Patents
Literature
326 results about "Melting Point Temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A melting point is essentially a set temperature that an element has where it begins to melt. Ice for example, begins to melt at 32° Fahrenheit. On the other hand, iron has a melting point of about 2,800° Fahrenheit.
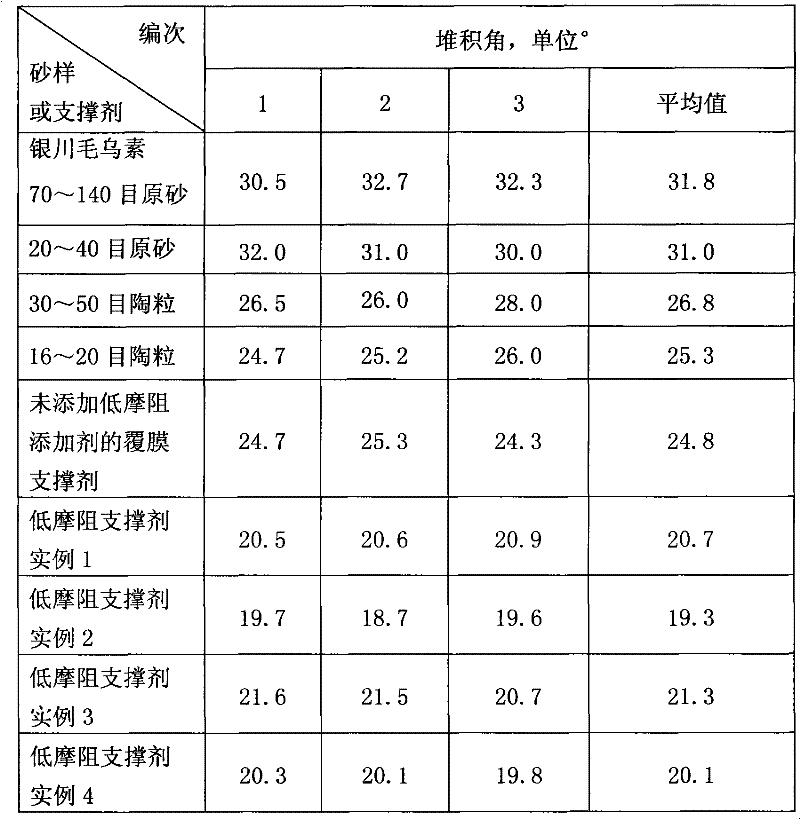
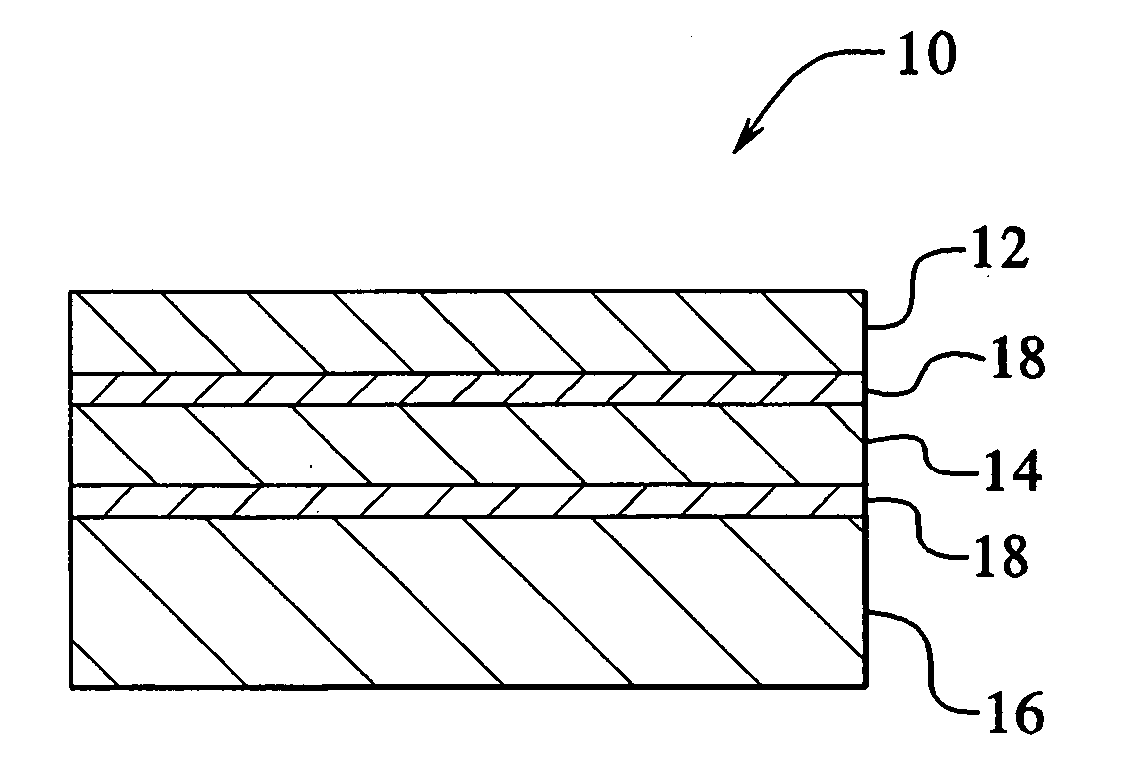
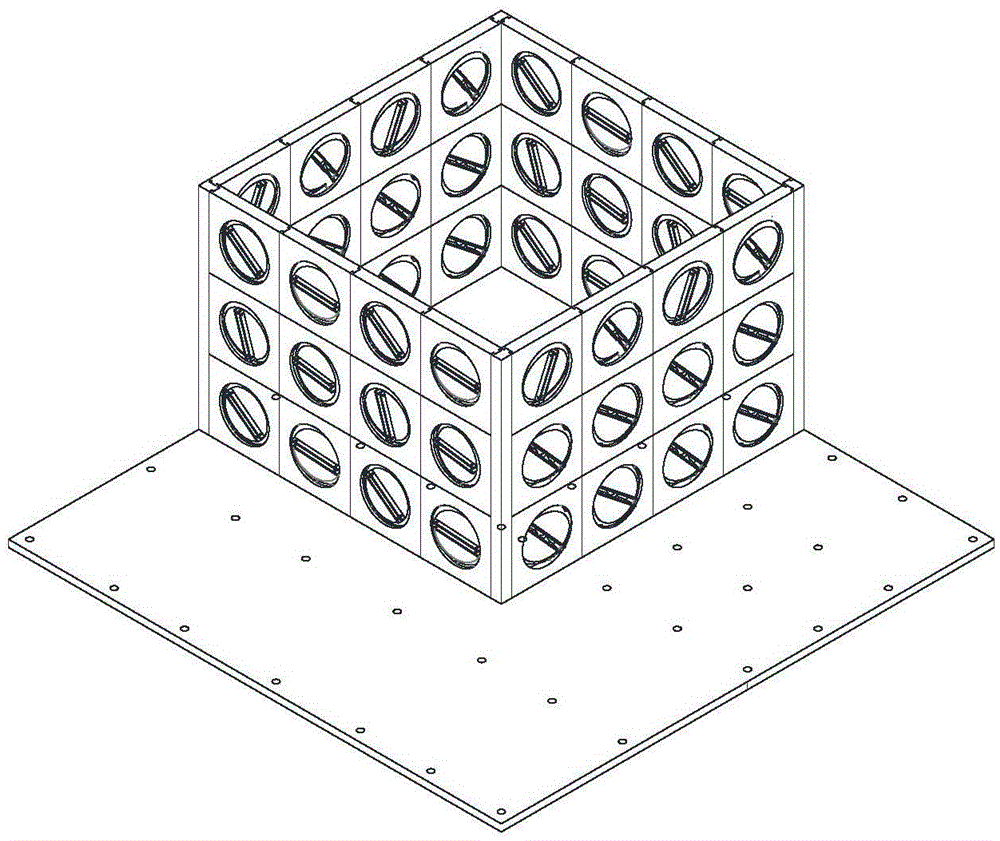
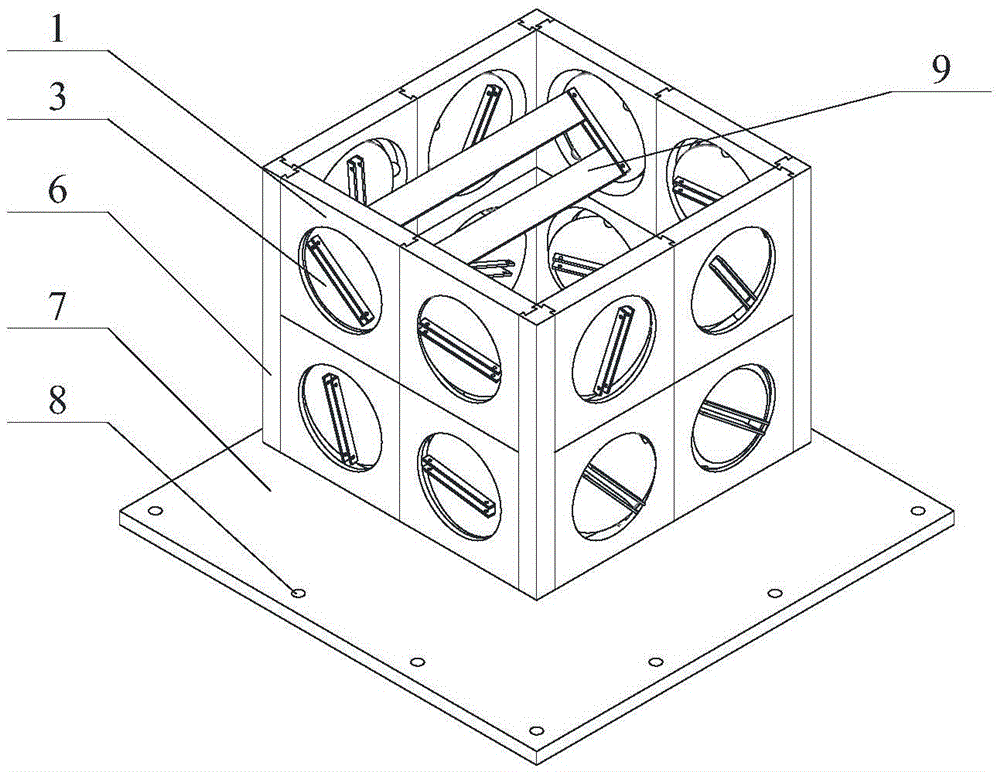
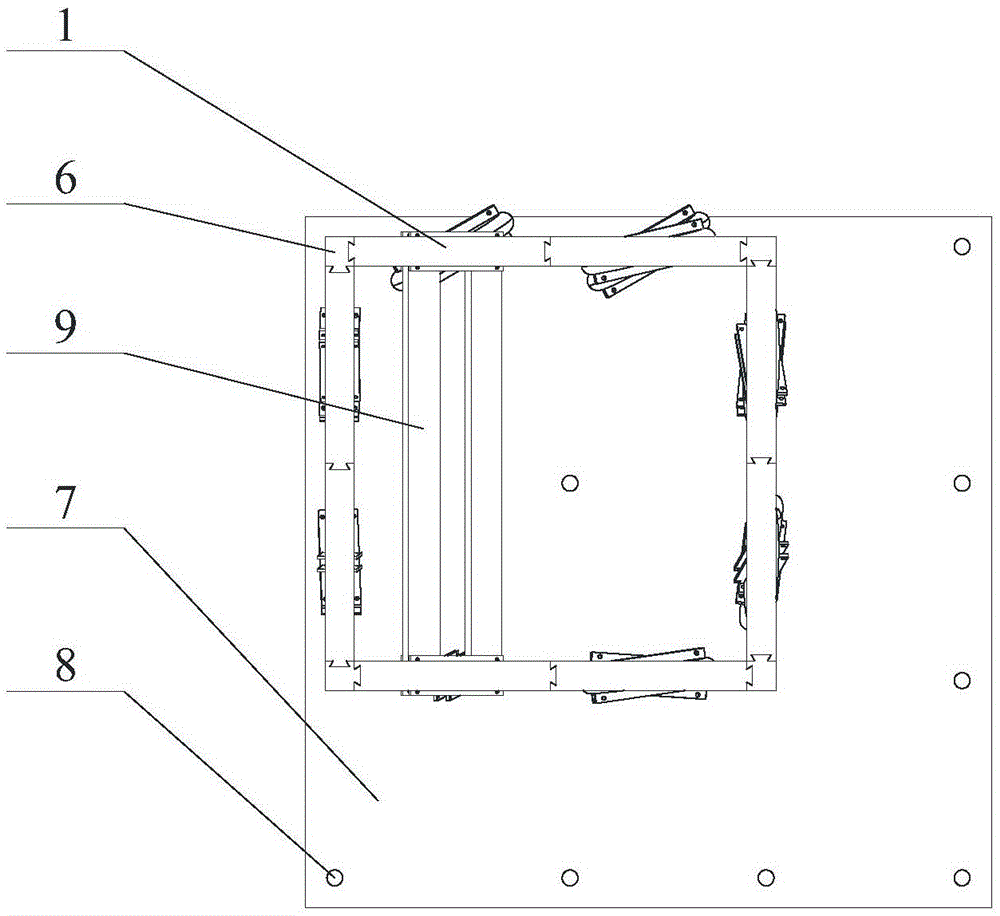
Solar cell modules with improved backskin
InactiveUS6660930B1High dielectric strengthExtended service lifePV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsIonomerEngineering
A laminated solar cell module comprises a front light transmitting support, a plurality of interconnected solar cells encapsulated by a light-transmitting encapsulant material, and an improved backskin formed of an ionomer / nylon alloy. The improved backskin has a toughness and melting point temperature sufficiently great to avoid any likelihood of it being pierced by any of the components that interconnect the solar cells.
Owner:SCHOTT SOLAR AG (DE)
Toner processes
ActiveUS20080236446A1Improve blocking propertiesExcellent heat cohesionInksDevelopersPolyesterPolymer chemistry
A toner process comprising the aggregation and coalescence of an amorphous polyester, a crystalline polyester and a colorant, and wherein the coalescence is conducted at a temperature that is about lower than the melting point temperature of the crystalline polyester.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Low temperature integrated via and trench fill process and apparatus
InactiveUS6139697AInhibition formationFacilitated DiffusionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVacuum evaporation coatingAir exposureCopper
The present invention relates generally to an improved process for providing complete via fill on a substrate and planarization of metal layers to form continuous, void-free contacts or vias in sub-half micron applications. In one aspect of the invention, a refractory layer is deposited onto a substrate having high aspect ratio contacts or vias formed thereon. A CVD metal layer, such as CVD Al or CVD Cu, is then deposited onto the refractory layer at low temperatures to provide a conformal wetting layer for a PVD Cu. Next, a PVD Cu is deposited onto the previously formed CVD Cu layer at a temperature below that of the melting point temperature of the metal. The resulting CVD / PVD Cu layer is substantially void-free. The metallization process is preferably carried out in an integrated processing system that includes both a PVD and CVD processing chamber so that once the substrate is introduced into a vacuum environment, the metallization of the vias and contacts occurs without the formation of an oxide layer over the CVD Cu layer. The via fill process of the present invention is also successful with air-exposure between the CVD Cu and PVD Cu steps.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Polypropylene composition useful for making solid state oriented film
Disclosed is a polypropylene composition useful for making solid state oriented film. The composition comprises two predominantly isotactic polypropylenes with the melting point temperature of one of the polypropylenes being substantially lower than the melting point temperature of the other. In one embodiment of the composition the higher melting point polypropylene is made by Ziegler-Natta catalysis, while the lower melting point polypropylene is made by metallocene catalysis. Compared to polypropylene with similar melt flow rate and made by Ziegler-Natta catalysis, and solid state oriented film thereof, the composition provides a better balance of elevated temperature draw characteristics and physical properties of oriented film made therefrom. Thus, at the same or lower elevated temperature yield stress, oriented film of the composition exhibits improved properties such as stiffness, elongation-at-break, dimensional stability, and oxygen barrier. Also disclosed is a method for the manufacture of oriented, flexible packaging film. In the method a cast sheet is melt extruded from the composition, and, after cooling until it is solid, the cast sheet is stretched to the desired extent of orientation at a temperature which the sheet does not break while being stretched, but below the Tm of the composition. The resulting film then is cooled to at least the crystallization temperature of the lower melting point polypropylene.
Owner:MONTELL TECH CO BV
Laser Cladding on Low Heat Resistant Substrates
InactiveUS20080226843A1Sufficient powerMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingMetal alloyLength wave
This invention relates to laser cladding of components used in high temperature-corrosive applications, such as those associated with metallurgical vessels' lances, nozzles and tuyeres, for extending their service life under such severe conditions. In particular, this invention relates to a method for applying a high melting point material onto a substrate, said substrate having a melting point temperature below the melting point temperature of the high melting point material, comprising: (a) moving a laser beam generated from a laser over the surface of said substrate, said laser beam comprised of wavelengths from about 300 to about 10,600 nanometers; (h) providing a metal, alloy, or metal-alloy composite powder to the surface of said substrate; and (c) generating sufficient power to the laser to superficially heat said substrate and to effect a fusion bond between the metal, alloy or metal-alloy composite powder and the surface of said substrate.
Owner:PRAXAIR ST TECH INC
Nano intermetallic compound soldering paste and preparation method thereof
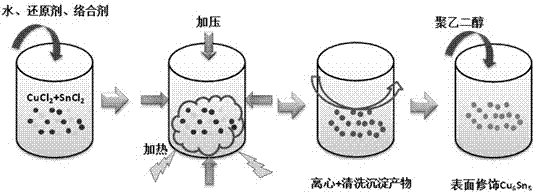
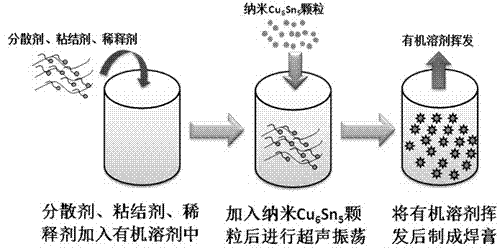
ActiveCN102922177ALow costHigh purityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSolid componentSolvent
The invention discloses nano intermetallic compound soldering paste and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of material technologies. The nano intermetallic compound soldering paste disclosed by the invention comprises the following materials in mass ratio: 80-90 of nano intermetallic compound particles, 2-8 of dispersant, 2-8 of binder, 2-8 of thinner and 2-8 of soldering flux. The specific method comprises the following steps of: preparing the nano intermetallic compound particles by using a co-precipitation hydrothermal reduction method; mixing the prepared nano intermetallic compound particles with the dispersant, the binder, the thinner and the soldering flux; uniformly dispersing the obtained mixture in an organic solvent by using an ultrasonic oscillation, manual stirring or mechanical stirring method; and volatilizing an excess solvent, so that the nano intermetallic compound soldering paste is prepared. The soldering paste takes nano intermetallic compound particles as solid components, and by using the size effect of nano materials, an interconnection process at a temperature lower than the melting point temperature of a block is realized, thereby avoiding the high-temperature damages to components, avoiding the overreaction of a connection interface, achieving an effect of long-term high-temperature serving, and reducing the packaging cost.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
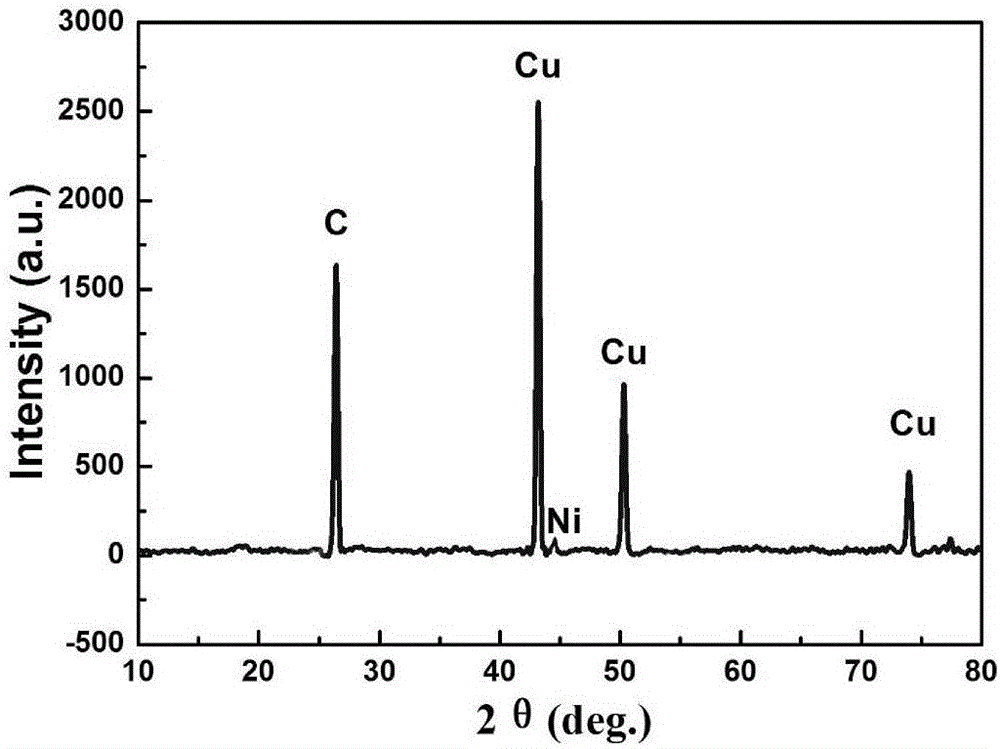
Copper-carbon composite material and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN106424713APromotes even distributionImprove performanceTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusFiberCarbon composites
The invention discloses a copper-carbon composite material and a preparing method thereof. Natural flake graphite, colloidal graphite, nano graphite, carbon fiber and the like can be selected as a carbon material in the copper-carbon composite material. The preparing method of the copper-carbon composite material includes the steps that firstly, a chemical nickel plating method is used for preparing a nickel plating carbon material; then a chemical copper plating method is used for plating copper on the nickel plating carbon material; and finally, vacuum semi-solid-state low-pressure sintering is conducted on the copper plating carbon material under the copper melting point temperature, and the copper-carbon composite material is prepared. The copper-carbon composite material and the preparing method thereof have the beneficial effects that a layer of even thin nickel plating layer is formed on the surface of carbon through the nickel plating method so as to reduce the wetting angle of the carbon material, the copper plating layer is formed on the surface of the nickel plating carbon material through the copper plating method so that a three-dimensional copper network can be formed by the material in the sintering process, and the bonding strength of a base body is improved through vacuum semi-solid-state low-pressure sintering. The two phases of the base body and the carbon of the copper-carbon composite material prepared through the method are distributed evenly and are well combined, and the good electricity and mechanical properties and the good frictional wear performance are achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
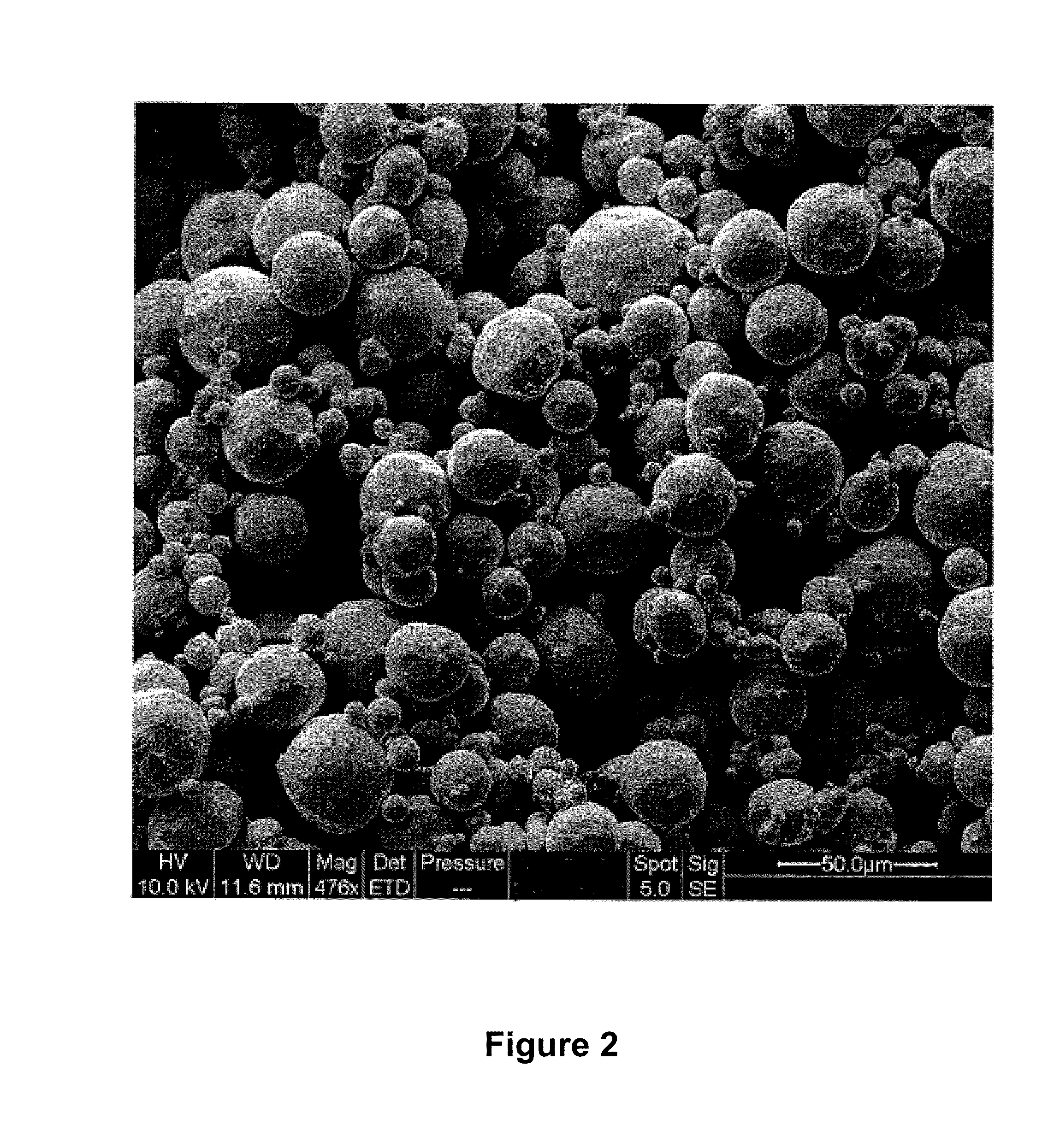
Manufacturing method of micron and nanometer metal spherical powder
ActiveCN104259469AImprove consistencyClear principleMaterial nanotechnologyRare earthSpherical shaped
The invention provides a manufacturing method of micron and nanometer metal spherical powder. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of 1 preparing metal powder; 2 preparing evenly mixed powder of the metal powder and carbon material powder or ceramic material powder; 3 performing high-temperature annealing to enable metal to be molten and solidify to form a metal ball, wherein the temperature for the high-temperature annealing is the temperature for metal melting, especially the temperature is higher than metal melting point temperature and ranges from 40 DEG C to 100 DEG C; 4 removing the carbon material powder or the ceramic material powder to obtain the micron and nanometer metal spherical powder. All metals of the metal spherical powder are elemental metals containing gold, silver, copper, aluminum, gallium, tin, zinc, lead, iron, cobalt, nickel, rare earth and the like, and alloy and compounds formed by the elemental metals are alloy and compounds formed by the metals including boron, silicon, carbon, phosphorus, germanium, nitrogen and the like and nonmetal.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
NbMoTaW high-entropy alloy, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106167870AImprove performanceEliminate composition segregationHigh entropy alloysSolid solution
The invention belongs to the technical field of high-entropy alloy, and discloses a NbMoTaW high-entropy alloy, and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method, mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering are combined for forming, alloying of Nb, Mo, Ta, and W which are high in melting points is realized at solid states, heating to the melting points is not necessary, block materials with excellent performance can be obtained via only one time of solid phase sintering ( the sintering temperature is 1600 DEG C or lower), a difficult problem that the melting temperature (>2900 DEG C) of smelting method is high is solved, processing temperature is reduced greatly, and technology is simplified. According to the microscopic structure of the NbMoTaW high-entropy alloy, dispersion distribution of a granular second phase in an isometric crystal substrate is observed, both the substrate phase and the second phase are BCC solid solution, the substrate average particle size is smaller than 6<mu>m, the second phase average particle size is smaller than 4<mu>m, the material crystal particles are small, the structure is uniform, no dendritic segregation is caused, and strength and hardness are high.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Propping agent particles and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102127417ALow friction hasLow density and high strengthFluid removalInorganic compoundResin coating
The invention discloses propping agent particles and a preparation method thereof. The propping agent particles comprise aggregate particles and a resin coating film for coating the aggregate particles, wherein the resin coating film comprises a low-friction additive; and the low-friction additive is a laminar solid material, an inorganic compound, a high polymer or any combination of the materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: 1, heating resin to be coated with a film to the melting point temperature and adding the low-friction additive into the molten resin; 2, adding the aggregate particles, adding the resin obtained in the step 1 into the aggregate particles, and stirring uniformly; and 3, cooling the mixture obtained in the step 2 and smashing to obtain film-coated propping agent particles. In the method, the low-friction additive is added into the resin, and the aggregate particles are coated with the film, so that the low-friction film-coated propping agent is obtained. The propping agent has the characteristics of low density, high intensity, temperature resistance, pressure resistance and low friction.
Owner:BEIJING RECHSAND SCI & TECH GRP
High impact strength film and non-pvc containing container and pouch and overpouch
A monolayer film of a polymer blend of a first component selected from the group consisting of an ethylene containing polymer, the first component present in an amount by weight of the film from about 60% to about 1%, the first component having a first melting point temperature determined by DSC, a second component selected from the group consisting of propylene containing polymers and methyl pentene containing polymers, the second component being present in an amount by weight of the film from about 99% to about 40%, the second component having a second melting point temperature determined by DSC; and the film being capable of withstanding steam sterilization at a temperature from about 100° C. to about 130° C.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
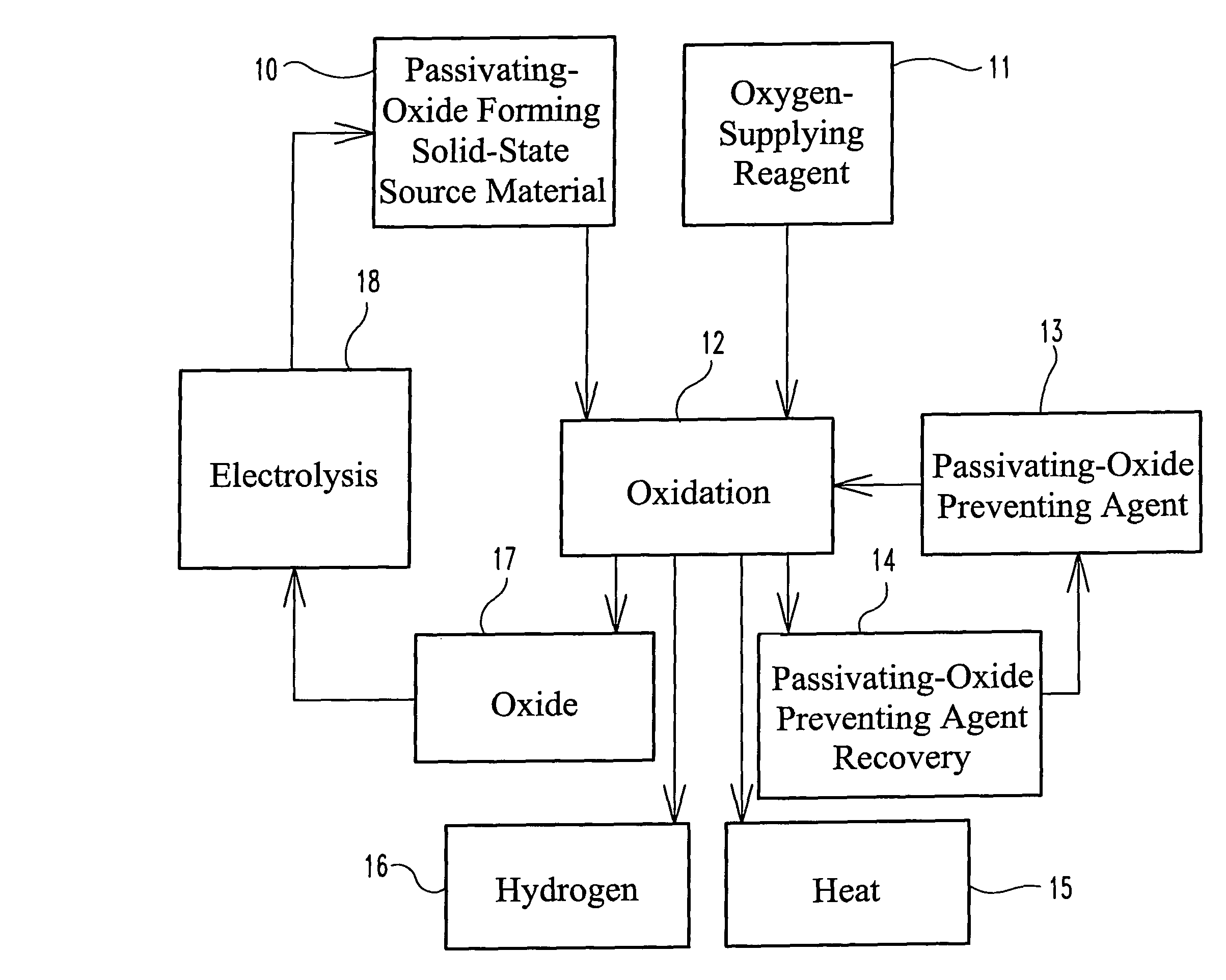
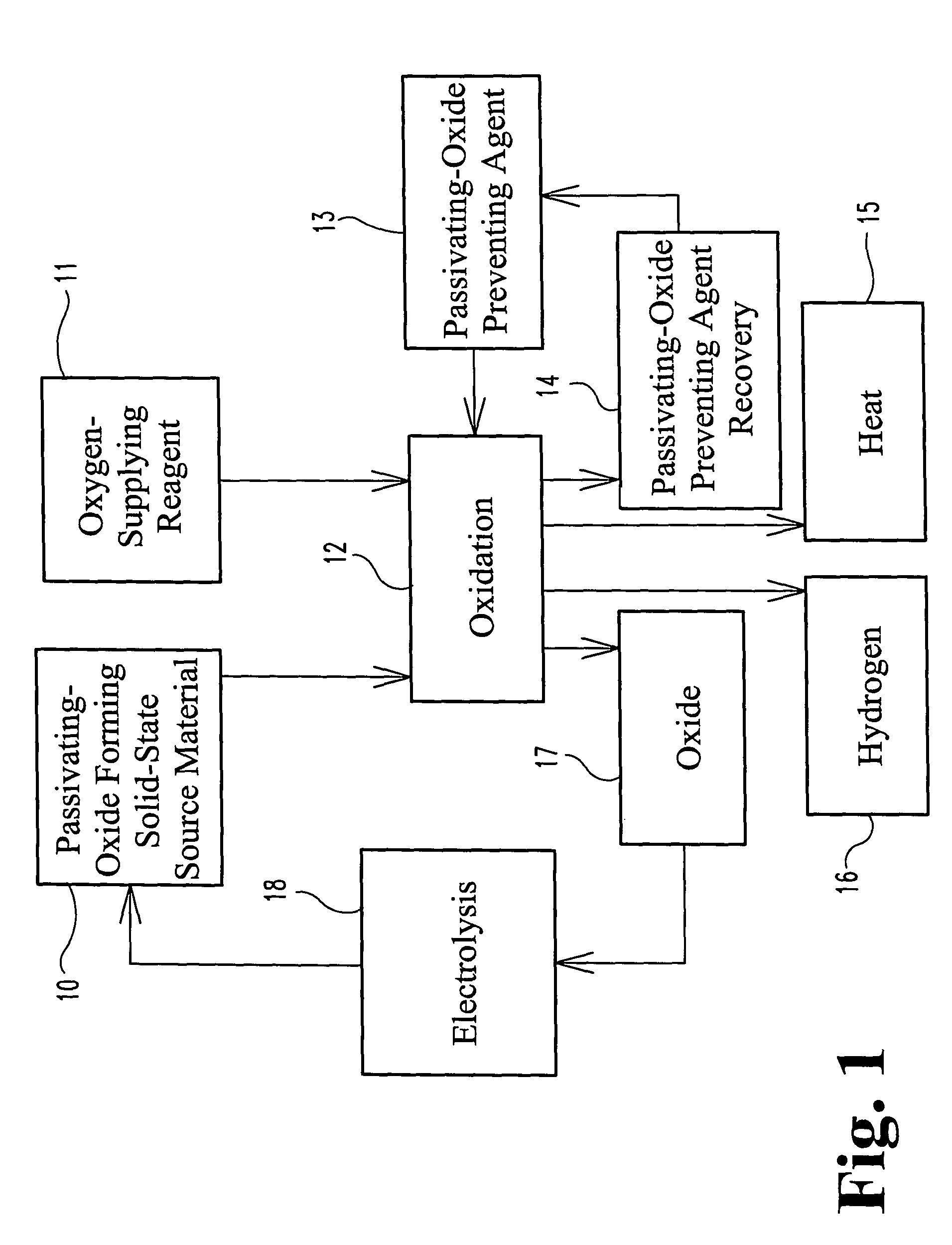
Power Generation From Solid Aluminum
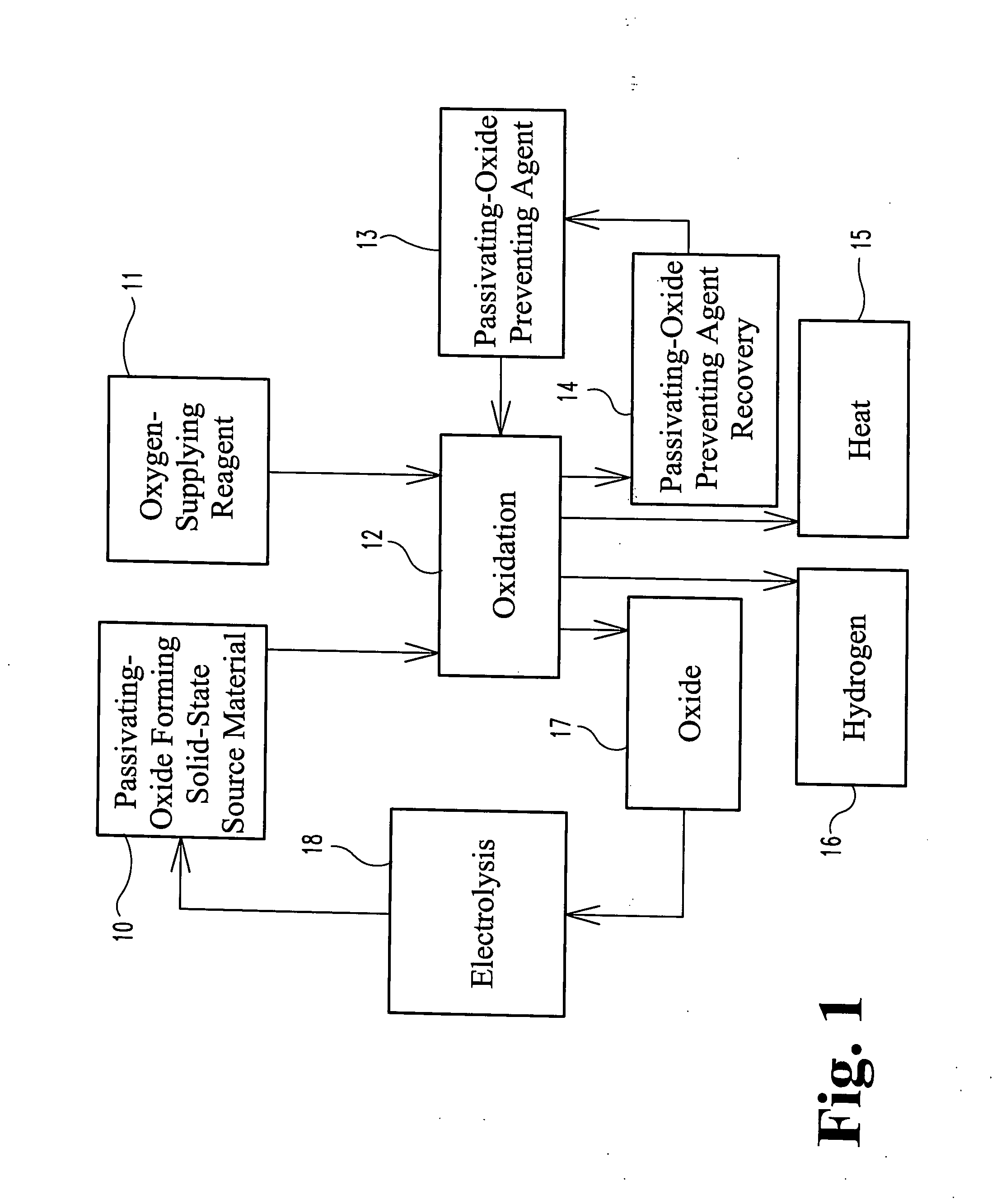
ActiveUS20080063597A1Efficiently splitting water into hydrogenEfficient productionSolid fuelsWaste based fuelHydrogenSurface layer
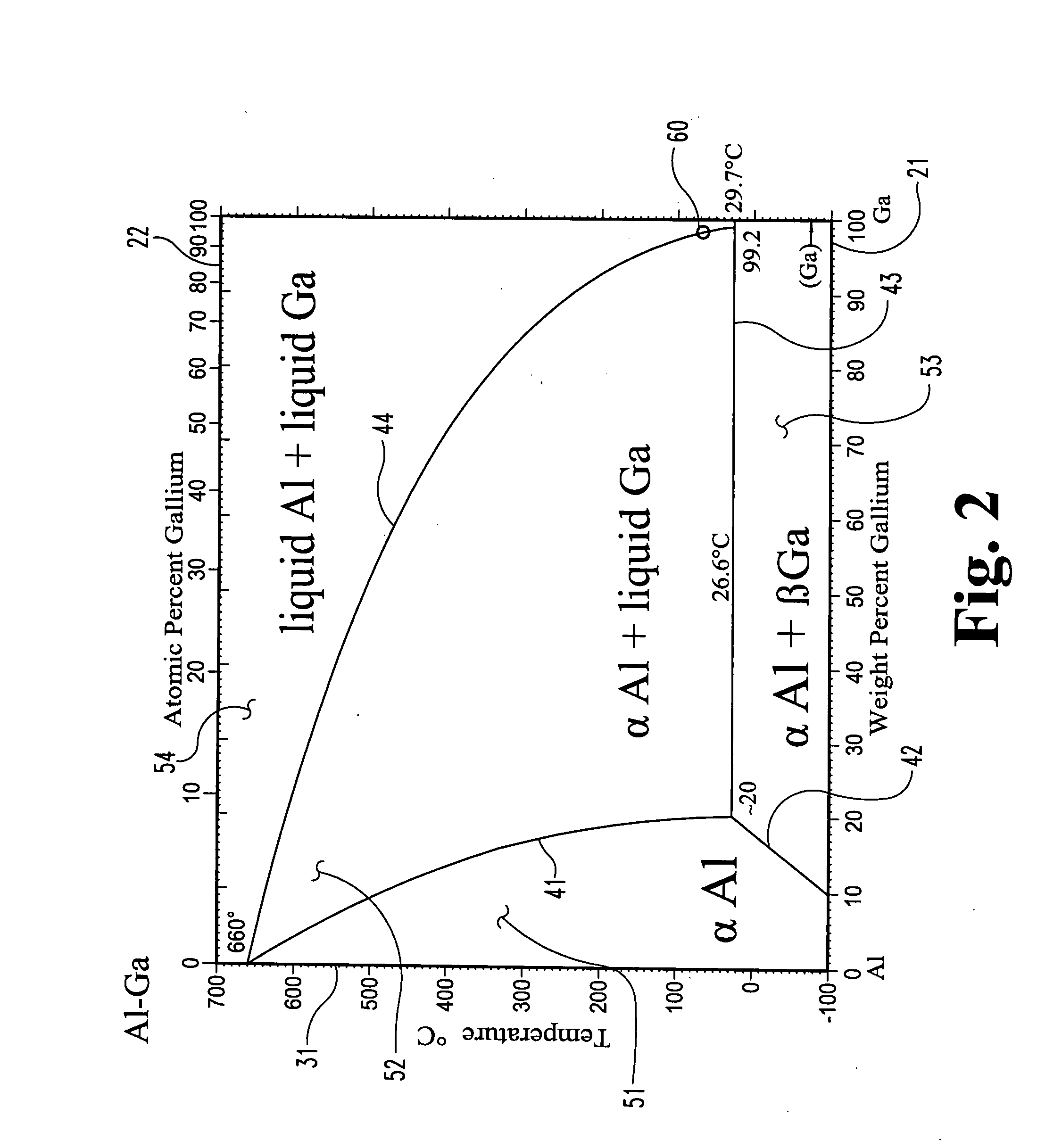
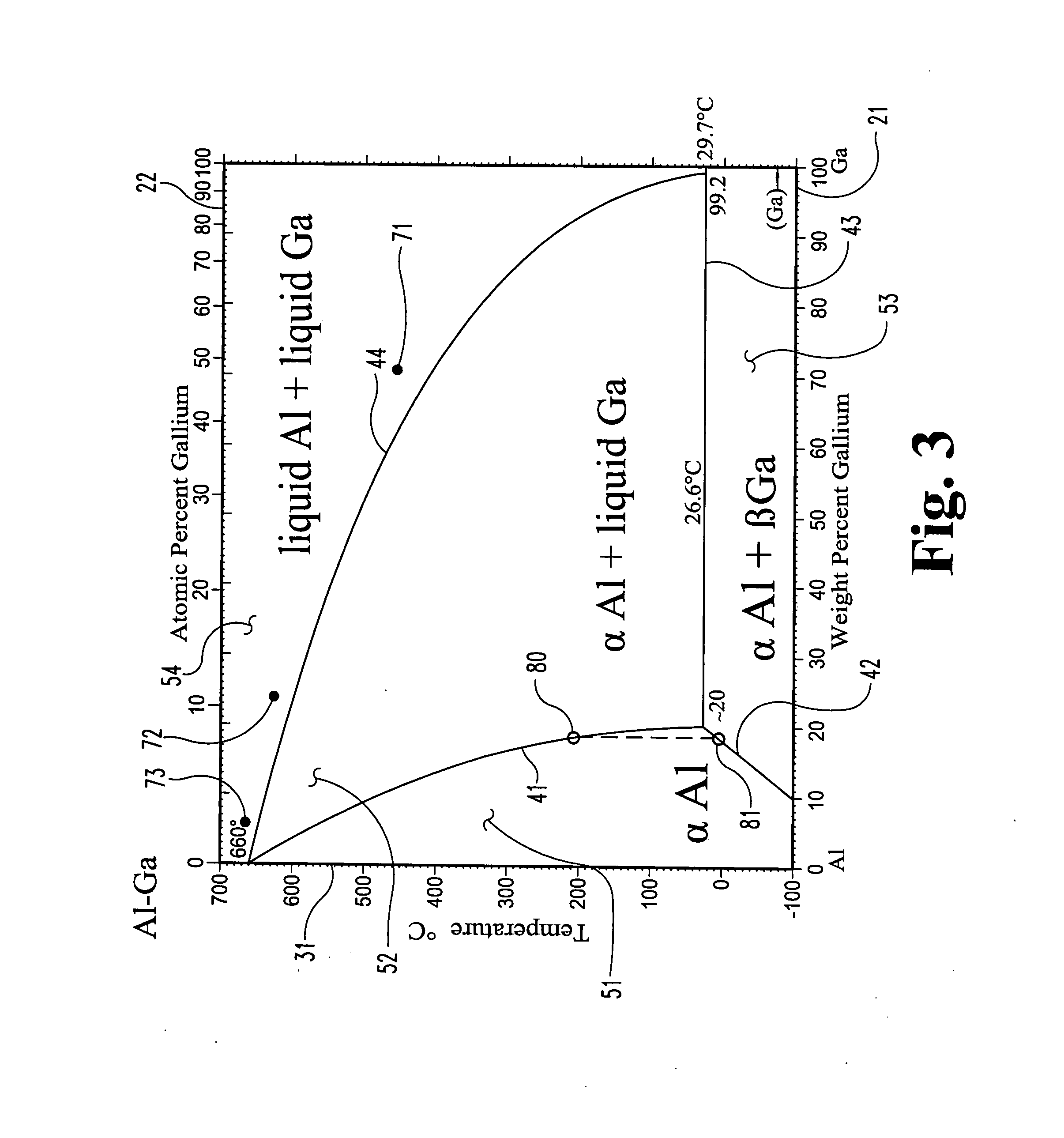
A fuel for splitting water into hydrogen and an oxide component comprises a substantially solid pellet formed from a solid-like mixture of a solid-state source material capable of oxidizing in water to form hydrogen and a passivation surface layer of the oxide component, and a passivation preventing agent that is substantially inert to water in an effective amount to prevent passivation of the solid-state material during oxidation. The pellets are brought into contact with an alloy of the passivation preventing agent having a melting point temperature below that of the solid-like mixture to initiate the hydrogen-producing reaction at a lower temperature.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Laser cladding on low heat resistant substrates
This invention relates to the laser coating of components used in high temperature-corrosive applications, such as those associated with lances, nozzles and tuyeres of metallurgical vessels, to extend their service life under such severe conditions. In particular, the present invention relates to a method of coating a high melting point material onto a substrate having a melting point temperature lower than that of the high melting point material, the method comprising: (a) moving a laser beam generated by a laser across the surface of the substrate a surface, said laser beam consisting of a wavelength of about 300 to about 10,600 nm; (b) supplying metal, alloy or metal-alloy composite powder to the surface of said substrate; and (c) generating sufficient power to the laser, to heat the surface of the substrate and achieve fusion bonding between the metal, alloy or metal-alloy composite material powder and the surface of the substrate.
Owner:PRAXAIR ST TECH INC
Acoustic cover part for a vehicle
A cover part for a vehicle, especially an underbody cover, has a porous core layer and at least one cover layer on each side, wherein the porous core layer is constructed such that it has acoustic transparency or an acoustically absorbent effect. Here, the porous core layer is made either from a thermoplastic matrix with embedded reinforcement fibers, especially glass fibers, whose melting point temperature is higher than the melting point temperature of the plastic matrix, or from a foam, which is either open-cell or closed-cell and perforated. The acoustically absorbent porous core layer is occupied on one or both sides with one or more acoustically transparent or absorbent covering layers.
Owner:ROECHLING AUTOMOTIVE SE & CO KG
High Temperature Solder Materials
InactiveUS20100096043A1Welding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaMetal alloyMelting Point Temperature
A solder material is formed utilizing a transient liquid phase sintering process, where a precursor material is first formed. The precursor material comprises a plurality of metal particles including a first metal having a first melting point temperature and a second metal having a second melting point temperature, the first melting point temperature being greater than the second melting point temperature. The precursor material is heated to a process temperature (Tp) that is greater than the second melting point temperature and less than the first melting point temperature, and the precursor material is isothermally held at the process temperature (Tp) for a preselected holding period so as to form a metal alloy material having a melting point temperature that is greater than the process temperature. The solder material can be used to bond two components together in a device specified for use at an application temperature (Ta), where Ta / Tp>1.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
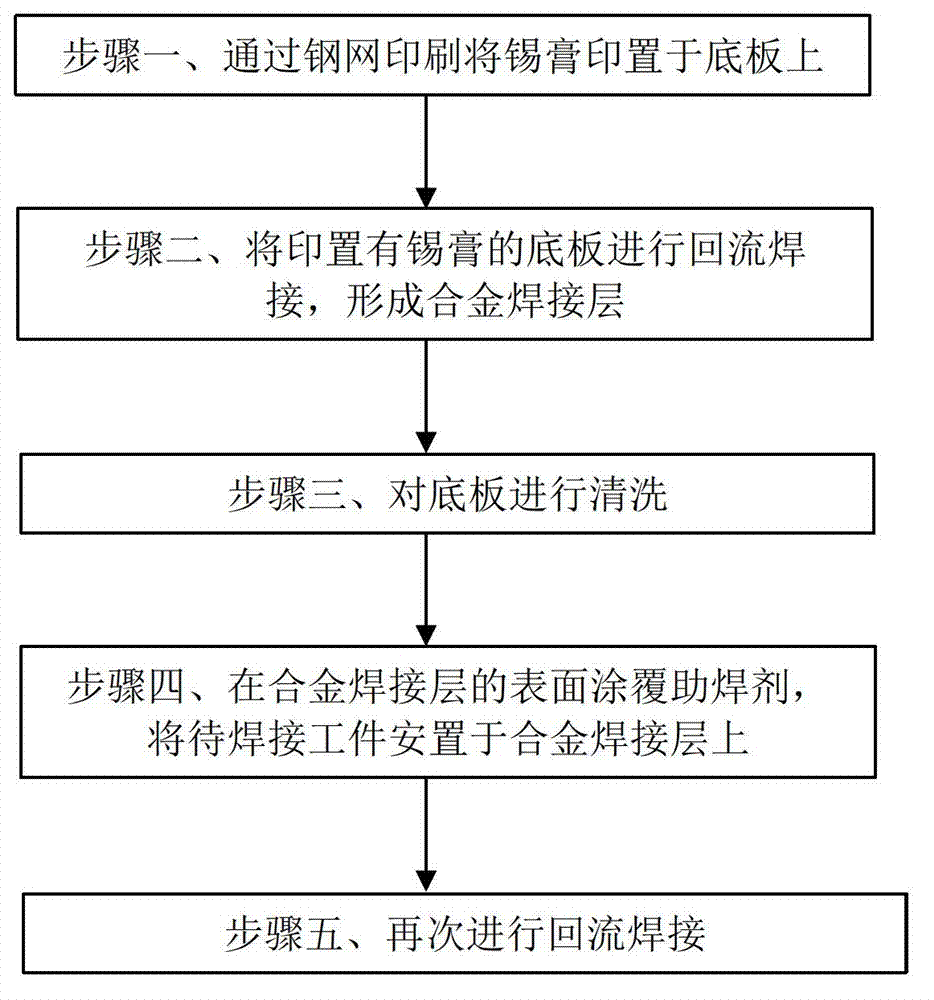
Reflow process welding method
ActiveCN103920956ANo pollutionCreate pollutionPrinted circuit assemblingSoldering apparatusStencil printingAlloy
Owner:WUXI CHINA RESOURCE MICRO ASSEMBLY TECH
Sample preparation mold for fractured rock mass model sample
The invention relates to a sample preparation mold for a fractured rock mass model sample. The sample preparation mold comprises a base and an outer frame structure, wherein an inner cavity of the outer frame structure is used for forming the fractured rock mass model sample, and the outer frame structure is positioned on the base. The sample preparation mold further comprises a plug board and a fracture position regulating structure, wherein the plug board is made of a fusible alloy material, the fusible alloy material is formed in a solid state at the normal temperature and can melt after being heated to a melting point temperature; the fracture position regulating structure is positioned in the outer frame structure and is connected with the plug board. The sample preparation mold provided by the invention can conveniently and quickly make the rock mass model sample with a complicated three-dimensional fracture, strictly control the size and the direction of the fracture, simultaneously consider the situation whether the fracture is filled or not filled or not, satisfy the requirements for repeated sample preparation and be combined and assembled according to different sample sizes, so that the practicability of the sample preparation mold is improved.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Power generation from solid aluminum
ActiveUS8080233B2Improve abilitiesIncrease contentSolid fuelsWaste based fuelAlloyMelting Point Temperature
A fuel for splitting water into hydrogen and an oxide component comprises a substantially solid pellet formed from a solid-like mixture of a solid-state source material capable of oxidizing in water to form hydrogen and a passivation surface layer of the oxide component, and a passivation preventing agent that is substantially inert to water in an effective amount to prevent passivation of the solid-state material during oxidation. The pellets are brought into contact with an alloy of the passivation preventing agent having a melting point temperature below that of the solid-like mixture to initiate the hydrogen-producing reaction at a lower temperature.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
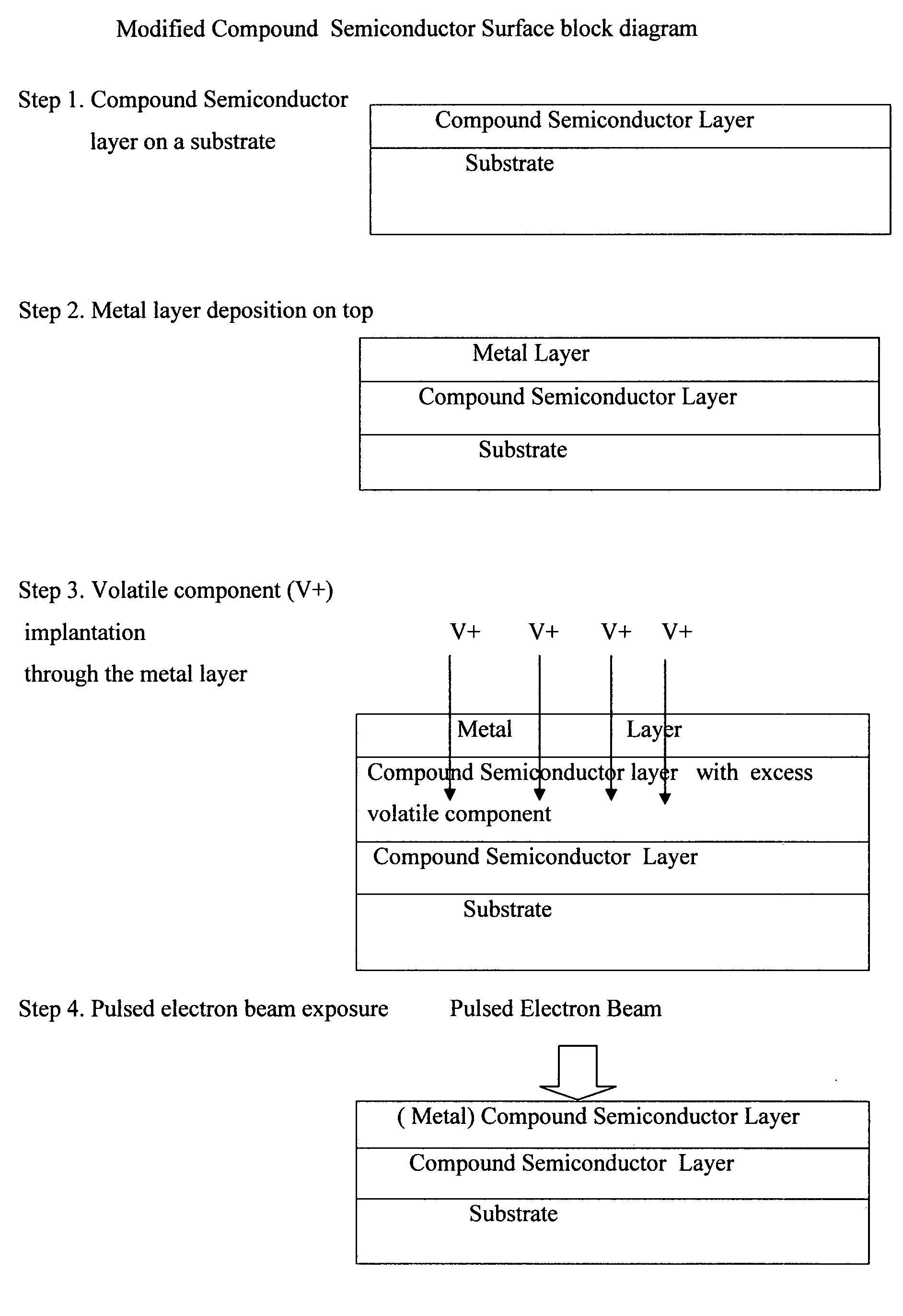
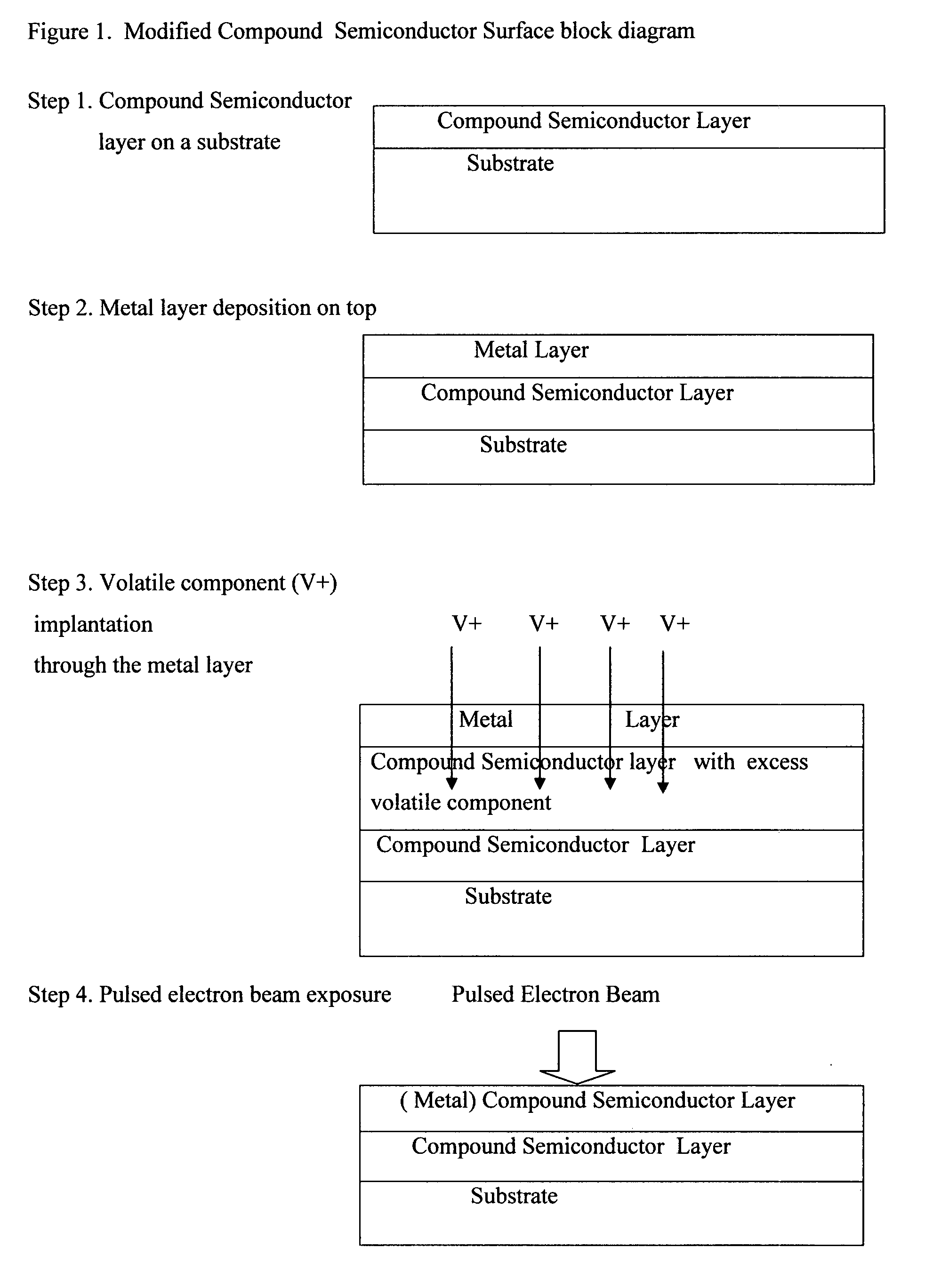
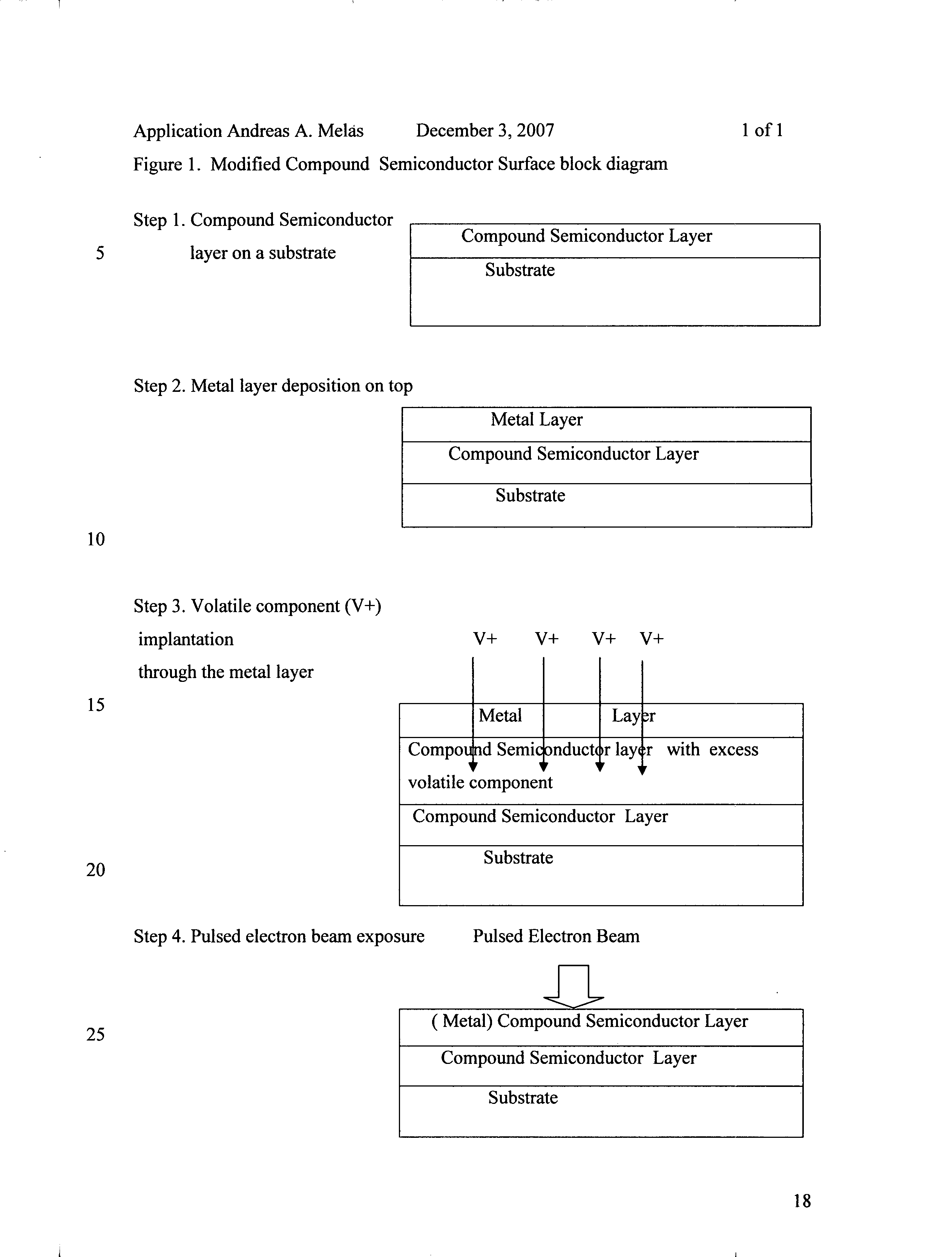
Compound semiconductor modified surface by use of pulsed electron beam and ion implantation through a deposited metal layer
InactiveUS20080087984A1Polycrystalline material growthDiffusion/dopingSingle crystalCrystallographic defect
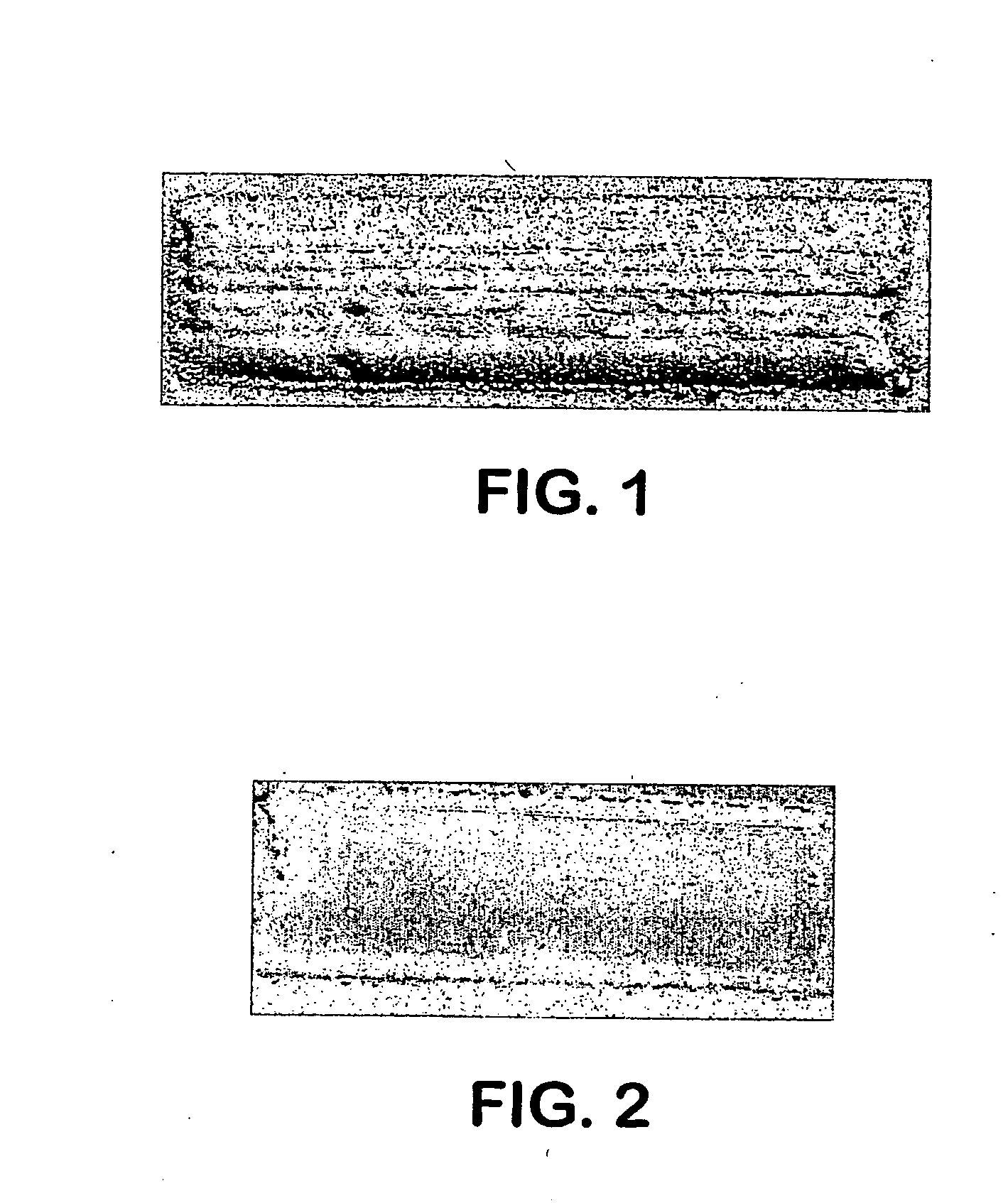
Thermally sensitive at elevated, near melting point temperature, compound semiconductor materials single crystals including Group III-Nitride, other Group III-V, Group II-VI and Group IV-IV are produced by a variety of methods. When produced as single crystal layers by epitaxy methods or is necessary to expose them to elevated temperatures or ion implanted to the non crystalline state, or their electrical or optical properties are modified, large numbers of crystal defects on the atomic or macro scale may be produced, which limit the yield and performance of opto- and electronic devices constructed out of and grown on top of these layers. It is necessary to be able to improve the crystal quality of such materials after being exposed to elevated temperature or ion implanted or modified by the presence of impurities. It is necessary, particularly for opto- and electronic devices that only the surface of such materials is processed, improved and thus the modified surface product. Generally, as shown in FIG. 1, the thermally sensitive compound semiconductor layer is first coated with a metal layer of approximate thickness of 0.1 microns. Next, the volatile component of the compound semiconductor is ion implanted through the metal layer so as to occupy mostly the top 0.1 to 0.5 microns of the compound semiconductor layer. Co-implantation may be used as well to improve the surface. Finally, through a pulsed directed energy beam of electrons with a fluence of approximately 1 Joule / cm2, the top approximately 0.5 microns acquire a level of the deposited metal and are converted into a single crystal with improved properties such as reduced defect density and or electrical dopant (FIG. 1).
Owner:MELAS ANDREAS A
Low temperature solder chip attach structure
InactiveUS6847118B2Improve connection reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureSolder ballAlloy
A solder interconnection uses preferably lead-rich solder balls for making a low temperature chip attachment directly to any of the higher levels of packaging substrate. After a solder ball has been formed using standard processes, a thin cap layer of preferably pure tin is deposited on a surface of the solder balls. An interconnecting eutectic alloy is formed upon reflow. Subsequent annealing causes tin to diffuse into the lead, or vice versa, and intermix, thereby raising the melting point temperature of the cap layer of the resulting assembly. This structure and process avoids secondary reflow problems during subsequent processing.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
Mixed paint for composite membrane of lithium ion battery, composite membrane and preparation method thereof, and lithium ion battery
InactiveCN105304850AImprove securityReduce or even prevent frizzCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersSecondary cellsMicrosphereBlock effect
The invention relates to mixed paint for a composite membrane of a lithium ion battery, and also relates to the composite membrane using the mixed paint and a preparation method thereof, and the lithium ion battery, and belongs to the technical field of the lithium ion batteries. The mixed paint for the composite membrane of the lithium ion battery is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 45 to 63 parts of organic macromolecule microspheres, 35 to 53 parts of inorganic ceramic particles and 2 to 10 parts of an additive, wherein a melting point temperature or a softening point temperature of the organic macromolecule microspheres is lower than a hot smelting temperature of a base membrane used for the membrane of the lithium ion battery. According to the composite membrane of the lithium ion battery, which utilizes the mixed paint, a micro-pore blocking effect of the organic macromolecule microspheres is more sufficient, a lithium ion transmission channel is completely cut off and the safety of the lithium ion battery is greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA AVIATION LITHIUM BATTERY LUOYANG
High-density thermodynamically stable nanostructured copper-based bulk metallic systems, and methods of making the same
ActiveUS20140026776A1Grain growth can be controlled and largely suppressedExplosive chargesBlasting cartridgesHigh densityHigh energy
High-density thermodynamically stable nanostructured copper-based metallic systems, and methods of making, are presented herein. A ternary high-density thermodynamically stable nanostructured copper-based metallic system includes: a solvent of copper (Cu) metal; that comprises 50 to 95 atomic percent (at. %) of the metallic system; a first solute metal dispersed in the solvent that comprises 0.01 to 50 at. % of the metallic system; and a second solute metal dispersed in the solvent that comprises 0.01 to 50 at. % of the metallic system. The internal grain size of the solvent is suppressed to no more than 250 nm at 98% of the melting point temperature of the solvent and the solute metals remain uniformly dispersed in the solvent at that temperature. Processes for forming these metallic systems include: subjecting powder metals to a high-energy milling process, and consolidating the resultant powder metal subjected to the milling to form a bulk material.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Graphene metal compound super capacitor electrode material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105185597AKeep high specific powerReduce usageHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureConductive polymerMetal alloy
The invention provides a graphene metal compound super capacitor electrode material. The material is a compound product obtained by compounding sheet-like graphene and sheet-like nano metals and / or sheet-like nano metal alloys and conductive polymers, and the conductive polymers are embedded into adjacent sheet metal layers and sheet graphene layers. The preparation method involves adding expanded graphite flakes, the metals and / or the metal alloys, the conductive polymers and meltable polymers in certain proportions into a graphene stripping machine, grinding for 10 to 16 hours at a vacuum state and preparing a mixed powder material of the sheet-like graphene, the sheet-like nano metals and / or the sheet-like nano metal alloys and granular high-molecular polymers; and pressurizing or vacuumizing the mixed powder material in a reactor, increasing the temperature to the melting point temperature of the meltable polymers, performing insulation for 2 to 4 hours, then reducing the temperature to a room temperature and obtaining the combined electrode material. When the material and method are implemented, graphene aggregation and accumulation can be prevented, the available surface area of graphene is improved, and the electrochemical performance is high.
Owner:深圳市来源新材料科技有限公司
Method for measuring temperature field in laser welding process
ActiveCN102967374AUnquestionable accuracyAccurate dataRadiation pyrometryLaser beam welding apparatusThermodynamicsMelting Point Temperature
The invention belongs to the technical field of measurement and relates to a method for measuring a temperature field in a laser welding process. In the laser welding process, a fusion line of a welding joint section and a represented temperature value (a material melting point temperature value) during metal welding are utilized, so that a method for measuring the temperature field in the laser welding process is designed, the thermal imagery and temperature field obtained by utilizing the conventional thermal infrared imager and software processing system thereof are accurately calibrated, and the important problems that the result of the temperature field obtained by the conventional thermal infrared image system has a large error compared with the actual result and an accurate calibration is absent because of the influence of essential factors such as metal steam / plasma radiation, fast temperature change and the like during the current laser welding are solved. The obstacle in the process of measuring the laser welding temperature field by utilizing the thermal infrared imager at present is offset, and a way is provided for accurately measuring the temperature field distribution of a fusion zone and a thermal influence area in the laser welding process.
Owner:BEIJING AERONAUTICAL MFG TECH RES INST
Nickel-based interlayer material suitable for instantaneous liquid phase diffusion welding
InactiveCN101966629AHigh strengthImprove toughnessWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaHeat-affected zoneChemical composition
The invention discloses a nickel-based interlayer material suitable for instantaneous liquid phase diffusion welding. The material is characterized by comprising the following chemical elements in percentage by weight: 4.3 to 7 percent of Si, 3 to 8 percent B and the balance of nickel. The melting point temperature of a quickly solidified Ni-B-Si alloy foil belt with thickness of 30 microns is 950 to 1,050 DEG C; the material is suitable for instantaneous liquid phase diffusion welding among low-alloy steel, stainless steel and low-alloy steel / stainless steel composite materials, has high strength of seams and heat affected zones, good toughness and wide application, and is simple and convenient to manufacture; and the tensile strength Rm is 620MPa, the bent shaft diameter D is 6t, and no crack is produced when bending 180 degrees.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Production technique of ball valve core
The invention discloses a production process for a ball valve core, comprising the main steps as follows: (1) forming: iron powder or copper powder or stainless steel powder is reduced or pulverized; the particle size is 80-100 mesh and the content is 90-98wt%; the residual quantity is impurity; the ball valve core blank is prepared in a press by a die; (2) sintering: the ball valve core blank is heated to 700-800DEG C in 20min-1h, sintered for 30min-1h within the temperature range of 700DEG C to melting point temperature of the raw material and slowly cooled to the temperature below 60 DEG C in 30min-1.5h; (3) shaping: the roundness of the sintered ball valve core blank is rectified; 4 electro-plating: the shaped ball valve core blank is processed by hole-sealing in molten zinc stearate or molten white oil or molten silicone oil, then electro-plating is carried out and finally the ball valve core which complies with the requirement is obtained. The method saves the material and has low processing cost; the produced ball valve core has light weight and high surface smoothness.
Owner:YANGZHOU TIANHE POWDER METALLURGY IND
Method for preparing zirconium-based amorphous alloy
The invention provides an amorphous alloy preparation method. The method comprises the following steps of: a, derusting, degreasing and cleaning a zirconium-based amorphous alloy cast ingot to obtain a processed zirconium-based amorphous alloy; b, after crushing the processed zirconium-based amorphous alloy, adding a deoxidizing agent for mixing, and performing vacuum melting, wherein the meltingtemperature is 250 to 350 DEG C over the melting point temperature of the zirconium-based amorphous alloy, and the melting time is 5 to 20 minutes; c, cooling a molten mixture to the temperature of 200 to 300 DEG C over the melting point of the zirconium-based amorphous alloy, standing and keeping the temperature to obtain a molten mixture; and d, introducing argon in the process of standing and keeping the temperature of the molten mixture, wherein the argon introducing time is 5 to 30 minutes and the flow rate is 2 to 10 L / min; and after finishing introducing the argon, injecting the moltenmixture into a copper mould through a filter plate, and cooling the molten mixture to room temperature at the cooling rate of 10 to 1,000 DEG C / s under the condition of protective atmosphere. The zirconium-based amorphous alloy prepared by the method has the advantages of low oxygen content and high amorphous forming capacity.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Production method of single-sided clad steel sheet and single-sided clad steel sheet
InactiveCN102021586AEasy to industrializeMetallic material coating processesSheet steelRoom temperature
The invention discloses a production method of a single-sided clad steel sheet and the single-sided clad steel sheet. The production method comprises: firstly, cleaning the steel sheet; and then carrying out surface activation. The production method is characterized in that cold spraying processing equipment is used for carrying out single-sided cold spraying on the steel sheet; then, the sprayed steel sheet is subject to heat treatment for 3-60 seconds at the coating melting point temperature of about 100 DEG C under the protective atmosphere in a continuous annealing furnace; and after being heated, the sprayed steel sheet is immediately cooled to room temperature in the continuous annealing furnace. The cladding of the obtained single-sided clad steel sheet can be various types of metals or alloys, the cladding thickness of the obtained single-sided clad steel is 5-1000 microns, and the alloy layer thickness of the obtained single-sided clad steel is less than 3 microns. The production method is practical and efficient and is easy to realize industrialization.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
A kind of polyolefin microporous film for lithium battery and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a polyolefin microporous film for a lithium battery and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps that 1, one or more polyolefin resins, one or more porous modification agents and a plasticizer are melted into a uniform solution at a temperature of 150 to 280 DEG C; 2, the melted solution obtained by the step 1 is extruded from a mold head and is cooled on a cooling roll at a temperature of 5 to 30 DEG C to be cast into a thick sheet; 3, the thick sheet is stretched in double directions to be made into a film, wherein the thick sheet is stretched in the vertical direction first and then is stretched in the transverse direction; a stretching temperature value is less than a value equal to the sum of a resin melting point temperature value and 10; and a total stretching rate is in a range of 10 to 80 times; and 4, the plasticizer is extracted from the film obtained by the step 3 and the polyolefin microporous film is obtained through heat shaping at a temperature of 80 to 150 DEG C. Through the added one or more porous modification agents with a high boiling point or a high flash point, aperture shapes and aperture sizes of the polyolefin microporous film are adjusted to realize that an average aperture size of the polyolefin microporous film is appropriate; the aperture shapes are nearly circular; and strength in either direction is uniform and consistent.
Owner:XINXIANG ZHONGKE SCI&TECH
Method and device for preparing polysilicon thin-film solar battery
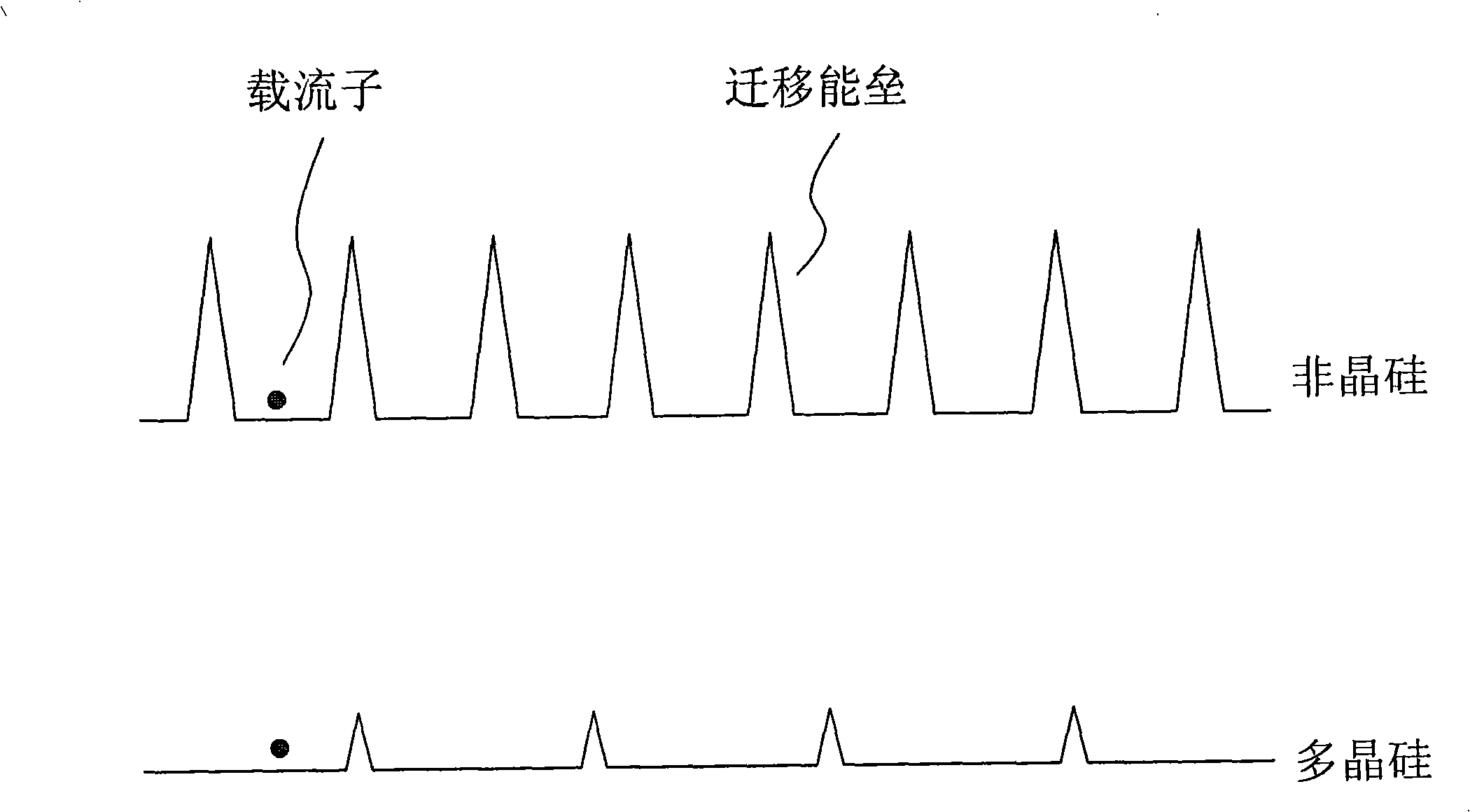
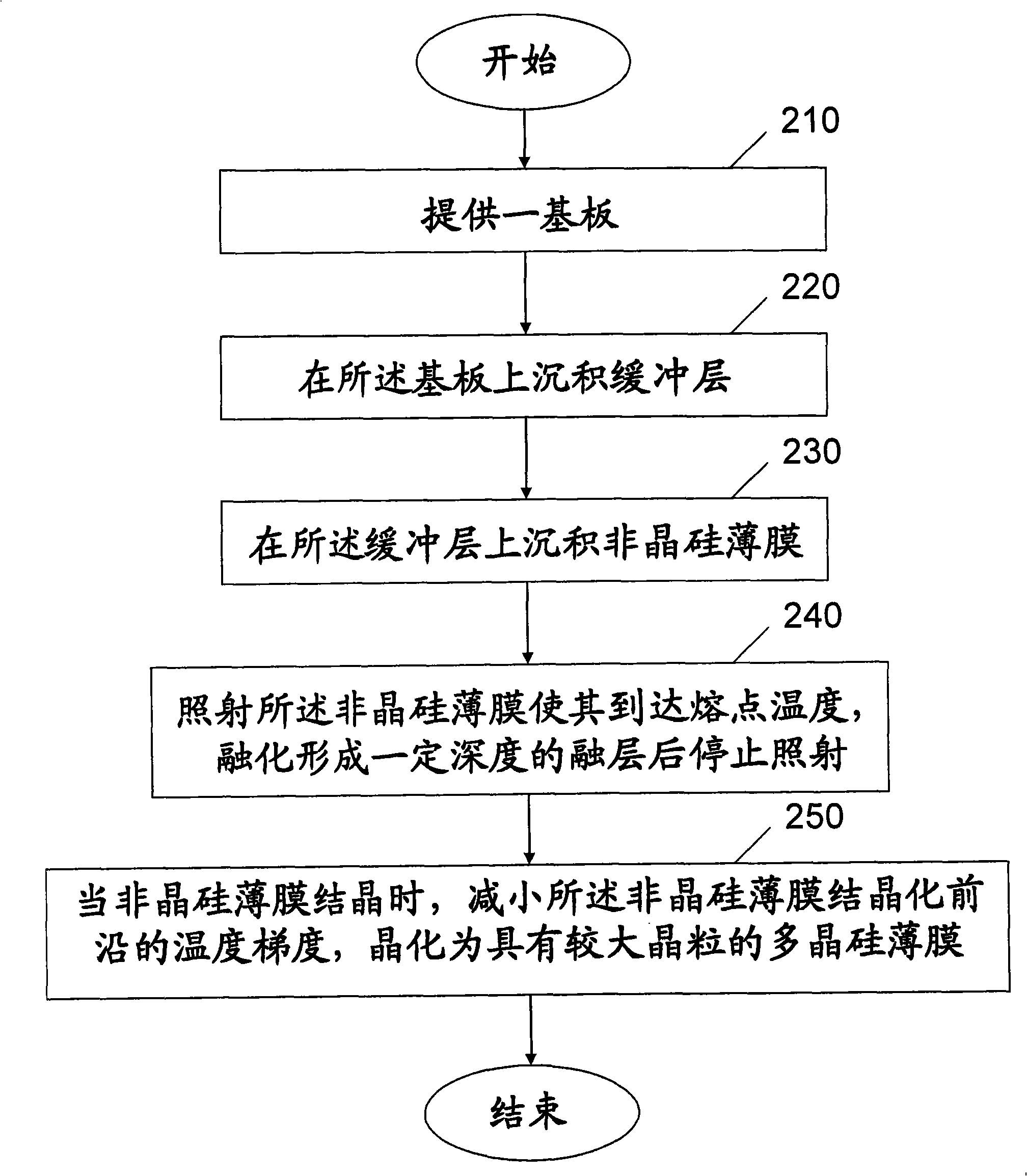
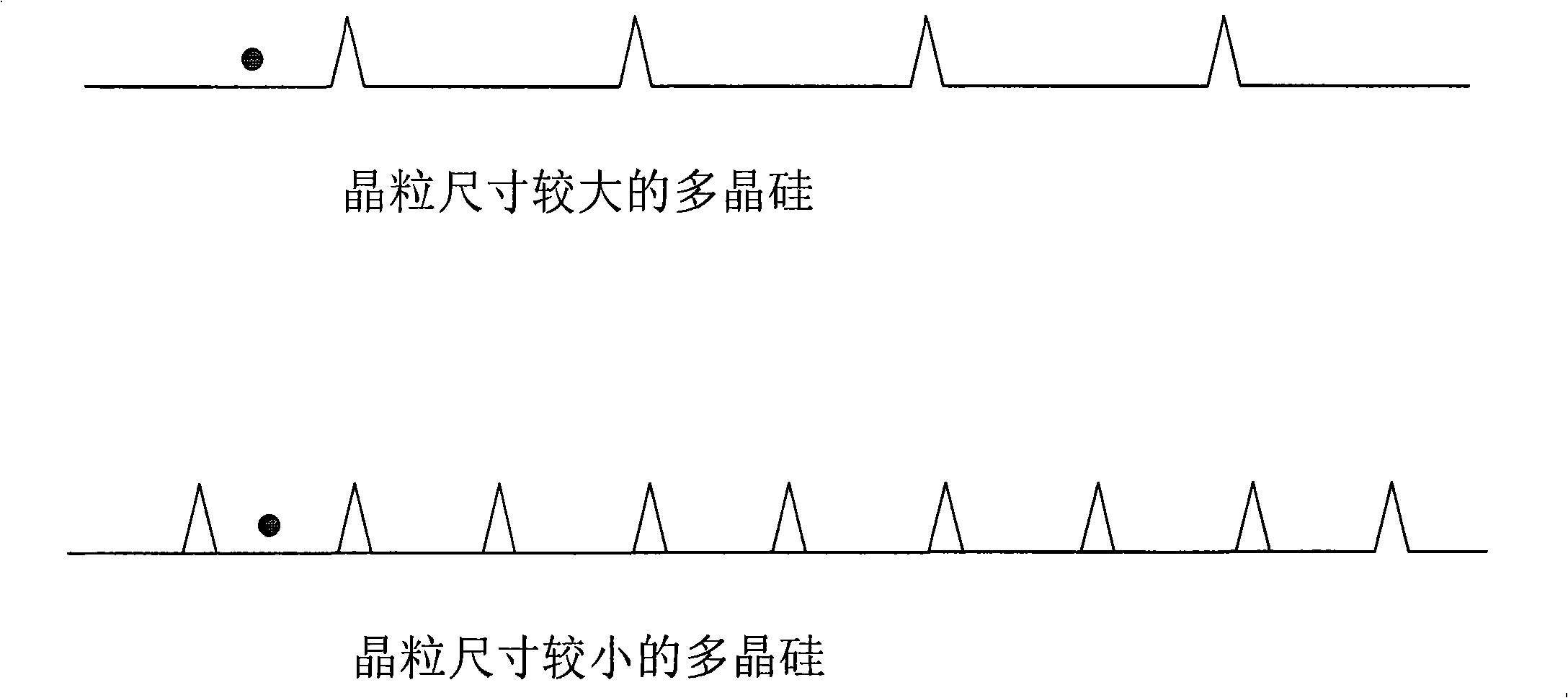
InactiveCN101325156ASmall temperature differenceExtended crystallization timeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsSolar battery
The invention provides a method for preparing polycrystalline silicon thin-film solar cell and a device thereof. The method comprises the steps of providing a substrate; depositing a front electrode and conducting etching on the substrate; depositing a non-crystalline silicon film on the front electrode; irradiating the non-crystalline silicon film to allow the non-crystalline silicon film to reach the melting point temperature thereof until the non-crystalline silicon film is melted to formed a molten layer with a certain depth; reducing the temperature difference between the non-crystalline silicon film and the substrate when the non-crystalline silicon film crystallizes, so as to obtain a polycrystalline silicon film with larger crystal grains; etching the polycrystalline silicon film; depositing a back electrode on the polycrystalline silicon film; etching the polycrystalline silicon film and the back electrode; and packaging the substrate, the front electrode, the polycrystalline silicon film and the back electrode to obtain a solar cell. The obtained solar cell by using the inventive method has low cost and high photoelectric transformation efficiency.
Owner:东莞晨真光伏有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com