Motor positioning and stopping mechanism
A stopping mechanism and stopping technology, which is applied in the field of motor positioning and stopping mechanism, can solve the problems of rarely seen pure mechanical structure motors, the volume of the control mechanism increases, and the complex control mechanism, etc., and achieves a simple and compact overall structure and small internal space. , Universal effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
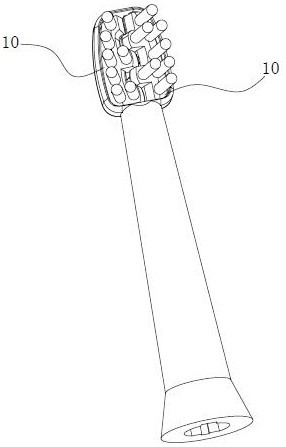
[0043] Such as Figure 1-6 As shown, in the motor positioning and stopping mechanism of this embodiment, the aforementioned inertial component 1 includes an inertia ring 1a sleeved on the power shaft, and a connecting through hole is opened on the inertia ring 1a, and a spiral shape is provided on the wall of the connecting through hole. The convex or concave structure is connected with the power shaft passing through the connection through hole through the spiral convex or concave structure. The movable ring 3a moving in the direction is provided with a stop structure on the movable ring 3a. After the motor is de-energized, the speed of the power shaft gradually decreases, and the inertia ring 1a rotates relative to the power shaft due to its own inertia, and rotates around the power shaft while moving along the axial direction of the power shaft under the action of the spiral protrusion or concave structure. Move towards the movable ring 3a, and the movable ring 3a is pushe...
Embodiment 2
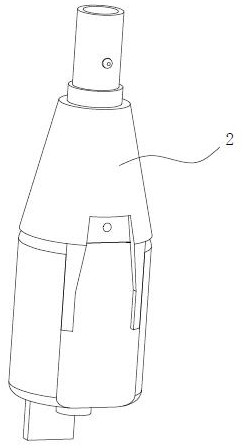
[0049] Different from Example 1, see Figure 8-12 As shown, in this embodiment, the inertial component 1 includes an inertia ring 1a that is looped outside the power shaft, the movable part 3 includes a rotating bracket 3b and a brake pawl 3c provided with a stop structure, and the rotating bracket 3b is fixedly connected to the power shaft The brake pawl 3c is rotatably connected to one of the two parts of the inertia ring 1a and the rotating bracket 3b, and the remaining part is also connected to the brake pawl 3c and leaves a gap at the joint between it and the brake pawl 3c. quantity. When the motor is de-energized, the speed of the power shaft gradually decreases, and the aforementioned inertia ring 1a rotates relative to the power shaft due to its own inertia and pulls the brake claw 3c, prompting the brake claw 3c to rotate, so that the stop structure on the brake claw 3c Close to and abut against the stop structure on the immovable part 2, thereby preventing the power...
Embodiment 3
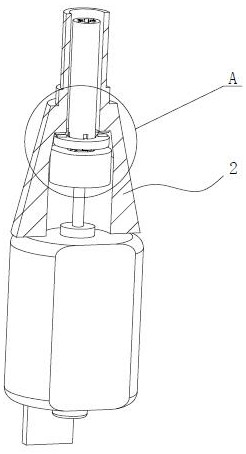
[0052] Similar to Embodiment 2, the inertial component 1 in this embodiment also includes an inertia ring 1a that is sheathed outside the power shaft, and the movable member 3 also includes a rotating bracket 3b and a brake pawl 3c provided with a stop structure, and the rotating bracket 3b The power shaft is also fixedly connected, and an accommodating cavity 3b1 is also provided in the rotating bracket 3b, and a gap 3b2 communicating with the accommodating cavity 3b1 is also provided on the side wall of the rotating bracket 3b, and the stop structure on the brake pawl 3c is also as follows: The front end of the arm claw, in addition, the fixed part 2 can also include a stationary ring 2a, and the stop structure on the fixed part 2 is also a protrusion 5 (of course, it can also be a groove) arranged on the stationary ring 2a. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 2 is that the inertia ring 1a is set in the accommodating cavity 3b1, the stationary ring 2a is set...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com