light emitting device
A light-emitting device and packaging layer technology, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of large package structure, increased package thickness, and high cost of quartz glass, so as to reduce costs, improve transmittance, and product size. The effect of shrinking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
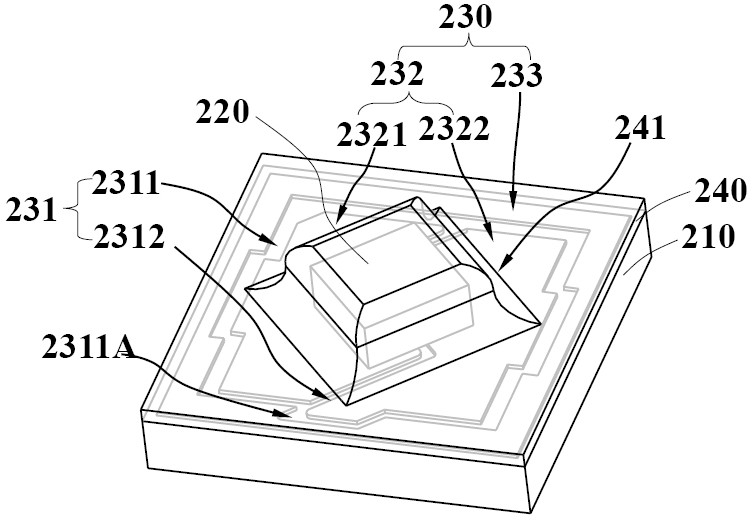
[0038] Please see attached. Figure 2 This embodiment discloses an ultraviolet packaging device, which comprises a packaging substrate 210, a patterned conductive layer 230 on the upper surface of the substrate, an LED chip 220 arranged on the substrate 210 and electrically connected with the conductive layer 230, and a packaging layer 240 covering the upper surface of the substrate and the LED chip 220. The packaging layer 240 forms an optical structure at the corresponding position of the LED chip 220, and the optical structure is above and / or above the LED chip.
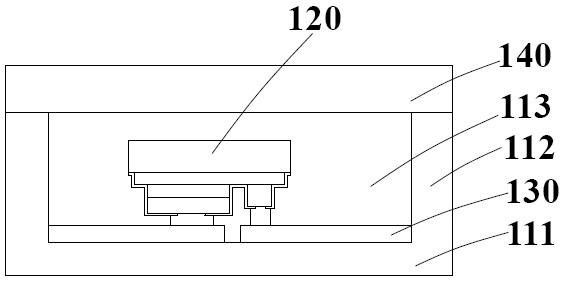
[0039] Specifically, the substrate 210 includes an upper surface and a lower surface, and the substrate 210 can be made of materials commonly used in the art, such as ceramic or silicon, preferably a ceramic substrate. The size of the substrate can be selected according to requirements, such as 3535 or 2319 or 1313.
[0040] The conductive layer 230 is formed on the upper surface of the substrate 210, patterned, and di...
Embodiment 2
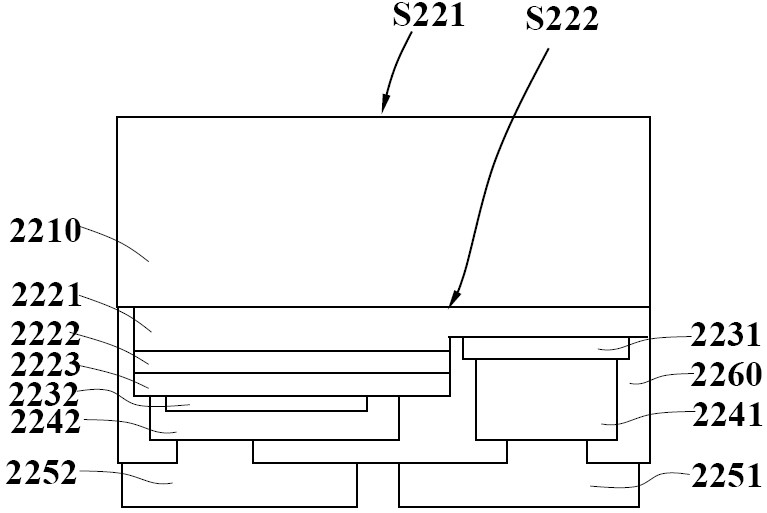
[0054] Figure 7 A light emitting device implemented according to the present invention is shown. at Figure 4 In the illustrated light emitting device, the thickness of the LED chip is more than 300μm, and the thickness t of the encapsulation layer 240 30 Less than the thickness of the LED chip. In the light emitting device shown in this embodiment, the thickness t of the LED chip 20 300μm or less, for example, 150μm to 200μm, or 200μm to 300μm, the first thickness T of the encapsulation layer 240 31 And the thickness t of the LED chip 220 20 The relationship is preferably 1.2T 20 ≥T 31 ≥0.5T 20 At this time, the packaging layer 240 can better cover the LED chip 240, and an optical structure with a curved surface, such as T, is formed above the LED chip. 31 ≈T 20 . Furthermore, 0μm≤T 31 -T 32 ≤50μm, that is, the thickness of the encapsulation layer 240 on the upper surface of the LED chip is relatively uniform. Furthermore, the thickness of the packaging layer 240 in each area is ...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Figure 8 A light emitting device implemented according to the present invention is shown. In this embodiment, based on the first embodiment, a series of additional grooves 2313 are formed in the edge region 233 of the patterned conductive layer 230 on the substrate, and the depth of the additional grooves 2313 is preferably more than half the thickness of the patterned conductive layer, or it can be greater than or equal to the thickness of the conductive layer 230. The encapsulation layer 240 fills the additional grooves 2313, thus increasing the bonding force between the encapsulation layer 240 and the substrate 210.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com