Method and system for additive manufacturing or repair with in-situ manufacturing and feeding of a sintered wire
A technology for additive manufacturing, sintering wire, applied in the field of materials, which can solve the problems of loss, LMD process is not effective, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0010] To facilitate understanding of the embodiments, principles and features of the present disclosure, they are explained below with reference to their implementation in illustrative embodiments. Embodiments of the present disclosure, however, are not limited to use in the systems or methods described.
[0011] The components and materials described below as making up the various embodiments are intended to be illustrative rather than limiting. Numerous suitable materials and components that will perform the same or a similar function as the materials described herein are intended to be within the scope of embodiments of the present disclosure.
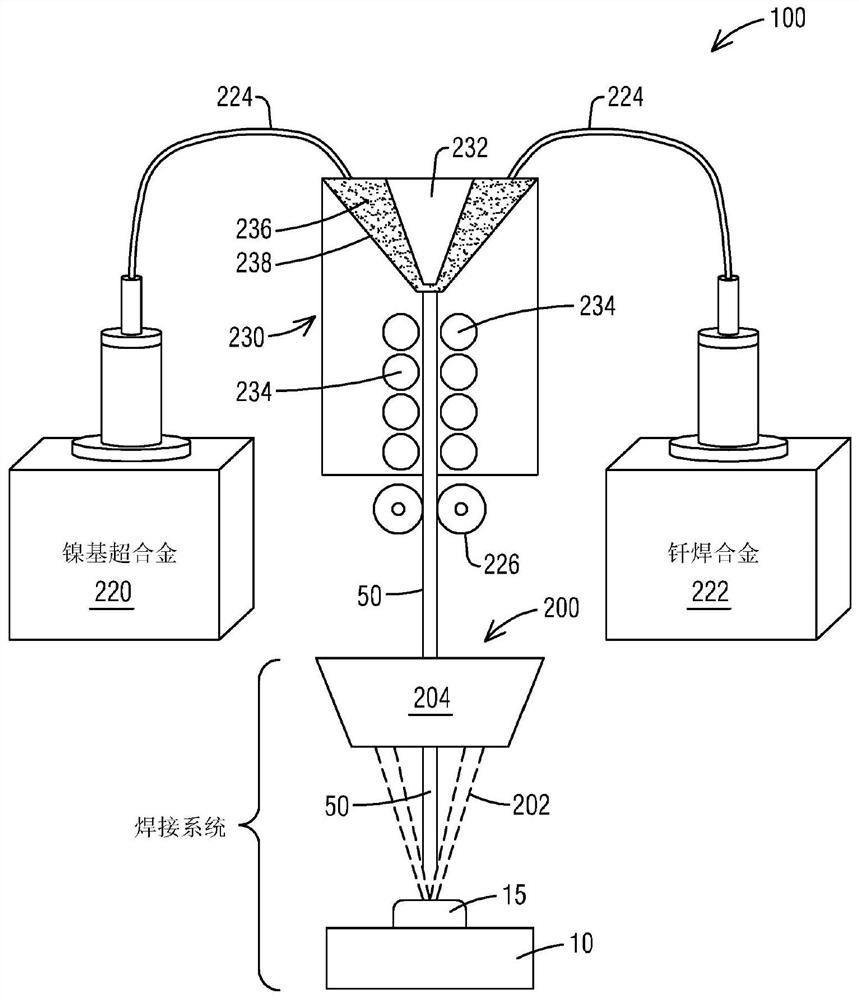
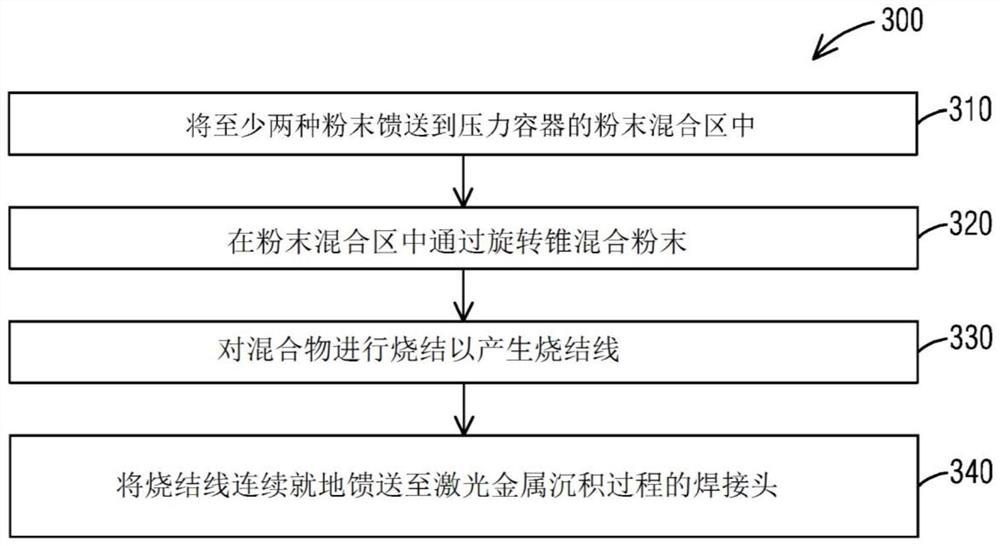
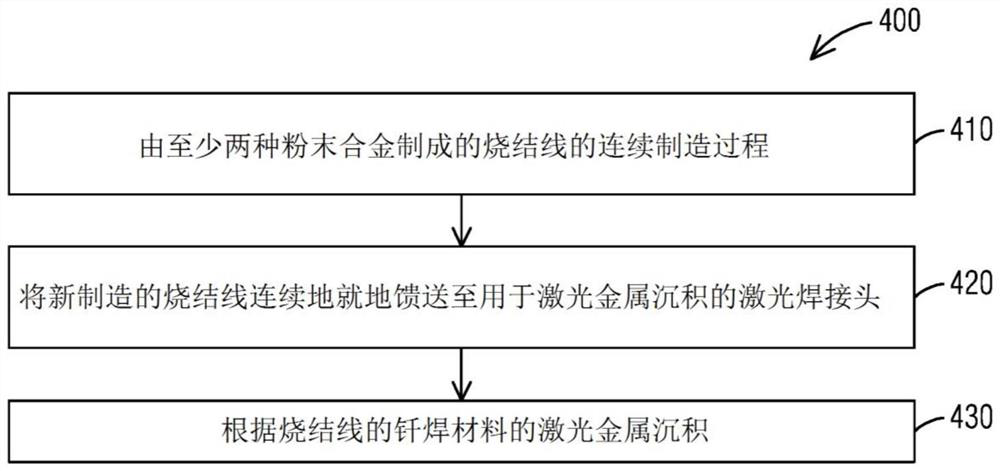
[0012] Referring now to the drawings, which are shown for purposes of illustrating embodiments of the subject matter herein only and not for purposes of limiting the embodiments of the subject matter herein, figure 1 A system 100 for fabricating a sintering wire 50 to be fed in situ to a laser wire welding system 200 is illustrate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com