Cooled free-form surface off-axis four-mirror optical system with large relative aperture
A relative aperture and optical system technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to adapt to cooled detectors, large volume envelope, and narrow imaging field of view
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0082] Various numerical data related to the optical system of the examples are as follows:
[0083] F / #=1.5, F# is the reciprocal of the ratio of the entrance pupil diameter to the focal length, that is, F=f / D
[0084] Adaptive detector array: 512×512
[0085] Adaptive detector pixel: 25μm×25μm
[0086] Working spectrum range: 8μm~14μm
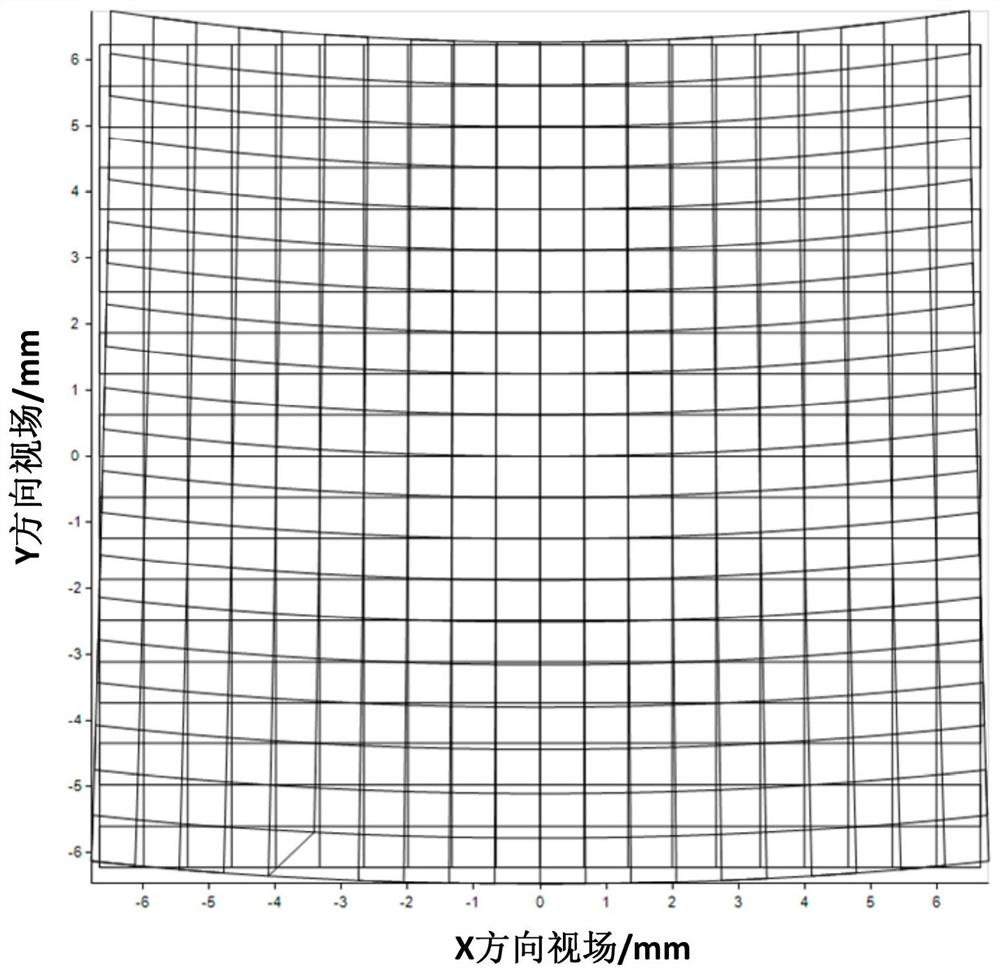
[0087] Full field of view range: 10°×10°
[0088] Full field of view relative distortion: ≤5%
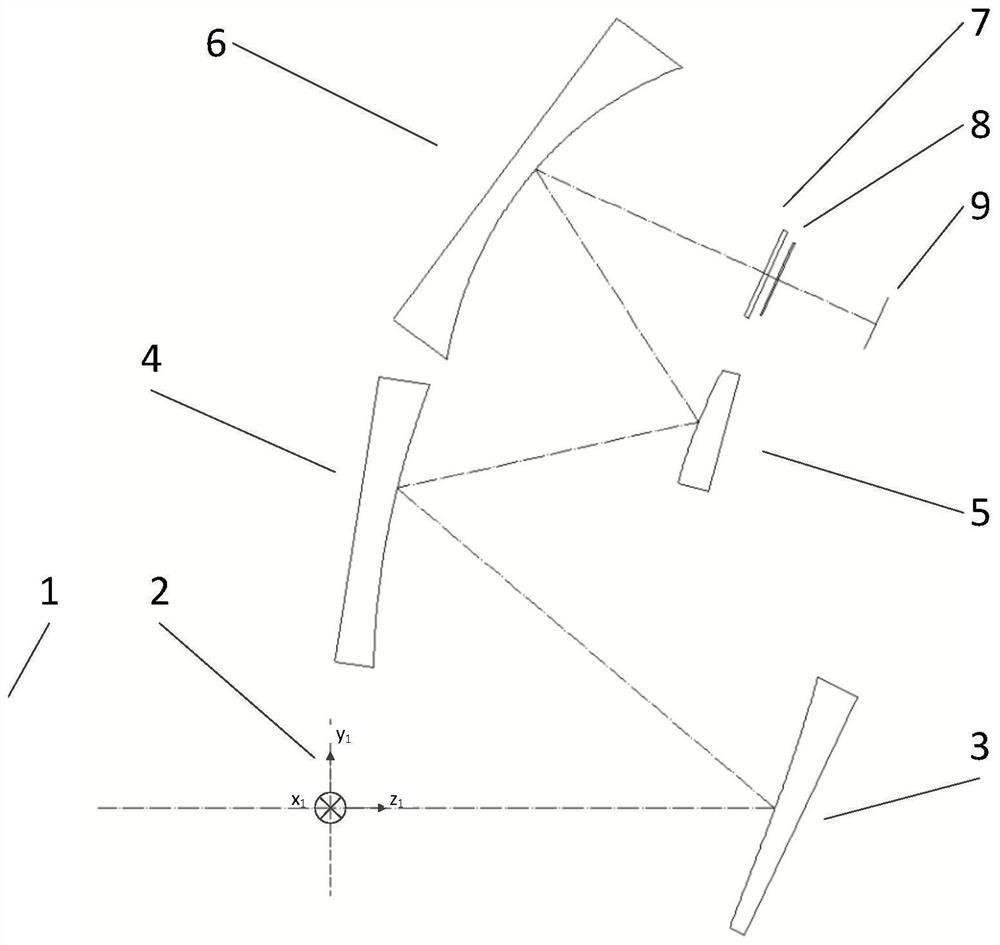
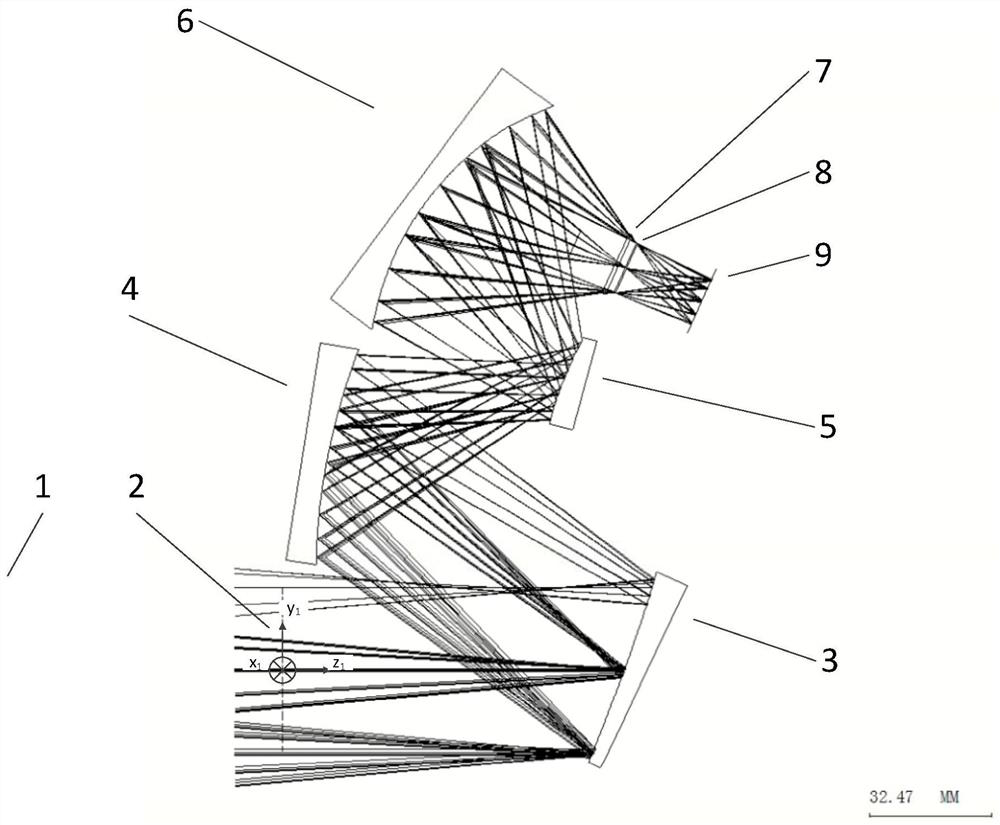
[0089] First reflector 3 reflective surface, second reflector 4 reflective surface, third reflector 5 reflective surface, fourth reflector 6 reflective surface apex, detector window center relative to the first three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system (x 1 ,y 1 ,z 1 ) and the partial surface parameter data of the reflective surface are shown in Table 2 below.
[0090] Table 2 The relative vertices of each mirror (x 1 ,y 1 ,z 1 ) coordinate system position and surface parameter table.
[0091]
[0092]
[0093]
[0094] Note...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com