Egg substitute mixture
A technology of mixture and composition, applied in the field of egg replacer composition and manufacture, can solve problems such as single egg
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0142] Liquid Mixture Preparation Instructions
[0143] After mixing the powder with water according to the instructions for the preparation, the product was stored in the refrigerator (-18°C). After thawing, the liquid product is safe to use for 7 days.
[0144] Preparation instructions: For every 1 kg of mixture powder, add 9 liters of cold water (0-4°C). Water was added first, then the powder was added to the mixer (Stephan) and mixed on high speed for 4-6 minutes until a smooth and creamy texture was obtained.
[0145] Examples of use in cinnamon bun recipes : Replace the required amount of egg by volume with an equal volume of liquid egg replacer.
[0146] Examples of use in mayonnaise : The required amount of eggs by volume is replaced by 14% by volume of liquid egg replacer.
[0147] Example of use in an omelet : Pour the same volume of liquid egg replacer on the pan as the volume of each egg that will be used.
Embodiment 2
[0149] egg replacer composition
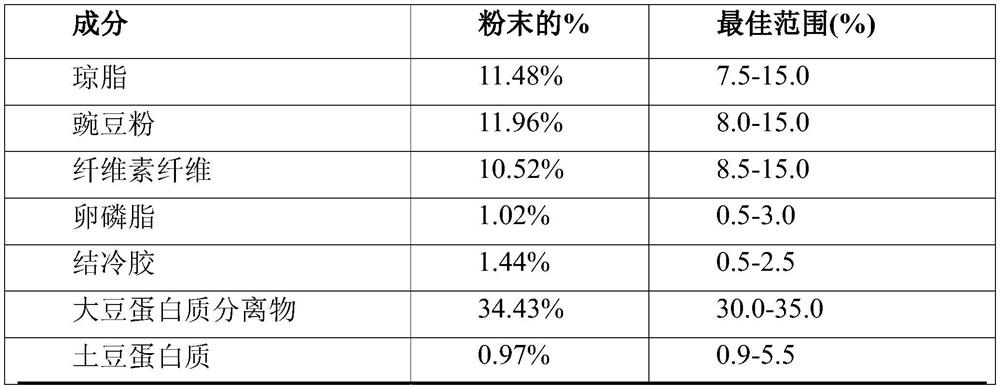
[0150] Table 1 presents Composition 1 of the egg replacer mixture.
[0151] Table 1.
[0152] Element % of powder agar 11.48% pea flour 11.96% Cellulose Fiber 10.52% Lecithin 1.02% gellan gum 1.44% Soy Protein Isolate 34.43% potato protein 0.97% chickpea protein 4.79% Methocel 5.07% dry yeast 8.61% sugar 3.82% salt 4.86% Toner 1.04% 100.00%
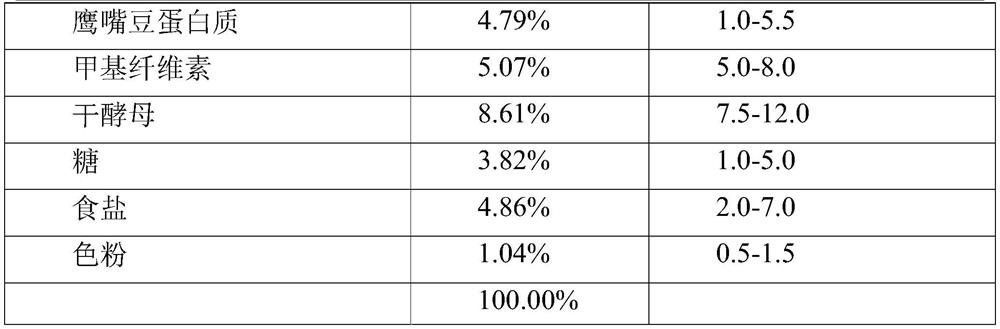
[0153] Table 2 presents Composition 2 of the egg replacer mixture.
[0154] Table 2.
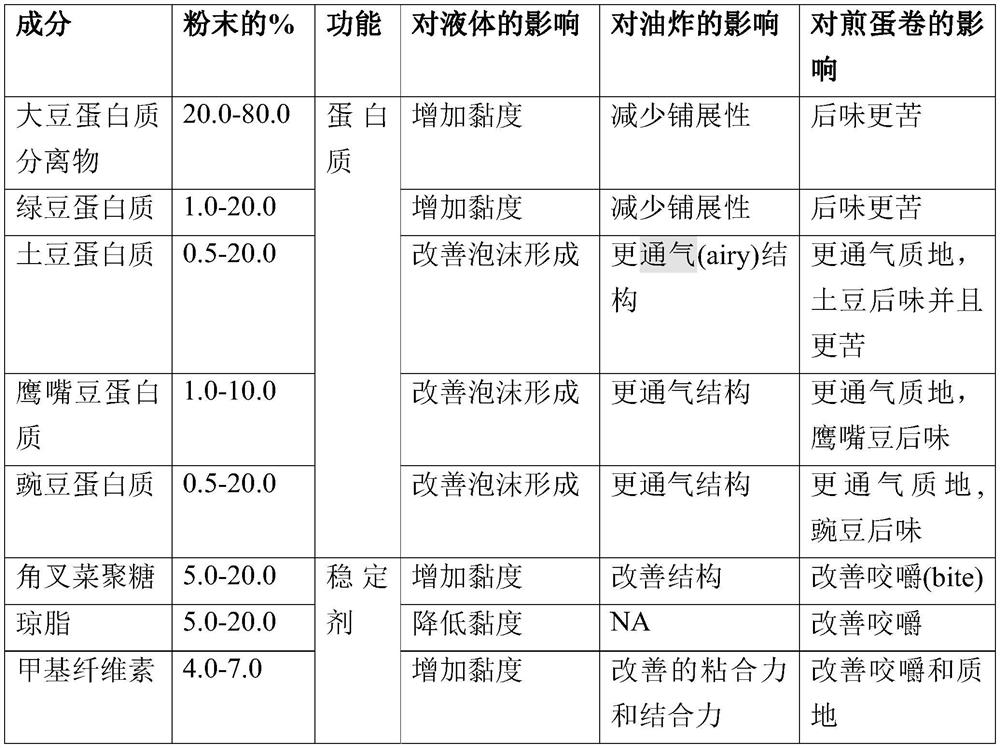
[0155] Element % of powder Features Soy Protein Isolate 20.0-80.0 protein mung bean protein 1.0-20.0 protein potato protein 0.5-20.0 protein chickpea protein 1.0-10.0 protein pea protein 0.5-20.0 protein carrageenan 5.0-20.0 stabilizer agar 5.0-20.0 stabilizer Cellulose Fiber 5.0-15.0 fiber inulin 5.0-15.0 fiber Lecithin 0.5-3.0 ...
Embodiment 3
[0167] Influence of Ingredients in Egg Replacer Compositions
[0168] The main technical challenges in the development of plant-based egg substitutes are: (a) obtaining a flowable fluid with relatively low viscosity, (b) that is thermally stable and does not disintegrate during frying (due to the binding forces at high temperature and adhesion); (c) produce omelet appearance, aroma and texture, and (d) have high nutritional value.
[0169] The unique composition of eggs is notoriously difficult to imitate. The functionality of proteins such as ovalbumin, ovotransferrin, ovomucoid, ovomucin in binding, foam formation, gel formation and attributed texture is almost exclusive. In addition, eggs are rich in fatty acids such as palmitic acid, stearic acid, palmitoleic acid, oleic acid, arachidonic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, arachidonic acid, EPA, DPA and DHA.
[0170] Thus, the composition of a plant-based egg replacer that would provide a full range of egg replacement ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com