FRP balcony thermal bridge cutoff structure and method
A technology for thermally broken bridges and balconies, which is applied to balconies, building components, building structures, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable control of structural bearing capacity and deflection, high research and development costs and cost of thermally broken bridges, and small internal force arms. Achieve the effect of convenient transportation and installation, controllable cost and reliable force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
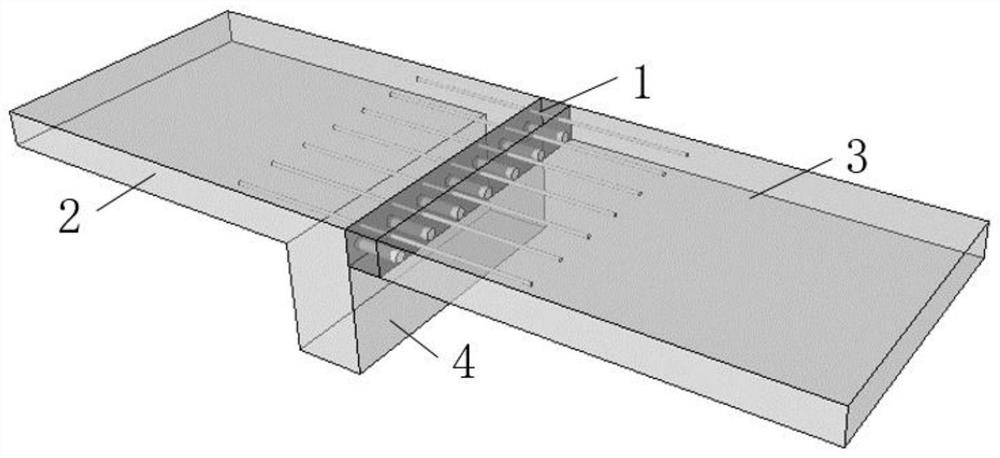
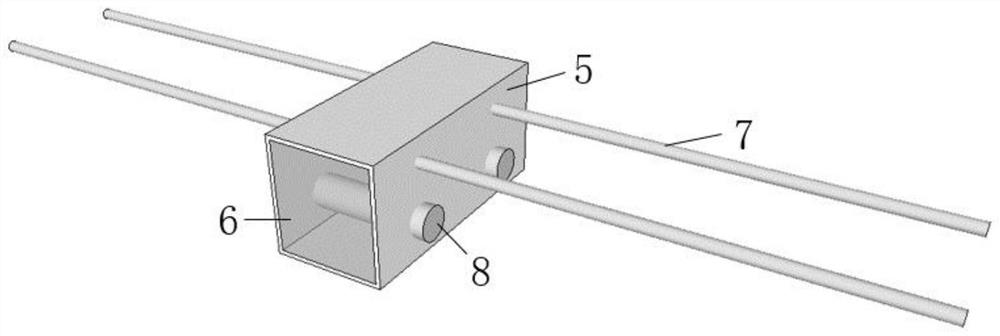
[0043] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the basic structure of a FRP balcony thermally broken bridge. In the embodiment, BFRP is selected as the main structural material. The thickness of the balcony plate is 130mm, and the span of the thermally broken bridge is 80mm. The diameter of the upper BFRP tension bar 7 is selected to be 20mm. The anchorage length is selected to be 500mm, the diameter of the lower large-diameter BFRP compressive reinforcement 8 is selected to be 40mm, and the length of insertion into the concrete is selected to be 20mm. In the example, XPS is selected as the thermal insulation filling material 6, which has low thermal conductivity and light weight, which can facilitate the transportation and construction of the thermal break bridge structure while ensuring the overall heat insulation capacity of the balcony thermal break bridge. The packaging part 5 is made of PVC, which wraps the periphery of the thermally broken bridge structure to reduce the ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of a reinforced structure of an FRP balcony thermally broken bridge containing shear plates. In the embodiment, BFRP is selected as the main structural material, and the cross-sectional dimensions and The length of the extension into the concrete is selected with figure 2 The basic structure of the FRP balcony thermal break bridge is the same. A shear plate 9 with a cross-section size of 50×5mm is added in the middle of the section of the thermally broken bridge. force.
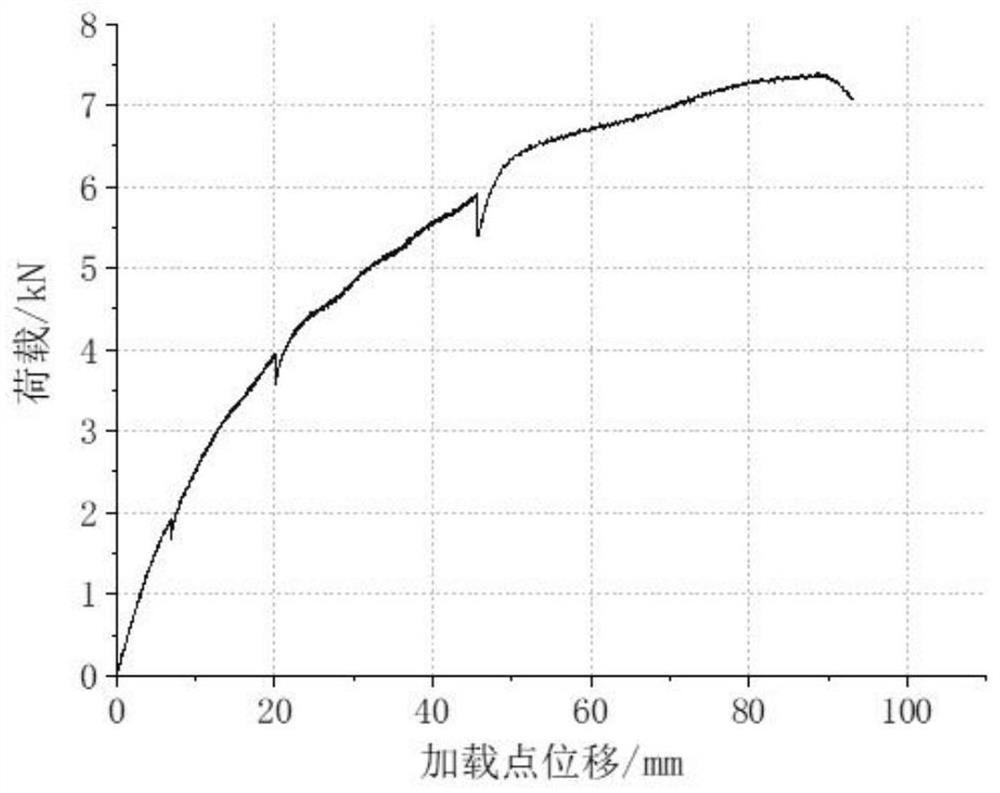
[0047] Figure 5 for Figure 4 The load-displacement curve of the segmental load-displacement curve of the reinforced structure of the FRP balcony thermally broken bridge with shear plates is shown. Here, a 300mm segment is selected for analysis. The segment contains two 20mm BFRP tension bars and two 40mm BFRP compression shear reinforcement, and a shear plate with a cross-sectional size of 50×5mm, the loading point is still selected to be 750mm away from the ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Figure 6 It is a schematic diagram of an FRP balcony thermally broken bridge reinforcement structure with oblique connectors, and BFRP is selected as the main structural material in the embodiment. The cross-sectional size of the upper BFRP tension bar 7 and the lower large-diameter BFRP compression bar 8 and the length of the extension into the concrete are selected in accordance with the figure 2 The basic structure of the FRP balcony thermal break bridge is the same, and an additional BFRP oblique connector 10 with a diameter of 10mm is added, and the horizontal distance between its end and the edge of the concrete is 50mm.
[0050] Figure 7 for Figure 6 The load-displacement curve of the segmental load-displacement curve of the FRP balcony thermally broken bridge reinforced structure with oblique connectors is shown. Here, a 300mm segment is selected for analysis. The segment contains two 20mm BFRP tension bars and two 40mm BFRP compression reinforcement, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com