Narrow-pulse high-current constant-current source and control method thereof
A control method and narrow pulse technology, applied in the direction of control/regulation system, regulation of electrical variables, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to increase signal rise and fall speed, difficult to reduce signal overshoot, etc., to achieve strong market application prospects , the effect of reducing heat
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
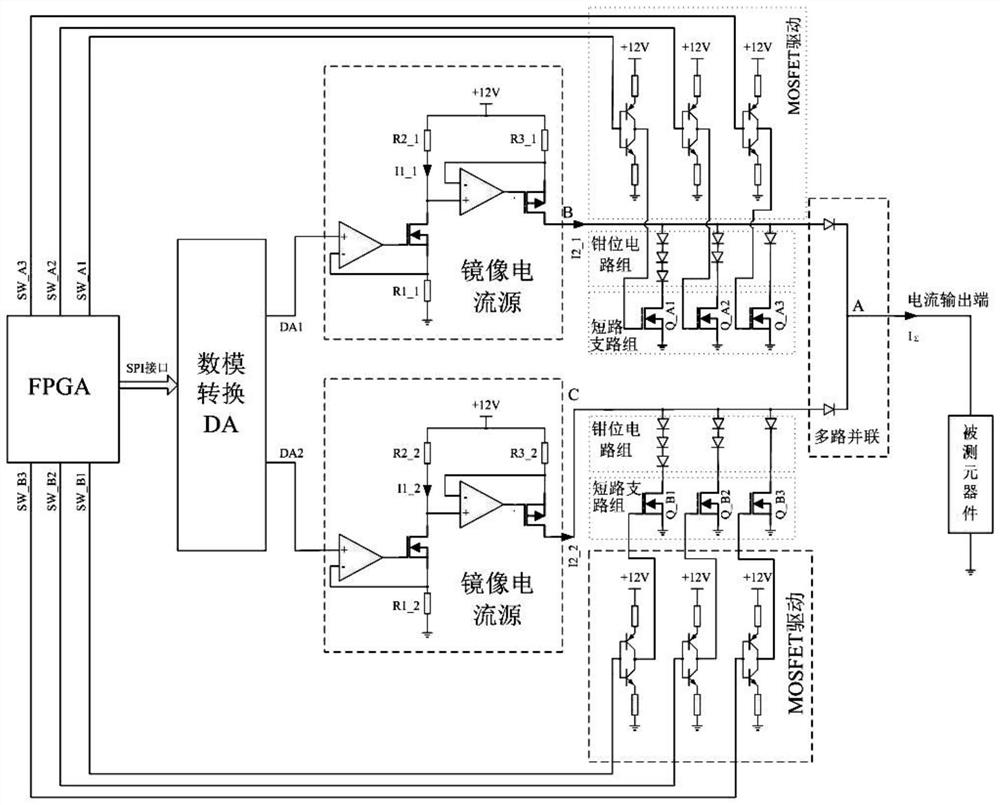
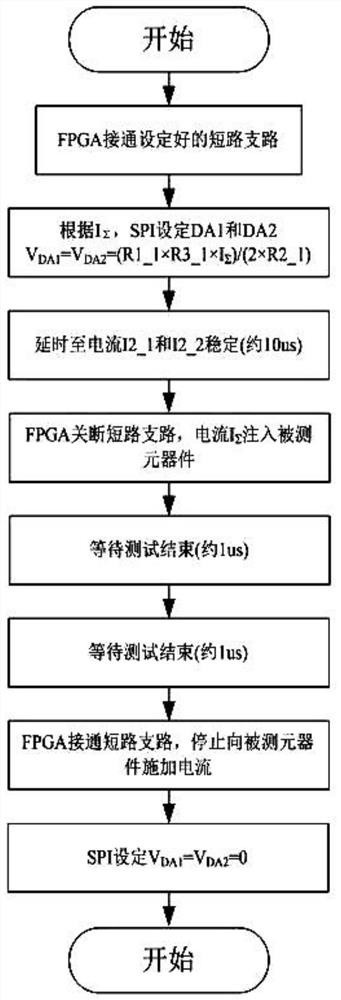
[0034] This embodiment discloses as figure 1 A narrow-pulse high-current constant-current source is shown, including a logic controller FPGA that drives the NMOS of the short-circuit branch through push-pull to increase the slope of the rising and falling edges of the pulse, and uses the SPI interface to connect the digital-to-analog converter DA to control the output voltage. After the mirror current source is op-amped, the current signal is output, and the MOSFET is driven to turn on or off the short-circuit branch through the multi-channel IO port. At the same time, the short-circuit branch is equipped with a clamp circuit to reduce the impact on the mirror current source. The overshoot of the narrow pulse; finally output the current to the component under test through multiple parallel connections.
[0035] In this embodiment, the FPGA adjusts the output voltage of the DA through the SPI interface, and also controls the driving of the MOSFET through multiple IO ports, so a...
Embodiment 2
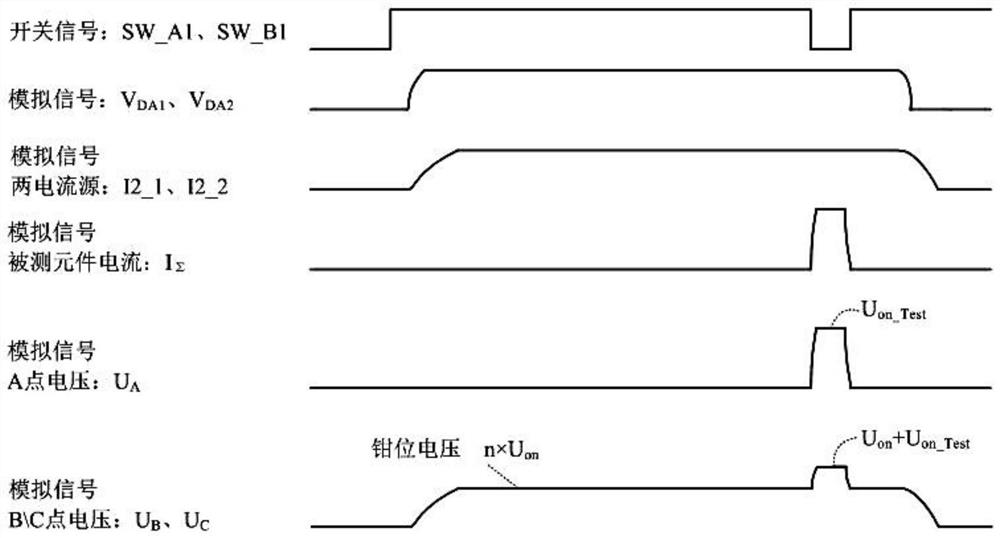
[0041] This embodiment discloses a short-circuit branch. The traditional constant current source does not have a short-circuit branch. Therefore, the magnitude and pulse width of the current IΣ are usually controlled by analog quantities DA1 and DA2. However, the slew rate index of the digital-to-analog conversion module and the operational amplifier circuit The rising and falling process of the current I2_1 and I2_2 is limited, and it is difficult to realize a pulse width current of less than 1us.
[0042] Further analysis shows that as long as the currents I2_1 and I2_2 change, the transition process will be subject to the slew rate of the operational amplifier in the current source, and an ideal transition process cannot be obtained. However, in the present invention, stable currents I2_1 and I2_2 have been obtained before the narrow pulse appears, and the two currents flow through the short-circuit branch, and the short-circuit branch is disconnected instantaneously to obta...
Embodiment 3
[0047] This embodiment discloses a clamping circuit, which is composed of multiple sets of diodes in series, and the conduction voltage of each diode is set as Uon, and each short-circuit branch group has an NMOS transistor connected to the clamping circuit to GND.
[0048] When the short-circuit branch is not conducting, the currents I2_1 and I2_2 are gathered to point A and pass through the component under test, so UB=Uon+Uon_Test. When the short-circuit branches Q_A1 and Q_B1 are turned on and satisfy Uon+Uon_Test>3Uon, the current I2_1 completely flows through the switch Q_A1, and the current I2_2 completely flows through the switch Q_B1, so UB=UC=3Uon, and UA=0V.
[0049] In this embodiment, the function of the clamping circuit group is that, as the aforementioned clamping circuit should satisfy n×Uon
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com