Treatment using oncolytic virus
A technology for oncolytic viruses and viruses, applied in the direction of viruses, virus antigen components, viruses/bacteriophages, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0270] Example 1. Clinical isolates with improved antitumor effects
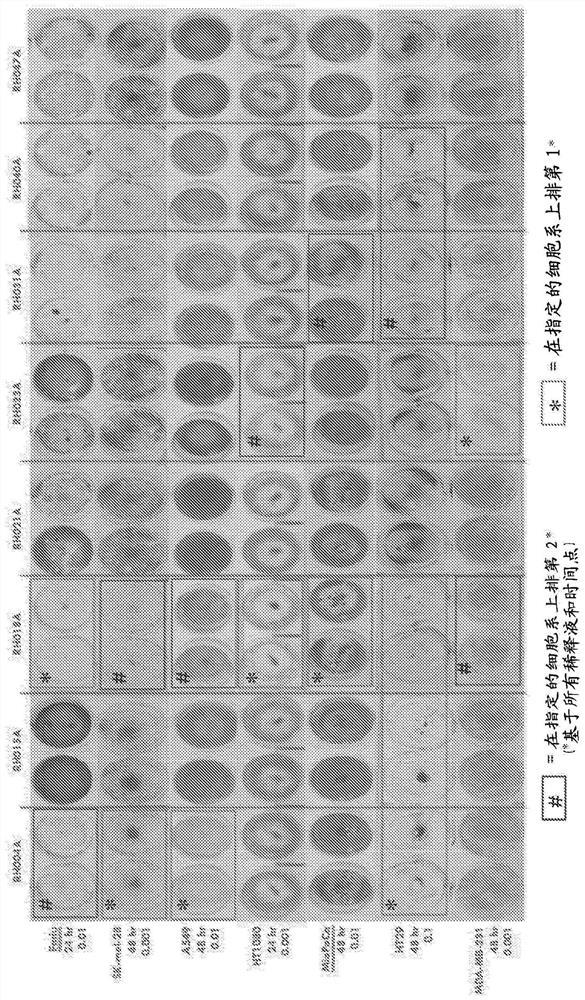
[0271] The virus species used to illustrate the invention is HSV, particularly HSV1. Cold sores were collected from more than 20 healthy volunteers. Samples from each swab were used to infect BHK cells. HSV1-containing samples were identified by the presence of cytopathic effect (CPE) 24-72 hours after infection and by immunohistochemistry, and virus stocks of major clinical isolates were generated from positive samples.
[0272] The primary clinical isolates of HSV1 were tested for their ability to kill a panel of human tumor-derived cell lines, and the strain with the greatest ability to rapidly kill large numbers of such cells at low doses was selected. The tumor cell lines used for this comparison were HT29 (colorectal cancer), MDA-MB-231 (breast cancer), SK-MEL-28 (melanoma), Fadu (squamous cell carcinoma), MCF7 (breast cancer), A549 (lung cancer), MIAPACA-2 (pancreatic cancer), CAPAN-1 (pancreatic c...
Embodiment 2
[0275] Example 2. Modification of clinical isolates
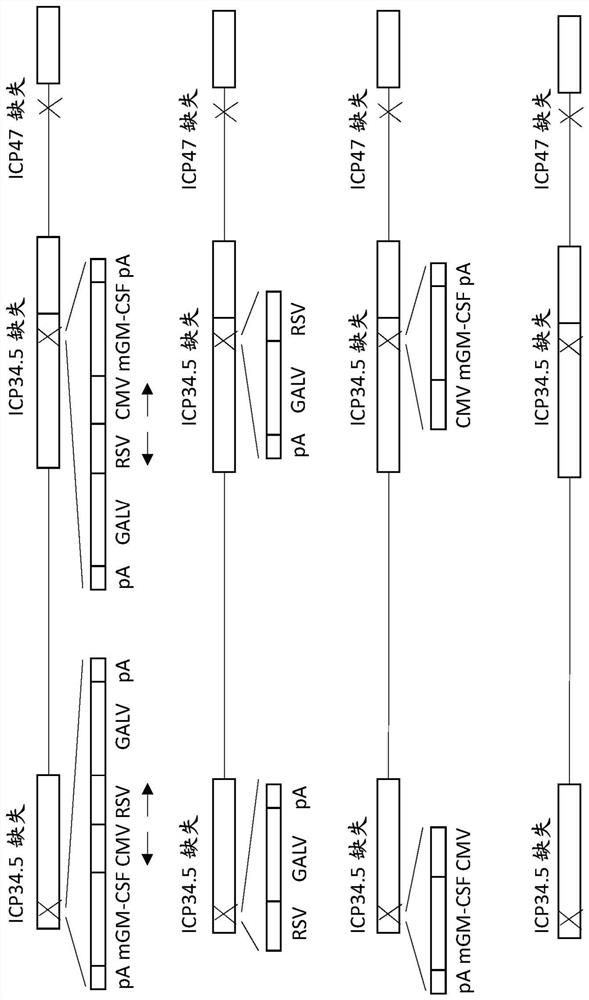
[0276] In this example, by using a plasmid (HSV1 nucleotides 145300 to 145582 is the sequence to be deleted; HSV1 strain 17 The clinical isolates selected in Example 1 were modified by homologous recombination (see Genbank file NC_001806.2 for sequence) by deleting ICP47 from the viral genome. Viral plaques expressing GFP were selected, then GFP was removed by homologous recombination with empty flanking regions, and plaques not expressing GFP were selected. This produces an ICP47-deficient virus in which US11 is expressed as an IE protein since it is now under the control of the ICP47 promoter. Then by using a plasmid (HSV1 nucleotides 124953 to 125727 is the sequence to be deleted; HSV1 strain 17 sequence is referring to Genbank file NC_001806 .2) Perform homologous recombination to delete ICP34.5. Viral plaques expressing GFP were again selected and then passed through with the same flanking regions (but in between ar...
Embodiment 3
[0281] Example 3. Expression of two immunostimulatory molecules from viruses expressing fusogenic proteins
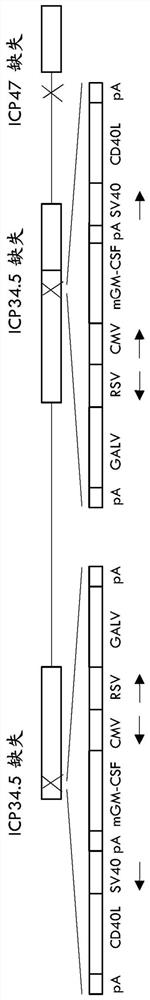
[0282] Viruses similar to those expressing GALV-R- and mGM-CSF above were constructed, but additionally expressing a CD40L form. Here, instead of using a plasmid containing an ICP34.5 flanking region and an expression cassette containing GM-CSF and GALV-R driven by CMV and RSV promoters, a plasmid containing an ICP34.5 flanking region and containing an expression cassette driven by CMV, RSV and Plasmids for the expression cassettes of GM-CSF, GALV, and CD40L driven by the SV40 promoter were used for recombination with viruses containing GFP inserted into ICP34.5, and again plaques that did not express GFP were selected.
[0283] In more detail, a plasmid (HSV1 nucleotides 145300 to 145582 is the sequence to be deleted; HSV1 strain 17 sequence see Homologous recombination of Genbank file NC_001806.2) deleted ICP47 from the viral genome. Viral plaques expressing GFP wer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com