ID cryptography-based anti-quantum computing group communication method and system
A technology of group communication and quantum computing, applied in key distribution, can solve the problems of huge amount of keys, low security, and difficulty in implementation, and improve the convenience of key management, enhance the security of use, and improve key management. easy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Example 1: Group communication when members are trusted
[0067] Assume that the message to be sent by group member A is NTF, and a timestamp TNTF is generated for the message. In this embodiment, TNTF is used as the initial message. Then, A calculates the group key for this group communication:
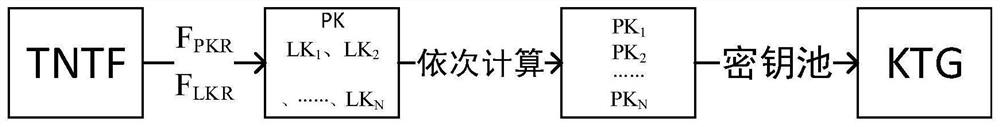
[0068] A takes out the group key KTG from the group key pool whose length is KPL. The key has N bits in total. The specific process of obtaining KTG is as follows: figure 2 Shown:
[0069] Calculate the initial position pointer PK=F of the group key KTG PK (TNTF) mod KPL, where mod represents a modulo operation. Calculate the step size in turn: LK 1 =F LK (PK||TNTF), LK 2 =F LK (LK 1 ||TNTF), LK 3 =F LK (LK 2 ||TNTF),...,LK N =F LK (LK N-1 ||TNTF). function F PK (*) and F LK (*) is any specified function. Then calculate the pointer PK used to extract the random code in turn 1 =PK+LK 1 mod KPL, PK 2 = PK 1 +LK 2 mod KPL,...,PK N = PK N-1 +LK N mod KPL...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Example 2: Group communication when a member is untrustworthy
[0074] 2.1: The group administrator sends a message.
[0075] Let the group administrator be A, another trusted member in the group be B, and the untrusted member be X.
[0076] A generates the first description message for declaring X illegal as NTF, and generates a timestamp TNTF for the first description information, and generates an update key as KR, the combination of the three is MSG=TNTF||NTF||KR, member A uses SK A Sign the MSG based on ID cryptography. The signing process is as follows:
[0077] Generate random number r and calculate PK A =H 1 (ID A ), UMSG=r*PK A , h=H 3 (MSG,UMSG), VMSG=(r+h)*SK A . Among them, H 3 (*) is a hash operation. get signed SIG A =SIGN(MSG,SK A ) = (UMSG, VMSG).
[0078] A calculates the symmetric key K with B AB =e(SK A , PK B ), according to K AB Take a total of N bits of K from the symmetric key pool TAB , the process is as follows:
[0079] Calcu...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Embodiment 3: Group communication of newly added trusted members.
[0098] Let the group administrator be A, another trusted member in the group be B, and the new trusted member be Y. The newly added member Y has the same group symmetric key pool as the group's current symmetric key pool.
[0099] A generates a second description message for declaring Y legal as NTF, and generates a time stamp for the second description information as TNTF. The combination of the two is MSG=TNTF||NTF, member A uses SK A Sign the MSG based on ID cryptography to get the SIG A =SIGN(MSG,SK A ), the signing process is the same as above.
[0100] A calculates the symmetric key K with B AB =e(SK A , PK B ), according to K AB Take a total of N bits of K from the symmetric key pool TAB , the process is the same as above. A gets K TAB After that, use K TAB and K AB Calculate KS AB =F KS (K TAB , K AB ). Use KS AB to NTF||SIG A Encrypt to get {NTF||SIG A}KS AB , calculate th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com