Color face recognition method based on quaternion non-convex penalty sparse principal component analysis
A sparse principal component and recognition method technology, applied in the field of pattern recognition and artificial intelligence, can solve the problems of reduced variance of sparse principal components, easy identification of principal components, wrong original variables, unsatisfactory load sparsity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
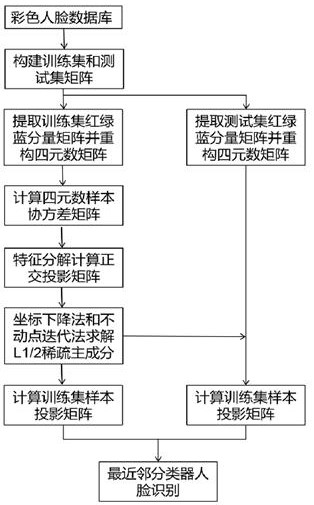
[0052] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0053] figure 1 It represents a color face recognition method based on quaternion non-convex penalty sparse principal component analysis, including the following steps:
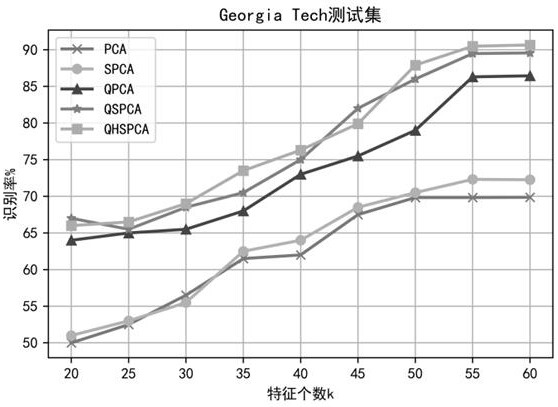
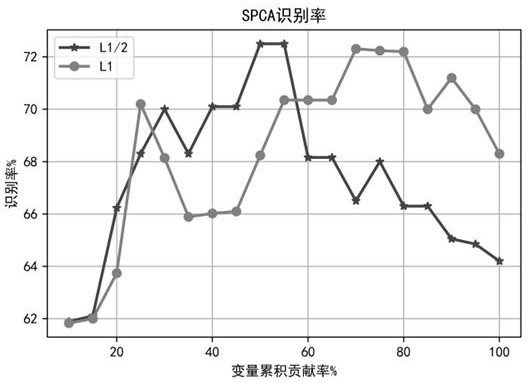
[0054] 1) Select 50 people from the Georgia Tech face database, 15 images per person, a total of 750 color images, and randomly divide the 15 images of each person into the training set and the test set according to 2:1 and number them in order, and uniformly set each If the pixels of an image are 20×20, then the number of training set samples m=500, the number of test set samples s=250, and the number of variables n=400 can be obtained.
[0055] 2) Extract the red, green, and blue component matrices of the training set sample matrix, and perform mean value removal respectively to obtain
[0056] 3) Construct the complex representation of the quaternion matrix by using the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com