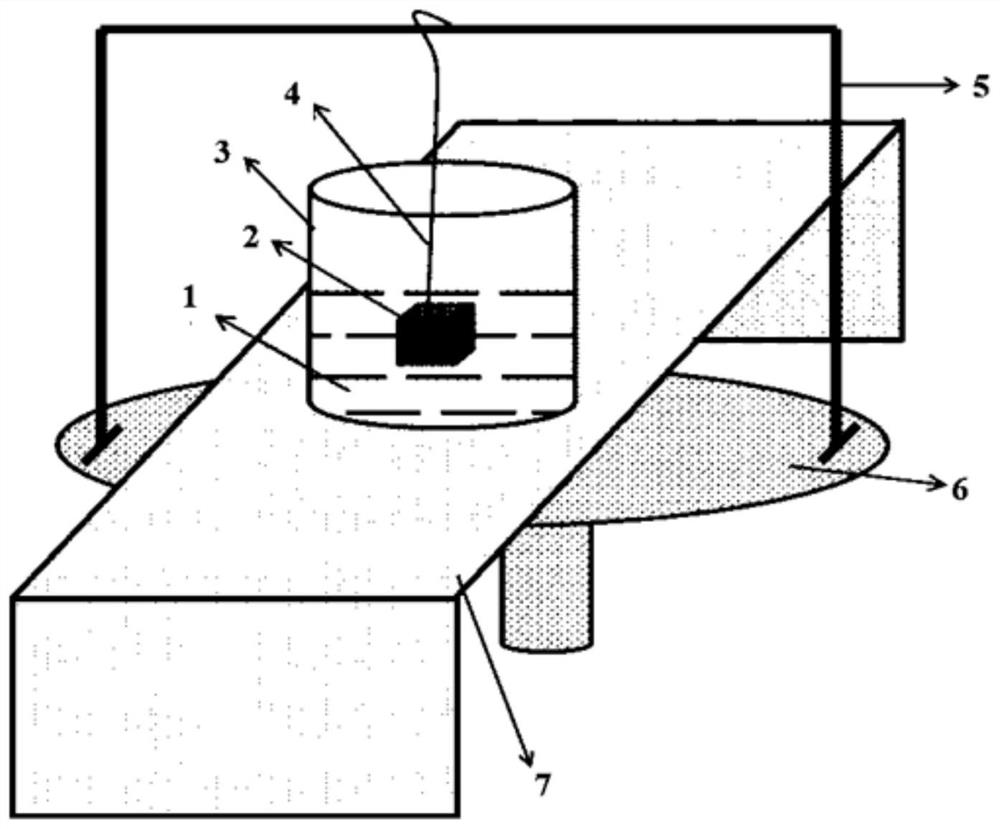
Method for testing solid-liquid phase change volume change rate of material
A technology of variable volume and rate of change, applied in the field of material science research, can solve problems such as precise measurement and large human errors, and achieve the effects of improving accuracy, meeting test requirements, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Prepare a dense block of pure tin about 2cm x 2cm x 2cm, and polish the surface, as well as a sufficient amount of tin for melting. Using DSC to calibrate the melting point of tin is 232°C. Weigh the mass m1 of the tin standard block in air. Put the bracket and thin copper wire on the weighing platform of the balance and clear the balance, then hang the tin standard block in the water with a metal filament, measure the mass m2 under the buoyancy of the sample block to be tested, the tin to be tested The density of the solid is ρ1, and the density of the solid is calculated using the following formula: m1 / ρ1=(m1-m2) / ρwater, and the density of water is 1g / cm 3 calculate.
[0049] Select pure copper as an auxiliary material to prepare a dense pure copper block of about 2cm×2cm×2cm, whose melting point is 1085°C, which is higher than that of tin. The coefficient of linear expansion of pure copper in the range of 20-300°C is 17.64×10 -6 / °C. Weigh the mass m3 of the cop...
Embodiment 2
[0055] A dense block of pure indium of about 1 cm×1 cm×1 cm is prepared, the surface is polished, and a sufficient amount of indium is used for melting. The melting point temperature of indium was calibrated by DSC to be 157°C. Weigh the mass m1 of the indium block in air. Put the bracket and thin copper wire on the weighing platform of the balance and clear the balance, then hang the indium standard block in the water with a metal filament, measure the mass m2 under the buoyancy of the sample block to be tested, and the indium to be measured The density of the solid is ρ1, and the density of the solid is calculated using the following formula: m1 / ρ1=(m1-m2) / ρwater, and the density of water is 1g / cm 3 calculate.
[0056] Select pure copper as the auxiliary material to prepare a dense pure copper block of about 1cm×1cm×1cm, and its melting point is 1085°C, which is higher than that of indium. The coefficient of linear expansion of pure copper in the range of 20-200°C is 17.2...
Embodiment 3
[0062] A dense block of epoxy resin approximately 2.5 cm x 2.5 cm x 2.5 cm was prepared and the surface was polished, along with sufficient epoxy resin for melting. The melting temperature range of epoxy resin calibrated by DSC is 140-160°C. Weigh the mass m1 of the epoxy resin block in air. Put the bracket and thin copper wire on the weighing platform of the balance and clear the balance, then hang the epoxy resin block in the water with metal filaments, measure the mass m2 under the buoyancy of the block, and the epoxy resin to be tested The density of the resin solid is ρ1, and the density of the solid is calculated using the following formula: m1 / ρ1=(m1-m2) / ρwater, and the density of water is 1g / cm 3 calculate.
[0063] Select pure aluminum as the auxiliary material to prepare a dense pure aluminum block of about 2.5cm×2.5cm×2.5cm, whose melting point is 660°C, which is higher than that of epoxy resin. The linear expansion coefficient of pure aluminum in the range of 20...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com