Method for verifying cultivation device performance
A chi-square test and bacterial cell technology, applied in the field of cell culture and high-throughput cell culture, can solve problems such as damage to model output and data input errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
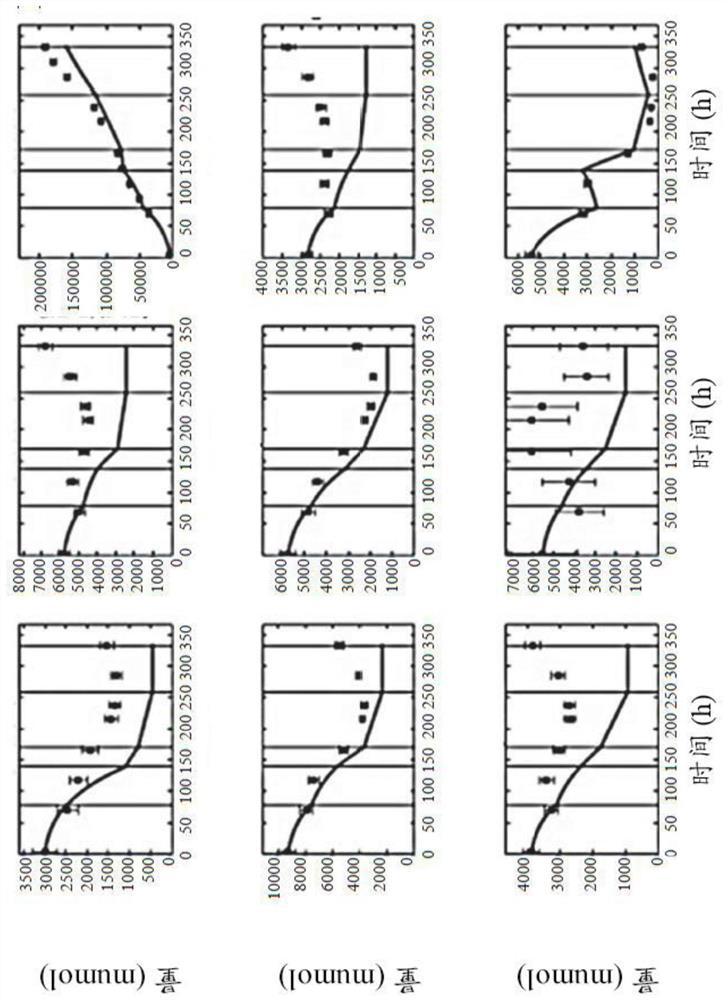
[0292] Comparison of recombinant CHO clones and ranking of metabolic performance indicators
[0293] For clone comparison experiments, ten recombinant CHO-K1 clones (CL4 to CL13) expressing the same monoclonal IgG4 antibody were used. For comparative studies of the different products, another clone CL14 expressing the same recombinant human IgG4 monoclonal antibody as above and two other production clones (CL2 and CL3) expressing the monoclonal IgG1 antibody were used. Recombinant CHO-K1 clones were grown in a protein-free, chemically defined proprietary medium for seed culture and subsequent batch feeding experiments. Seed cultures were performed in shake flasks using a humidified incubator with a set point control of 7% CO 2 and 37°C. Colonies were isolated every three to four days. For all experiments, clones of the same age (21 days) cultured up to the start of the experiments were used. For batch-fed comparison experiments, CL4 to CL13 were grown in 230 mL of medium i...
example 2
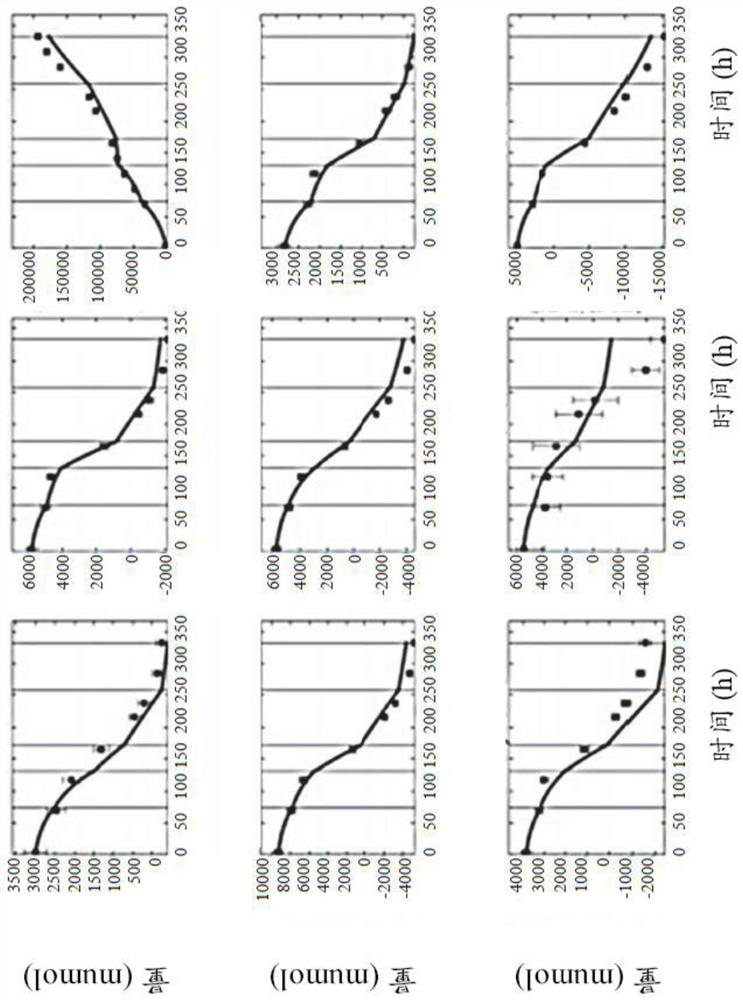
[0296] Comparison of Different Fermentation Scales of Recombinant CHO Cloning Culture
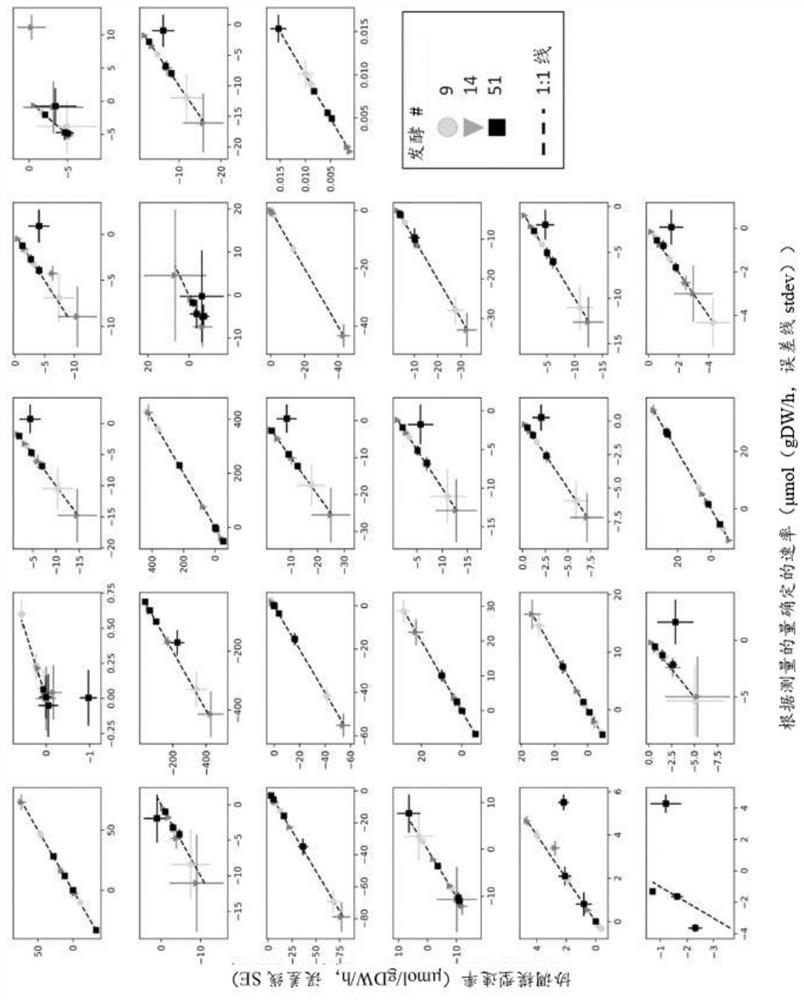
[0297] Metabolic flux analysis methods were used to establish automated CHO cell performance assays for high-throughput use. To this end, rich data sets can be exploited to disrupt cultures performed at various scales, expressing various mAbs, if desired (see Table 3). Methods used to design pipelines include genome-scale modeling of metabolic networks, identification of process stages, analysis of metabolic fluxes, and analysis of clonal performance metrics. Statistical analyzes performed included reduced χ 2 Testing, cross-validation, and repeated analysis. Analysis results can account for transformation and translation errors in the data set to determine the χ 2 The acceptance range for the inspection. In addition, the analysis considered the impact of other measured parameters in the form of host cell proteins and indicators of oxygen uptake.
[0298] In the initial phase, a compre...
example 3
[0300] Analysis of CHO clone performance by OUR and HCP metrics
[0301] To this end, the influence of cultured subsets representing the HCP and OUR datasets was analyzed (see Table 3). Here, it has been found that in both cases, taking into account the additional data, by increasing χ 2 The information content retrieved from experiments can be improved. In detail, when the host cell protein (13% increase point) and oxygen uptake rate (25% increase point) measurements were taken into account, the information content of the CHO fermentation was significantly improved (see Table 9).
[0302] Table 9: χ 2 The detailed results of the test. To analyze the impact of the HCP and OUR indicators, Model Scenario 1 (Model 1) was re-evaluated using only the cultivars for which HCP and OUR were measured.
[0303]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com