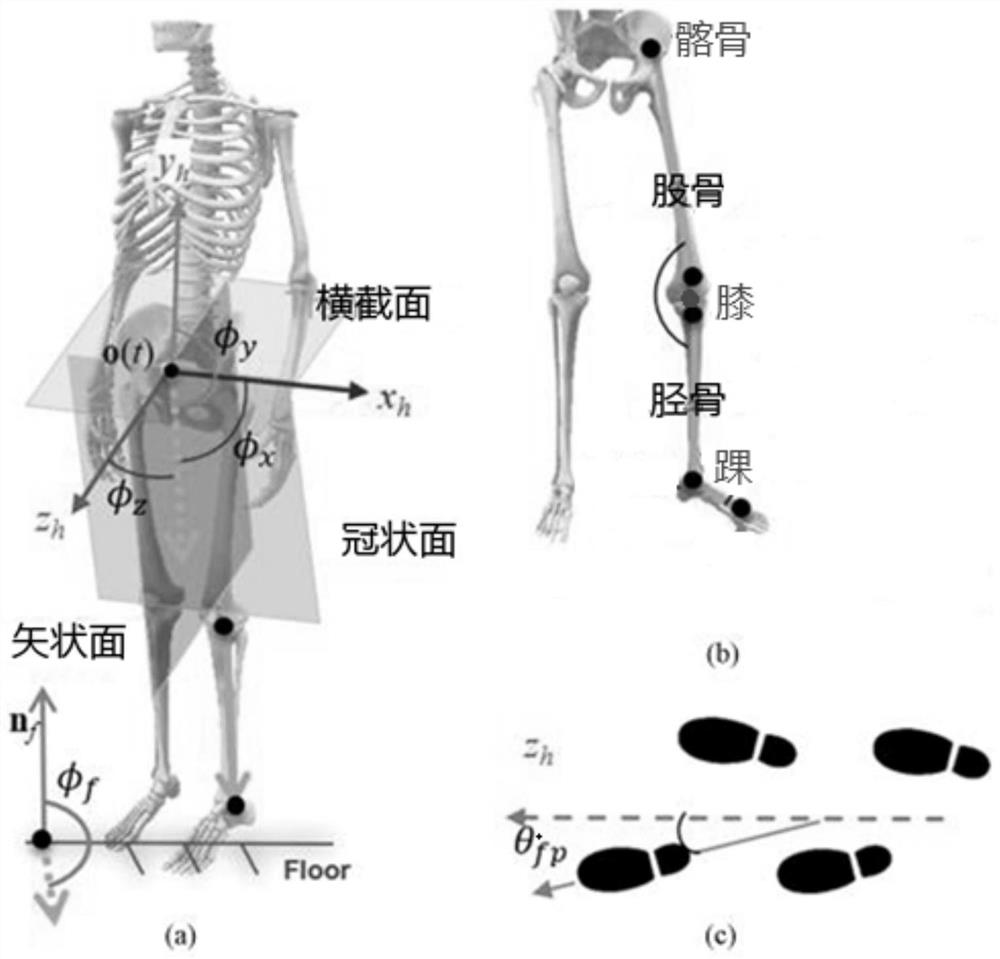
Human body lower limb joint angle measuring method and system
ActiveCN112998694ARealize automatic calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodyOrthopedic devices
The invention discloses a human body lower limb joint angle measuring method and system. The method comprises the following steps: S1, receiving pressure data and lower limb posture video data in real time; S2, aligning time sequences in the pressure data and the video data, and calibrating an imaging space; S3, determining a gait cycle, and dividing the video stream into a plurality of video clips according to the starting and ending time of the gait cycle; S4, detecting lower limb joint key points in each video clip by using an OpenPose open source algorithm, constructing a lower limb three-dimensional coordinate, and acquiring the spatial position of each lower limb joint key point; and S5, establishing a human body coordinate system, and calculating an included angle between the femur and the tibia and the human body coordinate system, an included angle between the femur and the tibia and an upward vector perpendicular to the ground, and an included angle between the femur and the tibia. According to the method, automatic calculation of the joint angles of the knee joint and the hip joint is realized by using multi-view imaging and plantar pressure data, so that a data basis is provided for design and improvement of a plantar orthopedic device, and a data basis is provided for conjoint analysis of follow-up plantar pressure distribution and the joint angles.
Owner:上海橙捷健康科技有限公司 +1
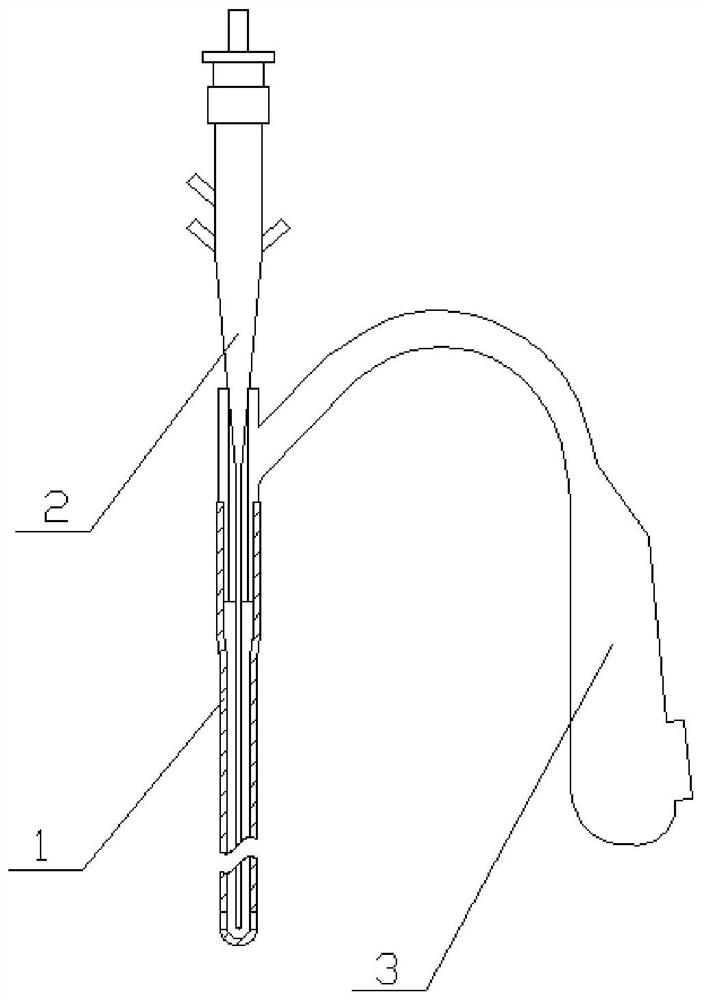
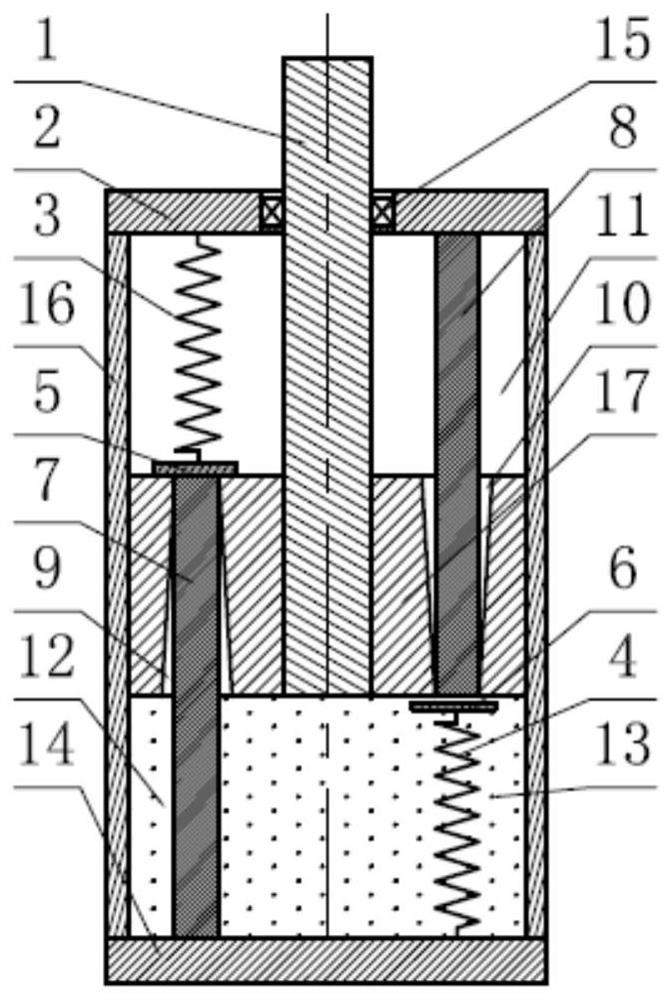
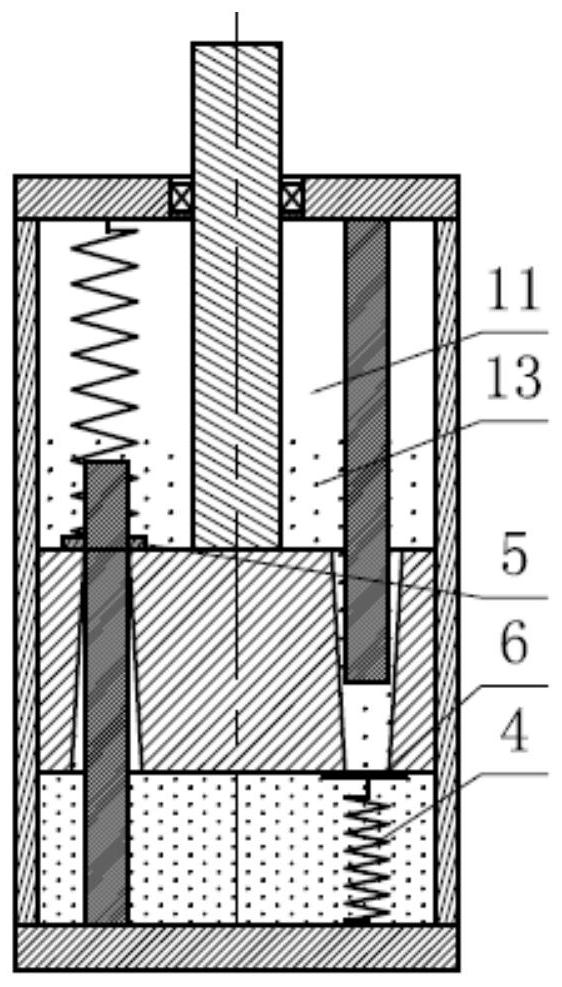
Thighbone and tibia gap balance dilator with pressure sensor
PendingCN112957086AData reading is intuitiveEasy to useSurgeryPhysical medicine and rehabilitationFemoral bone
The invention discloses a thighbone and tibia gap balance dilator with a pressure sensor, and relates to the technical field of medical instruments. The thighbone and tibia gap balance dilator comprises a first handle, a measuring rod, a second handle, a spiral spring, a fixing rod, the pressure sensor and a digital display meter, the first handle, the measuring rod and the second handle are hinged through a hinge shaft, a first supporting plate is arranged at the front end of the first handle, a second supporting plate is arranged at the front end of the measuring rod, a groove is formed in the inner side wall of the second handle, the pressure sensor is detachably arranged in the groove, one end of the spiral spring abuts against the pressure sensor, the other end of the spiral spring abuts against the tail end of the measuring rod, one end of the fixing rod is hinged to the rear end of the first handle, sawteeth engaged with the tail end of the second handle are arranged on the inner side of the fixing rod, the digital display meter is detachably arranged at the rear end of the measuring rod, and the pressure sensor is electrically connected with the digital display meter. The thighbone and tibia gap balance dilator can simultaneously indicate thighbone and tibia dilating distance, angle and surface pressure, is intuitive in data reading and convenient to use, and can be repeatedly disinfected and used.
Owner:山东良医医疗器械有限公司
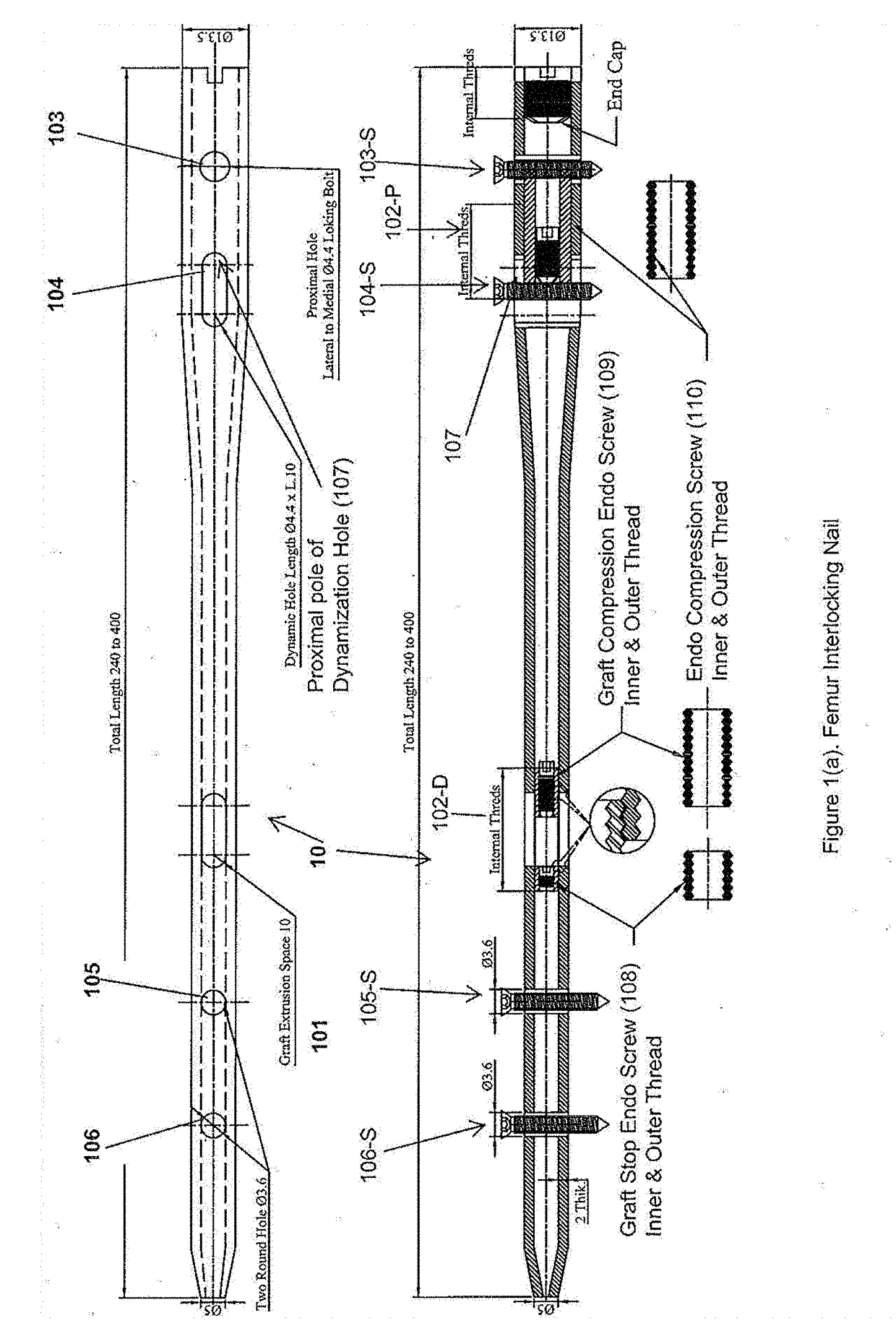
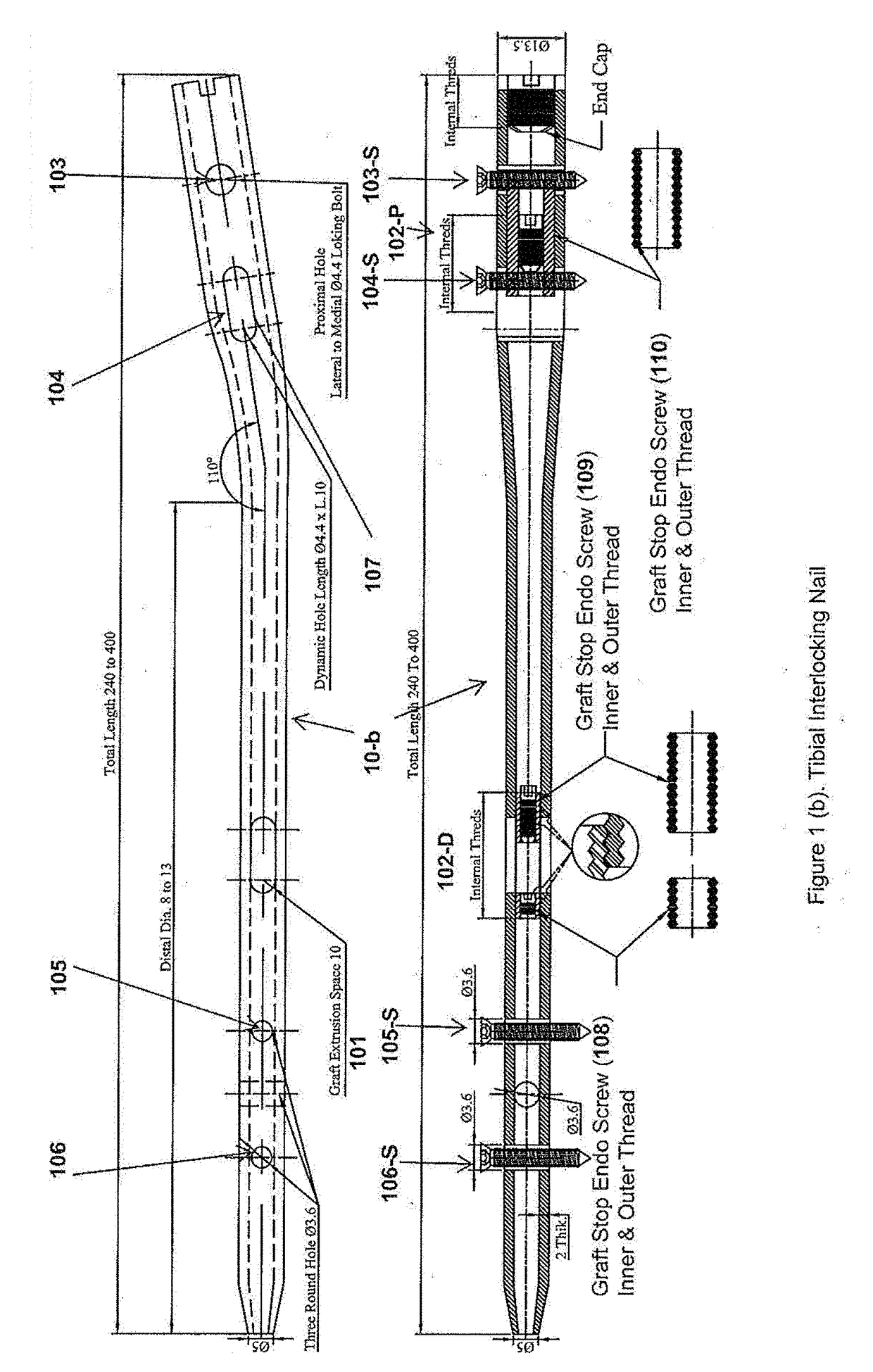
Interlocking Nail
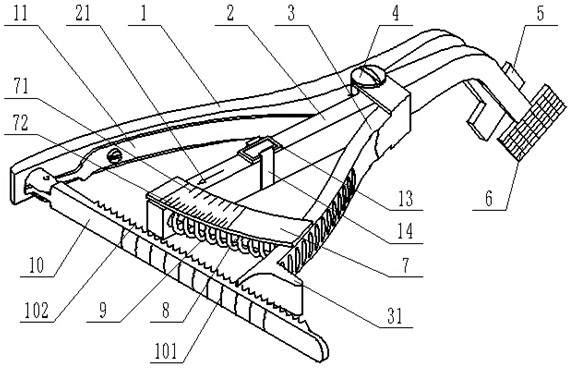
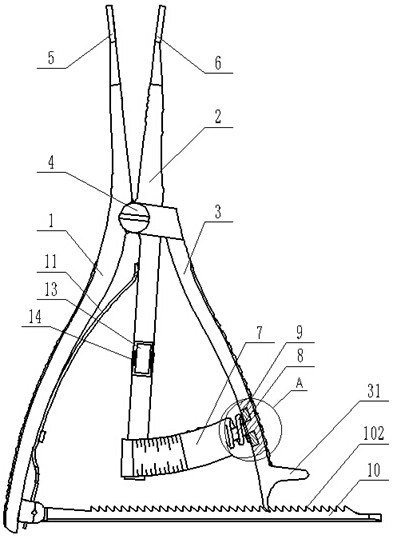
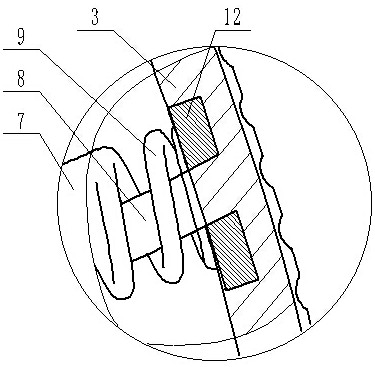
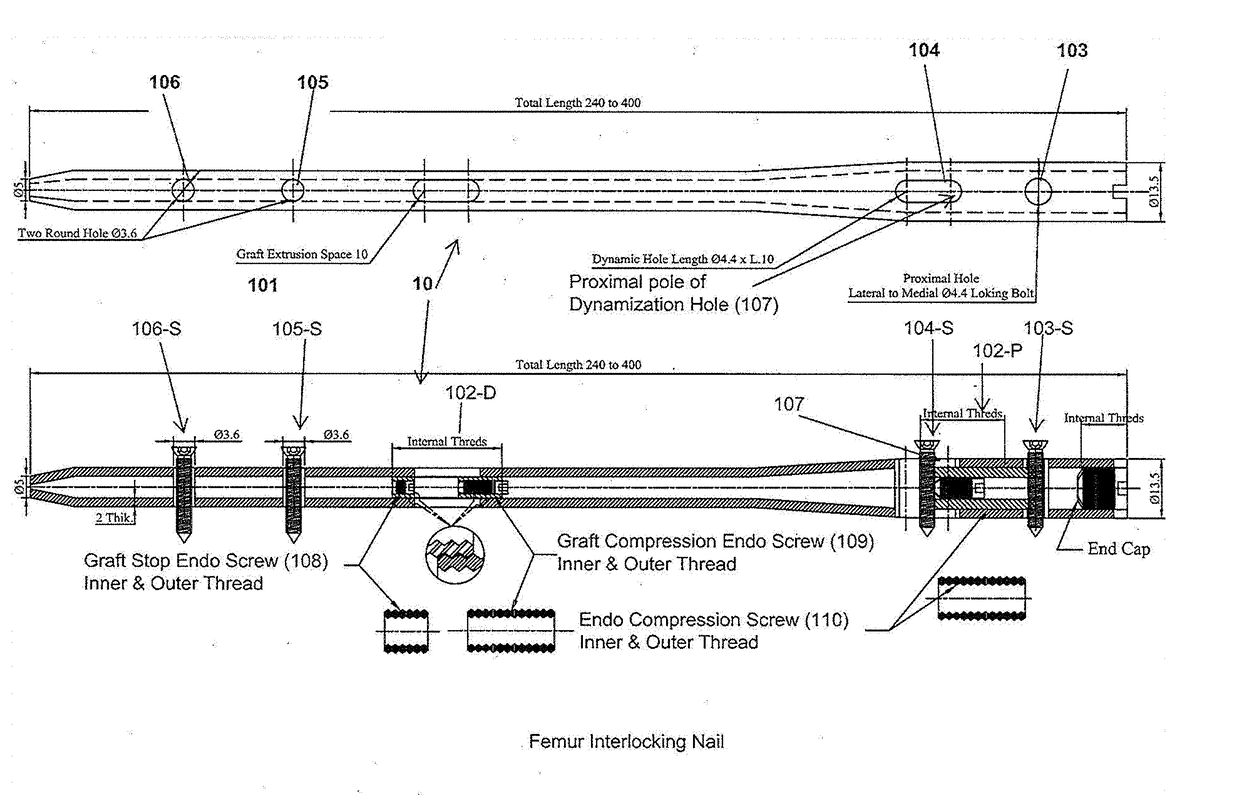
InactiveUS20170224394A1Maintain strengthEnhanced bone healingInternal osteosythesisNailing toolsTibiaWound healing
The invention relates to an interlocking nail (10) for fixation of transverse and short spiral fractures of, long bone, particularly shaft of the femur, tibia and humerus, having Graft extrusion space / slot (101) for holding stem cells graft and 4 or 5 holes for putting interlocking bolts from lateral to medial direction. Constant compression achieved (irrespective of weight bearing cycle) at the fracture site by tightening of the Endo-Compression Screws (108, 109 and 110) results in stimulation of stem cells and reduction in bone gap, thus enhances bone healing and union manifolds.
Owner:TANDIYA NITESH KUMAR
Apparatus and method for evaluating knee geometry
ActiveUS11298246B1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesJoint implantsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationFemoral bone
A method of evaluating a human knee joint which includes a femur bone, a tibia bone, a patella bone, a patellar tendon, and ligaments, wherein the ligaments and patellar tendon are under anatomical tension to connect the femur and tibia together, creating a load-bearing articulating joint, the method including: inserting into the knee joint a gap balancer that includes a tibial interface surface, an opposed femoral interface surface, and at least one force sensor, the method including: providing an electronic receiving device; moving the knee joint through at least a portion of its range of motion; while moving the knee joint, using the electronic receiving device to collect data from the at least one force sensor; processing the collected data to produce a digital geometric model of at least a portion of the knee joint; and storing the digital geometric model for further use.
Owner:LITTLE ENGINE LLC
System for rehabilitating the walk and weight supporting device for such
A system is described, for rehabilitating the walk comprising an active exoskeleton with a supporting structure for right leg and left leg, bearing and moving structures of femur, tibia and foot of the patient, a weight supporting device for patient and active exoskeleton, the weight supporting device ending with a structure connected to means for supporting exoskeleton and patient, handling means connected to the weight supporting device to allow its movement, means for transmitting to the weight supporting device electric and pneumatic supplies and electric signals for managing, controlling, monitoring and diagnosing the system, a managing system comprising a microprocessor for acquiring and processing data, and managing a motion neuro-rehabilitation session; a weight supporting device for a system for rehabilitating the walk is further described.
Owner:NIMBLE ROBOTICS SRL
Infrared ray equipment for robotic rehabilitation on a treadmill, having flexible pelvic attachment
PendingUS20220233880A1Facilitate robotic rehabilitationDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesRobotic rehabilitationInfrared
Rehabilitation device, comprising a motorized tapis roulant, a harness configured to support the weight of the patient; a plurality of infrared light sources, each one directed to light the muscles of a zone of the lower limbs of the patient; a motorized exoskeleton for lower limbs, configured such that it is fastened to the patient femur, tibia and foot and such that it guides his movements while walking in a combined manner with the movement of said tapis roulant; a user interface, arranged in a position visible for the user; a data processing and control unit, configured to control said motorized exoskeleton and said light sources, characterized in that said processing unit is configured to manage an intensity adjusting cycle of said light sources in a differentiated manner for each one of said sources, as a function of the movement cycle imposed by said exoskeleton to the lower limbs.
Owner:TRONCONE ENG S R L S
Visual intramedullary fixation system
PendingCN112754636AReduce surgical traumaFast postoperative recoveryInternal osteosythesisEndoscopesMedical equipmentOphthalmology
The invention provides a visual intramedullary fixation system, belongs to the technical field of medical equipment, and aims to solve the problems that when a patient has femoral and tibia fractures and needs to be operated, the condition of broken ends of fracture bones cannot be effectively observed, the body of the patient is severely wounded due to a direct operation, postoperative rehabilitation is slow, and the operation effect is poor. The visual intramedullary fixation system comprises a fiber soft lens device, a metal intramedullary nail and a phase developing system, wherein the fiber soft lens device is arranged in the metal intramedullary nail, and the phase developing system is electrically connected with the fiber soft lens device. Through the fiber soft lens device in the intramedullary nail, observation of the broken ends of the fracture bones is performed on the phase developing system; the broken ends of the fracture bones are accurately reset through prying and rotating reset operation, operation wounds caused to the patient are reduced, the postoperative rehabilitation is fast, and the operation effect is better.
Owner:刘刚 +1
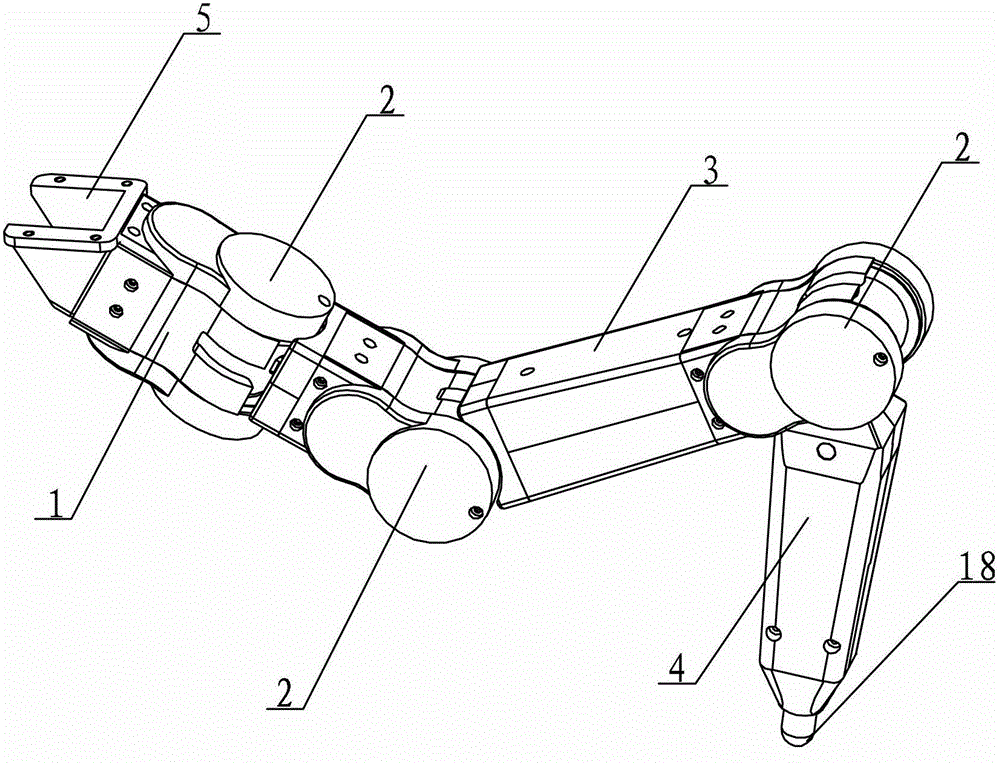
An Integrated Modular Leg System for Hexapod Robots
The invention relates to an integrated modular leg system, in particular to an integrated modular leg system for a hexapod robot. The integrated modular leg system solves the problems that the existing robot leg system is complicated in mechanical structure and inaccurate in positioning. a control part of the integrated modular leg system is mounted on a mechanical mechanism; a triangular connecting piece, a trunk-coxa joint, a coxa beam, a coxa-femur joint, a femur beam and a femur-tibia joint are sequentially connected; a flange is connected with the femur-tibia joint; the upper end of a foot end frame is arranged in a flange hole of the flange; a first one-dimensional force sensor is arranged on the coxa beam; a second one-dimensional force sensor is arranged between the femur beam and the coxa-femur joint; a three-dimensional force sensor is arranged on the foot end frame; a data acquisition card is fixed on the three-dimensional force sensor; a first angular position sensor is arranged on the trunk-coxa joint; the second angular position sensor is arranged on the coxa-femur joint; and a third angular position sensor is arranged on the femur-tibia joint. The integrated modular leg system is suitable for the hexapod robot.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Gap detector used in knee joint replacement surgery
The invention relates to a gap detector used in knee joint replacement surgery, the gap detector comprises a straightening gap detection box and a buckling gap detection box, the straightening gap detection box comprises a first box bottom plate and a first box top plate capable of moving up and down relative to the first box bottom plate, the detector further comprises a first driving shaft, and the axis of the first driving shaft extends in the left-right direction; the flexion gap detection box comprises a second box bottom plate and a second box top plate capable of moving up and down relative to the second box bottom plate, the upper end face of the second box top plate is an arc-shaped concave face matched with a flexion femur, the detector further comprises a second driving shaft with the axis extending in the left-right direction, and the first driving shaft is of a hollow structure; and a movable gap is formed between the inner hole wall of the first driving shaft and the outer peripheral surface of the second driving shaft in the vertical direction. The technical problems that in the prior art, when a detector fills a straightening gap and a buckling gap, the number of filling plates can be increased only by expanding a thighbone tibia by a large size, labor intensity is large, and ligaments are prone to being damaged are solved.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF QINGDAO UNIV
Novel tibial tuberosity traction model
PendingCN111951653AEasy to useUnderstanding Traction EffectsCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsHuman anatomyHuman body
Owner:王俊杰
Display and registration method for total knee arthroplasty
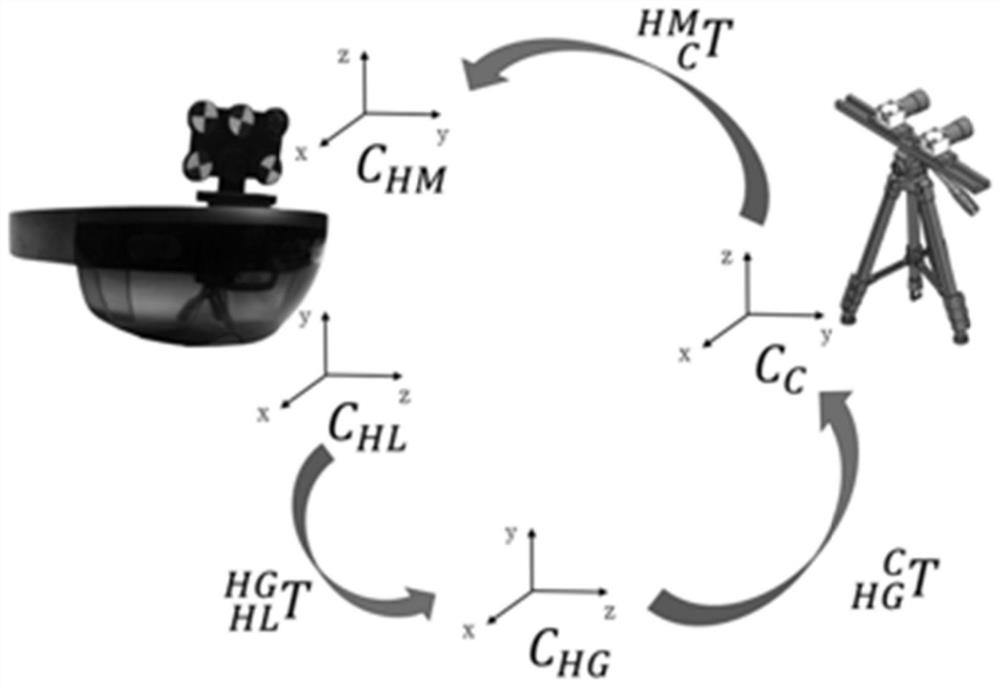
ActiveCN109620406BReduce matching timeExact matchCosmonautic condition simulationsDiagnosticsVirtual spaceKnee Joint
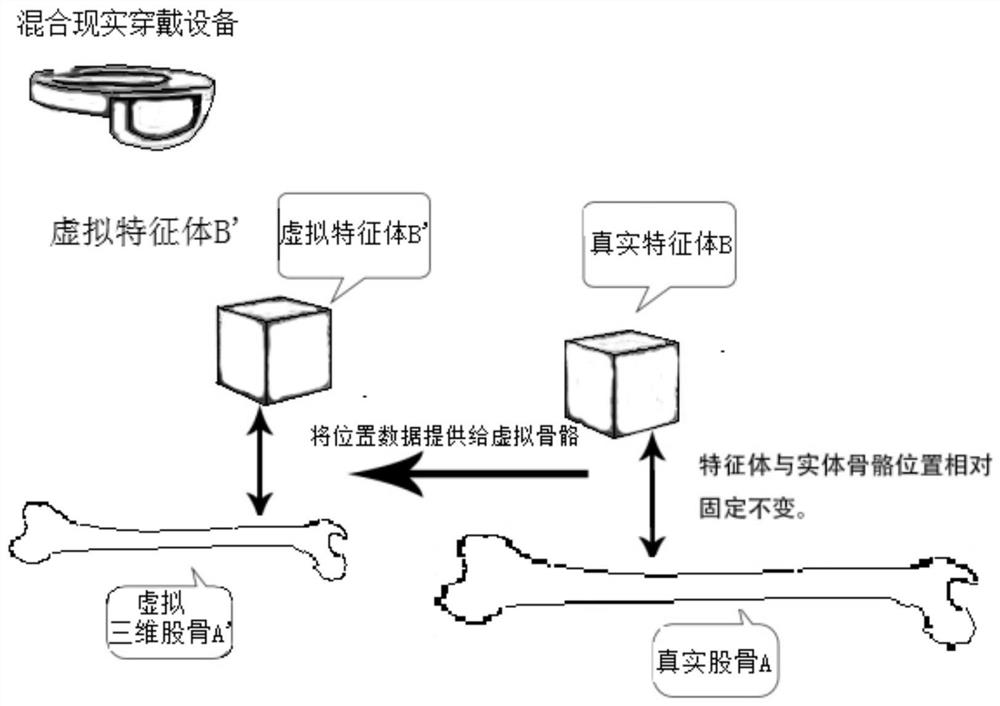
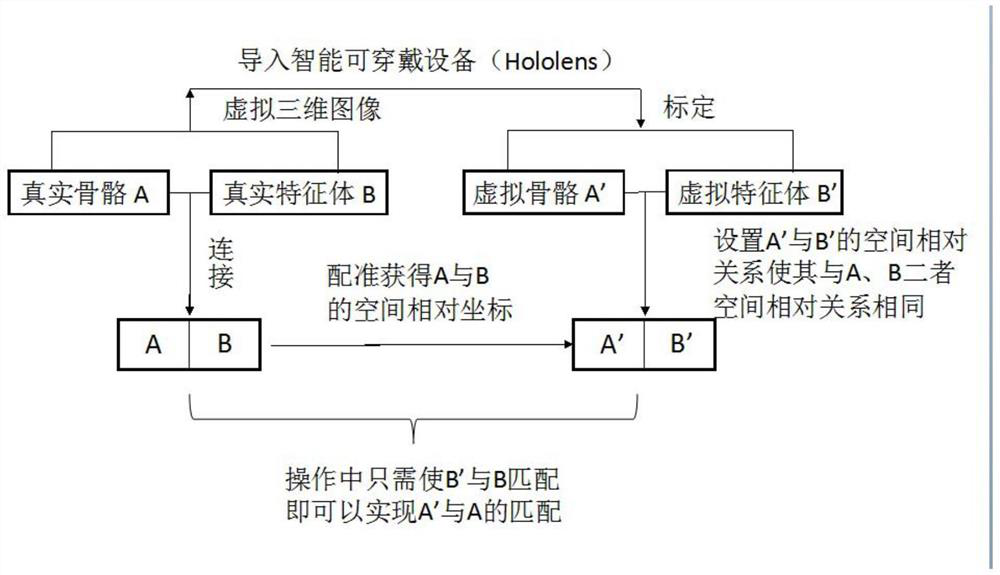
The invention relates to a display and registration method of a virtual bone used in total knee replacement in a mixed reality scene. A three-dimensional virtual image that is completely consistent with the femur and the tibia is established, and the space relative to the actual bone and the feature body is determined. On the basis of the relationship, by identifying the feature body, the three-dimensional virtual bone image in the virtual space is matched with the relative relationship of the femur in the actual space, and the model can follow the movement of the bone. Using the method of the present invention to match the speed block has high accuracy. .
Owner:西安和华瑞博科技有限公司
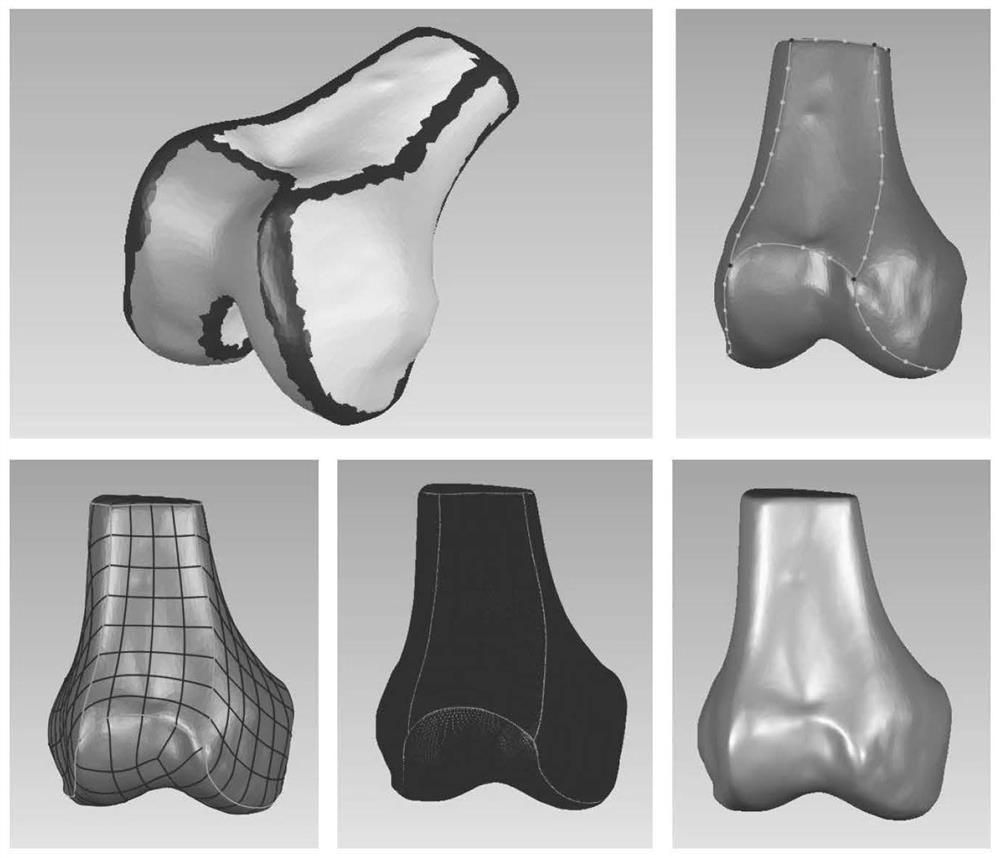
Rapid construction method and system for personalized knee joint prosthesis model
PendingCN114191075ARapid designImprove accuracyComputer-aided planning/modellingPhysical medicine and rehabilitationFemoral bone
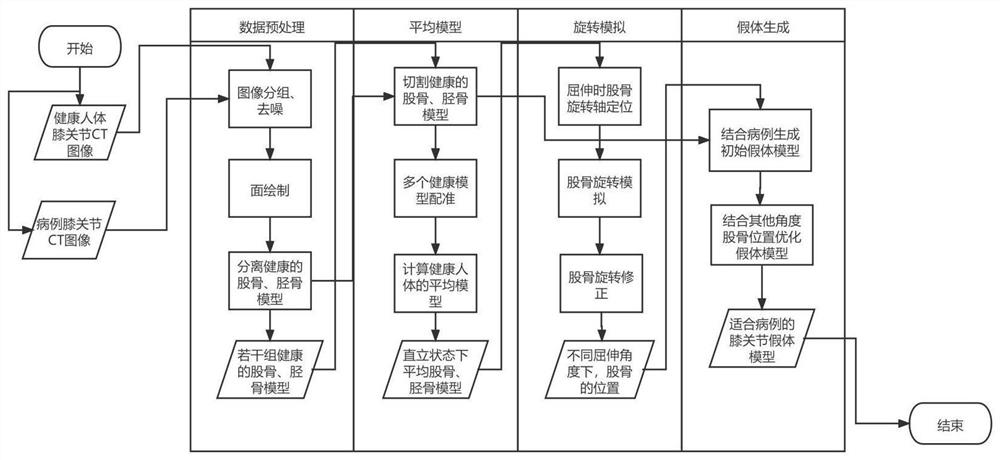
The invention discloses a rapid construction method and system for a personalized knee joint prosthesis model, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the preprocessing of all CT images, obtaining a denoised binary image, and carrying out the surface drawing reconstruction based on the binary image, and obtaining a plurality of knee joint overall models; cutting the separated thighbone model and the separated tibia model at the required fixed length respectively; all the health models in the thighbone model and the tibia model are approximately overlapped in a registration mode, retention adjustment is conducted on the basis of a set retention ratio threshold value, an average thighbone model and an average tibia model which do not contain any health individual case characteristics are obtained, and the average thighbone model close to the size of a case and the thighbone model of the case are subjected to registration alignment; displaying and analyzing the illness state of the case, determining a diseased part needing to be cut off in the case thighbone model and cutting off the diseased area, performing cutting operation on the same position on the average thighbone model, and correcting the meniscus part in the prosthesis model by combining the accurate position of the thighbone model at each flexion and extension angle to obtain a meniscus prosthesis model; therefore, a knee joint prosthesis model conforming to human motion characteristics at each flexion and extension angle is obtained.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
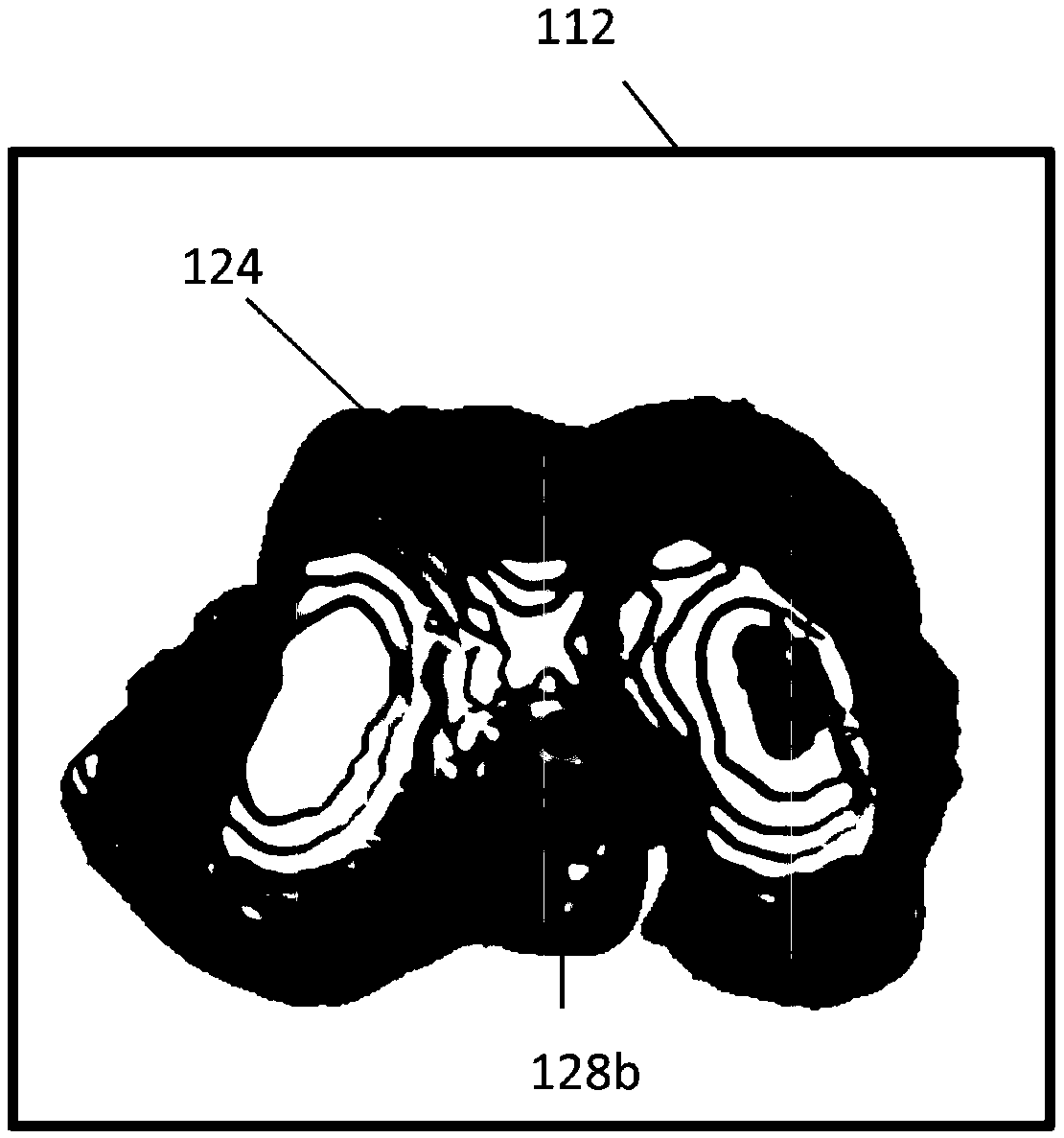
Morphological recognition and visualization method for tendon-bone joint part of knee joint posterior-lateral complex
ActiveCN110766789ASolve elusive problemsAnatomical study helpsSustainable transportationMedical imagesAnatomical structures3d image
The invention discloses a form recognition and visualization method for a tendon-bone joint part of a knee joint posterior-lateral complex. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a cross-section thin-layer true-color high-resolution image of a rear outer side structure of a human knee joint is recognized and segmented; on the basis, three-dimensional reconstruction based on surfacedrawing is carried out on the knee joint rear outer side complex and the adjacent structure thereof; then the thighbone, the tibia and the fibula of the knee joint and the three-dimensional images reconstructed by the FCL, the PT, the PFL and the BT of the PLC are exported in the form of triangular grids; all contact surfaces of the FCL, PT, PFL and BT are marked with the tendon-bone joint partsof the femur and fibula respectively; the tendon-bone joint parts and the central points of the anatomical structures on the femur and the fibula are obtained, the areas of the tendon-bone joint partsof the anatomical structures and the mutual distances between the central points of the tendon-bone joint parts of the anatomical structures are measured, finally, an interactive 3d-pdf model is created for visualization, and the problem that the attachment parts of the tendon-bone joint parts are difficult to determine and observe is solved.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Apparatus and method for evaluating knee geometry
PendingUS20220183859A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesJoint implantsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationFemoral bone
Owner:LITTLE ENGINE LLC
Method and system, storage medium and electronic equipment for identifying force lines using neural network
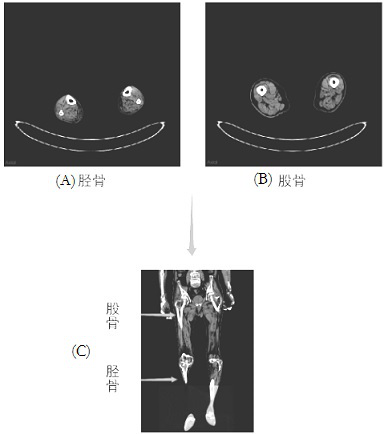
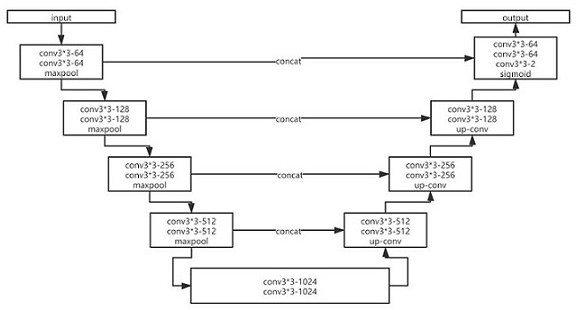
ActiveCN113870261BFavorable assistanceImage enhancementImage analysisRight femoral headActivation function
A method and system for assisting identification of force lines using a neural network, which can be used to detect force lines before and after surgery, assist surgery and understand postoperative recovery status. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining a first image by combining lines of CT file sequences into a complete three-dimensional image, and then performing slices from the coronal plane, and inputting the first image into a first multi-class segmentation based on unet and using a softmax activation function The neural network classifies the femur and tibia differently, thereby segmenting the models of the femur and tibia at one time; and using the second segmentation to find the center point of the femoral head on the femoral model with the neural network to determine the line of force, which is also based on the point cloud Calculate other key physiological points: the center point of the femoral knee joint, the center point of the tibial knee joint and the center point of the tibial ankle joint. Wherein, bilinear quantization processing is performed on the first image, so that down-quantization can also be performed while upward interpolation is performed through bilinear interpolation.
Owner:LANCET ROBOTICS CO LTD
Flexible leg launch adjustment mechanism
ActiveCN106644501BImprove deformation resistanceExtended service lifeVehicle shock testingFemoral boneMechanical engineering
The invention provides an emission adjusting mechanism of a flexible leg. The mechanism is composed of a support plate, a fixed plate, and a baffle plate. The support plate is arranged between the fixed plate and the baffle plate; and the two sides of the support plate are connected with the fixed plate and the baffle plate respectively. The baffle plate has a first mounting surface and a second mounting surface opposite to the first mounting surface; the support plate is connected to the first mounting surface of the baffle plate; and the second mounting surface of the baffle plate is used for placing a first buffer plate and a second buffer plate of a flexible leg, wherein the first buffer plate and the second buffer plate are opposite to each other. According to the adjusting mechanism, a thighbone and a shin bone of a flexible leg can be supported well and thus deformation of the thighbone, the shin bone and the knee due to emission of the flexible leg can be avoided. And the sensing value of the flexible leg during the flight process can meet the regulatory requirement.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GEELY HLDG GRP CO LTD +1
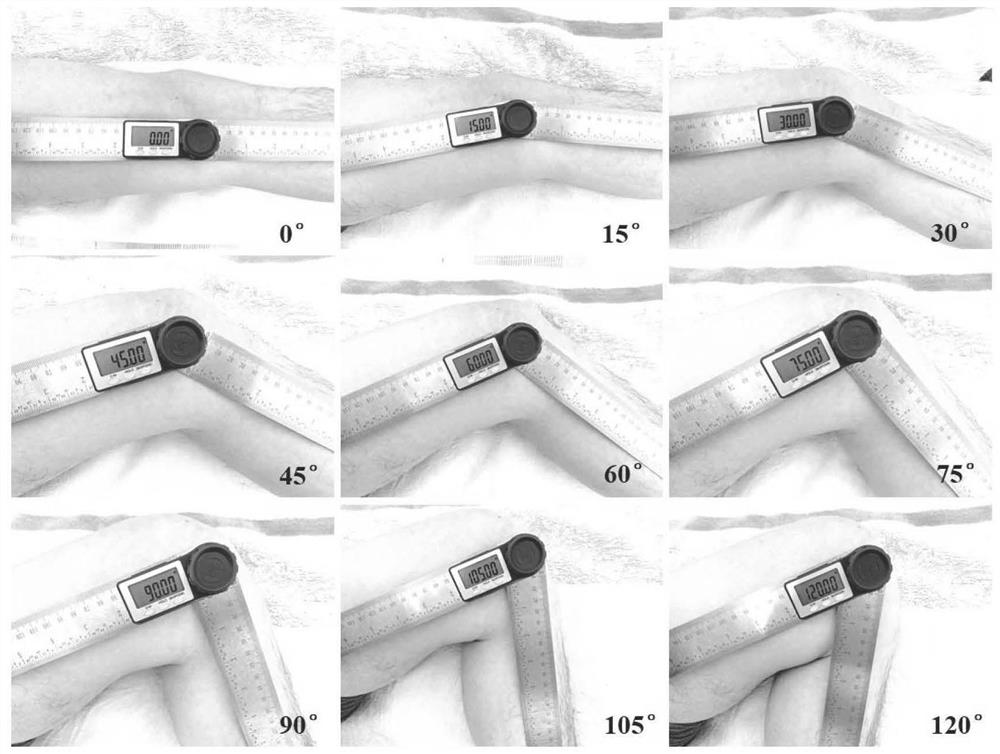
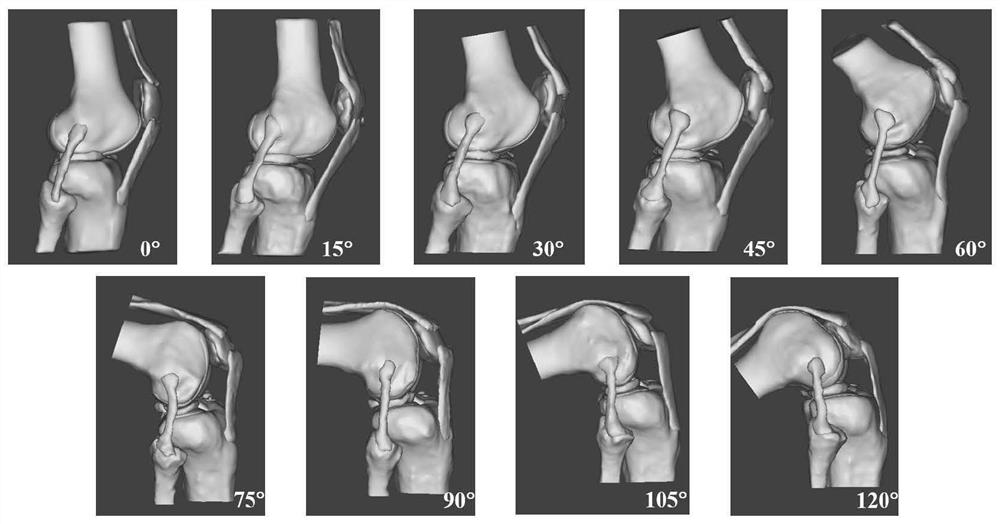
Multi-knee-bending-angle knee joint finite element model and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN113868906ACumbersome operationEasy to operateMedical simulationDesign optimisation/simulationPosterior cruciate ligamentElement model
The invention relates to a multi-knee-bending-angle knee joint finite element model and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of joint anatomy. The model reversely reconstructs the main structure of the knee joint according to MRI data of healthy adults. The model collects and reconstructs a healthy knee joint three-dimensional model when actively bending the knee at 0 degree, 15 degrees, 30 degrees, 45 degrees, 60 degrees, 75 degrees, 90 degrees, 105 degrees and 120 degrees. The model comprises sixteen parts including a femur, a tibia, a fibula, a patella, a femur cartilage, a tibial plateau medial cartilage, a tibial plateau lateral cartilage, a patella cartilage, a medial meniscus, a lateral meniscus, an anterior cruciate ligament, a posterior cruciate ligament, a medial collateral ligament, a lateral collateral ligament, a quadriceps femoris tendon and a patellar tendon. The multi-knee-bending-angle knee joint finite element model is based on a real human knee joint, is complete in structure, is suitable for anatomical learning of the knee joint, and provides a unwonted real knee joint bending and stretching prediction model for simulating the actual condition of the knee joint, researching an injury mechanism, formulating a preoperative plan, clinical teaching and the like.
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF KUNMING MEDICAL UNIV
A vertically flexible telescopic knee joint that can be used as a robot leg
ActiveCN107972012BAchieve variable damping characteristicsRealize the vertical scaling featureProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationKnee Joint
The invention discloses a vertical flexible telescopic knee joint used as a robot leg, and belongs to the technical field of robot joints. The knee joint comprises a femur, a tibia, a tibial cover A,a tibial cover B, a femoral piston installed in the tibia and can freely slide, an upper guide column installed on the tibial cover A, and a lower guide column installed on the tibial cover B; the femoral piston is provided with a forward conical gap and a reverse conical gap with the same structure and the same size, and are in opposite symmetry relative to a center line of the femur; one end ofa compression spring is connected with the tibial cover A, and the other end of the compression spring is provided with a compression spring cover capable of freely sliding along the lower guide column; and one end of a free spring is connected with the tibial cover B, and the other end of the free spring is provided with a free spring cover. The vertical telescopic joint has the advantages of being stable in initial length and capable of freely stretching and deforming.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com