Polypeptide inhibitor and application thereof
A polypeptide inhibitor and sequence technology, applied in the fields of chemical biology and computational chemistry, can solve the problems of poor efficacy of Alzheimer's disease, achieve the effect of reducing the production of oligomers and reducing toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] The design of embodiment 1 polypeptide inhibitor
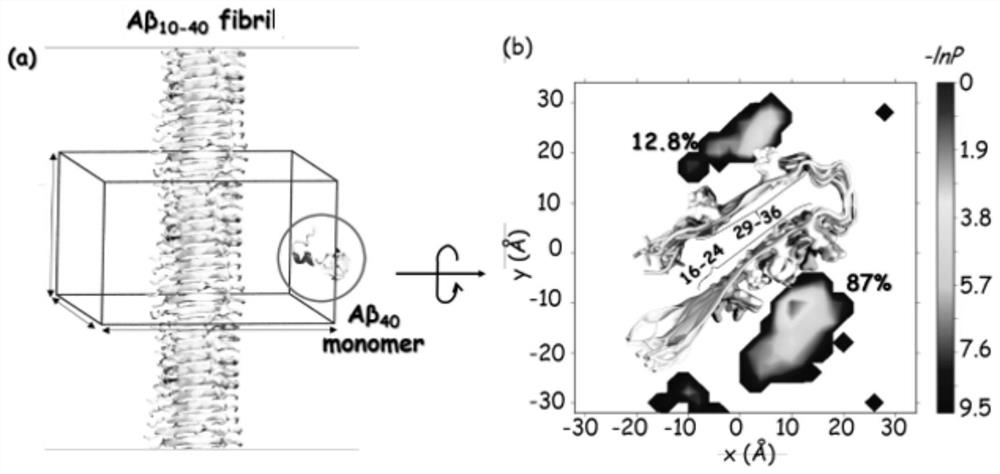
[0041] The present invention analyzes the binding mode of Aβ40 monomer and Aβ40 fiber by means of computational simulation, and the model diagram of the mixed system of Aβ40 monomer and Aβ40 fiber is as follows figure 2 shown. Specifically, first select one of the fiber chains from the solved Aβ40 fiber structure (PDB ID: 2LMN) as a template and place it on the xy-plane, along the direction of the z-axis to The fiber chain is translated at intervals of , and finally a fiber containing 12 chains is obtained, the fiber axis coincides with the z-axis, and the simulated box is a cuboid box ( figure 2 a). In order to obtain a one-dimensional infinitely long fiber model, the periodic boundary condition of the simulation box is used here, so that the distance between the two chains of the adjacent box is also equal to The advantage of the one-dimensional infinitely long fiber model is that it restores the ratio of fiber...
Embodiment 2
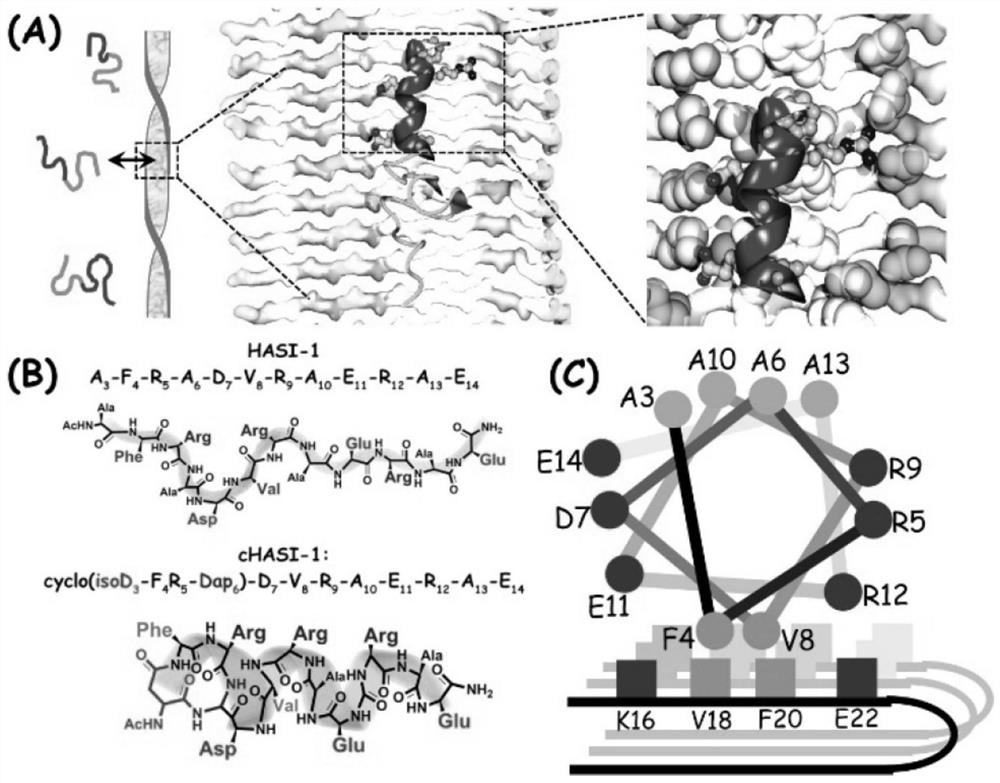
[0054] Example 2 Binding mode of cHASI--1 and Aβ40 fibers
[0055] Since Aβ40 is highly heterogeneous, we cannot rule out that cHASI-1 can also interact with Aβ40 monomers as well as oligomers. In order to better demonstrate the type of binding of cHASI-1 to Aβ40, we detected the binding ability of cHASI-1 to freshly prepared Aβ40 monomers. Size exclusion chromatography (size exclusion chromatograms) showed that only Aβ40 monomer ( Figure 8 ). Both FP and ITC experiments failed to detect the obvious interaction between cHASI-1 and Aβ40 monomer ( Figure 4 B and Figure 5 G). Therefore, cHASI-1 is unlikely to interact with Aβ40 monomers. According to the preparation method of Luo et al., we prepared Aβ40 oligomers, and measured the binding ability of cHASI-1 and Aβ40 oligomers (16.5 μM) by FP method ( Figure 4 B). Thus, cHASI-1 exhibited moderate binding ability to Aβ40 oligomers and strong binding ability to Aβ40 fibrils. We conclude that cHASI-1 can specifically rec...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3 cHASI-1 can specifically inhibit the pathway of Aβ40 fiber secondary nucleation to generate oligomers
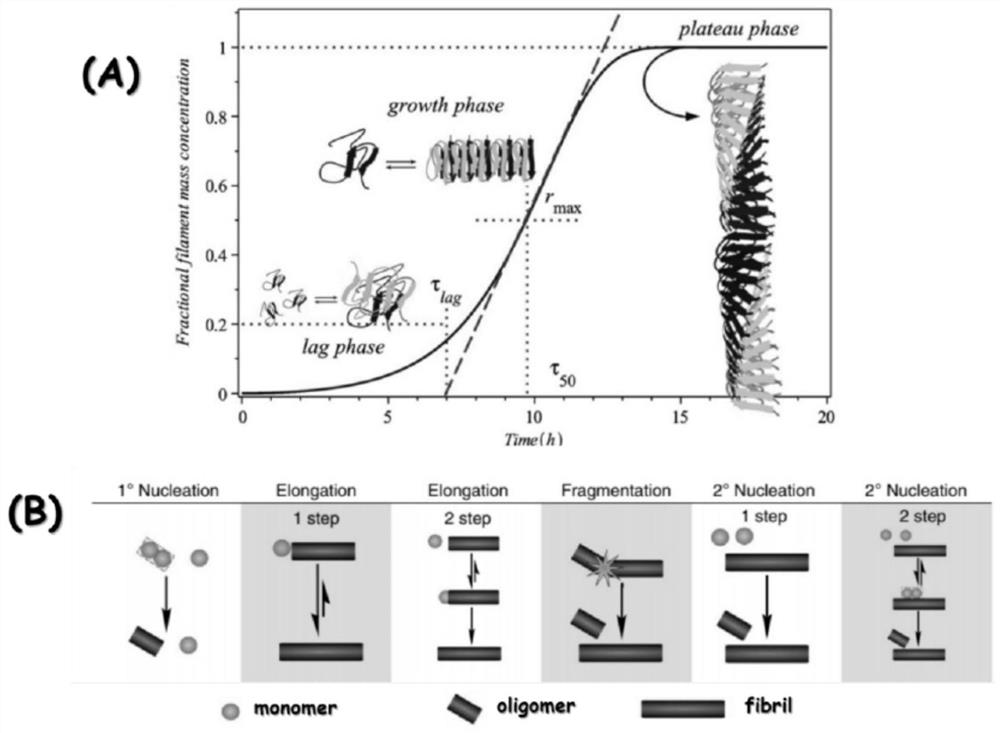
[0060] We used Thioflavin T (ThT) to measure Aβ40 aggregation, and explored how different concentrations of cHASI-1 affect the kinetics of Aβ40 aggregation. We first obtained the Aβ40 monomer by FPLC separation. This is to ensure that the initial state of Aβ40 (including only primary nucleation) does not contain existing fibers. The fibers existing in this system are called "seeds" (seeds). ), they will greatly promote the aggregation of Aβ40 (secondary nucleation, and elongation) ( Figure 8 ). In all cases, the aggregation kinetics curves exhibited a typical S-shaped curve, including a lag phase, a growth phase, and a plateau ( figure 1 ), see the Front and Background section for more details. cHASI-1 can effectively slow down the lag phase of 10μM Aβ40 monomer aggregation in a concentration-dependent manner (1-5 equivalents, 10-50μM) ( Figure 13 A) W...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com