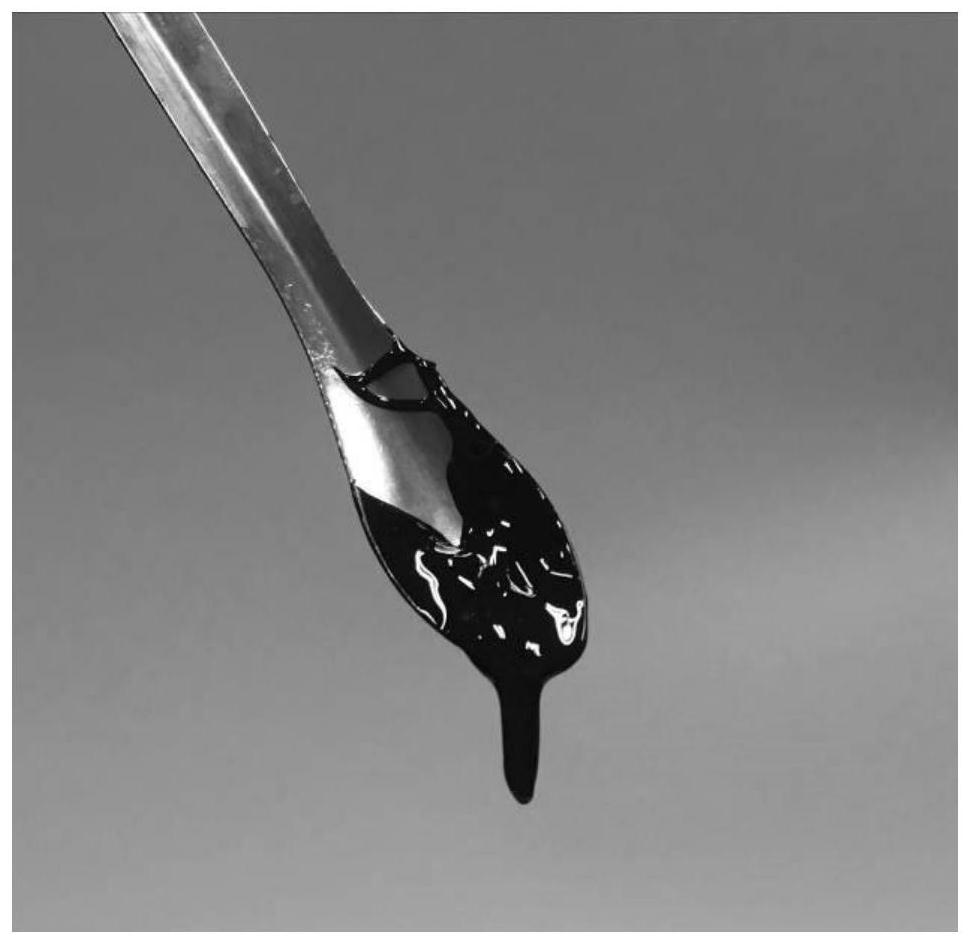
A kind of mxene-based solvent-free nanofluid and preparation method thereof
A nanofluid, solvent-free technology, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the problems such as MXene-based solvent-free nanofluid preparation methods and properties that have not been reported, and achieve improvement Processing and application performance, high stability, and the effect of improving barrier performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
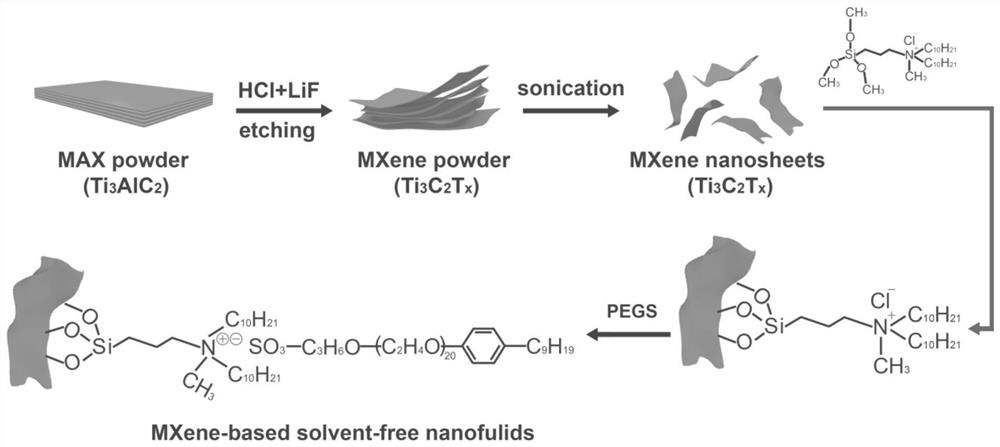
[0042] Preparation method of the present invention sees attached figure 1 (Take organosilane SID 3392.0 as an example):
[0043] The main component is MXene, the neck layer is organic silane SID 3392.0, and the crown layer is organic oligomer.
[0044] The MXene nanosheet Ti 3 C 2 T x , average size ≤ 100nm.
[0045] The organosilane used was dichloride, SID 3392.0.
[0046] The outer oligomer (coronal layer) is 4-nonylphenol-polyvinyl ether potassium sulfonate (PEGS).
[0047] The method for preparing MXene nanosheets is as follows:
[0048] a) LiF and HCl (9mol / L) with a molar ratio of 1:1 were stirred for 5 minutes to fully dissolve to obtain a solution.
[0049] b) Add 1g Ti 3 AlC 2 Add to the solution obtained in a, and stir at 25°C for 24h to obtain an acidic mixed solution B.
[0050] c) The above solution B was repeatedly washed with deionized water (5000rmp / min), centrifuged, and the supernatant was poured until the pH of the supernatant was 7, and the lower...
Embodiment 2
[0057] a) MXene (Ti 3 C 2 Tx) Preparation of nanosheets: 1.6 g of LiF was mixed with 20 mL of HCl solution (9 mol / L), and stirred for 5 min to fully dissolve. Then add 1g of precursor raw material Ti 3 AlC 2 , and stirred at 25°C for 24h to obtain an acidic mixed solution. This solution was repeatedly washed with deionized water, centrifuged (5000rmp / min), and the supernatant was poured until the pH of the supernatant=7, the lower layer of sediment was removed, and freeze-dried for 48h to obtain MXene (Ti 3 C 2 T x )Nanosheets.
[0058] b) Use the organosilane N,N-didecyl-N-methyl-N-(3-trimethoxysilylpropyl)ammonium chloride (decacinium chloride, SID 3392.0) as the neck layer, adding 0.05 g of MXene (Ti 3 C 2 T x ) nanosheets are dispersed in the aqueous solution, add 0.1~0.1.0mL SID 3392.0 (30% aqueous solution), stir at 60℃~70℃ for 24 hours, the silane is hydrolyzed and linked to MXene(Ti 3 C 2 Tx) on the surface of nanosheets, the coronal layer adopts organic ol...
Embodiment 3
[0060] a) Preparation of MXene nanosheets: 1.6 g of LiF was mixed with 20 mL of HCl solution (9 mol / L), and stirred for 5 min to fully dissolve. Then add 1g of precursor raw material Ti 3 AlC 2 , and stirred at 25°C for 24h to obtain an acidic mixed solution. This solution was repeatedly washed with deionized water (5000rmp / min), centrifuged, and the supernatant was poured until the pH of the supernatant was 7, the lower layer of precipitate was removed, and MXene (Ti 3 C 2 T x )Nanosheets.
[0061] b) Preparation of neck layer-corona layer: Add 1.4g organosilane KH560 and 12g DOPO-based organic oligomer of corona layer into a 250mL three-necked flask, and add 120mL methanol to ultrasonically disperse evenly, condense and reflux at 50°C under magnetic stirring After 24 hours, the reaction was stopped, cooled to room temperature, and the outer layer solution was obtained.
[0062] c) 0.25g of MXene (Ti 3 C 2 Tx) The nanosheets are added to the above solution, and the st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com